Video (VideoObject, Clip, BroadcastEvent) structured data
While Google tries to automatically understand details about your video, you can influence the
information that's shown in video results, such as the description, thumbnail URL, upload date, and duration, by marking up
your video with VideoObject. Adding video structured data
to your watch pages can also make it easier
for Google to find your video. Videos can appear in several different places on Google, including
the main search results page, Video mode, Google Images, and
Google Discover.

Based on how you mark up your watch page, your videos may also be eligible for the following specific video features:
| Video features | |
|---|---|
LIVE badge: Get a LIVE badge added to your video by marking your video with
Make sure you follow the LIVE badge guidelines and use the Indexing API to make sure Google crawls your page at the right time. |

|
|
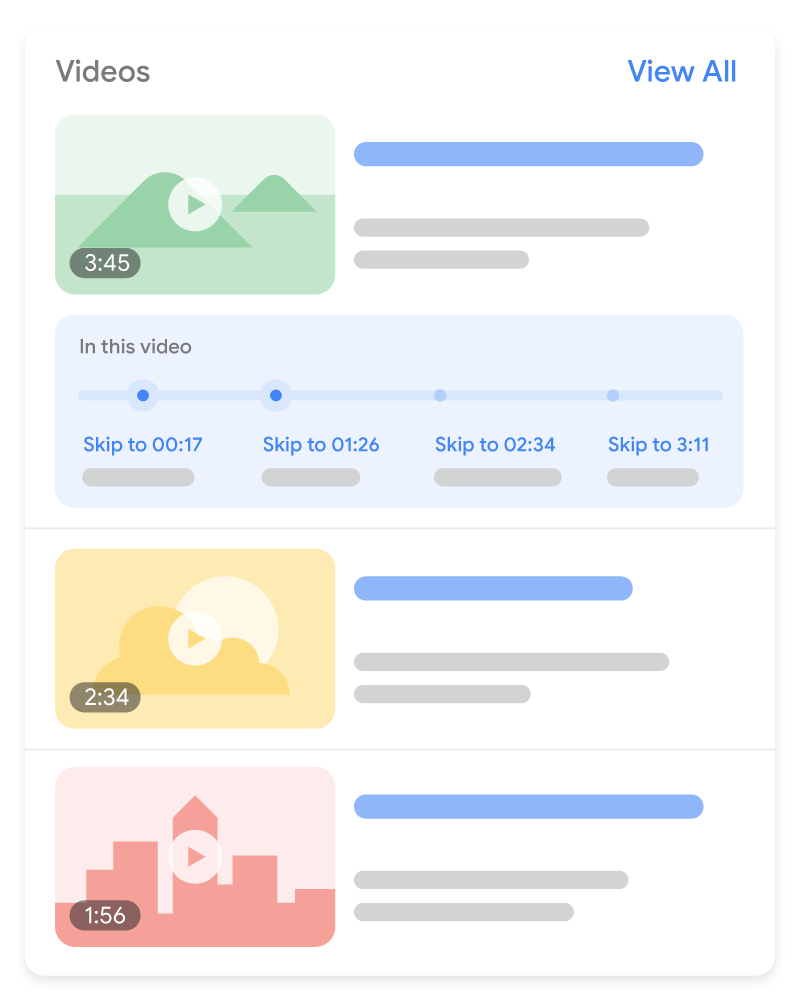
Key moments The key moments feature is a way for users to navigate video segments like chapters in a book, which can help users engage more deeply with your content. Google Search tries to automatically detect the segments in your video and show key moments to users, without any effort on your part. Alternatively, you can tell Google about the important points of your video. We will prioritize key moments set by you, either through structured data or the YouTube description.
To opt out of the key moments feature completely (including any efforts Google may make to show
key moments automatically for your video), use the
|
|
How to add structured data
Structured data is a standardized format for providing information about a page and classifying the page content. If you're new to structured data, you can learn more about how structured data works.
Here's an overview of how to build, test, and release structured data.
- Add the required properties. Based on the format you're using, learn where to insert structured data on the page.
- Follow the guidelines.
- Validate your code using the Rich Results Test and fix any critical errors. Consider also fixing any non-critical issues that may be flagged in the tool, as they can help improve the quality of your structured data (however, this isn't necessary to be eligible for rich results).
- Deploy a few pages that include your structured data and use the URL Inspection tool to test how Google sees the page. Be sure that your page is
accessible to Google and not blocked by a robots.txt file, the
noindextag, or login requirements. If the page looks okay, you can ask Google to recrawl your URLs. - To keep Google informed of future changes, we recommend that you submit a sitemap. You can automate this with the Search Console Sitemap API.
Examples
Standard video result

Here's an example of a single VideoObject.
<html>
<head>
<title>Introducing the self-driving bicycle in the Netherlands</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"name": "Introducing the self-driving bicycle in the Netherlands",
"description": "This spring, Google is introducing the self-driving bicycle in Amsterdam, the world's premier cycling city. The Dutch cycle more than any other nation in the world, almost 900 kilometres per year per person, amounting to over 15 billion kilometres annually. The self-driving bicycle enables safe navigation through the city for Amsterdam residents, and furthers Google's ambition to improve urban mobility with technology. Google Netherlands takes enormous pride in the fact that a Dutch team worked on this innovation that will have great impact in their home country.",
"thumbnailUrl": [
"https://example.com/photos/1x1/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/4x3/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/16x9/photo.jpg"
],
"uploadDate": "2024-03-31T08:00:00+08:00",
"duration": "PT1M54S",
"contentUrl": "https://www.example.com/video/123/file.mp4",
"embedUrl": "https://www.example.com/embed/123",
"interactionStatistic": {
"@type": "InteractionCounter",
"interactionType": { "@type": "WatchAction" },
"userInteractionCount": 5647018
},
"regionsAllowed": ["US", "NL"]
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html><html itemscope itemprop="VideoObject" itemtype="https://schema.org/VideoObject">
<head>
<title itemprop="name">Introducing the self-driving bicycle in the Netherlands</title>
</head>
<body>
<meta itemprop="uploadDate" content="2024-03-31T08:00:00+08:00" />
<meta itemprop="duration" content="PT1M54S" />
<p itemprop="description">This spring, Google is introducing the self-driving bicycle in Amsterdam, the world's premier cycling city. The Dutch cycle more than any other nation in the world, almost 900 kilometres per year per person, amounting to over 15 billion kilometres annually. The self-driving bicycle enables safe navigation through the city for Amsterdam residents, and furthers Google's ambition to improve urban mobility with technology. Google Netherlands takes enormous pride in the fact that a Dutch team worked on this innovation that will have great impact in their home country.</p>
<div itemprop="interactionStatistic" itemtype="https://schema.org/InteractionCounter" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="userInteractionCount" content="5647018" />
<meta itemprop="interactionType" itemtype="https://schema.org/WatchAction" />
</div>
<link itemprop="embedUrl" href="https://www.example.com/embed/123" />
<meta itemprop="contentUrl" content="https://www.example.com/video/123/file.mp4" />
<meta itemprop="regionsAllowed" content="US" />
<meta itemprop="regionsAllowed" content="NL" />
<meta itemprop="thumbnailUrl" content="https://example.com/photos/1x1/photo.jpg" />
</body>
</html>LIVE badge

Here's an example of VideoObject and BroadcastEvent.
<html>
<head>
<title>Bald Eagle at the Park - Livestream</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"contentURL": "https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park.mp4",
"description": "Bald eagle at the park livestream.",
"duration": "PT37M14S",
"embedUrl": "https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park",
"expires": "2024-10-30T14:37:14+00:00",
"regionsAllowed": "US",
"interactionStatistic": {
"@type": "InteractionCounter",
"interactionType": { "@type": "WatchAction" },
"userInteractionCount": 4756
},
"name": "Bald eagle nest livestream!",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park",
"uploadDate": "2024-10-27T14:00:00+00:00",
"publication": [
{
"@type": "BroadcastEvent",
"isLiveBroadcast": true,
"startDate": "2024-10-27T14:00:00+00:00",
"endDate": "2024-10-27T14:37:14+00:00"
},
{
"@type": "BroadcastEvent",
"isLiveBroadcast": true,
"startDate": "2024-10-27T18:00:00+00:00",
"endDate": "2024-10-27T18:37:14+00:00"
}
]
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html><html itemscope itemprop="VideoObject" itemtype="https://schema.org/VideoObject">
<head>
<title itemprop="name">Bald Eagle at the Park - Livestream</title>
</head>
<body>
<meta itemprop="uploadDate" content="2024-10-27T14:00:00+00:00" />
<meta itemprop="duration" content="PT37M14S" />
<p itemprop="description">Bald eagle at the park livestream.</p>
<div itemprop="interactionStatistic" itemtype="https://schema.org/InteractionCounter" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="userInteractionCount" content="4756" />
<meta itemprop="interactionType" itemtype="https://schema.org/WatchAction" />
</div>
<link itemprop="embedUrl" href="https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park" />
<meta itemprop="expires" content="2024-10-30T14:37:14+00:00" />
<meta itemprop="contentUrl" content="https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park.mp4" />
<meta itemprop="regionsAllowed" content="US" />
<meta itemprop="thumbnailUrl" content="https://example.com/bald-eagle-at-the-park" />
<div itemprop="publication" itemtype="https://schema.org/BroadcastEvent" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="isLiveBroadcast" content="true" />
<meta itemprop="startDate" content="2024-10-27T14:00:00+00:00" />
<meta itemprop="endDate" content="2024-10-27T14:37:14+00:00" />
</div>
<div itemprop="publication" itemtype="https://schema.org/BroadcastEvent" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="isLiveBroadcast" content="true" />
<meta itemprop="startDate" content="2024-10-27T18:00:00+00:00" />
<meta itemprop="endDate" content="2024-10-27T18:37:14+00:00" />
</div>
</body>
</html>
Clip

Here's an example of VideoObject
and Clip.
<html>
<head>
<title>Cat jumps over the fence</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"name": "Cat video",
"duration": "PT10M",
"uploadDate": "2024-07-19T08:00:00+08:00",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://www.example.com/cat.jpg",
"description": "Watch this cat jump over a fence!",
"contentUrl": "https://www.example.com/cat_video_full.mp4",
"ineligibleRegion": "US",
"hasPart": [{
"@type": "Clip",
"name": "Cat jumps",
"startOffset": 30,
"endOffset": 45,
"url": "https://www.example.com/example?t=30"
},
{
"@type": "Clip",
"name": "Cat misses the fence",
"startOffset": 111,
"endOffset": 150,
"url": "https://www.example.com/example?t=111"
}]
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html><html itemscope itemprop="VideoObject" itemtype="https://schema.org/VideoObject">
<head>
<title itemprop="name">Cat jumps over the fence</title>
</head>
<body>
<meta itemprop="uploadDate" content="2024-07-19" />
<meta itemprop="duration" content="P10M" />
<p itemprop="description">Watch this cat jump over a fence!</p>
<div itemprop="interactionStatistic" itemtype="https://schema.org/InteractionCounter" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="userInteractionCount" content="5647018" />
<meta itemprop="interactionType" itemtype="https://schema.org/WatchAction" />
</div>
<div itemprop="hasPart" itemtype="https://schema.org/Clip" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="name" content="Cat jumps" />
<meta itemprop="startOffset" content="30" />
<meta itemprop="endOffset" content="45" />
<meta itemprop="url" content="https://www.example.com/example?t=30" />
</div>
<div itemprop="hasPart" itemtype="https://schema.org/Clip" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="name" content="Cat misses the fence" />
<meta itemprop="startOffset" content="111" />
<meta itemprop="endOffset" content="150" />
<meta itemprop="url" content="https://www.example.com/example?t=111" />
</div>
<link itemprop="embedUrl" href="https://www.example.com/embed/123" />
<meta itemprop="contentUrl" content="https://www.example.com/cat_video_full.mp4" />
<meta itemprop="ineligibleRegion" content="US" />
<meta itemprop="thumbnailUrl" content="https://www.example.com/cat.jpg" />
</body>
</html>
SeekToAction
Here's an example of a single VideoObject
that includes the additional properties needed for SeekToAction markup.
<html>
<head>
<title>John Smith (@johnsmith123) on VideoApp: My daily workout! #stayingfit</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "VideoObject",
"potentialAction" : {
"@type": "SeekToAction",
"target": "https://video.example.com/watch/videoID?t={seek_to_second_number}",
"startOffset-input": "required name=seek_to_second_number"
},
"name": "My daily workout!",
"uploadDate": "2024-07-19T08:00:00+08:00",
"thumbnailUrl": "https://www.example.com/daily-workout.jpg",
"description": "My daily workout!",
"embedUrl": "https://example.com/daily-workout"
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html><html itemscope itemprop="VideoObject" itemtype="https://schema.org/VideoObject">
<head>
<title itemprop="name">John Smith (@johnsmith123) on VideoApp: My daily workout! #stayingfit</title>
</head>
<body>
<meta itemprop="uploadDate" content="2024-07-19" />
<p itemprop="description">My daily workout!</p>
<div itemprop="potentialAction" itemtype="https://schema.org/SeekToAction" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="target" content="https://video.example.com/watch/videoID?t={seek_to_second_number}" />
<meta itemprop="startOffset-input" content="required name=seek_to_second_number" />
</div>
<link itemprop="embedUrl" href="https://example.com/daily-workout" />
<meta itemprop="thumbnailUrl" content="https://www.example.com/daily-workout.jpg" />
</body>
</html>Guidelines
For your video structured data to be eligible for usage in Google Search, you must follow the Search Essentials, general structured data guidelines, and video indexing requirements.
In addition, we recommend that you check out these guidelines if they apply to your video content:
- Livestream guidelines
ClipandSeekToActionguidelines- Best practices for marking timestamps on YouTube
LIVE badge guidelines
If you're adding BroadcastEvent to livestream
videos, follow these guidelines:
- Don't use vulgar or potentially offensive language in the structured data.
- To make sure Google crawls your livestream video at the right time, use the
Indexing API. Call the API for the
following events:
- When the video goes live
- When the video has stopped streaming, and the page's markup has been updated
to indicate the
endDate - Whenever a change has happened in the markup and Google needs to be notified
Best practices for marking timestamps on YouTube
If your video is hosted on YouTube, Google Search may automatically enable key moments for your video based on the video description on YouTube, and you may not have to mark specific timestamps in your YouTube description. However, you can tell us more explicitly about the important points in your video and we will prefer that information. The following diagram shows how timestamps and labels in a YouTube video description can appear in search results:
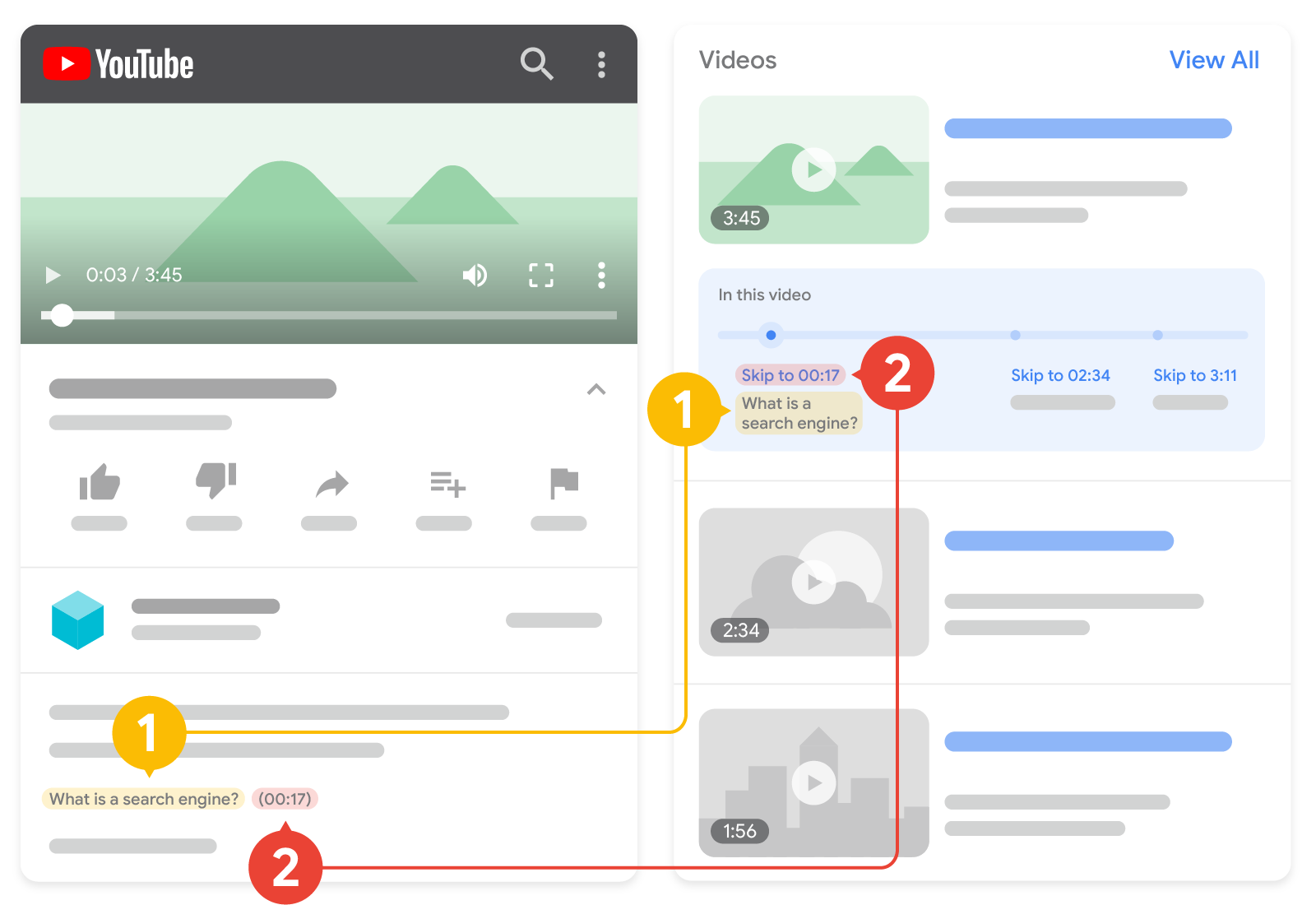
2. Timestamp: When a clip starts.
Keep in mind the following guidelines when formatting timestamps and labels for YouTube descriptions:
- Format the timestamp in the following format:
[hour]:[minute]:[second]. If there's no hour, you don't need to include it. - Specify the label of the timestamp on the same line as the timestamp.
- Place each timestamp on a new line in the video description.
- Link the timestamp to the specified point in the video.
- Make sure the label contains at least one word.
- List the timestamps in chronological order.
If you want to enable Video Chapters on YouTube, follow these additional guidelines.
Clip and SeekToAction guidelines
If you're adding Clip or SeekToAction
structured data to mark video segments, follow these guidelines:
- The video must have the ability to deep link into some point other than the start
point in the video URL. For example,
https://www.example.com/example?t=30starts 30 seconds into a video. VideoObjectstructured data must be added to a page where users can watch the video. It's a bad user experience to point users to a page where they can't watch the video.- The total video duration must be a minimum of 30 seconds.
- The video must include the required properties that are listed in the
VideoObjectstructured data documentation. - For
Clipstructured data only: Make sure that no two clips on the same video defined on the same page share a start time. - For
SeekToActionstructured data only: Google must be able to fetch your video content files.
Structured data type definitions
This section describes the structured data types related to video features in Google Search.
You must include the required VideoObject properties for your
markup to be eligible for usage in Google Search. You can also include the
recommended properties to add more information about your VideoObject, which could provide a better
user experience. In addition to VideoObject, you can add the
following data types to enable video enhancements in Google Search:
BroadcastEvent: Mark up livestream videos to enable a LIVE badge on your video.Clip: Mark important segments in your video to help users quickly navigate to specific points in a video.SeekToAction: Enable key moments by indicating how your URL structure works, so that Google can automatically identify key moments and link users to those points within the video.
VideoObject
The full definition of VideoObject is available at
schema.org/VideoObject.
If you don't include the required properties, Google may not be able to extract
any information about the video. You can also include the recommended properties to
add more information about your content, which could provide a better user experience.
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
name |
The title of the video. Make sure to use unique text in the |
thumbnailUrl |
Repeated A URL pointing to the video's unique thumbnail image file. Follow the thumbnail image guidelines. |
uploadDate |
The date and time the video was first published, in ISO 8601 format. We recommend that you provide timezone information; otherwise, we will default to the timezone used by Googlebot. |
| Recommended properties | |
|---|---|
contentUrl
|
A URL pointing to the video file's actual content bytes, in one of the supported file types. Don't link to the page where the video lives; this must be the URL of the video file's actual content bytes itself. "contentUrl": "https://www.example.com/video/123/file.mp4" Make sure to follow our video best practices. |
description |
The description of the video. Make sure to use unique text in the |
duration |
The duration of the video in
ISO 8601 format.
For example, |
embedUrl
|
A URL pointing to a player for the specific video. Don't link to the page where the
video lives; this must be the URL of the video player itself. Usually this is the information in
the "embedUrl": "https://www.example.com/embed/123" Make sure to follow our Video best practices. |
expires |
DateTime
If applicable, the date and time after which the video will no longer be available, in ISO 8601 format. Don't supply this information if your video does not expire. We recommend that you provide timezone information; otherwise, we will default to the timezone used by Googlebot. |
hasPart
|
If your video has important segments, nest the required <script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org/", "@type": "VideoObject", "name": "Cat video", "hasPart": { "@type": "Clip", "name": "Cat jumps", "startOffset": 30, "url": "https://www.example.com/example?t=30" } } </script> |
ineligibleRegion
|
The region where the video isn't allowed, if applicable. If not specified, then Google assumes the video is
allowed everywhere. Specify the countries in
two- or three-letter ISO 3166-1 format. For
multiple values, use multiple country codes (for example, a JSON-LD array or multiple
|
interactionStatistic |
The number of times the video has been watched. For example: "interactionStatistic": { "@type": "InteractionCounter", "interactionType": { "@type": "WatchAction" }, "userInteractionCount": 12345 } |
publication
|
If your video is happening live and you want to be eligible for the LIVE badge, nest
the <script type="application/ld+json"> { "@context": "https://schema.org/", "@type": "VideoObject", "name": "Cat video", "publication": { "@type": "BroadcastEvent", "name": "First scheduled broadcast", "isLiveBroadcast": true, "startDate": "2018-10-27T14:00:00+00:00", "endDate": "2018-10-27T14:37:14+00:00" } } </script> |
regionsAllowed
|
The regions where the video is allowed, if applicable. If not specified, then Google assumes the video is
allowed everywhere. Specify the countries in
two- or three-letter ISO 3166-1 format.
For multiple values, use multiple country codes (for example, a JSON-LD array or multiple
|
BroadcastEvent
To be eligible for display with a LIVE badge, nest the following
properties in your VideoObject. While
BroadcastEvent properties aren't required, you must add the following properties if you
want your video to display with a LIVE badge.
The full definition of BroadcastEvent is available at
schema.org/BroadcastEvent.
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
publication
|
Describes when the video is to be streamed live. Can be a list or a single instance. |
publication.endDate
|
Time and date of when the livestream ends or is expected to end, in ISO 8601 format. It's required to provide the If |
publication.isLiveBroadcast |
Boolean
Set to |
publication.startDate
|
Time and date of when the livestream starts or is expected to start, in
ISO 8601 format. If
|
Clip
To tell Google what timestamp and label to use for the key moments feature, nest the following properties in your
VideoObject. While
Clip properties aren't required, you must add the following properties if you
want Google to show the timestamps and labels that you specify for your video, instead of the
video segments that Google may automatically show for your video.
The full definition of Clip is
available at schema.org/Clip.
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
name |
A descriptive title for the content of the clip. |
startOffset |
The start time of the clip expressed as the number of seconds from the beginning of the work. |
url |
A URL that points to the start time of the clip. The clip URL must point to the same URL path as the video with additional query parameters that specify the time. For example, the following URL means the video starts at 2:00 minutes: "url": "https://www.example.com/example?t=120" |
| Recommended properties | |
|---|---|
endOffset |
The end time of the clip expressed as the number of seconds from the beginning of the work. |
SeekToAction
To tell Google how your URL structure works (so that Google can display key moments
that are automatically identified for your video), nest the following properties in your
VideoObject. While
SeekToAction properties aren't required, you must add the following properties if you
want Google to understand how your URL structure works, so Google can link users to a point within the video.
The full definition of SeekToAction is
available at schema.org/SeekToAction.
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
potentialAction
|
Indicates a potential action. Include the following nested properties For example: { "@context": "https://schema.org", "@type": "VideoObject", "potentialAction" : { "@type": "SeekToAction", "target": "https://video.example.com/watch/videoID?t={seek_to_second_number}", "startOffset-input": "required name=seek_to_second_number" } } |
potentialAction.startOffset-input
|
The placeholder string that Google will identify as your timestamp structure and then replace with the number of seconds to skip to. Use the following value: "startOffset-input": "required name=seek_to_second_number"
|
potentialAction.target
|
The URL of the page that contains this {seek_to_second_number}For example, replace the timestamp part of the URL: "target": "https://video.example.com/watch/videoID?t=30" So that the timestamp now looks like this: "target": "https://video.example.com/watch/videoID?t={seek_to_second_number}" |
Monitor rich results with Search Console
Search Console is a tool that helps you monitor how your pages perform in Google Search. You don't have to sign up for Search Console to be included in Google Search results, but it can help you understand and improve how Google sees your site. We recommend checking Search Console in the following cases:
- After deploying structured data for the first time
- After releasing new templates or updating your code
- Analyzing traffic periodically
After deploying structured data for the first time
After Google has indexed your pages, look for issues using the relevant Rich result status report. Ideally, there will be an increase of valid items, and no increase in invalid items. If you find issues in your structured data:
- Fix the invalid items.
- Inspect a live URL to check if the issue persists.
- Request validation using the status report.
After releasing new templates or updating your code
When you make significant changes to your website, monitor for increases in structured data invalid items.- If you see an increase in invalid items, perhaps you rolled out a new template that doesn't work, or your site interacts with the existing template in a new and bad way.
- If you see a decrease in valid items (not matched by an increase in invalid items), perhaps you are no longer embedding structured data in your pages. Use the URL Inspection tool to learn what is causing the issue.
Analyzing traffic periodically
Analyze your Google Search traffic using the Performance Report. The data will show you how often your page appears as a rich result in Search, how often users click on it and what is the average position you appear on search results. You can also automatically pull these results with the Search Console API.Troubleshooting
If you're having trouble implementing or debugging structured data, here are some resources that may help you.
- If you're using a content management system (CMS) or someone else is taking care of your site, ask them to help you. Make sure to forward any Search Console message that details the issue to them.
- Google does not guarantee that features that consume structured data will show up in search results. For a list of common reasons why Google may not show your content in a rich result, see the General Structured Data Guidelines.
- You might have an error in your structured data. Check the list of structured data errors and the Unparsable structured data report.
- If you received a structured data manual action against your page, the structured data on the page will be ignored (although the page can still appear in Google Search results). To fix structured data issues, use the Manual Actions report.
- Review the guidelines again to identify if your content isn't compliant with the guidelines. The problem can be caused by either spammy content or spammy markup usage. However, the issue may not be a syntax issue, and so the Rich Results Test won't be able to identify these issues.
- Troubleshoot missing rich results / drop in total rich results.
- Allow time for re-crawling and re-indexing. Remember that it may take several days after publishing a page for Google to find and crawl it. For general questions about crawling and indexing, check the Google Search crawling and indexing FAQ.
- Post a question in the Google Search Central forum.
