The RVV vector execution engine of Coral NPU is illustrated below.
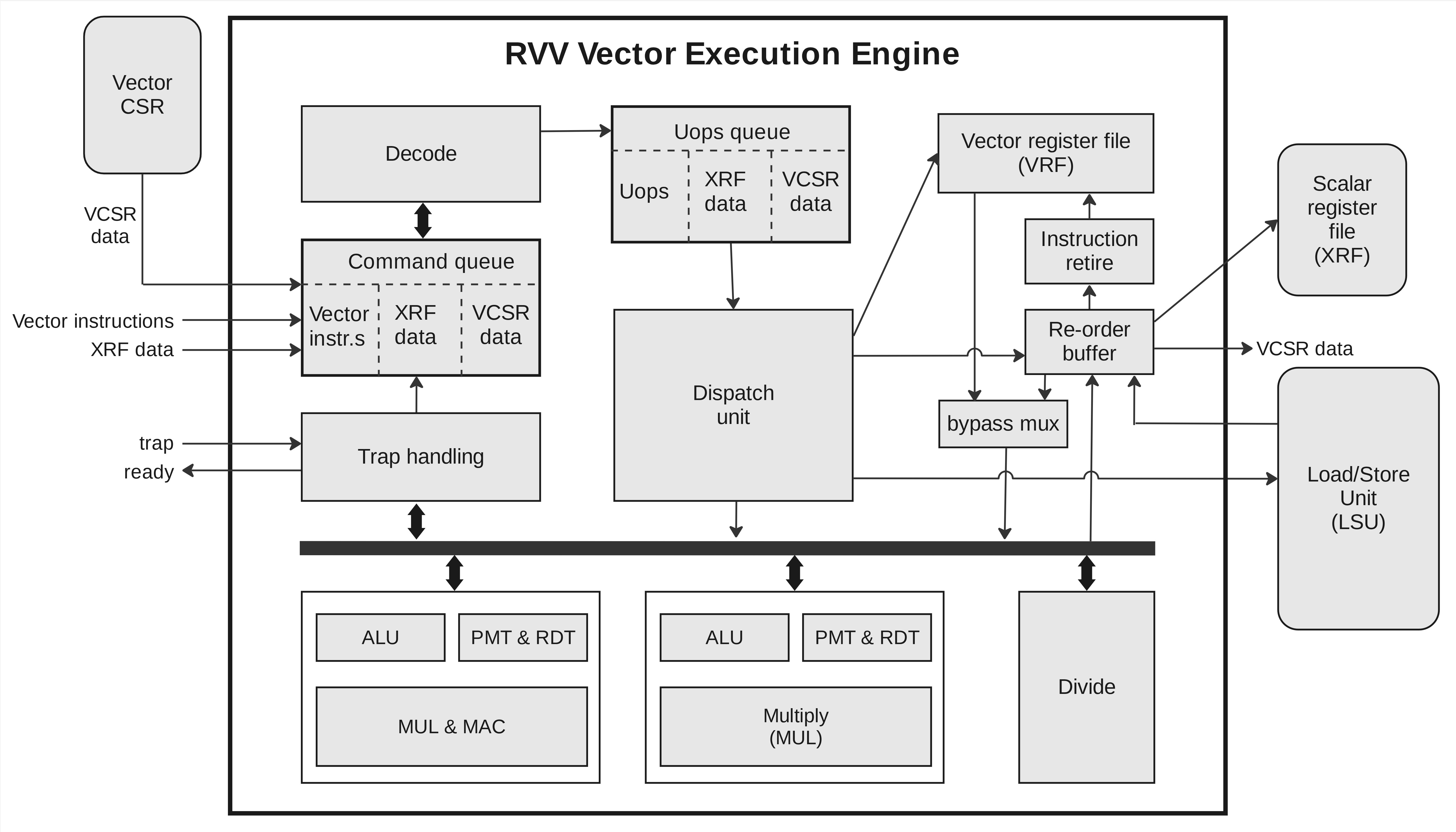
Coral's RVS scalar core decodes all incoming instructions and sends vector
instructions (with XRF scalar operands and vector CSR values) to the RVV command
queue. The vector instructions are decoded into micro-operations (µops)
according to vtype.lmul, the nf field in vld/vst instructions, and the
encoding (widening, narrowing, whole-register instructions) — the results are
then written to the µops queue.
vtype.lmul refers to the Vector Register Group Multiplier (LMUL) field within
the Vector Type Register (vtype). This field is a critical part of the RISC-V
vector programming model, as it determines how vector registers are grouped and
how instructions are processed.
The vtype CSR, which is updated only by vsetvli, vsetivli, and vsetvl
instructions, provides the default type used to interpret the contents of the
Vector Register File (VRF). Specifically, vtype.lmul determines how multiple
vector registers are combined to form a vector register group.
Micro-operations
A micro-operation (μop) is the fundamental unit into which vector instructions are decomposed for processing.
μops are generated during the decode stage of the RVV pipeline. The decode unit reads instructions from the command queue (CQ) and converts the instructions into μops. A single vector instruction may be decoded into multiple μops, particularly when the instruction involves large data sizes or multiple register groups.
An instruction (or the results of its μops) is ready to be retired only if all of its constituent μops are ready in the re-order buffer.
Example: Whole register load
A single instruction to load four whole registers
vl4re32.v v8, (a0)
is decoded into four separate μops: uop1 – uop4, corresponding to registers v8 – v11.
Scalar-to-vector interface
The following figure describes how Coral NPU's scalar core and vector engine work together.
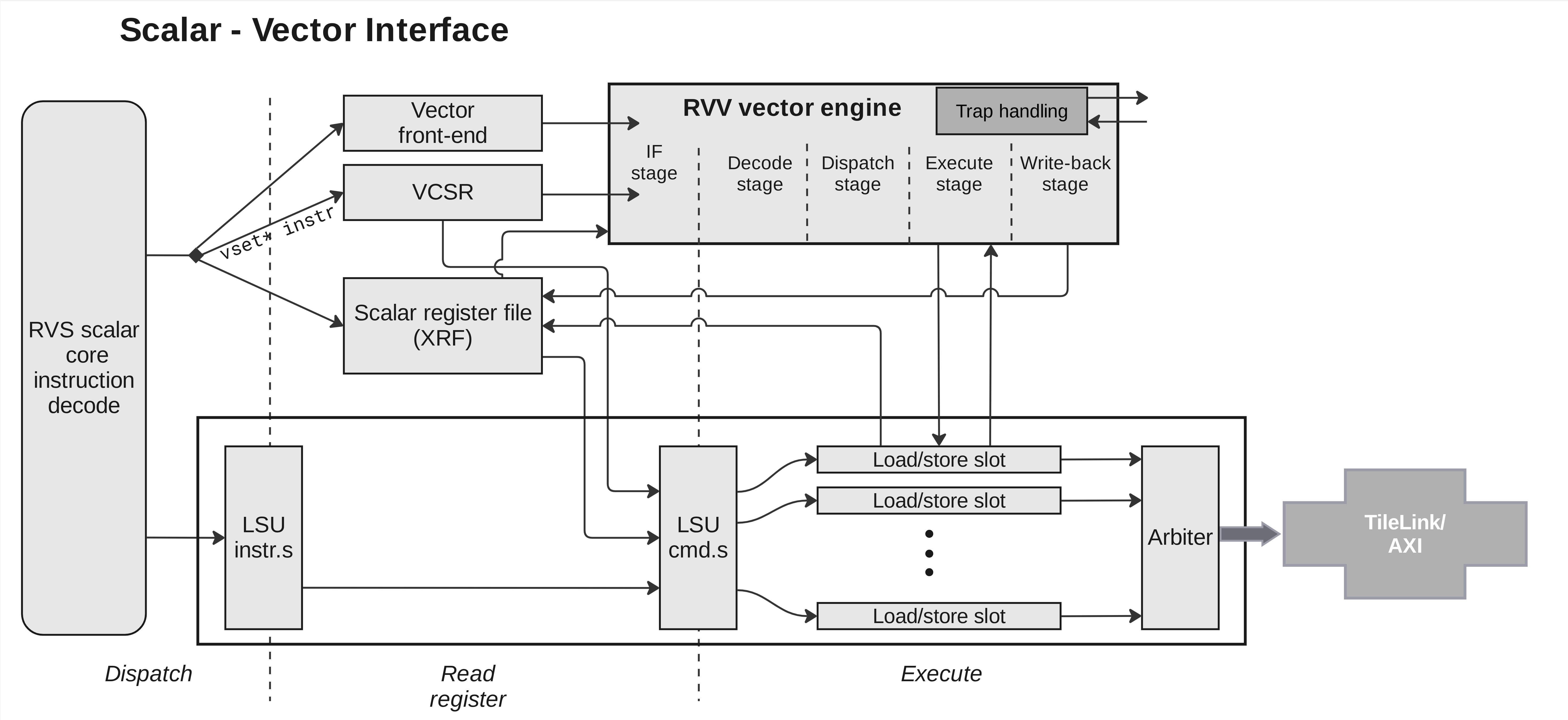
Coral NPU's RVS scalar core dispatcher sends vld/vst instructions to the
LSU instructions queue and to the RVV vector frontend. The LSU decodes the
vld/vst instructions into µops.
If the instruction is a vector segment vld/vst, it is decoded into
stride/indexed vld/vst µops.
AXI tile link is a combination of the AXI bus protocol and the TileLink protocol, often used in RISC-V ML accelerators for efficient communication between processing cores and accelerators. The AXI protocol is a point-to-point interface for data transfer, while TileLink is a message-based protocol that facilitates memory coherence and high-speed interconnects.
