Komponent: Pojęcie
Zadbaj o dobrą organizację dzięki kolekcji
Zapisuj i kategoryzuj treści zgodnie ze swoimi preferencjami.
Element: Koncepcja / informacje
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Informacje tekstowe, takie jak nazwa i opis
koncepcję. |
| Diagram |
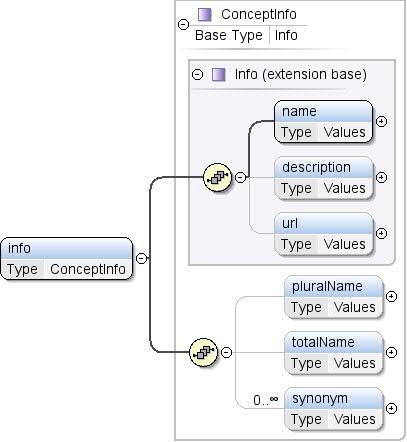 |
| Typ |
ConceptInfo |
| Hierarchia typów |
|
| Właściwości |
|
| Model |
name , description{0,1} , url{0,1} , pluralName{0,1} , totalName{0,1} , synonim* |
| Dzieci |
description, name, pluralName,
synon, totalName, url |
| Instancja |
<info>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</info>
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Temat, z którym powiązane jest dane słowo. |
| Diagram |
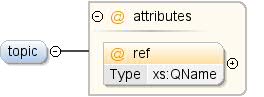 |
| Właściwości |
| treść: |
Złożone |
| min.: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
nieograniczony |
|
| Atrybuty |
| QName |
Typ |
Naprawiono |
Domyślny |
Użyj |
Adnotacja |
| źródło |
xs:QName |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Unikalny identyfikator tematu, który jest związany z tym zagadnieniem
z którymi jest powiązana. Wskazany temat może być zdefiniowany w tym samym
lub zewnętrznie, np. w innym zbiorze danych. Odwołanie do
Temat zewnętrzny musi mieć postać
„prefix:other_topic_id”, gdzie „prefiks” to
prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw zewnętrznego zbioru danych (patrz XML
przestrzeni nazw). |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
Element: Pojęcie / typ
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Typ danych związanych z zagadnieniem. Koncepcja musi określać typ
deklaracji lub rozszerzenia innego koncepcji. W sytuacji, gdy
Rozszerzając pojęcie, może również dodać deklarację typu. Typ
koncepcja rozszerzona musi być mniej restrykcyjna niż typ
koncepcję jego rozszerzenia. „Mniej restrykcyjne niż” (LRT) to
kolejność częściowa zdefiniowana w następujący sposób: ciąg znaków zmiennoprzecinkowa LRT, liczba zmiennoprzecinkowa LRT
string LRT date string LRT, wartość logiczna |
| Diagram |
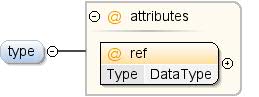 |
| Właściwości |
|
| Atrybuty |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
Element: Pojęcie / atrybut
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Atrybut koncepcji. Atrybuty reprezentują dodatkowe
informacje o danym zagadnieniu (np. PKB to wartość procentowa). |
| Diagram |
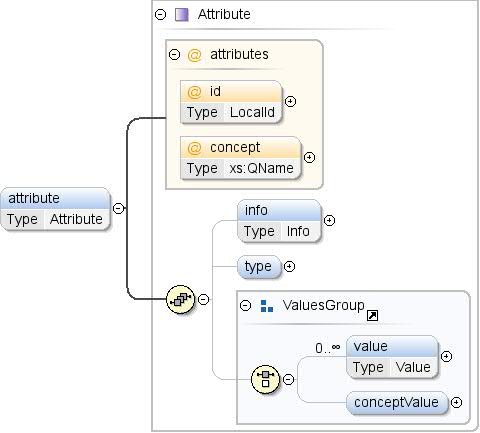 |
| Typ |
Atrybut |
| Właściwości |
| treść: |
Złożone |
| min.: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
nieograniczony |
|
| Model |
info{0,1} , type{0,1} , (wartość*
| conceptValue{0,1}) |
| Dzieci |
conceptValue, info, type,
wartość |
| Instancja |
<attribute concept="" id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type format="" ref="">{0,1}</type>
</attribute>
|
| Atrybuty |
| QName |
Typ |
Naprawiono |
Domyślny |
Użyj |
Adnotacja |
| koncepcja |
xs:QName |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Odniesienie do pojęcia, który odpowiada wartościom.
atrybutu. Jeśli atrybut określa typ, to
musi pasować do typu wskazanej koncepcji. Odwołanie do
koncepcja zewnętrzna musi mieć postać
„prefix:other_koncepcja”, gdzie „prefiks” to
prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw zewnętrznego zbioru danych (patrz XML
przestrzeni nazw). |
| id |
LocalId |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Identyfikator atrybutu koncepcja. Ten identyfikator musi być:
które są unikalne (w odniesieniu do różnych atrybutów i właściwości).
„id” można pominąć, jeśli określono atrybut „koncepcja”. Pod tym kątem
, identyfikator to prostota, którą określa się z wartością lokalną
wymienionego pojęcia. Na przykład <atrybut
concept="unit:currency"/> jest odpowiednikiem funkcji
<attribute id="currency"
concept="unit:currency"/> |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
Element: Pojęcie / właściwość
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Właściwość koncepcji. Właściwości reprezentują dodatkowe
informacje o przykładach danej koncepcji (np. koncepcja
„miasto” może zawierać właściwość „country”). |
| Diagram |
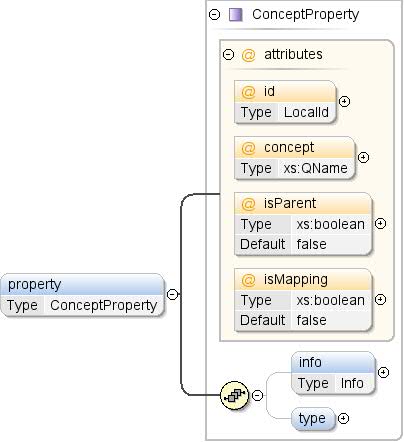 |
| Typ |
ConceptProperty |
| Właściwości |
| treść: |
Złożone |
| min.: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
nieograniczony |
|
| Model |
info{0,1} , type{0,1} |
| Dzieci |
info, typ |
| Instancja |
<property concept="" id="" isMapping="false" isParent="false">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type ref="">{0,1}</type>
</property>
|
| Atrybuty |
| QName |
Typ |
Naprawiono |
Domyślny |
Użyj |
Adnotacja |
| koncepcja |
xs:QName |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Odniesienie do pojęcia, który odpowiada wartościom.
usługi. Jeśli właściwość określa typ, zostanie użyty typ
musi pasować do typu wskazanej koncepcji. Odwołanie do
koncepcja zewnętrzna musi mieć postać
„prefix:other_koncepcja”, gdzie „prefiks” to
prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw zewnętrznego zbioru danych (patrz XML
przestrzeni nazw). |
| id |
LocalId |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Identyfikator właściwości koncepcji. Ten identyfikator musi być:
które są unikalne (w odniesieniu do różnych atrybutów i właściwości).
Identyfikator może zostać pominięty, jeśli określono właściwość koncepcji. Pod tym kątem
, domyślnie tworzony jest identyfikator z wartością lokalną nazwę tagu
wymienionego pojęcia. Na przykład <property
concept="geo:country"/> jest odpowiednikiem elementu <property
id="country"
concept="geo:country"/> |
| isMapping |
xs:boolean |
|
fałsz |
opcjonalnie |
Jeśli ma wartość true (prawda), ta właściwość musi odnosić się do koncepcji,
ta właściwość wskazuje na mapowanie (1 do 1) między
i powiązanej koncepcji. Każde wystąpienie odwołania do
pojęcie jest wskazywane przez co najmniej 1 wystąpienie tego argumentu
koncepcję. |
| isParent |
xs:boolean |
|
fałsz |
opcjonalnie |
Jeśli ma wartość true (prawda), ta właściwość musi odnosić się do koncepcji,
ta właściwość określa hierarchiczną relację między
i pojęcie, do którego się odwołuje (np. kontynent
kraj). |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
Element: Concept / defaultValue
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Domyślna wartość koncepcji, która będzie używana przez aplikacje
gdy muszą wybrać jedną z możliwych wartości argumentu
koncepcję. |
| Diagram |
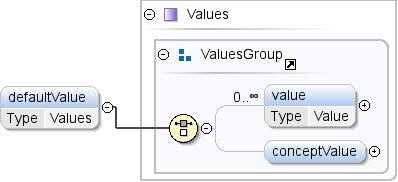 |
| Typ |
Wartości |
| Właściwości |
|
| Model |
wartość* | conceptValue{0,1} |
| Dzieci |
conceptValue, value |
| Instancja |
<defaultValue>
<value lang="">{0,unbounded}</value>
<conceptValue concept="">{0,1}</conceptValue>
</defaultValue>
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
Element: Pojęcie / tabela
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Odwołanie do tabeli, która zawiera wszystkie możliwe wartości
koncepcji i jej właściwości niestałych. |
| Diagram |
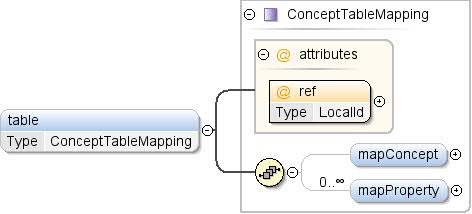 |
| Typ |
ConceptTableMapping |
| Właściwości |
|
| Model |
mapConcept{0,1} , mapProperty* |
| Dzieci |
mapConcept i mapProperty |
| Instancja |
<table ref="">
<mapConcept toColumn="">{0,1}</mapConcept>
<mapProperty lang="" ref="" toColumn="">{0,unbounded}</mapProperty>
</table>
|
| Atrybuty |
| QName |
Typ |
Naprawiono |
Domyślny |
Użyj |
Adnotacja |
| źródło |
LocalId |
|
|
wymagane |
Identyfikator tabeli, która zawiera dane
koncepcję. |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
Typ złożony: pojęcie
| Przestrzeń nazw |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| Adnotacje |
Pojęcie to definicja typu danych pojawiających się
zbiór danych (np. „PKB” lub „hrabstwo”). Koncepcja może być
związane z wyliczeniem wszystkich możliwych wartości. O
koncepcja zdefiniowana w jednym zbiorze danych może być przywoływana w innych
i zbiory danych. |
| Diagram |
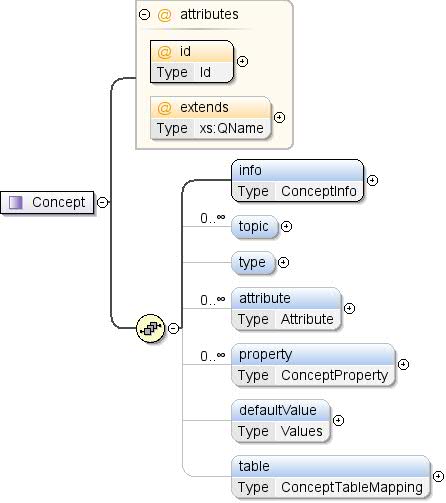 |
| Używane przez |
|
| Model |
info , topic* , type{0,1} ,
attribute* , property* , defaultValue{0,1} , table{0,1} |
| Dzieci |
attribute, defaultValue, info,
property, table, topic,
typ |
| Atrybuty |
| QName |
Typ |
Naprawiono |
Domyślny |
Użyj |
Adnotacja |
| rozszerza |
xs:QName |
|
|
opcjonalnie |
Unikalny identyfikator elementu, do którego odnosi się dana koncepcja
Wspomniane pojęcie może być zdefiniowane w tym samym zbiorze danych
lub zewnętrznie, np. w innym zbiorze danych. Odniesienie do zasobu zewnętrznego
koncepcja musi mieć format „prefix:identyfikator_innego_koncepcji”,
gdzie „prefiks” to prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw
w zewnętrznym zbiorze danych (patrz: przestrzenie nazw XML). |
| id |
Identyfikator |
|
|
wymagane |
Unikalny identyfikator koncepcji, którym musi być
unikalne globalnie w obrębie zbioru danych. |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:complexType name="Concept">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A concept is a definition of a type of data that appears in the
dataset (e.g., "GDP" or "County"). A concept may be associated with
an enumeration of all its possible values or not. A concept defined in
some dataset may be referenced in other datasets.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
|
| Przestrzeń nazw |
Brak przestrzeni nazw |
| Adnotacje |
Unikalny identyfikator tematu, z którym powiązana jest ta koncepcja
z naszymi usługami. Przywoływany temat może być zdefiniowany w tym samym zbiorze danych lub
np. w innym zbiorze danych. Odniesienie do tematu zewnętrznego
musi mieć format „prefix:other_topic_id”, gdzie
„prefiks” to prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw zewnętrznego
zbiór danych (patrz przestrzenie nazw XML). |
| Typ |
xs:QName |
| Właściwości |
|
| Używane przez |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
| Przestrzeń nazw |
Brak przestrzeni nazw |
| Typ |
DataType |
| Właściwości |
|
| Aspekty |
| wyliczenie |
ciąg znaków |
|
| wyliczenie |
liczba zmiennoprzecinkowa |
|
| wyliczenie |
liczba całkowita |
|
| wyliczenie |
wartość logiczna |
|
| wyliczenie |
data |
|
| wyliczenie |
pomysł : koncepcja |
|
|
| Używane przez |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
|
Atrybut: Concept / @id
| Przestrzeń nazw |
Brak przestrzeni nazw |
| Adnotacje |
Unikalny identyfikator koncepcji, który musi być globalny.
unikalne w obrębie zbioru danych. |
| Typ |
Identyfikator |
| Właściwości |
|
| Aspekty |
|
| Używane przez |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Atrybut: Concept / @extends
| Przestrzeń nazw |
Brak przestrzeni nazw |
| Adnotacje |
Unikalny identyfikator zagadnienia, którego dotyczy ta koncepcja.
Wspomniane pojęcie może być zdefiniowane w tym samym zbiorze danych lub zewnętrznie,
czyli w innym zbiorze danych. Odniesienie do koncepcji zewnętrznej musi być
format „prefix:other_Concept_id”, gdzie „prefiks” to
prefiks używany dla przestrzeni nazw zewnętrznego zbioru danych (patrz XML
przestrzeni nazw). |
| Typ |
xs:QName |
| Właściwości |
|
| Używane przez |
|
| Źródło |
<xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
Utworzono za pomocą
oXygen XML Editor.
O ile nie stwierdzono inaczej, treść tej strony jest objęta licencją Creative Commons – uznanie autorstwa 4.0, a fragmenty kodu są dostępne na licencji Apache 2.0. Szczegółowe informacje na ten temat zawierają zasady dotyczące witryny Google Developers. Java jest zastrzeżonym znakiem towarowym firmy Oracle i jej podmiotów stowarzyszonych.
Ostatnia aktualizacja: 2025-07-25 UTC.
[[["Łatwo zrozumieć","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["Rozwiązało to mój problem","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["Inne","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["Brak potrzebnych mi informacji","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["Zbyt skomplikowane / zbyt wiele czynności do wykonania","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["Nieaktualne treści","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["Problem z tłumaczeniem","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["Problem z przykładami/kodem","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["Inne","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["Ostatnia aktualizacja: 2025-07-25 UTC."],[],["Concepts, within a dataset (namespace: `http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010`), define data types and are globally unique. Concepts can extend others, using `prefix:other_concept_id` for external references. They include `info` (textual details), `topic` (associated topics via `ref`), `type` (data type, `ref`), `attribute` (additional information), `property` (instance information), `defaultValue`, and `table` (data source, `ref`). Key concept attributes are `id` (unique), and `extends` (referencing another concept). External references are in `prefix:identifier` format. A concept must have a `type` or `extends`.\n"]]







