DSPL-Schema
Mit Sammlungen den Überblick behalten
Sie können Inhalte basierend auf Ihren Einstellungen speichern und kategorisieren.
Diese Seite und ihre verknüpften Unterseiten dokumentieren das DSPL-XML-Schema.
Dieses Material richtet sich an fortgeschrittene Nutzer, die mehr über
die Low-Level-Details der Sprache; für die meisten Nutzenden
im
Der Entwicklerleitfaden sollte zum Erstellen und Bearbeiten
DSPL-Datasets.
Das vollständige XML-Schema steht im XSD-Format zum Download zur Verfügung.
am
DSPL-Code-Website.
Element: dspl
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
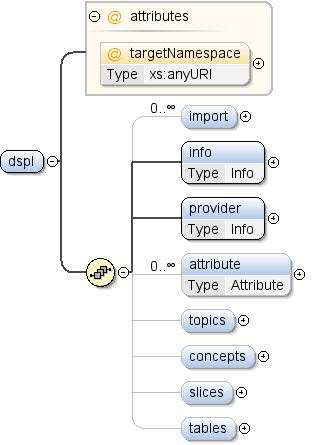
Eine DSPL-Spezifikation beschreibt ein Dataset. Ein Dataset ist
die durch ihren Namensraum identifiziert werden. Ein Dataset besteht aus
-Elemente: - Tabellen: Daten für die Konzepte und Segmente, die in den
Dataset – Konzepte: Benutzerdefinierte Definitionen und Strukturen, die in den
Dataset – Segmente: Kombinationen aus Dimensionen und Messwerten in der
Dataset – Themen: Hierarchische Labels zur Organisation der Konzepte
des Datasets |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Attribute |
|
| Modell |
import*, info, provider
Attribut* , Themen{0,1} , Konzepte{0,1} , Segmente{0,1} , Tabellen{0,1} |
| Children |
Attribut, Konzepte, Import,
Info, Anbieter, Segmente,
Tabellen, Themen |
| Instanz |
<dspl targetNamespace="">
<import location="" namespace="">{0,unbounded}</import>
<info>{1,1}</info>
<provider>{1,1}</provider>
<attribute concept="" id="">{0,unbounded}</attribute>
<topics>{0,1}</topics>
<concepts>{0,1}</concepts>
<slices>{0,1}</slices>
<tables>{0,1}</tables>
</dspl>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| targetNamespace |
xs:anyURI |
|
|
optional |
Jedes Dataset kann einen Ziel-Namespace bereitstellen. Das Ziel
Namespace ist ein URI, der das Dataset eindeutig identifiziert. Weitere Informationen
Informationen zur Verwendung von Namespaces in XML finden Sie unter:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/ Wenn kein targetNamespace festgelegt ist
bereitgestellt wird, wird ein Namespace generiert, wenn das Dataset
importiert. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="dspl">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A DSPL specification describes a dataset. A dataset is
identified by its namespace. A dataset is comprised of the
following elements:
- Tables: Data for the concepts and slices defined in the
dataset
- Concepts: User-specified definitions and structures used in
the dataset
- Slices: Combinations of dimensions and metrics present in
the dataset
- Topics: Hierarchical labels used to organise the concepts of
the dataset</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="import" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Import directive for external datasets -- modeled after
the XML Schema import directive. In order to use
elements defined in an external dataset, the external
dataset must be referenced using an import directive.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="namespace" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The namespace of the imported dataset, specified as
a URI. A prefix must be associated with this
namespace before its contents can be referenced. See
[XML Namespaces] for more information about the use
of namespaces and prefixes in XML.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="location" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An optional location where the definition of the
imported dataset can be found, specified as a
URL. If the location is omitted, the system
processing this DSPL dataset must already know the
imported dataset.
Implementation note: The Google dataset importer
ignores the location attribute. Any imported dataset
must be known by the Google importer beforehand.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="info" type="Info" minOccurs="1">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>General information about the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="provider" type="Info">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>General information about the dataset provider.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Attribute associated with the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="topics" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A hierarchy of topics used to organize the contents of
the dataset. The order in which topics are given is
meaningful and should be respected by visualizations
that displays these topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="topic" type="Topic" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="concepts" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of concepts defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="concept" type="Concept" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="slices" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of slices defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="slice" type="Slice" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tables" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of tables defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="table" type="Table" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="targetNamespace" type="xs:anyURI" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Each dataset may provide a target namespace. The
target namespace is a URI that uniquely identifies the
dataset. For more information about the use of namespaces in XML,
see:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/
If no targetNamespace is provided, then a namespace will be
generated when the dataset is imported.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
Element: dspl / import
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Importanweisung für externe Datasets – modelliert nach der XML-Datei
Schemaimportanweisung. Um Elemente zu verwenden, die in einer externen
Dataset, muss das externe Dataset über einen Import referenziert werden
der Richtlinie. |
| Diagramm |
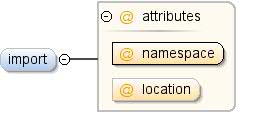 |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| den Standort |
|
|
|
optional |
Optionaler Speicherort, an dem die Definition des importierten
Dataset gefunden werden kann, angegeben als URL. Wenn der Standort
ausgelassen wird, muss das System, das diesen DSPL-Datensatz verarbeitet, bereits wissen,
des importierten Datasets. Implementierungshinweis: Das Google-Dataset
Importer ignoriert das Standortattribut. Jedes importierte Dataset muss
dem Google-Importeur bekannt gegeben werden. |
| Namespace |
|
|
|
erforderlich |
Der Namespace des importierten Datasets, angegeben als
URI. Ein Präfix muss mit diesem Namespace verknüpft werden, bevor dessen
kann auf Inhalte verwiesen werden. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter [XML-Namespaces].
Informationen zur Verwendung von Namespaces und Präfixen in
XML. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="import" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Import directive for external datasets -- modeled after
the XML Schema import directive. In order to use
elements defined in an external dataset, the external
dataset must be referenced using an import directive.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="namespace" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The namespace of the imported dataset, specified as
a URI. A prefix must be associated with this
namespace before its contents can be referenced. See
[XML Namespaces] for more information about the use
of namespaces and prefixes in XML.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="location" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An optional location where the definition of the
imported dataset can be found, specified as a
URL. If the location is omitted, the system
processing this DSPL dataset must already know the
imported dataset.
Implementation note: The Google dataset importer
ignores the location attribute. Any imported dataset
must be known by the Google importer beforehand.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
Element: dspl / info
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
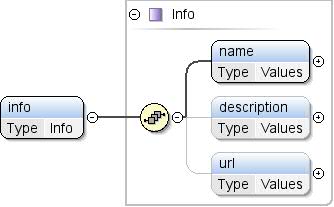
Allgemeine Informationen zum Dataset. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Info |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
1 |
|
| Modell |
name , description{0,1} , url{0,1} |
| Children |
Beschreibung, Name, url |
| Instanz |
<info>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</info>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="info" type="Info" minOccurs="1">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>General information about the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
Element: dspl / Anbieter
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
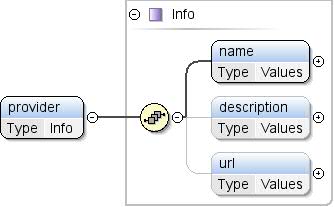
Allgemeine Informationen zum Dataset-Anbieter. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Info |
| Attribute |
|
| Modell |
name , description{0,1} , url{0,1} |
| Children |
Beschreibung, Name, url |
| Instanz |
<provider>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</provider>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="provider" type="Info">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>General information about the dataset provider.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
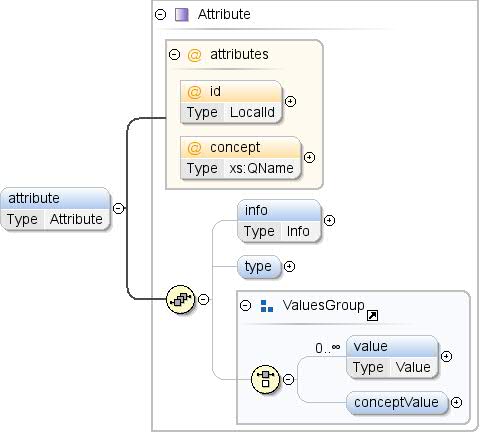
Element: dspl / Attribut
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Mit dem Dataset verknüpftes Attribut. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Attribut |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
| Modell |
info{0,1} , type{0,1} , (Wert*
| conceptValue{0,1}) |
| Children |
conceptValue, info, Typ,
Wert |
| Instanz |
<attribute concept="" id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type format="" ref="">{0,1}</type>
</attribute>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| Konzept |
xs:QName |
|
|
optional |
Ein Verweis auf ein Konzept, das den Werten entspricht
des Attributs. Wenn das Attribut einen Typ angibt,
muss mit dem Typ des referenzierten Konzepts übereinstimmen. Ein Verweis auf eine
muss das Format eines externen Konzepts
„prefix:other_concept_id“, wobei „präfix“ ist
Das für den Namespace des externen Datasets verwendete Präfix (siehe XML)
Namespaces). |
| id |
LocalId |
|
|
optional |
Die ID des Konzeptattributs. Diese Kennung muss
innerhalb des Konzepts (über Attribute und Eigenschaften hinweg) eindeutig sein sollte. Die
id [ID] kann weggelassen werden, wenn das Konzeptattribut angegeben ist. Dabei
wird implizit eine ID mit dem lokalen Namen des
Konzept verwendet. Beispiel: <attribute
concept="unit:currency"/> entspricht
<attribute id="currency"
concept="unit:currency"/> |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Attribute associated with the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
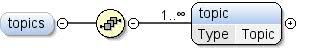
Element: dspl / themen
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Eine Themenhierarchie zur Organisation der Inhalte der
Dataset. Die Reihenfolge, in der Themen angegeben werden, ist aussagekräftig und sollte
von Visualisierungen, die diese Themen darstellen, respektiert werden. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
|
| Modell |
topic+ |
| Children |
Thema |
| Instanz |
<topics>
<topic id="" parentTopic="">{1,unbounded}</topic>
</topics>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="topics" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A hierarchy of topics used to organize the contents of
the dataset. The order in which topics are given is
meaningful and should be respected by visualizations
that displays these topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="topic" type="Topic" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Diagramm |
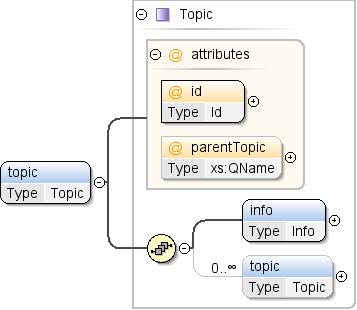 |
| Typ |
Thema |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
| Modell |
info , thema* |
| Children |
Info, Thema |
| Instanz |
<topic id="" parentTopic="">
<info>{1,1}</info>
<topic id="" parentTopic="">{0,unbounded}</topic>
</topic>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung des Themas in der
Dataset. |
| parentTopic |
xs:QName |
|
|
optional |
Die ID des übergeordneten Themas, falls vorhanden.
„parentTopic“ kann nicht für Themen angegeben werden, die innerhalb von Inline-Themen enthalten sind
andere Themen. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="topic" type="Topic" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
|
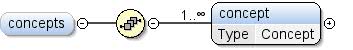
Element: dspl / Konzepte
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Eine Liste der in diesem Dataset definierten Konzepte. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
|
| Modell |
konzept+ |
| Children |
Konzept |
| Instanz |
<concepts>
<concept extends="" id="">{1,unbounded}</concept>
</concepts>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="concepts" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of concepts defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="concept" type="Concept" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Konzept |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
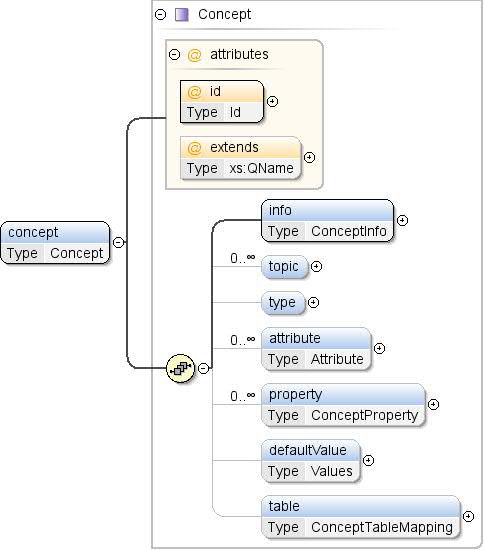
| Modell |
info , topic* , type{0,1} ,
Attribut* , Property* , defaultValue{0,1} , Tabelle{0,1} |
| Children |
Attribut, defaultValue, info,
Property, Tabelle, Thema
Typ |
| Instanz |
<concept extends="" id="">
<info>{1,1}</info>
<topic ref="">{0,unbounded}</topic>
<type ref="">{0,1}</type>
<attribute concept="" id="">{0,unbounded}</attribute>
<property concept="" id="" isMapping="false" isParent="false">{0,unbounded}</property>
<defaultValue>{0,1}</defaultValue>
<table ref="">{0,1}</table>
</concept>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| erweitert |
xs:QName |
|
|
optional |
Die eindeutige Kennung eines Konzepts, das von diesem Konzept
erweitert. Das referenzierte Konzept kann im selben Dataset definiert werden
oder extern, d.h. in einem anderen Dataset. Ein Verweis auf eine externe
Konzept muss das Format "prefix:other_concept_id" haben,
wobei „Präfix“ ist das Präfix, das für den Namespace von
Das externe Dataset (siehe XML-Namespaces) |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung des Konzepts. Diese muss
global nur einmal im Dataset. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="concept" type="Concept" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
|
Element: dspl / segment
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Eine Liste der in diesem Dataset definierten Slices. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
|
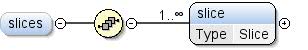
| Modell |
slice+ |
| Children |
Slice |
| Instanz |
<slices>
<slice id="">{1,unbounded}</slice>
</slices>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="slices" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of slices defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="slice" type="Slice" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Segment |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
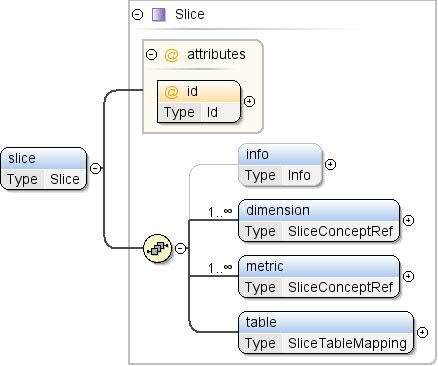
| Modell |
info{0,1} , Dimension+ , Messwert+
, Tabelle |
| Children |
Dimension, Informationen, Messwert
Tabelle |
| Instanz |
<slice id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<dimension concept="">{1,unbounded}</dimension>
<metric concept="">{1,unbounded}</metric>
<table ref="">{1,1}</table>
</slice>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung des Slice. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="slice" type="Slice" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
|
Element: dspl / Tabellen
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Eine Liste der in diesem Dataset definierten Tabellen. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
|
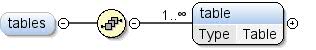
| Modell |
Tabelle+ |
| Children |
Tisch |
| Instanz |
<tables>
<table id="">{1,unbounded}</table>
</tables>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="tables" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A list of tables defined in this dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="table" type="Table" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Tabelle |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
| Modell |
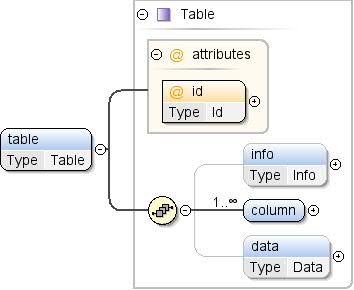
info{0,1} , Spalte+ , Daten{0,1} |
| Children |
Spalte, Daten, Informationen |
| Instanz |
<table id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<column format="" id="" type="">{1,unbounded}</column>
<data>{0,1}</data>
</table>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung der Tabelle im
Dataset. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="table" type="Table" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
|
Attribut: dspl / import / @namespace
| Namespace |
Kein Namespace |
| Annotationen |
Der Namespace des importierten Datasets, angegeben als URI. A
Präfix muss mit diesem Namespace verknüpft werden, bevor sein Inhalt geändert werden kann
auf die verwiesen wird. Siehe [XML-Namespaces] für weitere Informationen zur Verwendung von
Namespaces und Präfixe in XML. |
| Attribute |
| verwenden Sie zum Beispiel: |
erforderlich |
|
| Verwendet von |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:attribute name="namespace" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The namespace of the imported dataset, specified as
a URI. A prefix must be associated with this
namespace before its contents can be referenced. See
[XML Namespaces] for more information about the use
of namespaces and prefixes in XML.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Attribut: dspl / import / @location
| Namespace |
Kein Namespace |
| Annotationen |
Optionaler Speicherort, an dem die Definition des importierten
Dataset gefunden werden kann, angegeben als URL. Wenn der Standort weggelassen wird,
dem System, das dieses DSPL-Dataset verarbeitet, das importierte
Dataset. Implementierungshinweis: Der Google Dataset-Importeur ignoriert den Parameter
location. Jedes importierte Dataset muss dem Google-Team bekannt sein.
importieren. |
| Attribute |
| verwenden Sie zum Beispiel: |
optional |
|
| Verwendet von |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:attribute name="location" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An optional location where the definition of the
imported dataset can be found, specified as a
URL. If the location is omitted, the system
processing this DSPL dataset must already know the
imported dataset.
Implementation note: The Google dataset importer
ignores the location attribute. Any imported dataset
must be known by the Google importer beforehand.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Attribut: dspl / @targetNamespace
| Namespace |
Kein Namespace |
| Annotationen |
Jedes Dataset kann einen Ziel-Namespace bereitstellen. Das Ziel
Namespace ist ein URI, der das Dataset eindeutig identifiziert. Weitere Informationen
Informationen zur Verwendung von Namespaces in XML finden Sie unter:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/ Wenn kein targetNamespace angegeben ist,
wird ein Namespace generiert, wenn das Dataset
importiert. |
| Typ |
xs:anyURI |
| Attribute |
| verwenden Sie zum Beispiel: |
optional |
|
| Verwendet von |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:attribute name="targetNamespace" type="xs:anyURI" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Each dataset may provide a target namespace. The
target namespace is a URI that uniquely identifies the
dataset. For more information about the use of namespaces in XML,
see:
http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml-names/
If no targetNamespace is provided, then a namespace will be
generated when the dataset is imported.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Erstellt mit dem
oXygen XML Editor
Sofern nicht anders angegeben, sind die Inhalte dieser Seite unter der Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License und Codebeispiele unter der Apache 2.0 License lizenziert. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in den Websiterichtlinien von Google Developers. Java ist eine eingetragene Marke von Oracle und/oder seinen Partnern.
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 2025-07-25 (UTC).
[[["Leicht verständlich","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["Mein Problem wurde gelöst","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["Sonstiges","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["Benötigte Informationen nicht gefunden","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["Zu umständlich/zu viele Schritte","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["Nicht mehr aktuell","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["Problem mit der Übersetzung","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["Problem mit Beispielen/Code","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["Sonstiges","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["Zuletzt aktualisiert: 2025-07-25 (UTC)."],[],["The DSPL XML schema defines a dataset's structure using key components: `tables`, `concepts`, `slices`, and `topics`. The root `dspl` element encapsulates the dataset, utilizing `import` to reference externals, `info` and `provider` for metadata, `attribute` for dataset attributes, and `topics` to hierarchically organize the concepts. `concepts`, `slices`, `tables` are for concept definition, slice definition, and data table, respectively. Each element like `import`, `info`, `provider`, `attribute`, `topic`, `concept`, `slice`, `table` uses specific attributes and child elements for configuration. Each element has a specific cardinality that is defined in the document.\n"]]












