Page Summary
-
Daydream provides motion controller visualization, laser/reticle display, arm model, and input system features for both Unity and Unreal Engine.
-
Unreal developers can integrate motion controller visualization using the
GoogleVRMotionControllercomponent and handle input events using theGoogleVRPointerInputcomponent. -
The arm model's behavior in Unreal Engine can be adjusted or disabled through Blueprint or C++ by calling specific functions within the
GoogleVRControllerFunctionLibrary. -
Daydream supports both gaze-based interactions with
UGoogleVRGazeReticleComponentand motion controller interactions withGoogleVRMotionControllerfor varied user experiences.
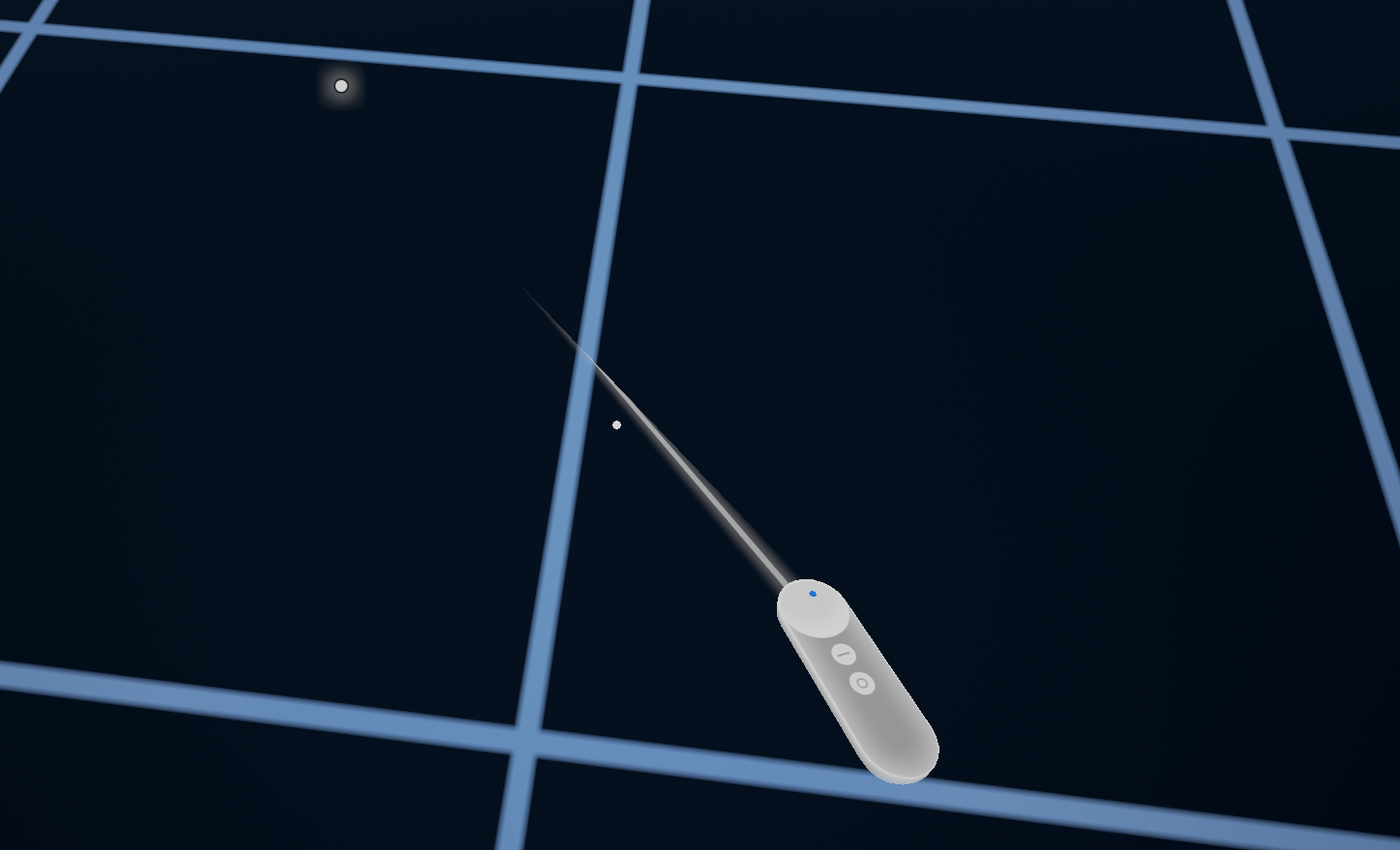

Daydream offers motion controller support for Unity and Unreal. These features include:
Controller visualization: A 3D model of the Daydream controller that displays which button the user is currently pressing and where the user is currently touching the Daydream controller's touchpad.
Laser and reticle visualization: Displays a laser and reticle so the user can easily interact with the VR environment.
Arm model: A mathematical model to make the 3D controller model in VR approximate the physical location of the Daydream controller.
Input System: A standard and extensible framework for raycasting from the controller model. The input system integrates with the laser and reticle visualization to make it easy to interact with the UI and other objects in VR.
All visualization elements are optional and reskinnable.
Controller support in Unreal
Currently this functionality is only available in Unreal with Google VR.
Motion Controller with visualization support
- Enable the Google VR Motion Controller plugin. (instructions).
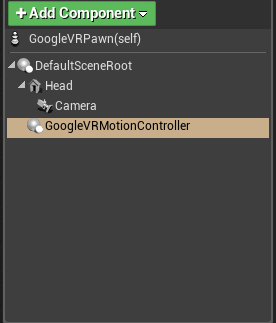
- Open the Blueprint for the Player Pawn.
- Add the
GoogleVRMotionControllerto the Components list at the same level as the VR Camera root. - Modify the properties on the
GoogleVRMotionControllerComponent to adjust it.
Cardboard apps should use UGoogleVRGazeReticleComponent instead, for a
gaze-based reticle.
Motion Controller without visualization support
Use the official Unreal MotionControllerComponent.
Input system
- Open the Blueprint for the Player Pawn.
- Add the
GoogleVRPointerInputComponent to the Blueprint. - Use the
GoogleVRPointerInputComponent's API to listen and react to events triggered by the pointer. - If desired, subclass the
GoogleVRPointerInputComponent in C++ to add additional events, to add custom processing of the raycast, or to override the raycast implementation.
The GoogleVrPointerInput Component works with both GoogleVRGazeReticle and
GoogleVRMotionController. It is also integrated with UE4 Widgets, allowing you
to interact with the standard UE4 UI with the pointer.
To respond to events generated by the GoogleVRPointerInput Component, use the
interfaces IGoogleVRActorPointerResponder and
IGoogleVRComponentPointerResponder in either C++ or Blueprint.
Adjusting the Arm Model
Blueprint:
- Open your Player Pawn Blueprint.
- Create a node, and search for the term "ArmModel” to see what tuning parameters are available.
- Attach the node to the
BeginPlayevent.
C++
- Add
#include "GoogleVRControllerFunctionLibrary.h"to your code. - Include
GoogleVRControlleras a dependency in yourBuild.csfile. Call tuning functions, for example:
UGoogleVRControllerFunctionLibrary::SetArmModelPointerTiltAngle(20.0f);
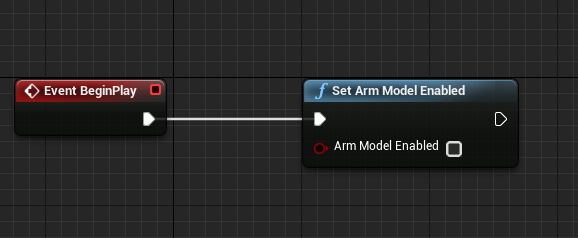
Disabling the Arm Model
You can disable or enable the Arm Model by calling the function
SetArmModelEnabled either in a Blueprint or in code as described in the
“Adjusting the Arm Model” section of this document. If disabled, the
MotionControllerComponent will behave the same as it did the previous version
of Unreal, in that orientation will change based on the controller.