Page Summary
-
Agents are categorized as non-conversational or conversational, which determines how messages are charged.
-
Non-conversational agents are billed per message, suitable for one-way communication like alerts and promotions.
-
Conversational agents are billed per conversation, covering messages exchanged within a 24-hour window, ideal for interactive exchanges.
-
Billing events, such as basic messages, single messages, and conversations, are tracked to help carriers bill for agent messages.
-
User responses like sending a file, text message, or tapping a suggested reply contribute to billing events.
RCS for Business uses two billing models: the standard billing model for non-US traffic and the US billing model for US traffic. This document covers common questions about the standard billing model. For details about US billing classifications, refer to the US billing model guide.
Billing categories
What are agent billing categories?
A billing category is a classification for your RCS for Business agent that informs the billing logic for the messages your agent sends. You choose this category when you create your agent, and it can't be changed later.
The two main billing categories are described in the following table.
| Billing category | Agent type | Example use cases | Billing method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-conversational | Agents that primarily send one-way messages |
|
Billed per message. |
| Conversational | Agents that are designed for back-and-forth exchanges with users |
|
Billed per conversation: If one party (the agent or user) replies to a message from the other party within 24 hours, a conversation starts. During the conversation window (24 hours after the first reply), the agent and user can exchange any number of messages, and the agent will be billed a fixed rate for the conversation. Billed per message: If the agent delivers a message that the user doesn't reply to within 24 hours, the agent will be billed for the individual message, similar to a non-conversational agent. |
How do I know which billing category to select for my agent?
There are two main billing categories: conversational and non-conversational.
- Non-conversational agents are billed per message they deliver to the
user.
- This category is best for agents that don't expect frequent replies.
- Conversational agents are billed a flat rate for
conversations, which include all messages
exchanged within a 24-hour period.
- This category is best for agents that engage in multi-turn conversations with users.
Choose the billing category that best fits your use case and expected user engagement. Your agent can send any message type, regardless of the category.
That's because the billing category determines how messages are charged, not what types of messages your agent can send. For example, a Conversational agent can still send basic messages, and a Non-conversational agent can send multiple messages, including rich cards.
Non-conversational billing category
How does the consolidation of the Basic Message and Single Message categories into one Non-conversational category affect my agents?
On November 20, 2025, we simplified the billing structure by combining the two legacy billing categories, Basic Message and Single Message, into one Non-conversational billing category.
From now on, every agent will be classified as either Conversational or Non-conversational.
This change impacts the RcsBusinessMessagingAgentBillingConfig and applies to
all developers using the
Developer Console
or Management API,
and all carriers using the
Operations API.
Existing agent migration (no action required)
All existing agents that are classified as Basic Message or Single Message will be automatically migrated to the Non-conversational category by the RBM Support team. This migration will begin on March 16, 2026.
No action required: The migration of existing agents will be handled automatically by Google, and no action is required from you.
Billable events
What are billable events?
Billable events are interactions between an RCS for Business agent and a user that are tracked for billing purposes. Events are categorized based on the message type and timing of interactions.
Google tracks and reports these events to help carriers bill partners for messages sent by their agents.
Which billable events apply to each message type?
Five types of billable events are recorded in the billing reports. These events include MT and MO events, which are referred to as A2P and P2A events.
- A2P (Application-to-Person) is MT (Mobile Terminated): A message sent by the business.
- P2A (Person-to-Application) is MO (Mobile Originated): A message or action initiated by the user.
The following table describes each billable event as it applies to non-conversational and conversational agents.
| Event type | Description | Non-conversational agents | Conversational agents |
|---|---|---|---|
basic_message |
A2P message that includes only text with 160 characters or less. See example. |
Always treated as an individual billable event, regardless of whether the user replies. | Treated as an individual billable event, unless the user replies within 24 hours. In that case, the message becomes part of an a2p_conversation. |
single_message |
A2P message that either has rich content or is a text-only message over 160 characters. See example |
Always treated as an individual billable event, regardless of whether the user replies. | Treated as an individual billable event, unless the user replies within 24 hours. In that case, the message becomes part of an a2p_conversation. |
a2p_conversation (business initiated) |
Initiated when a user responds to an A2P message within 24 hours of receiving it, outside of an existing conversation. See example. |
N/A. Non-conversational agents never generate this type of event. | If a P2A message is delivered within 24 hours of multiple A2P messages, only the A2P message that immediately preceded the P2A message is used to initiate the conversation. This A2P message, and any messages delivered within the next 24 hours, are part of the a2p_conversation. |
p2a_conversation (user initiated) |
Initiated when an agent responds to a P2A message within 24 hours of receiving it, outside of an existing conversation. See example. |
N/A. Non-conversational agents never generate this type of event. | If an A2P message is delivered within 24 hours of multiple P2A messages, only the P2A message that immediately preceded the A2P message is used to initiate the conversation. This P2A message, and any messages delivered within the next 24 hours, are part of the p2a_conversation. |
p2a_message |
P2A message of any type. See example. |
Always treated as an individual billable event, regardless of whether the agent replies. | Treated as an individual billable event, unless the agent replies within 24 hours. |
What are examples of messages that trigger each billable event?
Basic Message
Note that the following screenshot shows the URL preview within the text message. This is not a rich card.
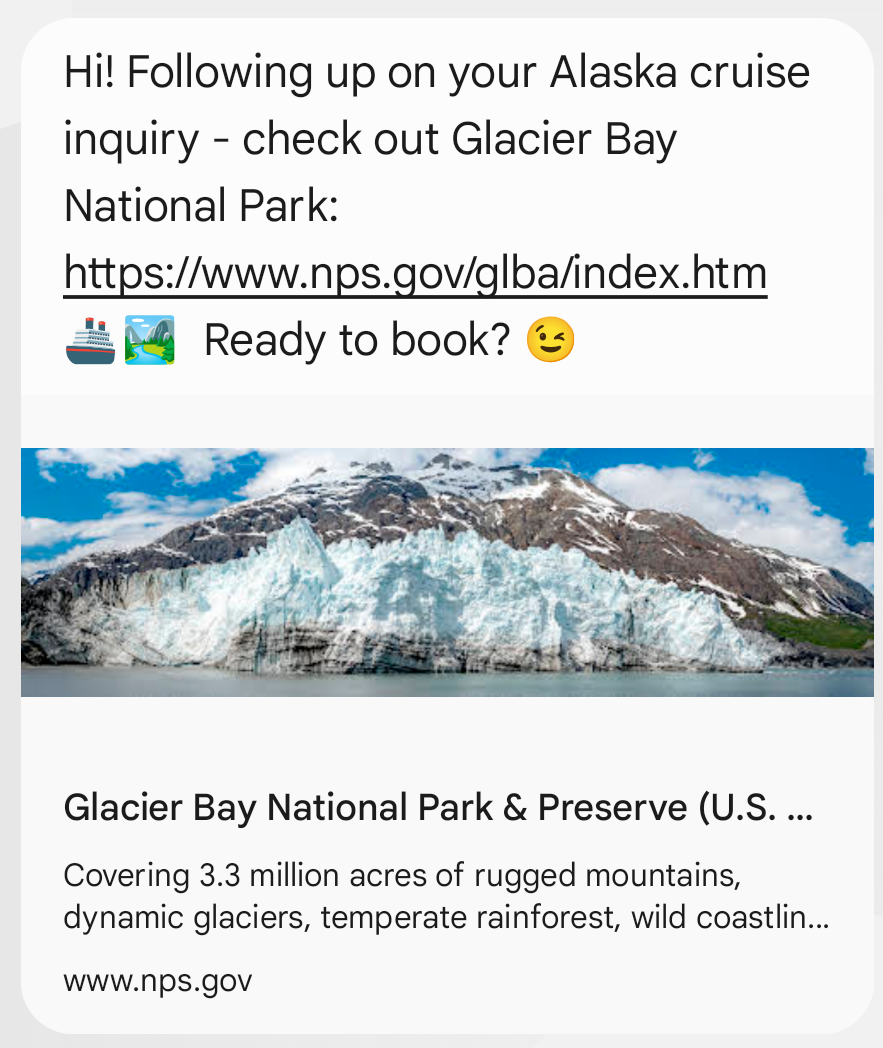
Single Message

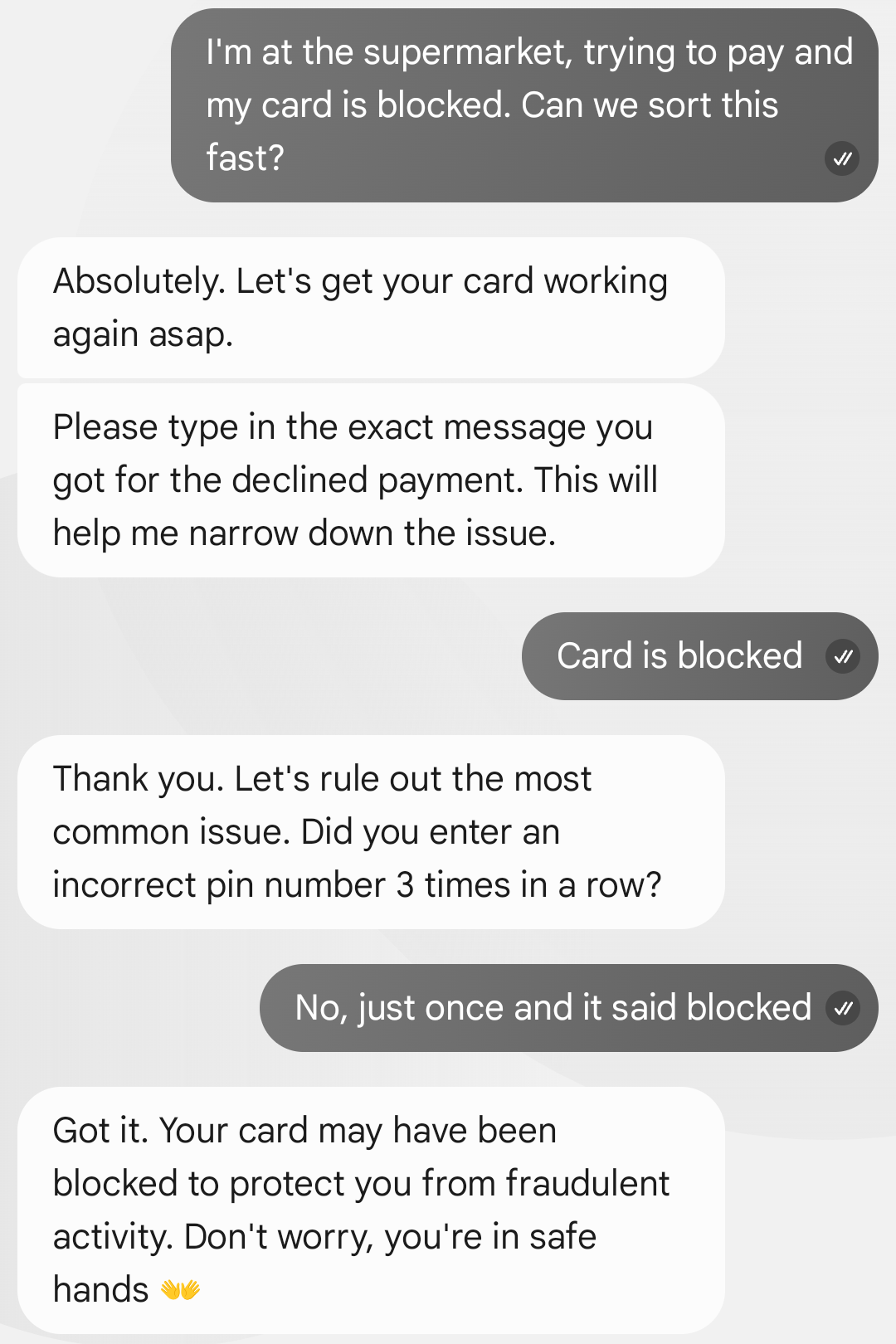
A2P Conversation
P2A Message

P2A Conversation
What are the benefits of each billable event?
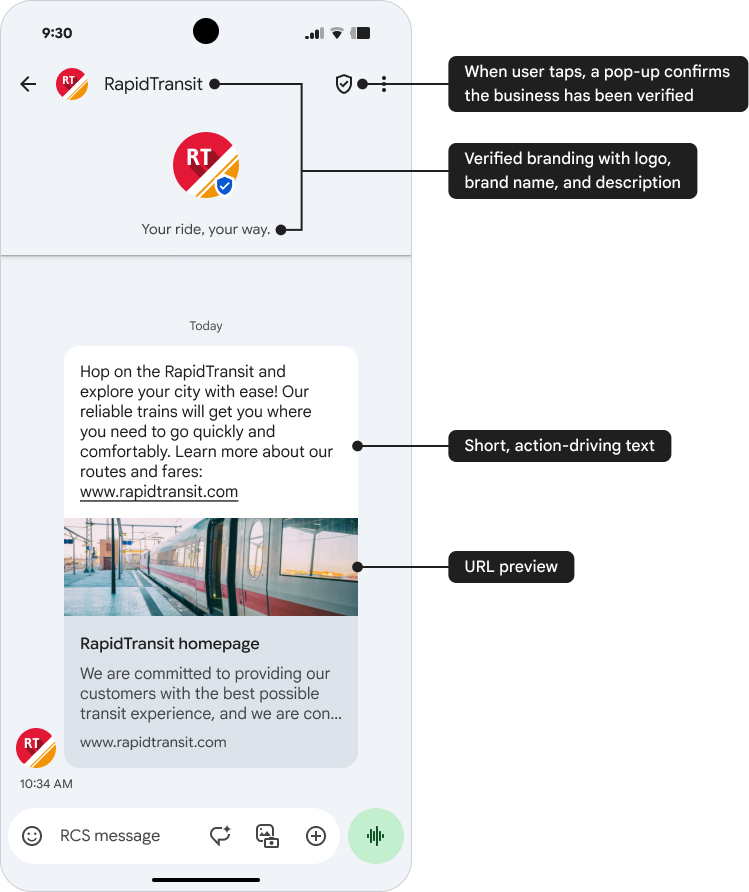
Basic Message
Key benefits of a Basic Message:
- Building trust: Verification and branding establish trust and credibility.
- URL preview: Basic Messages may contain text and a clickable URL preview image.
- Tactical one-off promotions: Ideal for short-term promotions or informational messages that don't require a user response.
- Driving traffic: Basic Messages can direct users to the brand's app, website, or other resources.
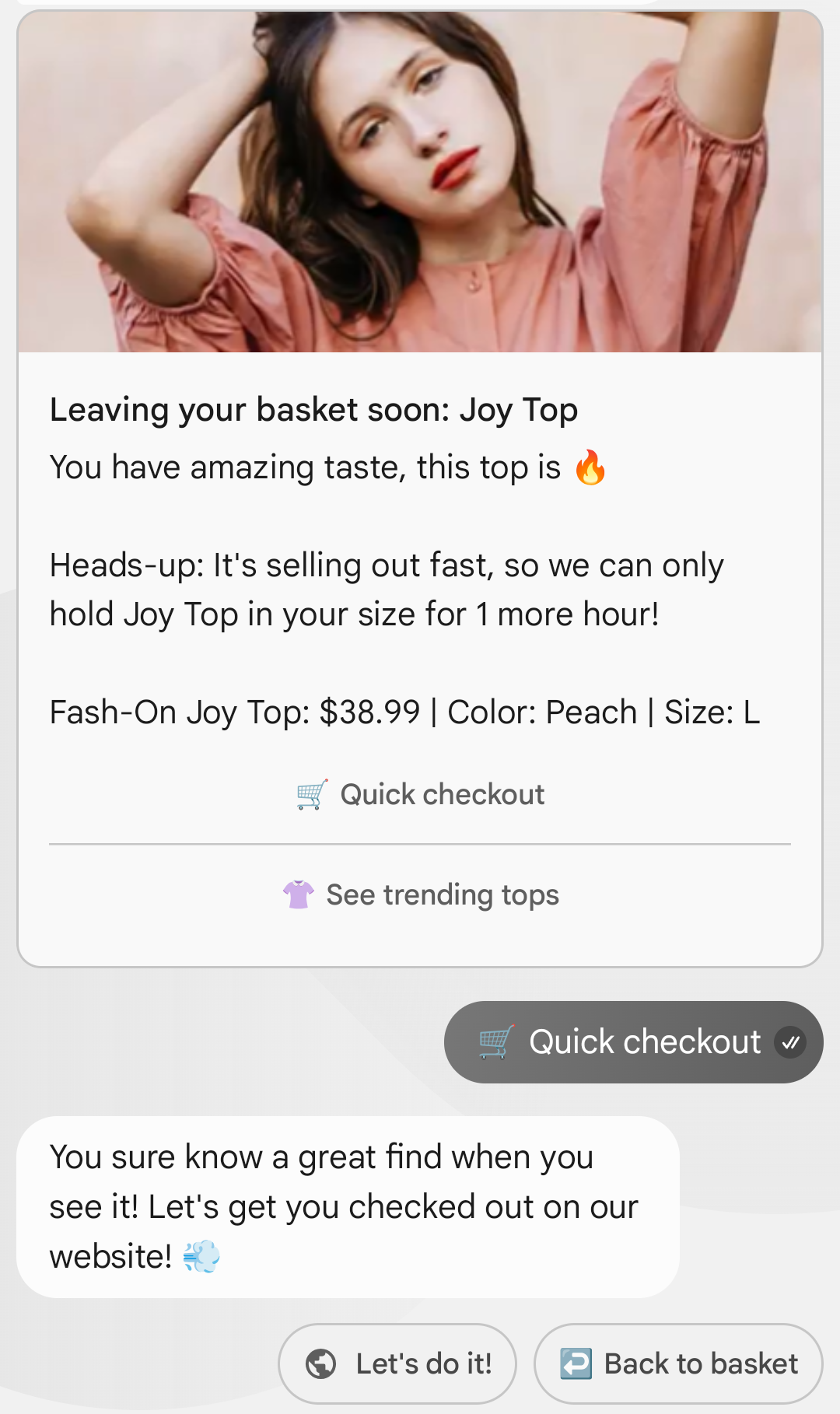
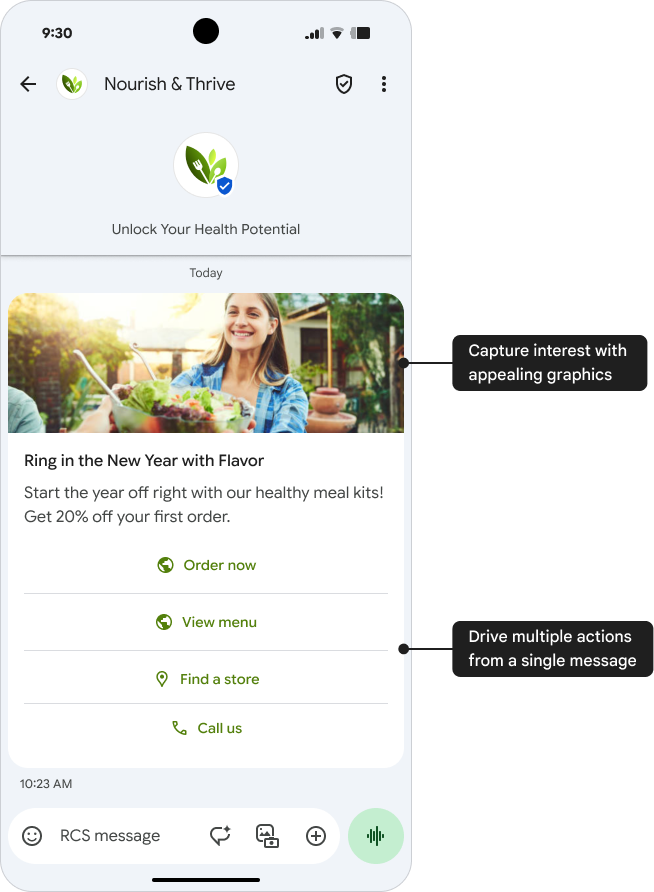
Single Message
Key benefits of a Single Message:
- Visual impact: High-quality graphics capture attention and clarify options, boosting user engagement.
- One card, multiple actions: A rich card or carousel can drive multiple actions with suggestions to create a calendar event, find a location, dial a number, or open a URL — all from a single message.
- Clear value, concise message: Encourage users to take the next step.
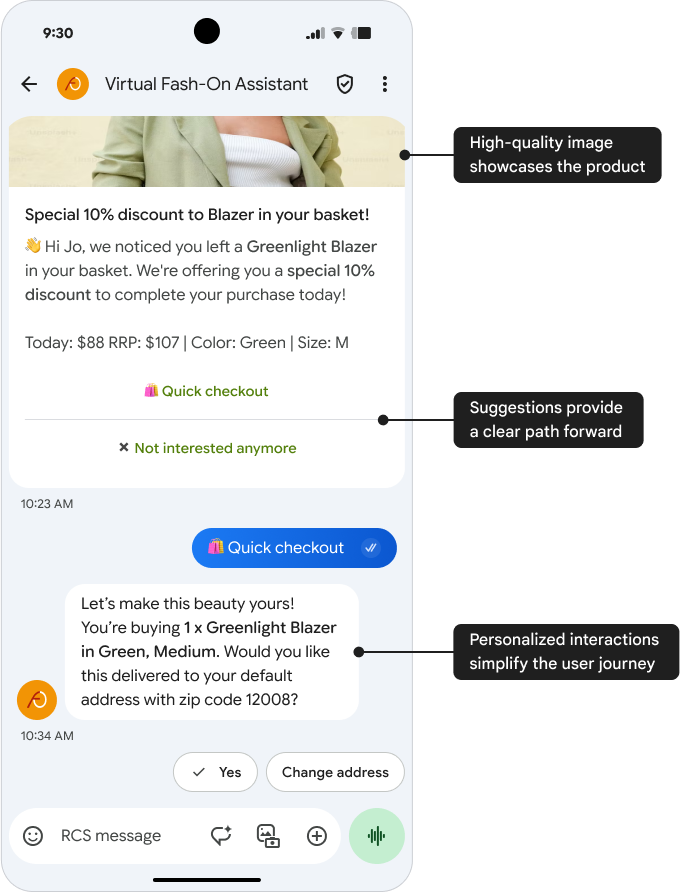
Conversational
Key benefits of A2P and P2A conversations:
- Rich media integration: Incorporate various media, such as images, videos, and PDFs, as well as suggested actions and replies.
- Personalized interactions: Allow for back-and-forth dialogue, providing tailored help, and product recommendations.
- Conversion opportunities: Enable users to take action within the conversation, reducing friction and increasing conversion rates.
How do agent billing categories relate to billable events?
The basic_message and single_message billable events shouldn't be confused
with the Basic Message and Single Message billing categories.
- Any agent (no matter its
billing category) can generate
basic_messageandsingle_messagebillable events. - The Basic Message and Single Message billing categories are used to classify
non-conversational agents. Agents in these billing categories don't generate
conversational billable events (
a2p_conversationsorp2a_conversations). Instead, they generate individualbasic_message,single_message, andp2a_messagebillable events.
What billable events are generated if the agent sends several messages before a user replies?
The billing category of your agent and the user's reply timing determine what type of events are generated.
For non-conversational agents: Every message generates its own event
- An agent message generates a
basic_messageorsingle_messageevent. - A user message generates a
p2a_messageevent.
For conversational agents: The outcome depends on when the user replies to the agent's last message
- If the user replies within 24 hours:
- An
a2p_conversationevent begins. This event covers the agent's last message, the user's reply, and all messages exchanged within a 24-hour window after the user's reply. - Any agent messages delivered before the last agent message are not part
of the conversation; they each generate their own
basic_messageorsingle_messageevent.
- An
- If the user replies after 24 hours:
- The agent messages each generate a
basic_messageorsingle_messageevent. - The user's reply generates a
p2a_conversationevent if the agent responds within 24 hours. If the agent doesn't respond within that timeframe, ap2a_messageevent is generated instead.
- The agent messages each generate a
Which user responses contribute to billable events?
Only specific user responses contribute to
billable events. These include responses that create
a p2a_message event or are part of an a2p_conversation or p2a_conversation
event. The following table clarifies which user responses contribute to billable
events.
Here's a summary:
| User response | Contributes to billable events | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Sends a file | Yes | Treated as a mobile-originated (MO) message. |
| Sends a text message | Yes | Treated as an MO message. |
| Taps a suggested reply | Yes | Treated as an MO message. |
| Taps a suggested action | No | The postback data from the tap itself does not contribute to a billable event. |
| Shares a location | Yes | The MO message containing the user's location contributes to a billable event. This applies whether the location is shared manually or by suggested action. |
| Taps Unsubscribe or Subscribe | Yes | The resulting webhook event does not contribute to a billable event, but the automated STOP or START message that's delivered when the user taps the Unsubscribe or Subscribe option is treated as an MO message. |
When a user response generates a billable event (as outlined above), the event type depends on the agent's billing category.
For non-conversational agents:
- The billable event generated by a user's response is always a
p2a_message.
For conversational agents:
The event type is also determined by the timing of messages within a 24-hour window.
- When a user responds to the agent's message:
- Within 24 hours: The user's reply contributes to an existing
a2p_conversationevent. - After 24 hours: The user's reply generates a new
p2a_messageevent.
- Within 24 hours: The user's reply contributes to an existing
- When the agent responds to a user's message:
- Within 24 hours: The agent's reply creates a
p2a_conversation, starting with the user's initial message. - After 24 hours: The user's message generates a
p2a_messageevent.
- Within 24 hours: The agent's reply creates a
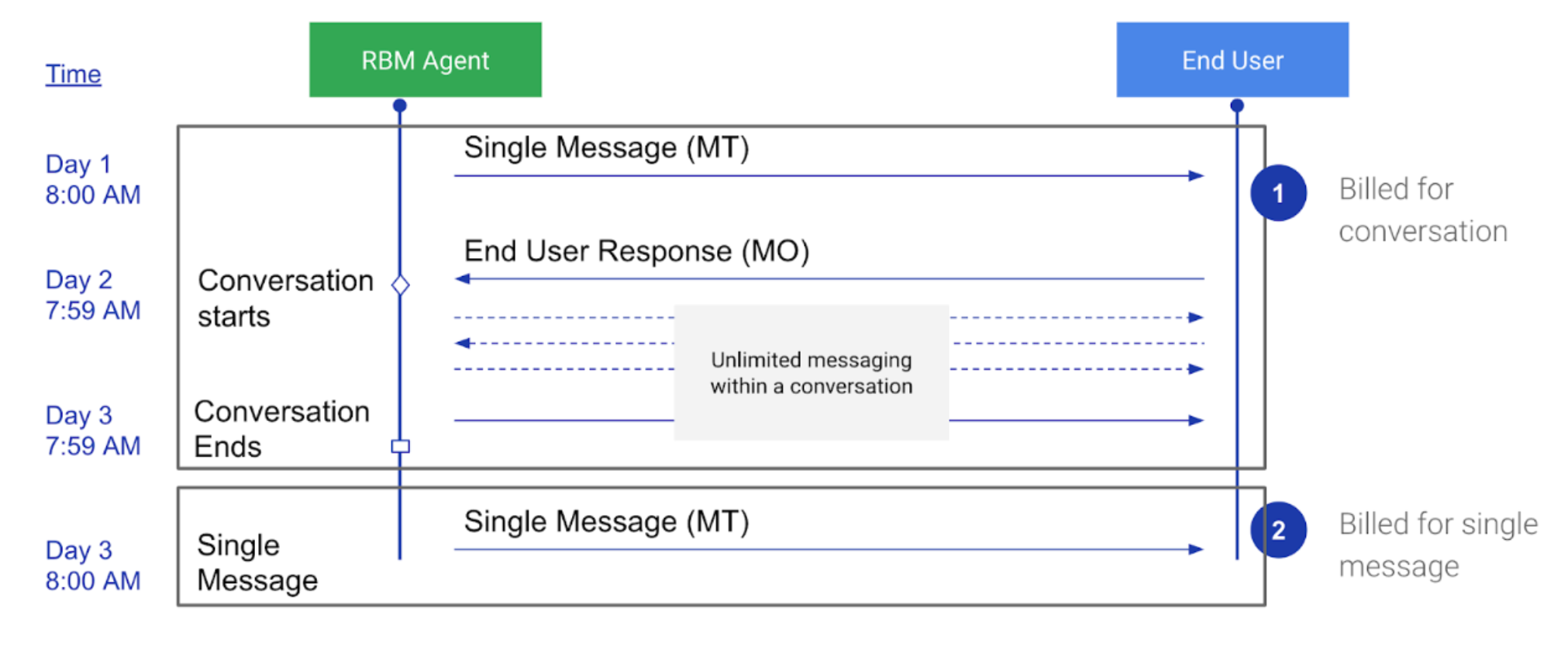
What is a conversation?
In RCS for Business, a conversation is a series of messages exchanged between a user and a conversational agent during a 24-hour period. Only agents with a Conversational billing category can generate conversations and be charged for these billable events:
- A2P (Application-to-Person): Sent by the business.
- P2A (Person-to-Application): Sent by the user.
How conversations work
- Start: A conversation begins when one party (the agent or user) responds
to a message from the other party within 24 hours of receiving it, outside
of any existing conversation.
- A2P conversation: Starts when the user responds to the agent's message.
- P2A conversation: Starts when the agent responds to the user's message.
- Conversation window: The conversation remains active for 24 hours after it started. The conversation includes all messages within this 24-hour window, as well as the very first message that was initially responded to.
- Billing: Instead of billing for each individual message, conversational agents are billed based on the entire conversation. This means the cost is associated with the conversation thread, not the number of messages within it.
The following diagram shows an example of an A2P billing session for conversational agents:
Important
- Conversations don't apply to non-conversational agents. Agents with a Basic Message or Single Message billing category are billed per message, regardless of whether the user replies.
- For conversational agents, the generation of billing event reports and activity logs can be delayed by up to two days. This delay allows RCS for Business to capture all messages within a conversation before calculating the billing event.
Billing reports
What is a billing report?
It's a record of billable events, which are calculated based on the agent's billing category and the types of messages it sends. Billing reports are available to all carriers who are actively operating RCS for Business.
For more information about billing reports, see Billing reports and activity logs.
Can I receive a billing report?
Only carriers who are actively operating RCS for Business receive billing reports. Partners don't receive billing reports.
To learn how to get billing reports, see File storage and access. These are instructions for retrieving billing reports using the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for carriers who have access to billing reports.
What if information is missing from the billing report?
If you notice that some information is missing from the report, troubleshoot the issue with the Support team. For more details, refer to the RCS for Business troubleshooting guide.
Why do I see charges in a month when I didn't send any messages?
RCS for Business billable events are recorded based on the time of message delivery, not the time the message was sent.
Example:
You send messages at the end of June, but they are delivered to the user's device in early July (for example, if the user's phone was offline), those charges will appear on your July billing reports. RCS for Business will attempt to deliver a message for up to 30 days before it expires.
Billing models
What are the key differences between the standard and US billing models?
Both the standard and US models use the agent's pre-selected billing category (conversational or non-conversational) to determine the overall rate structure. The primary difference is the set of classifications used for billable events.
Standard billing model (Non-US traffic)
This model applies to all traffic outside the US.
- Classification is based on the agent's billing category and the message content.
- Non-conversational agents: Billed per message. The message content determines the event: basic message or single message.
- Conversational agents: Billed per conversation. A conversation is a 24-hour window of unlimited message exchange between a user and an agent, billed at a fixed rate. If a user doesn't reply within 24 hours, the agent's message is billed individually as a basic message or single message.
- Billable events:
basic_messagesingle_messagea2p_conversationp2a_conversationp2a_message
- Billing logic: The final charge is determined by the agent's billing category, resulting in either a fixed rate per message (non-conversational) or a fixed rate per 24-hour conversation window (conversational).
US billing model
This model applies to all traffic to and from US phone numbers. For more information, refer to the US billing model guide.
- Classification of individual messages and user actions is automatic and based on content.
Regardless of the agent's billing category, every
billable event is classified as one of the following:
- Rich Message (MT/MO)
- Rich Media Message (MT/MO)
- Suggested Action Click (MO only)
- Billable events:
a2p_rich_messagea2p_rich_media_messagep2a_rich_messagep2a_rich_media_messagep2a_suggested_action
- Billing logic: The final charge is determined by the agent's billing category, using the billable event classifications to apply the correct rate structure.
Technical and reporting differences
- RBM API: The
AgentMessageandUserMessageAPI resources include arichMessageClassificationobject to define the message type for US traffic only. This is provided in real time upon API call and is separate from a later billing report. - Billing reports: Billing reports
are tailored to each model and include a
typecolumn that lists the billable events specific to that model. The US billing report also includes a column forsegment_count, which applies only to Rich Messages.