Page Summary
-
Coral NPU is a RISC-V based reference design for neural processing units composed of a scalar core, vector execution unit, and matrix execution unit.
-
The scalar core handles traditional CPU functions and drives the command queues for the vector and matrix units.
-
The vector execution unit performs a range of vector and ML computations based on a SIMD design.
-
The matrix execution unit accelerates Matmul operations essential for ML, though it is currently under development.
-
The Coral NPU roadmap outlines milestones for integrating a full RISC-V compliant scalar core, vector execution unit, matrix execution unit, and future enhancements like floating point support and CHERI.
Architecture components
Coral NPU is a complete reference design for neural processing units (NPUs) based on the open RISC-V standard. Coral NPU is a composition consisting of three core components:
- A scalar core for traditional CPU functions
- A vector execution unit for additional computational features
- A matrix execution unit for ML model operations
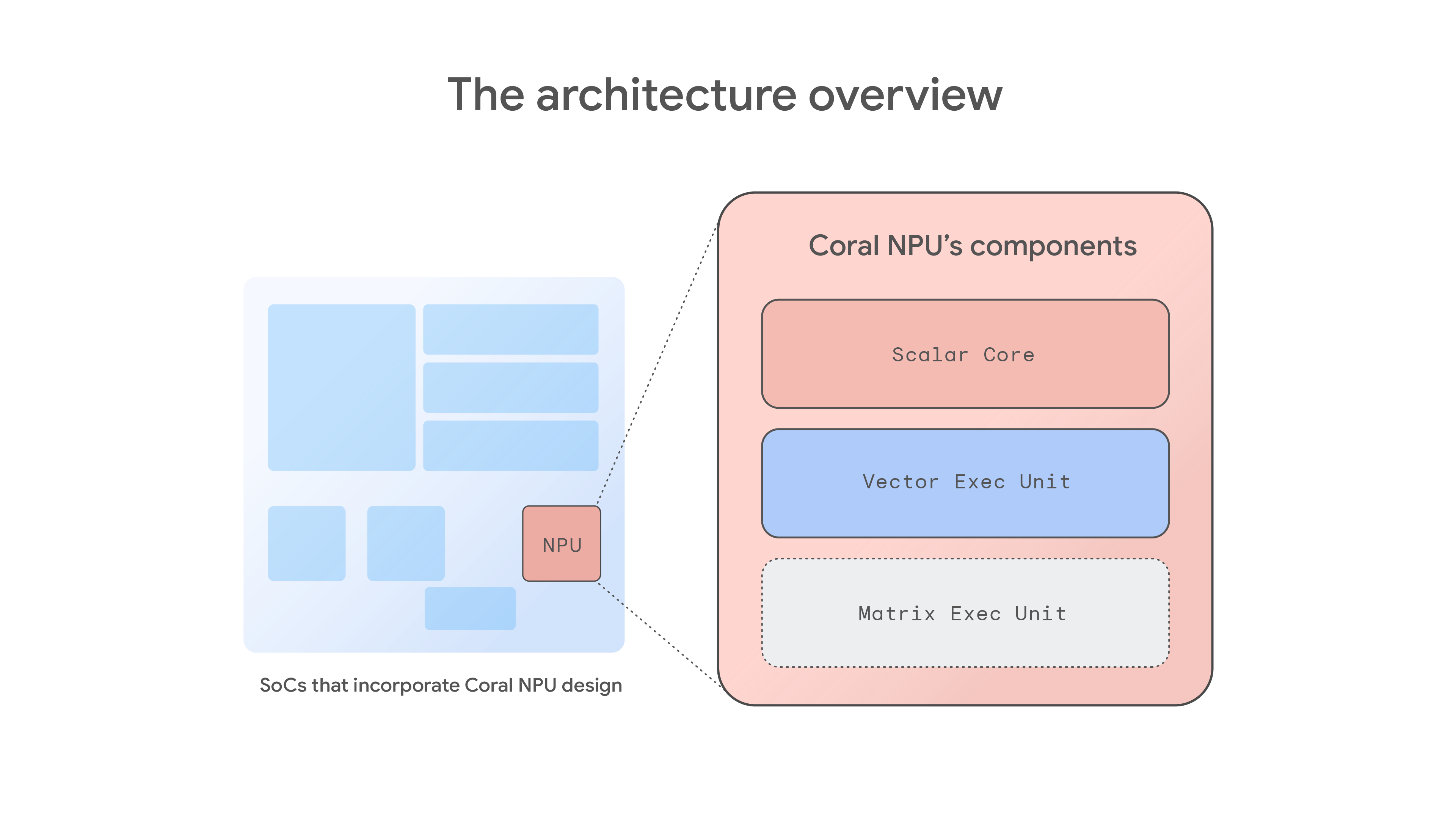
Together, these three components provide the complete feature set and performance required for a Coral NPU-based NPU. Any chip vendor designing a discrete NPU or integrating Coral NPU into a System-on-Chip (SoC) will need to incorporate all three components for a complete solution.
The main features and functions offered by each of the components are the following:
Scalar core:
- Serves as the in-order, non-speculative frontend processor.
- Drives the command queues for the vector and matrix execution units.
- Fully compliant with the open RISC-V 32-bit base ISA standard (RV32I).
- Features 31 general-purpose scalar registers, each 32 bits wide.
- Offers a C-programmable interface for managing loops, control flow, flexible type encodings, and instruction compression for the SIMD/vector backend.
Vector execution unit:
- Performs a wide range of vector and machine learning (ML) computations, including array operations, ML activation functions, and reductions.
- Based on a Single Instruction, Multiple Data (SIMD) design.
- Decoupled from the scalar frontend by a FIFO command queue, which buffers vector instructions.
- Equipped with 32 vector registers, each 256 bits wide (capable of holding eight 32-bit integers).
- Natively supports 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit data widths.
Matrix execution unit:
- Accelerates matrix multiply-accumulate (Matmul) operations essential for ML, such as matrix multiplication and convolutions.
- Features an outer-product engine capable of 256 multiply-accumulate (MAC) operations per cycle.
- Status: Under development and evaluation as part of the RISC-V matrix extension task group.
