يمكن عرض الصور التي تتألف منها ImageCollection إما كأحد
الصور المتحركة أو سلسلة من الصور المصغّرة التي يُشار إليها باسم "شريط صور". توفّر هذه
الطرق تقييمًا سريعًا لمحتويات ImageCollection
ووسيطًا فعّالاً لمشاهدة التغيُّر المكاني والزماني (الشكل 1).
getVideoThumbURL()تُنشئ سلسلة من الصور المتحركةgetFilmstripThumbURL()لإنشاء سلسلة من الصور المصغّرة
توضّح الأقسام التالية كيفية إعداد ImageCollection لأجل
العرض المرئي، وتقدّم أمثلة على الرموز البرمجية لكل طريقة من طرق العرض المرئي للمجموعات،
وتتناول العديد من تقنيات الرسوم المتحرّكة المتقدّمة.
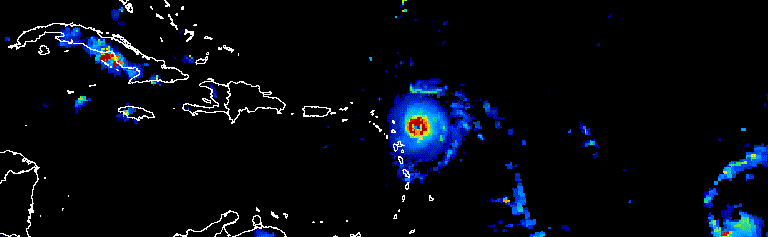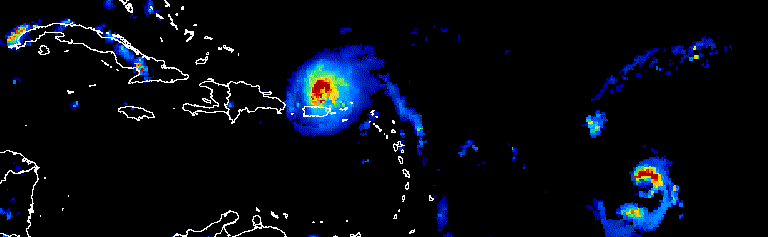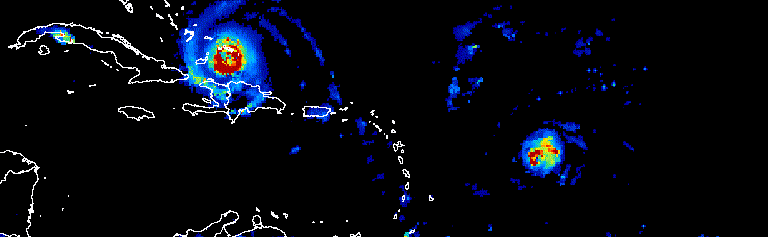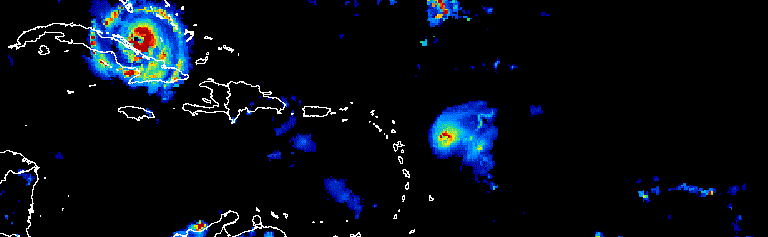
الشكل 1. صورة متحرّكة تعرض تقدّم الأعاصير الأطلسية على مدار ثلاثة أيام في
أيلول (سبتمبر) 2017
تحضير المجموعة
فلترة الصور ودمجها وترتيبها وتطبيق أنماط عليها ضمن مجموعة لعرض
الصور التي تهمّك فقط أو تسليط الضوء على ظاهرة معيّنة يمكن استخدام أي ImageCollection
كإدخال لدوالّ العروض المرئية، ولكن يمكن تحقيق نتائج أفضل باستخدام مجموعة منسَّقة
مع مراعاة النطاقات الزمنية بين السنوات وداخلها، وفترة قياس
الملاحظات، والنطاق الإقليمي، والجودة والتمثيل.
الفلترة
فلتِر مجموعة صور لتضمين البيانات ذات الصلة فقط التي تدعم الغرض من الرسم البياني. يجب مراعاة التواريخ والنطاق المكاني والجودة وغيرها من السمات الخاصة بمجموعة بيانات معيّنة.
على سبيل المثال، يمكنك فلترة مجموعة من قياسات انعكاس سطح Sentinel-2 حسب:
نطاق زمني واحد
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterDate('2018-01-01', '2019-01-01');
نطاق تسلسلي لأيام السنة
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filter(ee.Filter.calendarRange(171, 242, 'day_of_year'));
منطقة ذات أهمية
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.1, 37.2));
أو سمة صورة.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filter(ee.Filter.lt('CLOUDY_PIXEL_PERCENTAGE', 50));
ربط فلاتر متعددة
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterDate('2018-01-01', '2019-01-01') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.1, 37.2)) .filter('CLOUDY_PIXEL_PERCENTAGE < 50');
الدمج
نطاقات زمنية مركبة سنويًا وداخل السنة لتقليل عدد الصور في مجموعة وتحسين الجودة على سبيل المثال، لنفترض أنّك تريد إنشاء مخطّط بياني بياني لمؤشر NDVI السنوي لأفريقيا. أحد الخيارات هو فلترة مجموعة NDVI التي تبلغ مدتها 16 يومًا من MODIS لتضمين جميع الملاحظات لعام 2018.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var ndviCol = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/006/MOD13A2') .filterDate('2018-01-01', '2019-01-01') .select('NDVI');
تركيبة بين السنوات حسب الفلتر والحدّ الأدنى
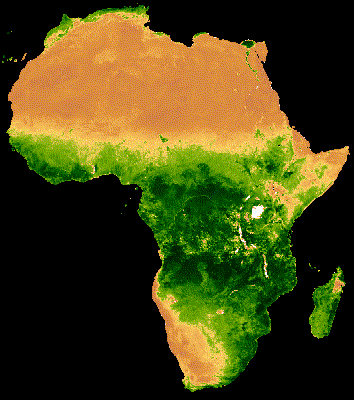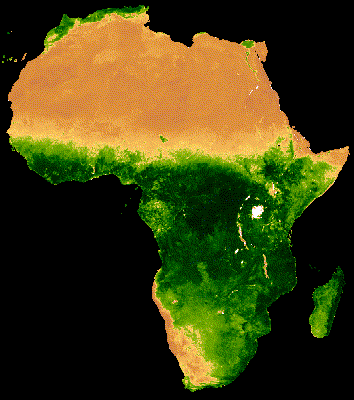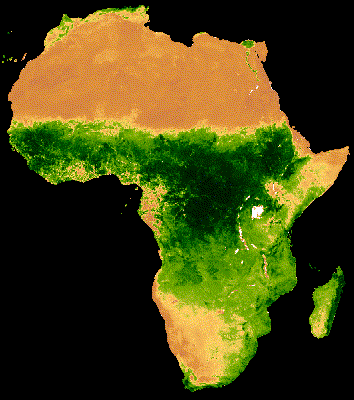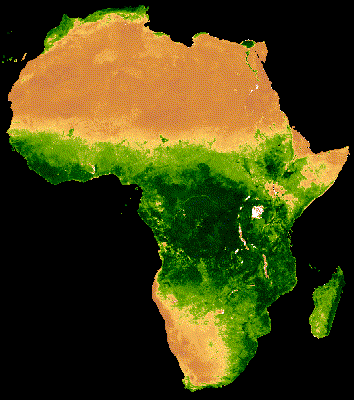
يُظهر العرض المرئي للمجموعة أعلاه تشويشًا كبيرًا في مناطق الغابات التي تغطّيها سحابة كثيفة (الشكل 2(أ)). يمكن تمثيل البيانات بشكلٍ أفضل من خلال تقليل النطاقات الزمنية التسلسلية حسب المتوسط على مستوى جميع السنوات في مجموعة MODIS.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Make a day-of-year sequence from 1 to 365 with a 16-day step. var doyList = ee.List.sequence(1, 365, 16); // Import a MODIS NDVI collection. var ndviCol = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/006/MOD13A2').select('NDVI'); // Map over the list of days to build a list of image composites. var ndviCompList = doyList.map(function(startDoy) { // Ensure that startDoy is a number. startDoy = ee.Number(startDoy); // Filter images by date range; starting with the current startDate and // ending 15 days later. Reduce the resulting image collection by median. return ndviCol .filter(ee.Filter.calendarRange(startDoy, startDoy.add(15), 'day_of_year')) .reduce(ee.Reducer.median()); }); // Convert the image List to an ImageCollection. var ndviCompCol = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(ndviCompList);
إنّ الصورة المتحركة الناتجة عن هذه المجموعة أقلّ تشويشًا، لأنّ كل صورة представлява متوسطًا لمؤشر NDVI المركب على مدار 16 يومًا لأكثر من 20 عامًا من البيانات (الشكل 1(ب)). اطّلِع على هذا الدليل التعليمي لمزيد من المعلومات عن هذه الصورة المتحركة.
 |
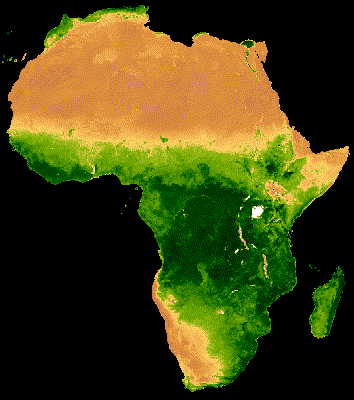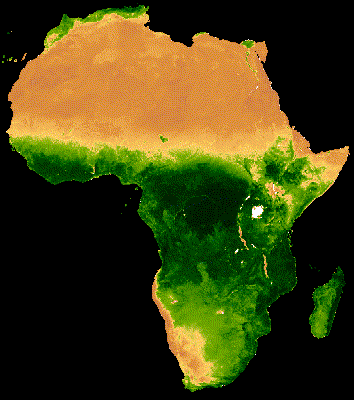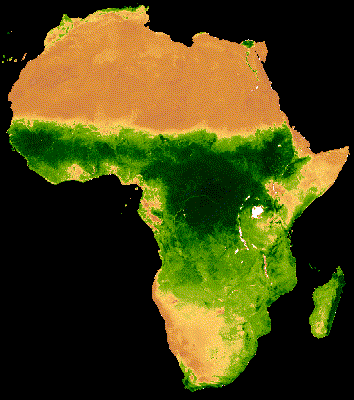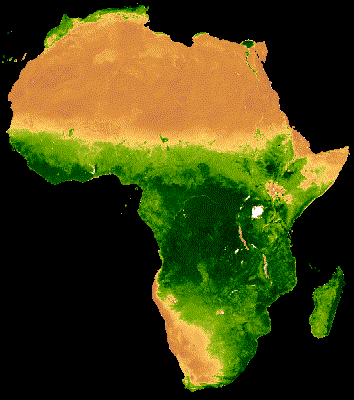 |
|---|---|
| الشكل 2(أ). مؤشر NDVI السنوي بدون دمج بين السنوات | الشكل 2(ب). مؤشر NDVI السنوي مع دمج بين السنوات |
تركيبة سنوية حسب الفلتر والحدّ الأدنى
يطبّق المثال السابق ميزة "دمج البيانات بين السنوات". وقد يكون من المفيد أيضًا تجميع سلسلة من الملاحظات خلال السنة. على سبيل المثال، يتم جمع بيانات Landsat كل ستة عشر يومًا لمشهد معيّن لكل أداة استشعار، ولكن غالبًا ما تحجب الغيوم بعض أجزاء من الصور. يمكن أن يؤدي حجب السحب وجمع عدة صور من الموسم نفسه إلى إنشاء تمثيل خالٍ من السحب. راجِع المثال التالي الذي تم فيه دمج صور Landsat 5 من شهرَي يوليو وأغسطس باستخدام المتوسط لكل عام من 1985 إلى 2011.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Assemble a collection of Landsat surface reflectance images for a given // region and day-of-year range. var lsCol = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LT05/C02/T1_L2') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.9, 43.6)) .filter(ee.Filter.dayOfYear(182, 243)) // Add the observation year as a property to each image. .map(function(img) { return img.set('year', ee.Image(img).date().get('year')); }); // Define a function to scale the data and mask unwanted pixels. function maskL457sr(image) { // Bit 0 - Fill // Bit 1 - Dilated Cloud // Bit 2 - Unused // Bit 3 - Cloud // Bit 4 - Cloud Shadow var qaMask = image.select('QA_PIXEL').bitwiseAnd(parseInt('11111', 2)).eq(0); var saturationMask = image.select('QA_RADSAT').eq(0); // Apply the scaling factors to the appropriate bands. var opticalBands = image.select('SR_B.').multiply(0.0000275).add(-0.2); var thermalBand = image.select('ST_B6').multiply(0.00341802).add(149.0); // Replace the original bands with the scaled ones and apply the masks. return image.addBands(opticalBands, null, true) .addBands(thermalBand, null, true) .updateMask(qaMask) .updateMask(saturationMask); } // Define a list of unique observation years from the image collection. var years = ee.List(lsCol.aggregate_array('year')).distinct().sort(); // Map over the list of years to build a list of annual image composites. var lsCompList = years.map(function(year) { return lsCol // Filter image collection by year. .filterMetadata('year', 'equals', year) // Apply cloud mask. .map(maskL457sr) // Reduce image collection by median. .reduce(ee.Reducer.median()) // Set composite year as an image property. .set('year', year); }); // Convert the image List to an ImageCollection. var lsCompCol = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(lsCompList);
مركب سنوي داخلي من خلال الدمج والتقليل
يُرجى العِلم أنّ طريقتَي الدمج السابقتَين تُحدِّدان List من الأيام
والسنوات لتحديد تواريخ جديدة بشكل تدريجي لفلترة البيانات ودمجها.
يُعدّ تطبيق عملية الربط طريقة أخرى لتنفيذ هذه العملية. في القطعة التالية، يتم تعريف مجموعة فريدة من السنوات، ثم يتم تطبيق saveAll
عملية ربط لتحديد جميع الصور التي تتوافق مع عام معيّن.
يتم تجميع الصور التي تنتمي إلى عام معيّن في عنصر List يتم تخزينه كخاصية لممثّل العام المعنيّ في مجموعة
السنوات المميزة. يتم إنشاء التقارير السنوية المركبة من هذه القوائم عن طريق تقليل
ImageCollections التي تحدّدها في دالة تمّ ربطها بمجموعة
السنوات المختلفة.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Assemble a collection of Landsat surface reflectance images for a given // region and day-of-year range. var lsCol = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LT05/C02/T1_L2') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.9, 43.6)) .filter(ee.Filter.dayOfYear(182, 243)) // Add the observation year as a property to each image. .map(function(img) { return img.set('year', ee.Image(img).date().get('year')); }); // Make a distinct year collection; one image representative per year. var distinctYears = lsCol.distinct('year').sort('year'); // Define a join filter; one-to-many join on ‘year’ property. var filter = ee.Filter.equals({leftField: 'year', rightField: 'year'}); // Define a join. var join = ee.Join.saveAll('year_match'); // Apply the join; results in 'year_match' property being added to each distinct // year representative image. The list includes all images in the collection // belonging to the respective year. var joinCol = join.apply(distinctYears, lsCol, filter); // Define a function to scale the data and mask unwanted pixels. function maskL457sr(image) { // Bit 0 - Fill // Bit 1 - Dilated Cloud // Bit 2 - Unused // Bit 3 - Cloud // Bit 4 - Cloud Shadow var qaMask = image.select('QA_PIXEL').bitwiseAnd(parseInt('11111', 2)).eq(0); var saturationMask = image.select('QA_RADSAT').eq(0); // Apply the scaling factors to the appropriate bands. var opticalBands = image.select('SR_B.').multiply(0.0000275).add(-0.2); var thermalBand = image.select('ST_B6').multiply(0.00341802).add(149.0); // Replace the original bands with the scaled ones and apply the masks. return image.addBands(opticalBands, null, true) .addBands(thermalBand, null, true) .updateMask(qaMask) .updateMask(saturationMask); } // Map over the distinct years collection to build a list of annual image // composites. var lsCompList = joinCol.map(function(img) { // Get the list of images belonging to the given year. return ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(img.get('year_match')) // Apply cloud mask. .map(maskL457sr) // Reduce image collection by median. .reduce(ee.Reducer.median()) // Set composite year as an image property. .copyProperties(img, ['year']); }); // Convert the image List to an ImageCollection. var lsCompCol = ee.ImageCollection(lsCompList);
مركب في اليوم نفسه من خلال الدمج والخفض
هناك حالة إضافية لاستخدام ميزة "دمج الصور" وهي إنشاء mosaics صور متسلسلة مكانيًا. لنفترض أنّ منطقة الاهتمام تمتد على صفَّين من صور Landsat ضمن المسار نفسه وأنّ هدفك هو عرض فسيفساء من الصورتين لكل مدار من مدارات Landsat 8 في عامَي 2017 و2018. هنا، بعد فلترة المجموعة حسب المسار والصف، يتم استخدام عملية دمج لإنشاء فسيفساء من صور Landsat من المسار نفسه، والذي يتم تحديده حسب تاريخ اكتساب البيانات.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var lsCol = ee.ImageCollection('LANDSAT/LC08/C02/T1_L2') .filterDate('2017-01-01', '2019-01-01') .filter('WRS_PATH == 38 && (WRS_ROW == 28 || WRS_ROW == 29)') .map(function(img) { var date = img.date().format('yyyy-MM-dd'); return img.set('date', date); }); var distinctDates = lsCol.distinct('date').sort('date'); var filter = ee.Filter.equals({leftField: 'date', rightField: 'date'}); var join = ee.Join.saveAll('date_match'); var joinCol = join.apply(distinctDates, lsCol, filter); var lsColMos = ee.ImageCollection(joinCol.map(function(col) { return ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(col.get('date_match')).mosaic(); }));
ترتيب
يمكنك ترتيب مجموعة حسب الوقت لضمان التسلسل الزمني الصحيح، أو يمكنك ترتيبها
حسب سمة من اختيارك. يتم تلقائيًا ترتيب سلسلة إطارات العروض المرئية بالترتيب الطبيعي للمجموعة. يمكن تعديل ترتيب السلسلة باستخدام طريقة جمع sort، حيث يتم اختيار سمة Image للترتيب تصاعديًا أو تنازليًا. على سبيل المثال، للتصنيف حسب وقت الرصد، استخدِم السمة system:time_start المتوفّرة في كل مكان.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.1, 37.2)) .sort('system:time_start');
أو ربما يجب تحديد الترتيب من خلال زيادة الغيوم، كما هو الحال في حالة صور Sentinel-2 هذه.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-122.1, 37.2)) .sort('CLOUDY_PIXEL_PERCENTAGE');
يمكن أيضًا تحديد الترتيب من خلال سمة مشتقة، مثل متوسط مؤشر NDVI الإقليمي. في ما يلي، تتم إضافة مؤشر NDVI الإقليمي كخاصية إلى كل صورة في دالة مرتبطة، يليها ترتيب على السمة الجديدة.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an area of interest geometry. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Point(-122.1, 37.2).buffer(1e4); // Filter MODIS NDVI image collection by a date range. var ndviCol = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD13A1') .filterDate('2018-01-01', '2019-01-01') .select('NDVI') // Map over the image collection to calculate regional mean NDVI and add // the result to each image as a property. .map(function(img) { var meanNdvi = img.reduceRegion({ reducer: ee.Reducer.mean(), geometry: aoi, scale: 500}); return img.set('meanNdvi', meanNdvi.get('NDVI')); }) // Sort the collection by descending regional mean NDVI. .sort('meanNdvi', false);
عرض الصور
تحوّل ميزة "تصور الصور" الأرقام إلى ألوان. هناك ثلاث طرق للتحكّم في كيفية تمثيل بيانات الصور بالألوان في طرق تمثيل المجموعات المرئية:
- قدِّم وسيطات العرض المرئية مباشرةً إلى
getVideoThumbURLوgetFilmstripThumbURL. - يمكنك ربط طريقة
visualizeللصور بمجموعة الصور قبل تطبيقgetVideoThumbURLوgetFilmstripThumbURL. - يمكنك ربط طريقة
sldStyleللصور بمجموعة الصور قبل تطبيقgetVideoThumbURLوgetFilmstripThumbURL. اطّلِع على وصف الطبقة المنسَّقة للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات.
تستخدِم الأمثلة الواردة في هذا الدليل الخيارَين 1 و2، حيث يتمّ التمثيل البصري من خلال ربط ثلاث نطاقات صور لصورة متعددة النطاقات بقنوات الألوان الأحمر والأخضر والأزرق أو ترتيب قيم نطاق واحد بشكل خطي على طول لوحة ألوان. تشمل مَعلمات التصور ما يلي:
| المَعلمة | الوصف | النوع |
|---|---|---|
| الفِرق | قائمة مفصولة بفواصل لأسماء ثلاث نطاقات ليتم ربطها بألوان RGB | قائمة |
| دقيقة | القيم المطلوب ربطها بـ 0 | رقم أو قائمة بثلاثة أرقام، رقم واحد لكل نطاق |
| max | القيم المطلوب ربطها بـ 255 | رقم أو قائمة بثلاثة أرقام، رقم واحد لكل نطاق |
| gain | القيم التي يتم ضرب كل قيمة بكسل بها | رقم أو قائمة بثلاثة أرقام، رقم واحد لكل نطاق |
| الانحياز | القيم المطلوب إضافتها إلى كل اسم نطاقات | رقم أو قائمة بثلاثة أرقام، رقم واحد لكل نطاق |
| gamma | عوامل تصحيح أشعة جاما | رقم أو قائمة بثلاثة أرقام، رقم واحد لكل نطاق |
| palette | قائمة سلاسل الألوان بتنسيق CSS (الصور ذات النطاق الواحد فقط) | قائمة سلاسل سداسية عشرية مفصولة بفواصل |
| التعتيم | شفافية الطبقة (0.0 شفافة تمامًا و1.0 معتمة تمامًا) | الرقم |
استخدِم الوسيطة bands لاختيار النطاقات التي تريد عرضها. قدِّم
قائمة بأسماء فرقة واحدة أو ثلاث فرق. بالنسبة إلى الصور المتعدّدة النطاقات، يتم تلقائيًا اختيار النطاقات الثلاثة الأولى. يحدِّد ترتيب أسماء النطاقات
تخصيص اللون، ويتم ربط النطاقات الأولى والثانية والثالثة المدرَجة بالألوان التالية:
الأحمر والأخضر والأزرق، على التوالي.
يُعدّ تغيير مقياس نطاق البيانات عاملاً مهمًا عند عرض الصور. يتم تلقائيًا تصغير قيم البيانات الكسور العشرية بين 0 و1 (بما في ذلك)
إلى ما بين 0 و255 (بما في ذلك). يتم ضبط القيم خارج هذا النطاق على 0 و
255 استنادًا إلى ما إذا كانت أقل من 0 أو أكبر من 1،
على التوالي. في ما يتعلّق بالبيانات الصحيحة، يتم توسيع النطاق الكامل الذي يحدّده نوعها
بين 0 و255 (على سبيل المثال، تتراوح البيانات الموقَّعة ذات الـ 16 بتًا بين
−32,768 و32,767، ويتم توسيع نطاقها تلقائيًا إلى [0، 255]). يمكن أن يؤدي قبول الإعدادات
التلقائية في كثير من الأحيان إلى إنشاء صور مرئية ذات تباين بسيط أو بدون تباين
بين ميزات الصورة. استخدِم min وmax لتحسين التباين وتمييز
نطاق بيانات معيّن. من القواعد الأساسية الجيدة ضبط min وmax على
قيم تمثّل المعدّلَين المئويَّين الثاني والـ 98 للبيانات ضمن
مجال اهتمامك. اطّلِع على المثال التالي لاحتساب هذه القيم لملف
نموذج رقمي للارتفاع.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Import SRTM global elevation model. var demImg = ee.Image('USGS/SRTMGL1_003'); // Define a rectangular area of interest. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[ [-103.84153083119054, 49.083004219142886], [-103.84153083119054, 25.06838270664608], [-85.64817145619054, 25.06838270664608], [-85.64817145619054, 49.083004219142886] ]], null, false); // Calculate the 2nd and 98th percentile elevation values from rescaled (to // 500m) pixels intersecting the area of interest. A Dictionary is returned. var percentClip = demImg.reduceRegion({ reducer: ee.Reducer.percentile([2, 98]), geometry: aoi, scale: 500, maxPixels: 3e7 }); // Print the regional 2nd and 98th percentile elevation values. Get the // dictionary keys and use them to get the values for each percentile summary. var keys = percentClip.keys(); print('Set vis min to:', ee.Number(percentClip.get(keys.get(0))).round()); print('Set vis max to:', ee.Number(percentClip.get(keys.get(1))).round());
تحدّد المَعلمة palette الألوان التي تمثّل صورة العروض المرئية التي تبلغ دقتها 8 بت. ولا ينطبق ذلك إلا على التمثيلات ذات النطاق الواحد، ويؤدي تحديده باستخدام صورة متعددة النطاقات إلى حدوث خطأ.
إذا كانت البيانات من نطاق واحد أو أردت عرض نطاق واحد من
صورة متعددة النطاقات، اضبط المَعلمة forceRgbOutput على true (غير ضروري
إذا تم تقديم الوسيطة palette). استخدِم المَعلمتَين min وmax لتحديد نطاق القيم التي سيتم توسيع نطاقها بشكل خطي بين 0 و255.
في ما يلي مثال على تعيين دالة تصور على مجموعة صور
تتضمّن نطاقًا واحدًا. يتم استيراد مجموعة MODIS NDVI، ويتم ضبط مفسّرات العروض المرئية لطريقة visualization، ويتم ربط دالة تحول القيم إلى تمثيلات صور RGB على مجموعة NDVI.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Filter MODIS NDVI image collection by a date range. var ndviCol = ee.ImageCollection('MODIS/061/MOD13A1') .filterDate('2018-01-01', '2019-01-01') .select('NDVI'); // Define visualization arguments. var visArgs = { min: 0, max: 9000, palette: [ 'FFFFFF', 'CE7E45', 'DF923D', 'F1B555', 'FCD163', '99B718', '74A901', '66A000', '529400', '3E8601', '207401', '056201', '004C00', '023B01', '012E01', '011D01', '011301' ] }; // Define a function to convert an image to an RGB visualization image and copy // properties from the original image to the RGB image. var visFun = function(img) { return img.visualize(visArgs).copyProperties(img, img.propertyNames()); }; // Map over the image collection to convert each image to an RGB visualization // using the previously defined visualization function. var ndviColVis = ndviCol.map(visFun);
في ما يلي مثال على ربط وظيفة العروض المرئية بمجموعة صور متعددة النطاقات:
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Assemble a collection of Sentinel-2 surface reflectance images for a given // region and date range. var s2col = ee.ImageCollection('COPERNICUS/S2_SR') .filterBounds(ee.Geometry.Point(-96.9037, 48.0395)) .filterDate('2019-06-01', '2019-10-01'); // Define visualization arguments. var visArgs = {bands: ['B11', 'B8', 'B3'], min: 300, max: 3500}; // Define a function to convert an image to an RGB visualization image and copy // properties from the original image to the RGB image. var visFun = function(img) { return img.visualize(visArgs).copyProperties(img, img.propertyNames()); }; // Map over the image collection to convert each image to an RGB visualization // using the previously defined visualization function. var s2colVis = s2col.map(visFun);
في هذه الحالة، لا يتم تقديم أيّ وسيطة لوحة ألوان لأنّه يتم تقديم ثلاث نطاقات،
تحدّد كثافة كلّ طبقة من طبقات RGB. يُرجى العِلم أنّ كلا المثالَين يستخدمان المَعلمتَين
min وmax للتحكّم في القيم التي يتم تمديدها إلى حدود
بيانات RGB ذات الـ 8 بت.
الصورة المصغّرة للفيديو
تنشئ الدالة getVideoThumbURL() رسمًا متحرّكًا من جميع الصور في
ImageCollection حيث تمثّل كل صورة لقطة. في ما يلي الخطوات العامة
لإنشاء صورة متحركة:
- حدِّد
Geometryتحدِّد حدوده النطاق الإقليمي للتأثير المتحرك. - حدِّد
ImageCollection. - ننصحك بالتفكير في العرض المرئي للصور: إما ربط وظيفة عرض مرئي للصور بالمجموعة أو إضافة مَعلمات العرض المرئي للصور إلى مجموعة مَعلمات الصور المتحركة.
- حدِّد وسيطات الصورة المتحركة واستدِع طريقة
getVideoThumbURL.
نتيجة getVideoThumbURL هي عنوان URL. اطبع عنوان URL في وحدة التحكّم
وانقر عليه لبدء تشغيل خوادم Earth Engine التي تنشئ الصورة المتحركة أثناء التشغيل في
علامة تبويب متصفّح جديدة. بدلاً من ذلك، يمكنك عرض الصورة المتحركة في وحدة تحكّم
أداة "محرر الرموز البرمجية" من خلال استدعاء دالة ui.Thumbnail في المجموعة ومَعلمات
الصورة المتحركة المقابلة لها. بعد التصدير، يصبح المشهد المتحرك متاحًا
للتنزيل من خلال النقر عليه بزر الماوس الأيمن واختيار الخيارات المناسبة
من قائمة السياقات.
يوضِّح المثال التالي إنشاء صورة متحركة تعرض ملفًا شخصيًا
للتعامُل مع درجات الحرارة على مستوى العالم على مدار 24 ساعة. يُرجى العِلم أنّ هذا المثال يتضمّن
وسيطات الرسم البياني مع وسيطات الرسوم المتحركة، بدلاً من
ربط وظيفة الرسم البياني أولاً على ImageCollection. عند تنفيذ
هذا النص البرمجي، من المفترض أن يظهر رسم متحرك مشابه للشكل 3 في وحدة تحكّم "محرِّر رموزالبرمجة".
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an area of interest geometry with a global non-polar extent. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[[-179.0, 78.0], [-179.0, -58.0], [179.0, -58.0], [179.0, 78.0]]], null, false); // Import hourly predicted temperature image collection for northern winter // solstice. Note that predictions extend for 384 hours; limit the collection // to the first 24 hours. var tempCol = ee.ImageCollection('NOAA/GFS0P25') .filterDate('2018-12-22', '2018-12-23') .limit(24) .select('temperature_2m_above_ground'); // Define arguments for animation function parameters. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: aoi, framesPerSecond: 7, crs: 'EPSG:3857', min: -40.0, max: 35.0, palette: ['blue', 'purple', 'cyan', 'green', 'yellow', 'red'] }; // Print the animation to the console as a ui.Thumbnail using the above defined // arguments. Note that ui.Thumbnail produces an animation when the first input // is an ee.ImageCollection instead of an ee.Image. print(ui.Thumbnail(tempCol, videoArgs)); // Alternatively, print a URL that will produce the animation when accessed. print(tempCol.getVideoThumbURL(videoArgs));
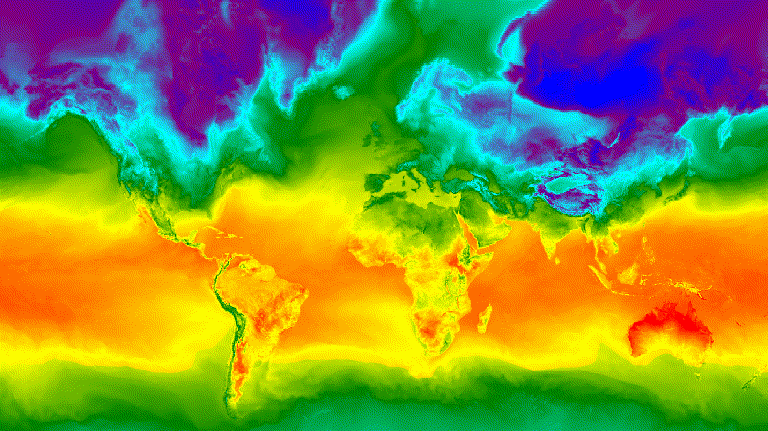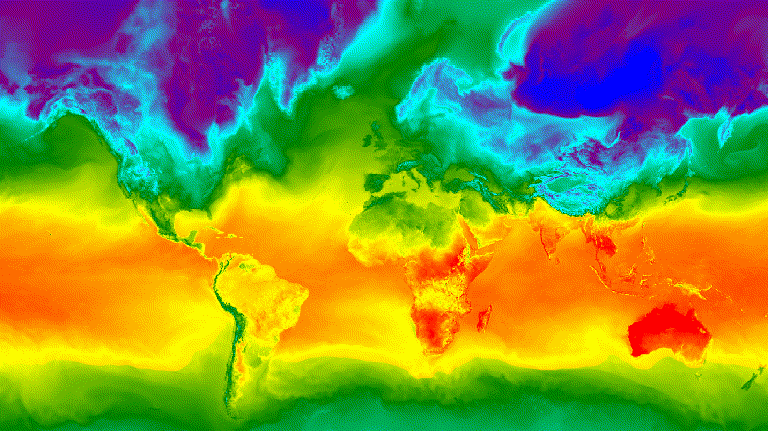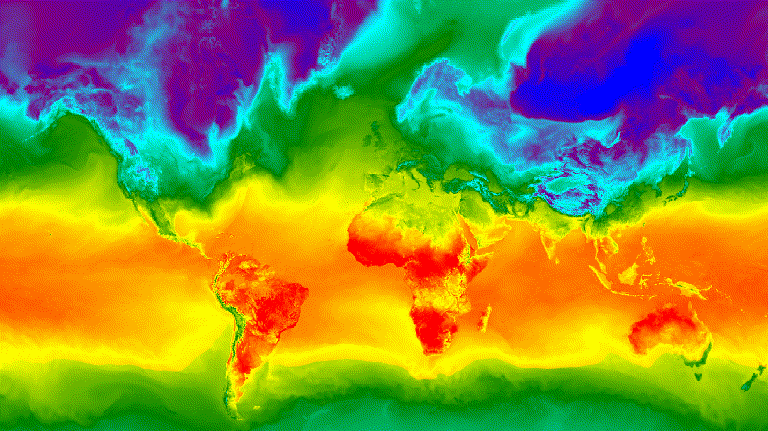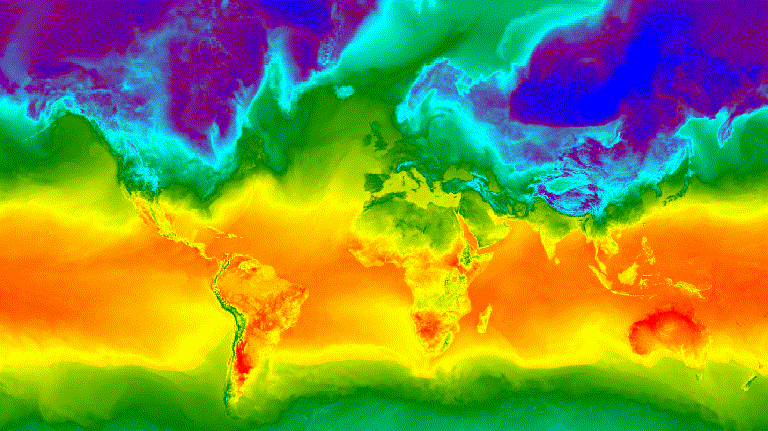
الشكل 3. درجة الحرارة السطحية بالساعة لانقلاب الشتاء الشمالي
ممثّلة كصورة GIF متحركة
شريط الصور
تنشئ الدالة getFilmstripThumbUrl صورة ثابتة واحدة
تمثّل تسلسل جميع الصور في ImageCollection في
سلسلة من الشمال إلى الجنوب. يتّبع تسلسل لقطات شريط الصور السينمائي الترتيب الطبيعي
للمجموعة.
نتيجة getFilmstripThumbUrl هي عنوان URL. اطبع عنوان URL في وحدة التحكّم
وانقر عليه لبدء تشغيل خوادم Earth Engine لإنشاء الصورة أثناء التنقل في
علامة تبويب متصفّح جديدة. بعد عرض الصورة، تصبح متاحة للتنزيل من خلال
النقر بزر الماوس الأيمن عليها واختيار الخيارات المناسبة من قائمة السياقات.
يستخدم المقتطف التالي من الرمز البرمجي المجموعة نفسها المستخدَمة في مثال الصورة المصغّرة للفيديو أعلاه. عند تنفيذ هذا النص البرمجي، من المفترض أن يظهر شريط صور مشابه للشكل 4 في وحدة تحكّم "محرِّر الرموز البرمجية".
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an area of interest geometry with a global non-polar extent. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[[-179.0, 78.0], [-179.0, -58.0], [179.0, -58.0], [179.0, 78.0]]], null, false); // Import hourly predicted temperature image collection for northern winter // solstice. Note that predictions extend for 384 hours; limit the collection // to the first 24 hours. var tempCol = ee.ImageCollection('NOAA/GFS0P25') .filterDate('2018-12-22', '2018-12-23') .limit(24) .select('temperature_2m_above_ground'); // Define arguments for the getFilmstripThumbURL function parameters. var filmArgs = { dimensions: 128, region: aoi, crs: 'EPSG:3857', min: -40.0, max: 35.0, palette: ['blue', 'purple', 'cyan', 'green', 'yellow', 'red'] }; // Print a URL that will produce the filmstrip when accessed. print(tempCol.getFilmstripThumbURL(filmArgs));
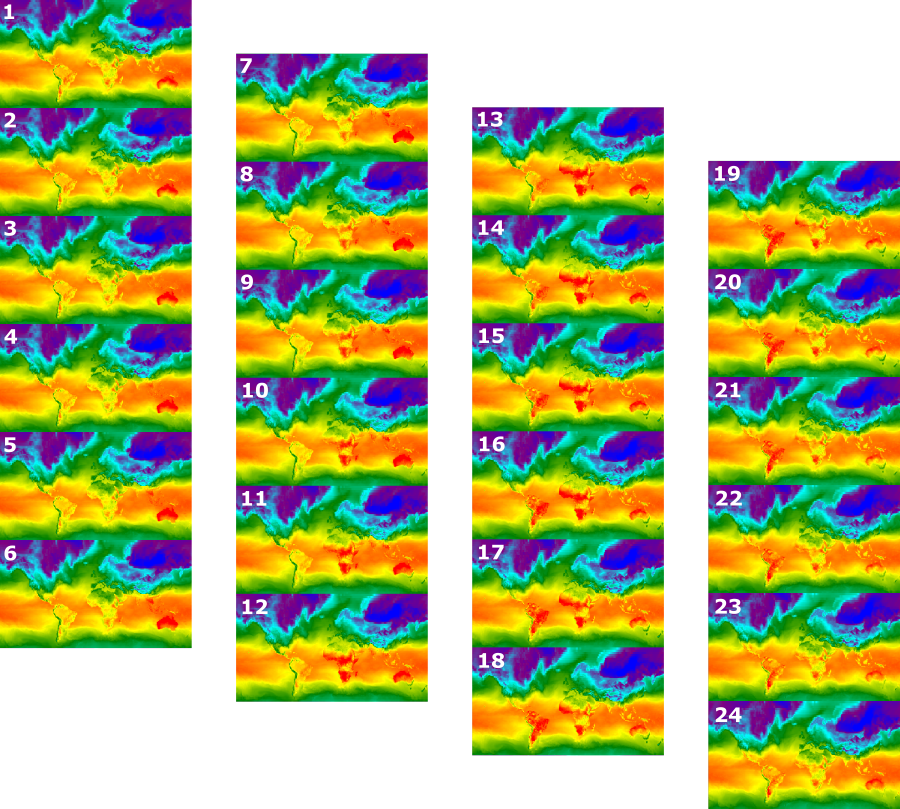
الشكل 4. درجة الحرارة على السطح كل ساعة في يوم الانقلاب الشتوي في نصف الكرة الشمالي
ممثّلة كصورة PNG لشريط سينمائي يُرجى العلم أنّه تم хувين شريط الفيلم
إلى أربعة أقسام للعرض، ونتيجة getFilmstripThumbURL
هي سلسلة واحدة من صور المجموعة تم ربطها من الشمال إلى الجنوب.
الأساليب المتقدّمة
توضِّح الأقسام التالية كيفية استخدام الاقتصاص والشفافية ودمج الطبقات لتحسين العروض المرئية من خلال إضافة حدود المضلّعات، والتأكيد على مناطق الاهتمام، ومقارنة الصور ضمن مجموعة.
يُرجى العِلم أنّ جميع الأمثلة التالية في هذا القسم تستخدِم القاعدة نفسها
ImageCollection المحدّدة هنا:
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Import hourly predicted temperature image collection for northern winter // solstice. Note that predictions extend for 384 hours; limit the collection // to the first 24 hours. var tempCol = ee.ImageCollection('NOAA/GFS0P25') .filterDate('2018-12-22', '2018-12-23') .limit(24) .select('temperature_2m_above_ground'); // Define visualization arguments to control the stretch and color gradient // of the data. var visArgs = { min: -40.0, max: 35.0, palette: ['blue', 'purple', 'cyan', 'green', 'yellow', 'red'] }; // Convert each image to an RGB visualization image by mapping the visualize // function over the image collection using the arguments defined previously. var tempColVis = tempCol.map(function(img) { return img.visualize(visArgs); }); // Import country features and filter to South American countries. var southAmCol = ee.FeatureCollection('USDOS/LSIB_SIMPLE/2017') .filterMetadata('wld_rgn', 'equals', 'South America'); // Define animation region (South America with buffer). var southAmAoi = ee.Geometry.Rectangle({ coords: [-103.6, -58.8, -18.4, 17.4], geodesic: false});
تراكبات
يمكن تراكب صور متعددة باستخدام طريقة blend Image التي يتم فيها دمج بكسل متداخل من صورتَين استنادًا إلى أقنعةهما (الشفافية).
تراكُب مرئي
يمكن أن تؤدي إضافة مضلّعات الحدود الإدارية والأشكال الهندسية الأخرى إلى صورة إلى توفير سياق مكاني قيّم. راجِع الصورة المتحركة أعلاه (الشكل 3) التي تعرض درجة حرارة سطح الأرض اليومية على مستوى العالم. يمكن تمييز الحدود بين اليابسة والمحيط إلى حدّ ما، ولكن يمكن توضيحها من خلال إضافة شكل هندسي ملتصق بالبلدان.
يتم رسم بيانات المتجهات (Features) على الصور من خلال تطبيق طريقة paint.
يمكن رسم العناصر على صورة حالية، ولكن من الأفضل
رسمها على صورة فارغة وتطبيق نمط عليها، ثم دمج النتيجة مع غيرها من
طبقات الصور المنمّقة. من خلال التعامل مع كل طبقة من حِزمة العروض المرئية
بشكل مستقل، يمكنك التحكّم بشكل أكبر في التصميم.
يوضّح المثال التالي رسم حدود بلدان أمريكا الجنوبية على سطح
Image فارغ ومزج النتيجة مع كل Image من مجموعة
الحرارة اليومية العالمية (الشكل 5). تُظهر حدود البلدان التي تمّت إضافتها فوق الخريطة
الفرق بين اليابسة والمياه، كما توفّر سياقًا لنماذج درجات الحرارة.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an empty image to paint features to. var empty = ee.Image().byte(); // Paint country feature edges to the empty image. var southAmOutline = empty .paint({featureCollection: southAmCol, color: 1, width: 1}) // Convert to an RGB visualization image; set line color to black. .visualize({palette: '000000'}); // Map a blend operation over the temperature collection to overlay the country // border outline image on all collection images. var tempColOutline = tempColVis.map(function(img) { return img.blend(southAmOutline); }); // Define animation arguments. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: southAmAoi, framesPerSecond: 7, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display the animation. print(ui.Thumbnail(tempColOutline, videoArgs));
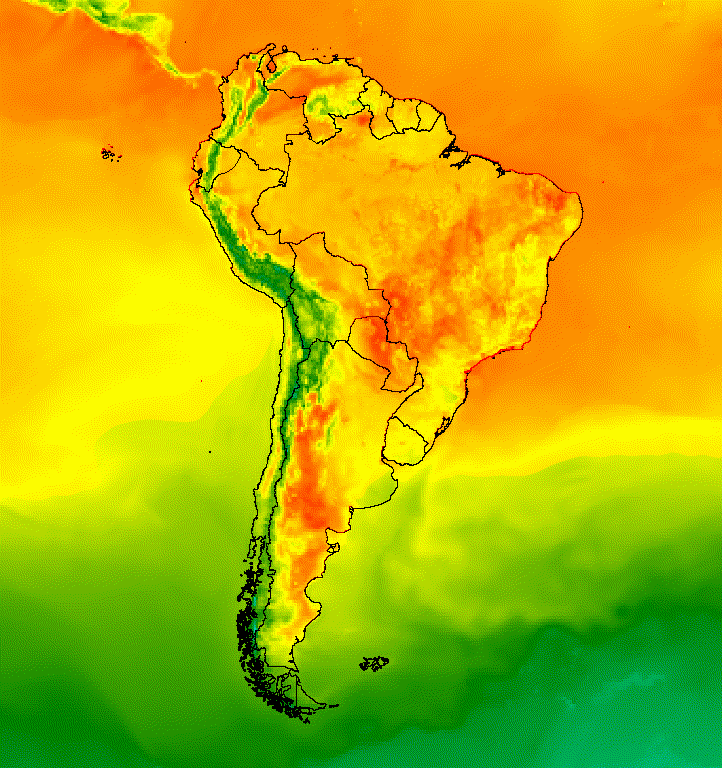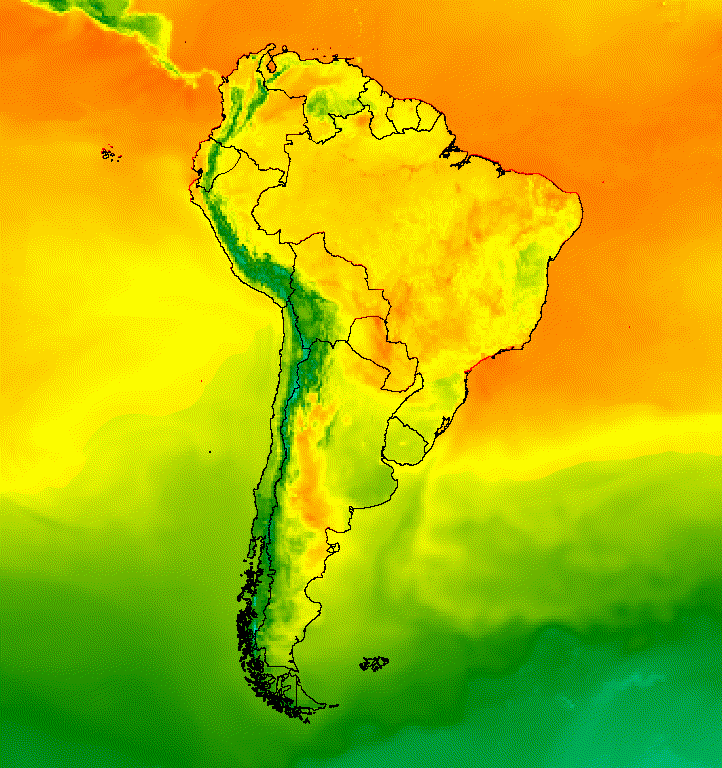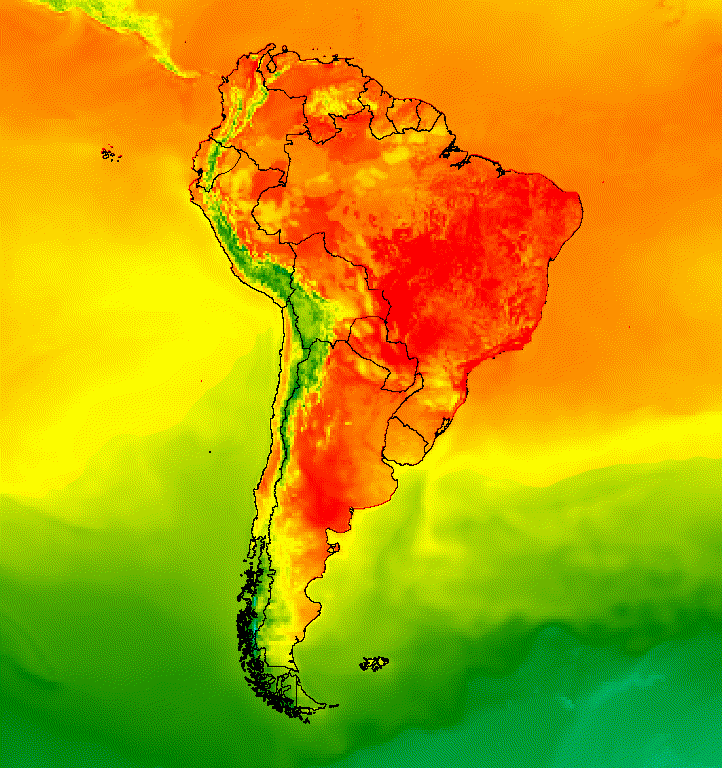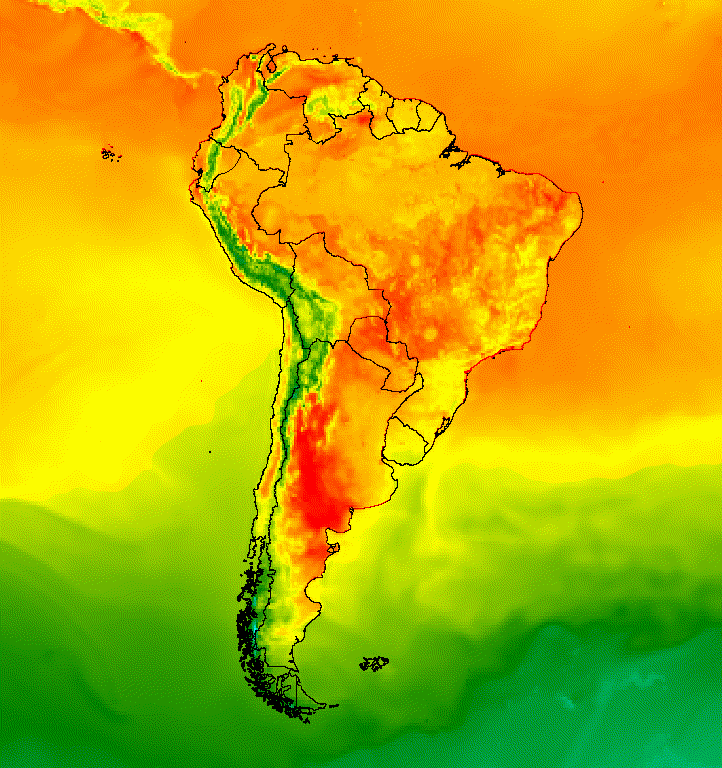
الشكل 5. أضِف صورًا مركبة متجهّة إلى الصور في مجموعة لتوفير سياق مكاني.
صورة فوق صورة
يمكن دمج عدّة صور لتحقيق النمط المطلوب. لنفترض أنّك تريد التأكيد على منطقة ذات أهمية. يمكنك إنشاء نسخة صامتة من تمثيل بصري لصورة كطبقة أساسية، ثمّ وضع نسخة مقتطعة من التمثيل البصري الأصلي فوقها. استنادًا إلى المثال السابق، يعرض الرمز البرمجي التالي الشكل 6.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an empty image to paint features to. var empty = ee.Image().byte(); // Paint country feature edges to the empty image. var southAmOutline = empty .paint({featureCollection: southAmCol, color: 1, width: 1}) // Convert to an RGB visualization image; set line color to black. .visualize({palette: '000000'}); // Map a blend operation over the temperature collection to overlay the country // border outline image on all collection images. var tempColOutline = tempColVis.map(function(img) { return img.blend(southAmOutline); }); // Define a partially opaque grey RGB image to dull the underlying image when // blended as an overlay. var dullLayer = ee.Image.constant(175).visualize({ opacity: 0.6, min: 0, max: 255, forceRgbOutput: true}); // Map a two-part blending operation over the country outline temperature // collection for final styling. var finalVisCol = tempColOutline.map(function(img) { return img // Blend the dulling layer with the given country outline temperature image. .blend(dullLayer) // Blend a clipped copy of the country outline temperature image with the // dulled background image. .blend(img.clipToCollection(southAmCol)); }); // Define animation arguments. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: southAmAoi, framesPerSecond: 7, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display the animation. print(ui.Thumbnail(finalVisCol, videoArgs));
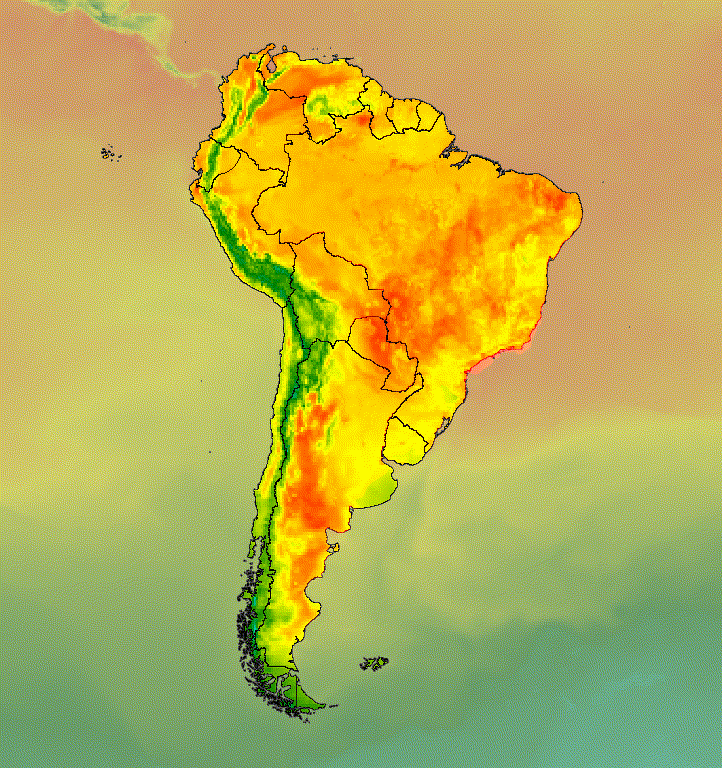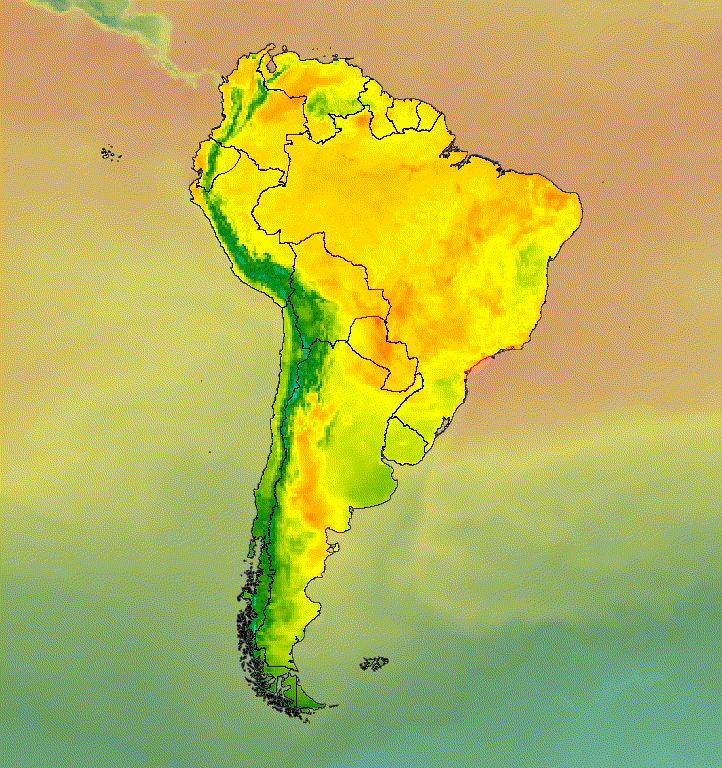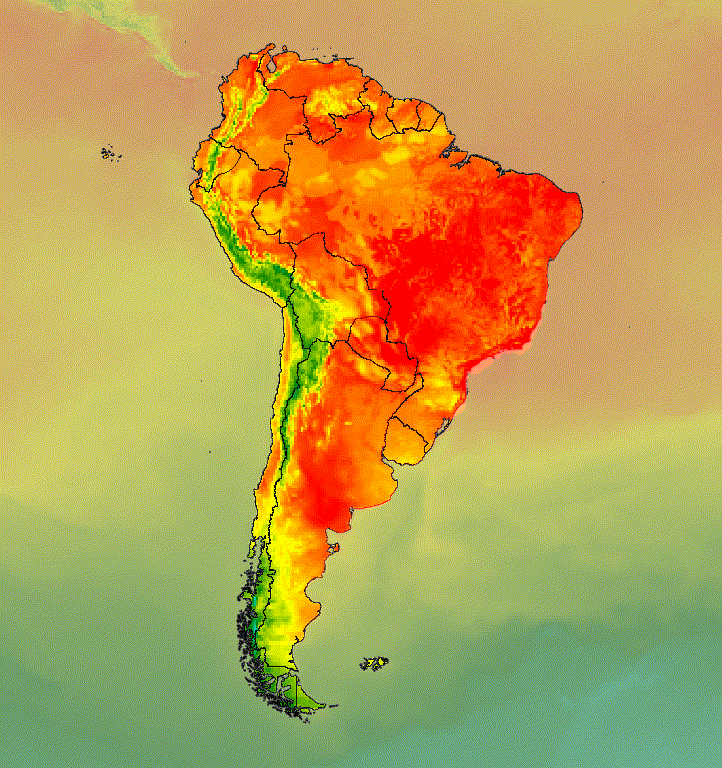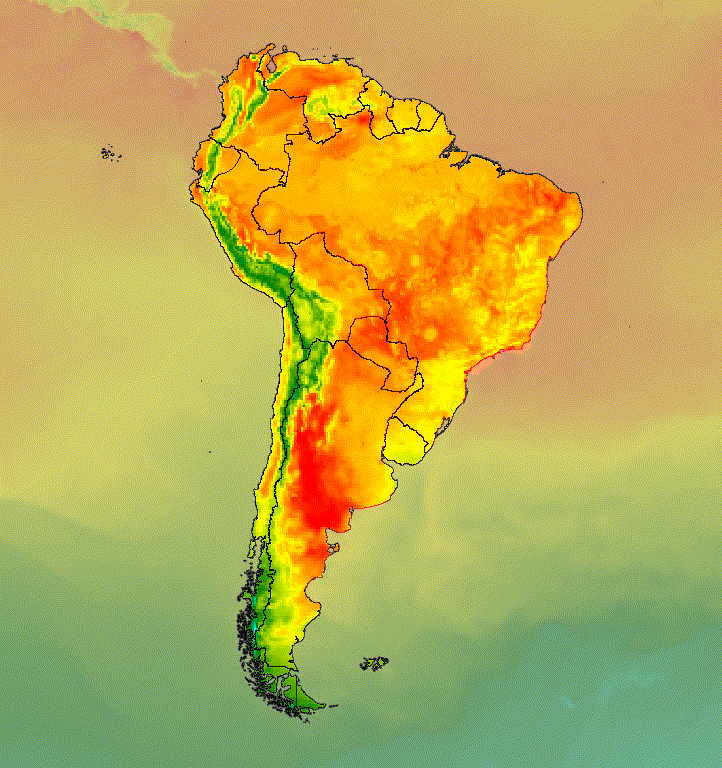
الشكل 6. يمكنك التأكيد على منطقة ذات أهمية من خلال اقتصاص الصورة ووضعها فوق نسخة تم كتم صوتها.
يمكنك أيضًا دمج بيانات الصور مع طبقة أساسية لظلال التلال للإشارة إلى التضاريس وإضفاء بعض العمق على العرض المرئي (الشكل 7).
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define a hillshade layer from SRTM digital elevation model. var hillshade = ee.Terrain.hillshade(ee.Image('USGS/SRTMGL1_003') // Exaggerate the elevation to increase contrast in hillshade. .multiply(100)) // Clip the DEM by South American boundary to clean boundary between // land and ocean. .clipToCollection(southAmCol); // Map a blend operation over the temperature collection to overlay a partially // opaque temperature layer on the hillshade layer. var finalVisCol = tempColVis.map(function(img) { return hillshade .blend(img.clipToCollection(southAmCol).visualize({opacity: 0.6})); }); // Define animation arguments. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: southAmAoi, framesPerSecond: 7, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display the animation. print(ui.Thumbnail(finalVisCol, videoArgs));

الشكل 7. عرض التضاريس من خلال تراكب بيانات صور شفافة جزئيًا على
طبقة تظليل التلال
الانتقالات
يمكنك تخصيص مجموعة صور لإنشاء صور متحركة تُظهر الاختلافات بين صورتَين ضمن مجموعة باستخدام انتقالات التمويه والوميض والانزلاق. تستخدِم كلّ من الأمثلة التالية الرسم البياني الأساسي نفسه الذي تم إنشاؤه باستخدام النص البرمجي التالي:
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define an area of interest geometry with a global non-polar extent. var aoi = ee.Geometry.Polygon( [[[-179.0, 78.0], [-179.0, -58.0], [179.0, -58.0], [179.0, 78.0]]], null, false); // Import hourly predicted temperature image collection. var temp = ee.ImageCollection('NOAA/GFS0P25') // Define a northern summer solstice temperature image. var summerSolTemp = temp .filterDate('2018-06-21', '2018-06-22') .filterMetadata('forecast_hours', 'equals', 12) .first() .select('temperature_2m_above_ground'); // Define a northern winter solstice temperature image. var winterSolTemp = temp .filterDate('2018-12-22', '2018-12-23') .filterMetadata('forecast_hours', 'equals', 12) .first() .select('temperature_2m_above_ground'); // Combine the solstice images into a collection. var tempCol = ee.ImageCollection([ summerSolTemp.set('season', 'summer'), winterSolTemp.set('season', 'winter') ]); // Import international boundaries feature collection. var countries = ee.FeatureCollection('USDOS/LSIB_SIMPLE/2017'); // Define visualization arguments. var visArgs = { min: -40.0, max: 35.0, palette: ['blue', 'purple', 'cyan', 'green', 'yellow', 'red'] }; // Convert the image data to RGB visualization images. // The clip and unmask combination sets ocean pixels to black. var tempColVis = tempCol.map(function(img) { return img .visualize(visArgs) .clipToCollection(countries) .unmask(0) .copyProperties(img, img.propertyNames()); });
Flicker
في حال توفّر صورتَين فقط في المجموعة، كما هو الحال هنا، يكون الوميض هو
العرض التلقائي عند عرض صورة المجموعة المتحركة. عدِّل الوسيطة
framesPerSecond للحركة لزيادة معدّل flicker
أو إبطائه. تؤدي الوسائط التالية للعرض التي تم تطبيقها على المجموعة أعلاه
إلى إنشاء الشكل 8.
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define arguments for animation function parameters. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: aoi, framesPerSecond: 2, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display animation to the Code Editor console. print(ui.Thumbnail(tempColVis, videoArgs));
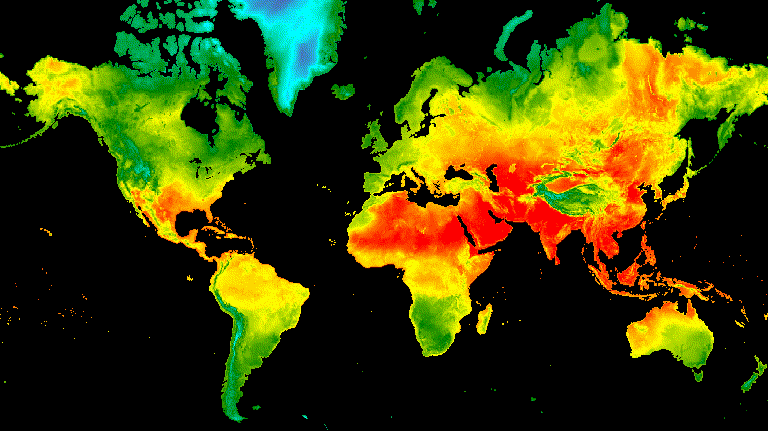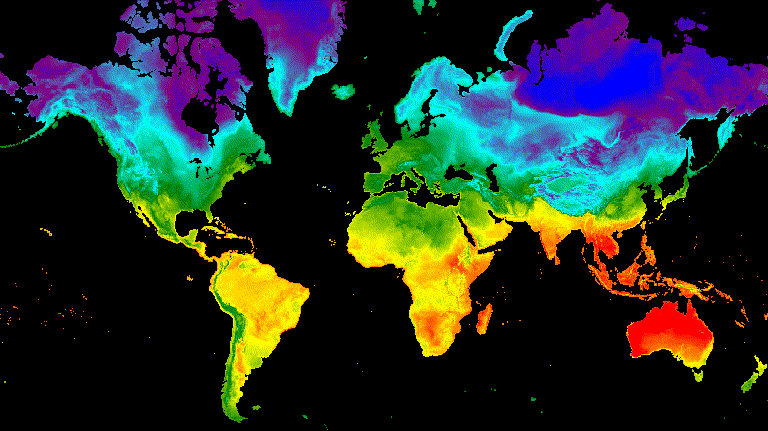
الشكل 8. مثال على الوميض بين درجة حرارة السطح عند الساعة 12 ظهرًا بالتوقيت العالمي المنسَّق لانقلابي الانقلاب الشتوي والانقلاب الصيفي في نصف الكرة الشمالي
تلاشي
يتم تحقيق انتقال تمويه بين طبقتَين عن طريق خفض مستوى التعتيم في إحدى الطبقتَين في الوقت نفسه مع زيادة مستوى التعتيم في الطبقة الأخرى على مدار تسلسل من زيادات التعتيم من 0 تقريبًا إلى 1 (الشكل 9).
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define a sequence of decreasing opacity increments. Note that opacity cannot // be 0, so near 1 and 0 are used. Near 1 is needed because a compliment is // calculated in a following step that can result in 0 if 1 is an element of the // list. var opacityList = ee.List.sequence({start: 0.99999, end: 0.00001, count: 20}); // Filter the summer and winter solstice images from the collection and set as // image objects. var summerImg = tempColVis.filter(ee.Filter.eq('season', 'summer')).first(); var winterImg = tempColVis.filter(ee.Filter.eq('season', 'winter')).first(); // Map over the list of opacity increments to iteratively adjust the opacity of // the two solstice images. Returns a list of images. var imgList = opacityList.map(function(opacity) { var opacityCompliment = ee.Number(1).subtract(ee.Number(opacity)); var winterImgFade = winterImg.visualize({opacity: opacity}); var summerImgFade = summerImg.visualize({opacity: opacityCompliment}); return summerImgFade.blend(winterImgFade).set('opacity', opacity); }); // Convert the image list to an image collection; the forward phase. var fadeForward = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(imgList); // Make a copy of the collection that is sorted by ascending opacity to // represent the reverse phase. var fadeBackward = fadeForward.sort({property: 'opacity'}); // Merge the forward and reverse phase frame collections. var fadeCol = fadeForward.merge(fadeBackward); // Define animation arguments. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: aoi, framesPerSecond: 25, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display the animation. print(ui.Thumbnail(fadeCol, videoArgs));
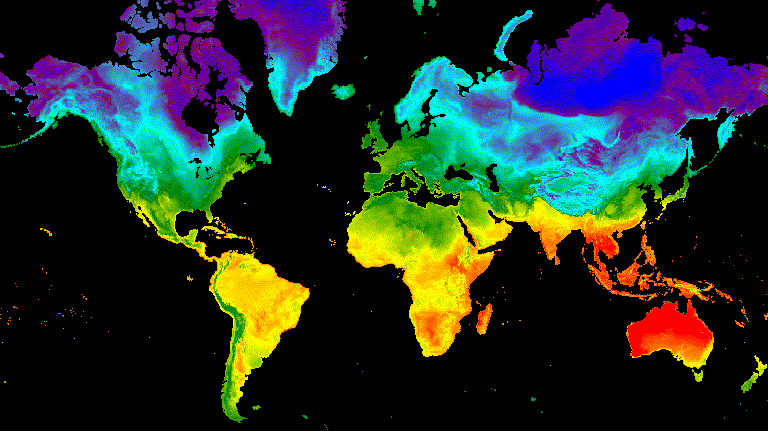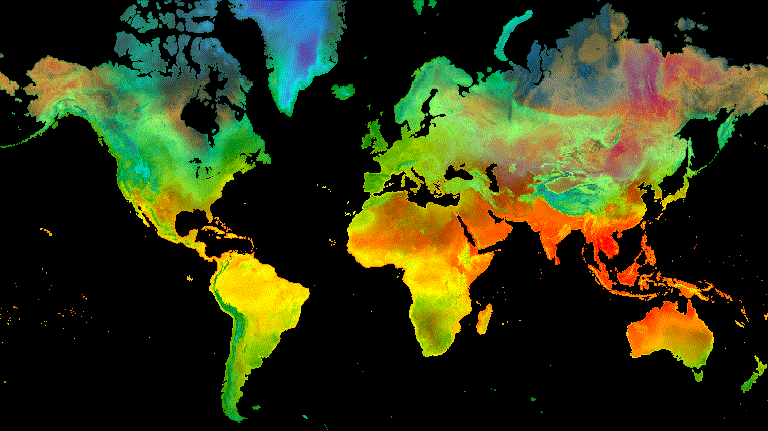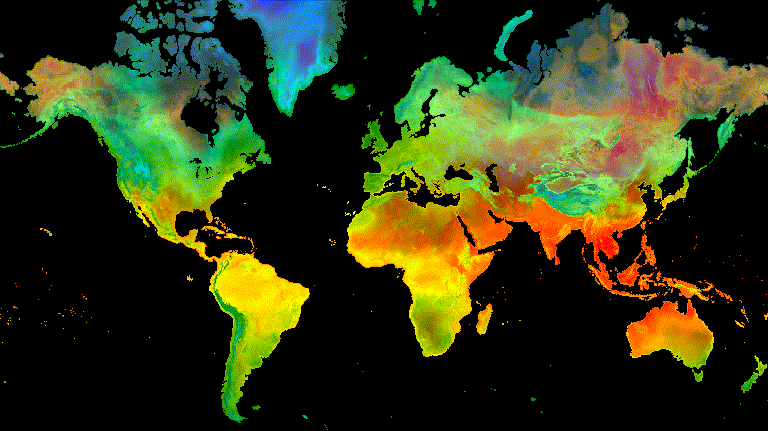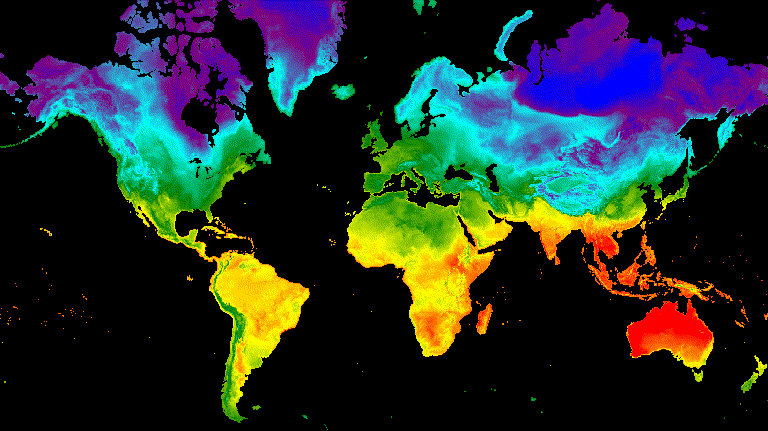
الشكل 9. مثال على تلاشي درجة حرارة سطح الأرض بين الساعة 12 ظهرًا بالتوقيت العالمي المتفق عليه في الصيف
وانقلاب الشمس الشتوي
شريط التمرير
تعرِض عملية انتقال شريط التمرير تدريجيًا طبقة الصورة الأساسية وتُخفيها. ويتم ذلك من خلال تعديل التعتيم بشكل متكرّر للصورة المتراكبة على مستوى مجموعة من خطوط الطول (الشكل 10).
محرِّر الرموز البرمجية (JavaScript)
// Define a sequence of longitude increments. Start and end are defined by the // min and max longitude of the feature to be provided to the region parameter // of the animation arguments dictionary. var lonSeq = ee.List.sequence({start: -179, end: 179, count: 20}); // Define a longitude image. var longitude = ee.Image.pixelLonLat().select('longitude'); // Filter the summer and winter solstice images from the collection and set as // image objects. var summerImg = tempColVis.filter(ee.Filter.eq('season', 'summer')).first(); var winterImg = tempColVis.filter(ee.Filter.eq('season', 'winter')).first(); // Map over the list of longitude increments to iteratively adjust the mask // (opacity) of the overlying image layer. Returns a list of images. var imgList = lonSeq.map(function(lon) { lon = ee.Number(lon); var mask = longitude.gt(lon); return summerImg.blend(winterImg.updateMask(mask)).set('lon', lon); }); // Convert the image list to an image collection; concealing phase. var sliderColForward = ee.ImageCollection.fromImages(imgList); // Make a copy of the collection that is sorted by descending longitude to // represent the revealing phase. var sliderColbackward = sliderColForward .sort({property: 'lon', ascending: false}); // Merge the forward and backward phase frame collections. var sliderCol = sliderColForward.merge(sliderColbackward); // Define animation arguments. var videoArgs = { dimensions: 768, region: aoi, framesPerSecond: 25, crs: 'EPSG:3857' }; // Display the animation. print(ui.Thumbnail(sliderCol, videoArgs));
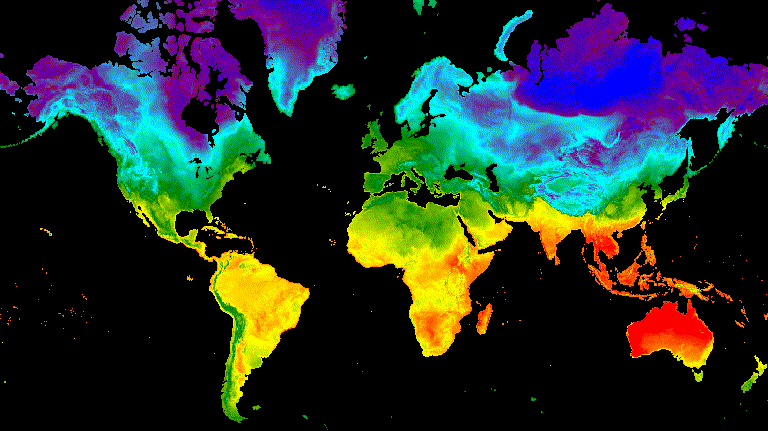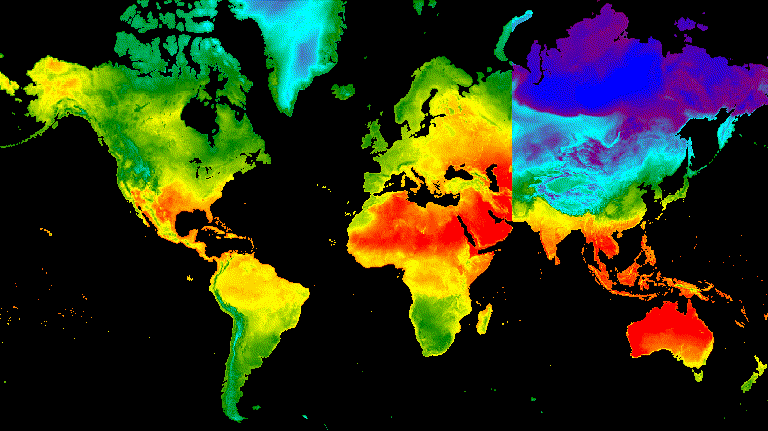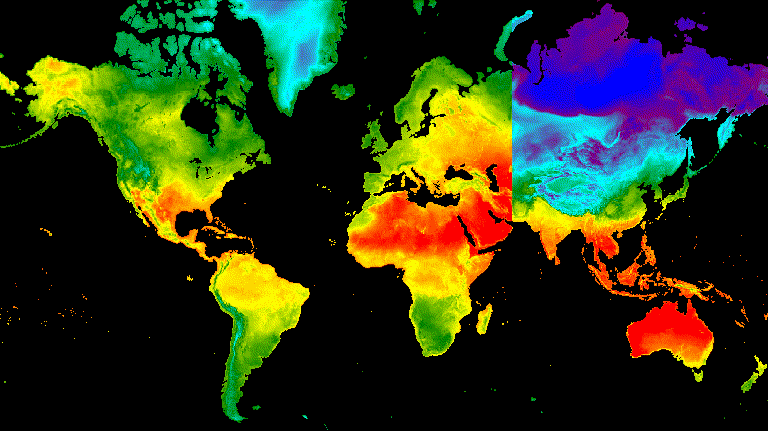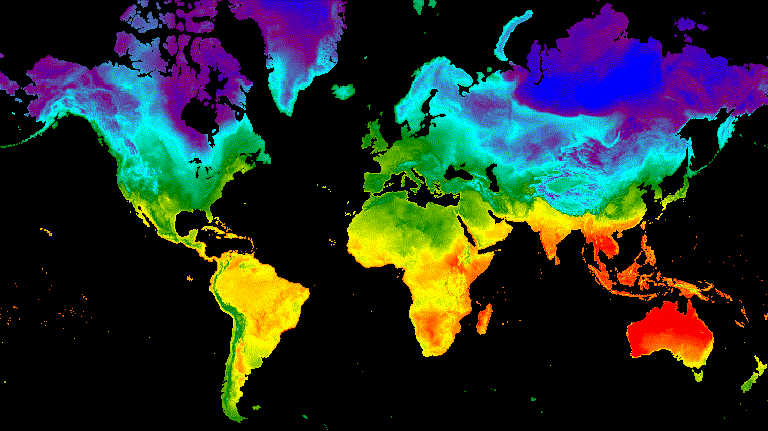
الشكل 10. مثال على انتقال سلس بين درجة حرارة السطح عند الساعة 12 ظهرًا بالتوقيت العالمي المتفق عليه
لانقلاب الصيف والشتاء