Komponente: Thema
Mit Sammlungen den Überblick behalten
Sie können Inhalte basierend auf Ihren Einstellungen speichern und kategorisieren.
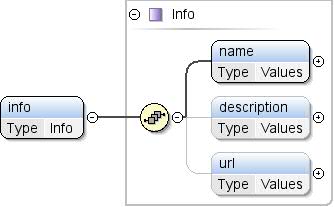
Element: Thema / info
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Textinformationen zum Thema. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Info |
| Attribute |
|
| Modell |
name , description{0,1} , url{0,1} |
| Children |
Beschreibung, Name, url |
| Instanz |
<info>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</info>
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="info" type="Info">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information about the topic.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
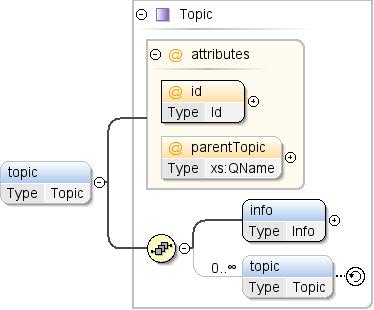
Element: Thema / Thema
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Untergeordnete Themen können innerhalb ihres übergeordneten Themas eingefügt werden. Wenn ja,
ist die Reihenfolge der untergeordneten Elemente
bedeutend und sollte respektiert werden,
Apps zu diesen Themen. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Typ |
Thema |
| Attribute |
| content: |
komplex |
| minOccurs (Mindestanzahl): |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
unbegrenzt |
|
| Modell |
info , thema* |
| Children |
Info, Thema |
| Instanz |
<topic id="" parentTopic="">
<info>{1,1}</info>
<topic id="" parentTopic="">{0,unbounded}</topic>
</topic>
|
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung des Themas im
Dataset. |
| parentTopic |
xs:QName |
|
|
optional |
Die ID des übergeordneten Themas, falls vorhanden.
„parentTopic“ kann nicht für Themen angegeben werden, die innerhalb von Inline-Themen enthalten sind
andere Themen. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:element name="topic" type="Topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Child topics can be inlined inside their parent topic. If
so, the order of children is meaningful and should be
respected by applications that display these topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
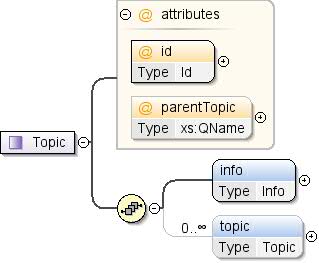
Komplexer Typ: Thema
| Namespace |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Annotationen |
Ein Thema ist ein Label, das Konzepten zugeordnet werden kann. Themen sind
sind hierarchisch organisiert. |
| Diagramm |
 |
| Verwendet von |
|
| Modell |
info , thema* |
| Children |
Info, Thema |
| Attribute |
| QName |
Typ |
Behoben |
Standard |
Verwenden |
Annotation |
| id |
ID |
|
|
erforderlich |
Die eindeutige Kennung des Themas in der
Dataset. |
| parentTopic |
xs:QName |
|
|
optional |
Die ID des übergeordneten Themas, falls vorhanden.
„parentTopic“ kann nicht für Themen angegeben werden, die innerhalb von Inline-Themen enthalten sind
andere Themen. |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:complexType name="Topic">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic is a label that can be attached to concepts. Topics
are organized hierarchically.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="info" type="Info">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information about the topic.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="topic" type="Topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Child topics can be inlined inside their parent topic. If
so, the order of children is meaningful and should be
respected by applications that display these topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic in the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="parentTopic" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The id of the parent topic of this topic, if it has one. parentTopic
cannot be specified for topics that are inlined inside other topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
|
Attribut: Thema / @id
| Namespace |
Kein Namespace |
| Annotationen |
Die eindeutige Kennzeichnung des Themas im Dataset. |
| Typ |
ID |
| Attribute |
| verwenden Sie zum Beispiel: |
erforderlich |
|
| Attribute |
|
| Verwendet von |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic in the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Attribut: Thema / @parentTopic
| Namespace |
Kein Namespace |
| Annotationen |
ID des übergeordneten Themas, falls vorhanden.
„parentTopic“ kann nicht für Themen angegeben werden, die innerhalb anderer Themen enthalten sind.
Themen. |
| Typ |
xs:QName |
| Attribute |
| verwenden Sie zum Beispiel: |
optional |
|
| Verwendet von |
|
| Quelle |
<xs:attribute name="parentTopic" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The id of the parent topic of this topic, if it has one. parentTopic
cannot be specified for topics that are inlined inside other topics.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Erstellt mit dem
oXygen XML Editor
Sofern nicht anders angegeben, sind die Inhalte dieser Seite unter der Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License und Codebeispiele unter der Apache 2.0 License lizenziert. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in den Websiterichtlinien von Google Developers. Java ist eine eingetragene Marke von Oracle und/oder seinen Partnern.
Zuletzt aktualisiert: 2025-07-25 (UTC).
[[["Leicht verständlich","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["Mein Problem wurde gelöst","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["Sonstiges","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["Benötigte Informationen nicht gefunden","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["Zu umständlich/zu viele Schritte","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["Nicht mehr aktuell","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["Problem mit der Übersetzung","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["Problem mit Beispielen/Code","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["Sonstiges","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["Zuletzt aktualisiert: 2025-07-25 (UTC)."],[],["The core content describes the \"Topic\" element and its \"Info\" component within a data structure. A topic has an `id` for unique identification and an optional `parentTopic` to establish hierarchy. Topics contain `info` (textual information), and can have child `topic` elements, respecting their order. The `info` includes `name`, `description`, and `url`. Applications should maintain this hierarchical structure. `id` is required, `parentTopic` is optional, and child topics are inlined.\n"]]


