Places Count functions are predefined SQL queries that run in BigQuery and are complementary to querying the dataset directly. The main difference between querying the data directly and using a function is that functions don't enforce a minimum count threshold but instead enforce a minimum search area:
- Place datasets queries can only return counts 5 and above, but enforce no limitations on the size of the search area.
- Places Count functions can return any counts, including 0, but enforce a minimum search area of 40.0 meters by 40.0 meters (1600 m2). Functions can also return Place IDs, which can be used to look up information about individual Places.
You might want to use Places Count functions if it's important to know when a query returns no results or if you need to know low counts of places below 5. It is also useful if you need to get individual place information to spot check your results.
Places Count functions only provide counts, so if you need to perform more complex queries such as data joins, or get additional insights such as the average rating of a group of places, then query the dataset directly.
Supported Places Count functions and countries
Places Insights supports the following functions:
PLACES_COUNT: Returns a single row containing a count of places.PLACES_COUNT_PER_TYPE: Returns a BigQuery table of place counts per places type.PLACES_COUNT_PER_GEO: Returns a BigQuery table of place counts per geographies.PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3: Returns a BigQuery table of place counts per H3 cell.
Along with the place counts, the PLACES_COUNT_PER_TYPE,
PLACES_COUNT_PER_GEO, and PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 functions also return up to
250 place IDs per element of the response. See all filter parameters.
Place IDs can be used with:
Write queries with functions
Use the following format to call the functions: [project name
(optional)].[table name].[function name].
If you changed the linked dataset name when setting up Places Insights, then use your custom name instead of the default table names listed in Reference place count functions in BigQuery. You can also optionally include your project name. If one is not included, the query will default to the active project.
For example:
PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT
Use a
JSON_OBJECT
to pass arguments to the function.
Filter your results
The Places Count functions support many filters to refine your search. These
parameters (for example, price_level or types) are case-sensitive and must
match the parameter names exactly. See the filter parameters reference for a
full list of
options.
In the next example you apply filters to limit the search by minimum user rating, price level, business status, and whether the restaurant allows dogs:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
Places Count function example
The following example uses the PLACES_COUNT function to return the number of
operational restaurants within 1000 meters of the Empire State Building in New
York City:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'types', ["restaurant"] ) ) as count;
The response contains a single count:
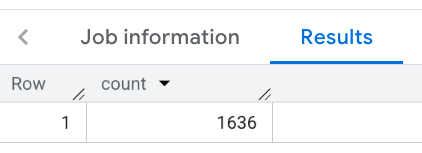
This example uses the BigQuery
ST_GEOGPOINT
function to return a GEOGRAPHY value from a point and then pass that value to
the geography parameter. It also passes the search radius around the point and
the place type, "restaurant", to search for.
Place count per type, geo, or H3 example
Along with the Place counts, the PLACES_COUNT_PER_TYPE,
PLACES_COUNT_PER_GEO, and PLACES_COUNT_PER_H3 functions also return up to
250 place IDs for the places included in the response.
For example, the PLACES_COUNT_PER_TYPE function returns a table of place
counts per place type. Included in the response is an array of place IDs for the
places that match each type. You can use the returned place IDs to look up
information about each place.
The following function call returns a count of places with the types:
restaurant, cafe, and bar:
SELECT * FROM `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT_PER_TYPE`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant", "cafe", "bar"], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'] ) );
This function returns a table with three columns: type, count, and
sample_place_ids. The count columns shows the place count for each type,
and the sample_place_ids column shows up to 250 place IDs for each type.

Visualize results
Analysis and business intelligence tools are crucial to helping you discover insights from your BigQuery data. BigQuery supports several Google and third-party data visualization tools that you can use to analyze the results of your functions on Places Insights data.
For an example of visualizing the results of a function, see Visualize results. For more information and example on visualizing Places Insights results, see Visualize query results.
Limitations and requirements
Places Count functions have the following limitations and requirements:
- Only
COUNTinsights are supported. - A minimum search area of 40.0 meters by 40.0 meters (1600 m2) is required.
- Place function count parameter input size is limit to 1 MB.
- No support for filtering by place ID, brands, EV charge options, or address component.
- You can only access the Places Count functions for the cities and countries you have subscribed to. See Set up Places Insights for dataset access.
- Filter parameters (for example,
geographyortypes) are case-sensitive and must match the parameter names exactly, or query will fail.
Reference Places Count functions in BigQuery
All of the cities in the sample dataset and the countries full dataset support Places Count functions.
You have access to the Places Count functions corresponding to the cities and countries datasets you have subscribed to. See Set up Places Insights for dataset access.
These tables list the available cities, countries, and their corresponding table names.
Sample data
| City, Country | Table names |
|---|---|
| Sydney, Australia | places_insights___au___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Sao Paulo, Brazil | places_insights___br___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Toronto, Canada | places_insights___ca___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Paris, France | places_insights___fr___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Berlin, Germany | places_insights___de___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Mumbai, India | places_insights___in___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Jakarta, Indonesia | places_insights___id___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Rome, Italy | places_insights___it___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Tokyo, Japan | places_insights___jp___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Mexico City, Mexico | places_insights___mx___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Madrid, Spain | places_insights___es___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Zurich, Switzerland | places_insights___ch___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| London, United Kingdom | places_insights___gb___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
| New York City, United States | places_insights___us___sample.FUNCTION_NAME |
Full data
| Country | Table names |
|---|---|
| Australia | places_insights___au.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Brazil | places_insights___br.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Canada | places_insights___ca.FUNCTION_NAME |
| France | places_insights___fr.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Germany | places_insights___de.FUNCTION_NAME |
| India | places_insights___in.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Indonesia | places_insights___id.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Italy | places_insights___it.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Japan | places_insights___jp.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Mexico | places_insights___mx.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Spain | places_insights___es.FUNCTION_NAME |
| Switzerland | places_insights___ch.FUNCTION_NAME |
| United Kingdom | places_insights___gb.FUNCTION_NAME |
| United States | places_insights___us.FUNCTION_NAME |
