Page Summary
-
The Tab template serves as a container for other templates, organizing content through a tab bar.
-
It includes a tab bar with an app icon and up to 4 tabs, and can embed various templates like List, Grid, and Search.
-
Only one tab view and its corresponding embedded template can be active at a time.
-
Developers must provide monochromatic vector icons for each tab and include between 2 and 4 tabs.
-
Developers should use short tab labels and not rely on headers or action strips within embedded templates.
The Tab template acts as a container for other templates listed below, providing tabs across the top (as shown in Anatomy of the Tab template).
The tabs allow switching among views. This capability is particularly useful for organizing content or views that users will want to browse or search.
Includes:
- Tab bar with app icon and up to 4 tabs (no back button)
- Embedded template, which can be any of the following types:
Each tab view corresponds to one embedded template, and only one tab view can be active at any given time.
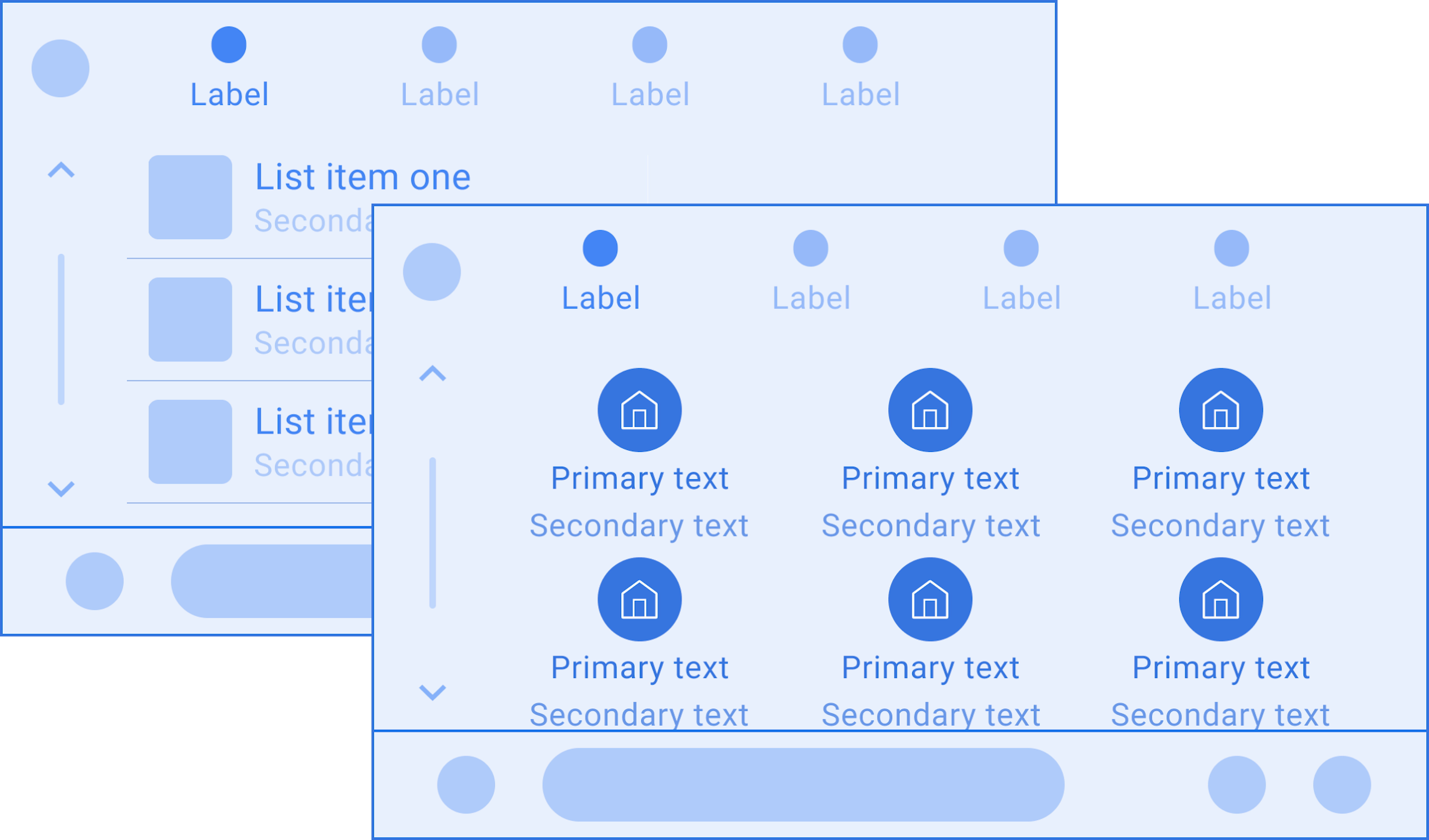
Anatomy of the Tab template
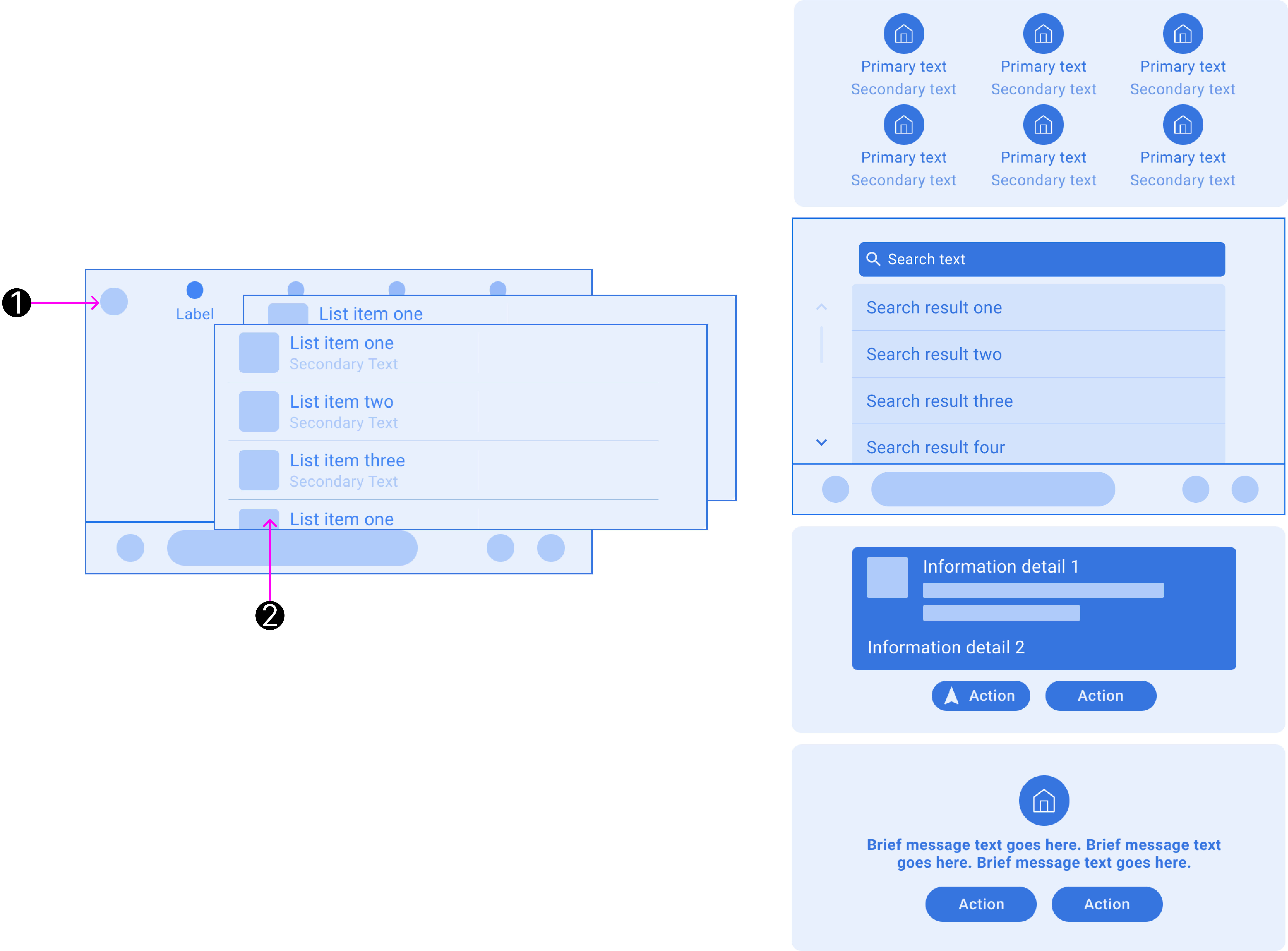
The Tab template consists of the following elements:
- Tab bar, which can show up to 4 tabs
- Embedded template, using one of the following templates: List, Grid, Search, Pane, Message, or Navigation
Tab template examples
Tab template UX requirements
App developers:
| MUST | Provide monochromatic vector icons for each tab. |
| MUST | Include at least 2 and no more than 4 tabs in the app header. |
| MUST NOT | Allow more than 1 tab to be active at a time. |
| MUST NOT | Create a secondary navigation by adding a second level of tabs. |
| SHOULD | Use short tab labels to avoid truncation. |
| SHOULD NOT | Rely on a header or action strip in embedded templates. |