次のセクションでは、制約プログラミング(CP)を チェスゲームに基づく組み合わせ問題です。チェスのクイーンは、 水平、垂直、対角線上に展開します。N クイーンズ問題では、
NxN のチェス盤に N 個のクイーンを置いて、二人から攻撃されないようにするには どうですか?
以下は、N = 4 の場合の N クイーン問題に対して、考えられる解の 1 つです。
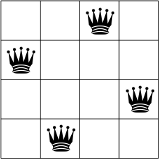
2 つのクイーンが同じ行、列、対角線上に存在することはできません。
なお、これは最適化の問題ではありません。 最適なソリューションではなく 制約プログラミングの考慮事項です 以降のセクションでは、N クイーン問題に対する CP のアプローチについて説明します。 CP-SAT ソルバーとオリジナルの CP を使って解くプログラムを提示する あります。
N クイーン問題に対する CP アプローチ
CP ソルバーは、体系的にすべてを試すことで機能する 問題内の変数への値の代入も考えられます。これにより、 具体的なソリューションを見ていきます。4 クイーン問題では、解法は左端から始まります。 各列にクイーンを 1 つずつ配置します。 過去に置かれたクイーンの攻撃を受けていません
伝播とバックトラック
制約プログラミングの検索には、次の 2 つの重要な要素があります。
- 伝播 - ソルバーが変数に値を割り当てるたびに、 制約を追加することで、割り当てられていないオブジェクトの 使用します。これらの制限は、今後の変数の割り当てにも反映されます。 たとえば、4 クイーン問題では、解法によってクイーンが 1 問出されるたびに、 他のクイーンをその行と対角線に配置することはできません。 伝播によって、一連の検出が減るため、検索が大幅に高速化されます。 変数値を求めます。
- バックトラッキングは、解法が次の値に値を代入できない場合に発生します。 変数に与えられるか、解答を見つけます。いずれの場合も、 バックトラックを行って前のステージにバックトラックし、 まだ試行されていない値に変更する必要があります。4 クイーンの例では、 つまり、クイーンを現在の列の新しい正方形に移動します。
次に、制約プログラミングが伝播とバックトラッキングを使用して、 クイーンの 4 つの問題を解きます
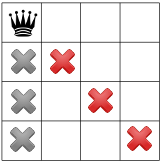
解法は、左上にクイーンを任意に配置することから始まります。 クリックします。これはある種の仮説で解決策がまったくないということが クイーンが左上に表示されます
この仮説を踏まえると、どのような制約を伝播できるでしょうか。制約の 1 つは、 1 つの列に 1 つのクイーン(下のグレーの X)しか存在せず、もう 1 つが 制約では、同じ対角線上に 2 つのクイーン(下の赤い X)を禁止します。
3 つ目の制約では、同じ行に対するクイーンを禁止します。
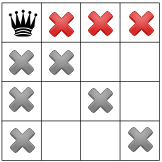
制約が伝播したら、別の仮説を検証して、 残りの正方形の 1 つに 2 番目のクイーンを表示します解法は 2 列目に使用可能な最初の正方形に配置します。
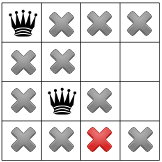
対角線の制約を伝播すると、制約が 使用可能な正方形を 3 列目か最終行に配置し、
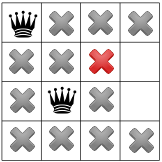
この段階では解決策が一切ないため、後戻りする必要があります。選択肢の一つとして 2 列目に利用可能なもう 1 つの正方形を選択します。 ただし、制約が伝播されると、クイーンは 4 番目のクイーンに有効なスポットが残っていないとします。
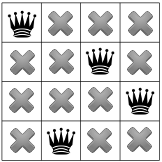
そのため、ソルバーは再びバックトラックを行う必要があり、 配置することにしましたクイーンたちの解決策は 隅の正方形が占有されることになります。
隅にクイーンはいないので、解法によって最初のクイーンが下に移動する。 2 番目のクイーンは 1 つのスポットしか残しません。
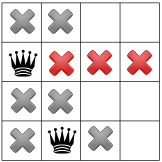
さらに伝播すると、3 人目のクイーンにはあと 1 つしか残っていないことがわかります。
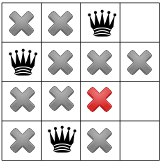
最後の 4 人目のクイーンは、
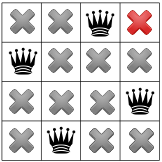
最初の解決策があります!見つけた後、ソルバーに指示を出して 終わりではありません。そうしないと、再度バックトラックが発生し、 最初のクイーンを最初の列の 3 行目に配置します。
CP-SAT を使用したソリューション
N クイーン問題は、制約プログラミングに適しています。この セクションでは、CP-SAT ソルバーを使用して 見つける必要があります。
ライブラリのインポート
次のコードは、必要なライブラリをインポートします。
Python
import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
モデルを宣言する
次のコードは CP-SAT モデルを宣言しています。
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
変数を作成する
解法は、問題の変数を queens という名前の配列として作成します。
Python
# There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
// There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
ここでは、queens[j] が列 j のクイーンの行番号であると仮定します。
つまり、queens[j] = i は、行 i、列 j にクイーンが存在することを意味します。
制約を作成する
以下は、問題の制約を作成するコードです。
Python
# All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2);
Java
// All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2);
C#
// All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2);
このコードは AddAllDifferent メソッドを使用します。このメソッドは、
異なる値にするためです。
これらの制約によって N クイーンの 3 つの条件がどのように保証されるかを見てみましょう。 (異なる行、列、対角線上のクイーン)。
同じ行に 2 人のクイーンは存在しない
ソルバーの AllDifferent メソッドを queens に適用すると、
queens[j] は j ごとに異なる。つまり、すべてのクイーンが
表示されます
同じ列に 2 つのクイーンがない
この制約は、queens の定義に暗黙的に含まれています。
queens の 2 つの要素に同じインデックスを設定できないため、2 つのクイーンを
表示されます
同じ対角線上に 2 つのクイーンはない
対角線の制約は、行と列の制約よりも少し複雑です。 まず、2 つのクイーンが同じ対角線上にある場合、次の条件のいずれかになります。 次の条件を満たしている必要があります。
- 2 つのクイーンのそれぞれの行番号と列番号は等しくなります。
つまり、
queens(j) + jは 2 つの異なるインデックスに同じ値を持ちます。j。 - 2 つのクイーンのそれぞれの行番号から列番号を引いた値は等しくなります。
この場合、
queens(j) - jは 2 つの異なるインデックスjに同じ値を持ちます。
これらの条件のいずれかは、クイーンが同じ昇順対角線上に位置していることを意味します( もう 1 つは同じ降順であることを表します。 対角線上。どの条件が昇順に対応し、どの条件が降順に対応するか 行と列の順序によって異なります。第 2 部の 前のセクションをご覧ください。順序は 可視化する方法を見ていきます。
したがって、対角線の制約は queens(j) + j の値がすべて
また、queens(j) - j の値は、すべて異なる必要があります。
異なる j。
AddAllDifferent メソッドを queens(j) + j に適用するには、N 個のインスタンスを
変数の 0 から N-1 までの j を、次のように配列 diag1 に変換します。
q1 = model.NewIntVar(0, 2 * board_size, 'diag1_%i' % i) diag1.append(q1) model.Add(q1 == queens[j] + j)
次に、AddAllDifferent を diag1 に適用します。
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1)
queens(j) - j の制約も同様に作成されます。
ソリューション プリンタを作成
N クイーン問題の全解を出力するには、 ソリューション プリンタと呼ばれます。コールバックは、 解き明かします次のコードは、 あります。
Python
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print()
C++
int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; }));
Java
static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; }
C#
public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; }
なお、解答作成装置は Python クラスとして記述する必要があります。これは、 基盤となる C++ ソルバーへの Python インターフェース。
解答は、解答プリンタに次の行によって印刷されます。
for v in self.__variables: print('%s = %i' % (v, self.Value(v)), end = ' ')
この例では、self.__variables は変数 queens で、各 v は
queens の 8 つのエントリの 1 つに対応します。これにより
x0 = queens(0) x1 = queens(1) ... x7 = queens(7) の形式になります。
xi は、行 i のクイーンの列番号です。
次のセクションでは、ソリューションの例を示します。
ソルバーを呼び出して結果を表示する
次のコードはソルバーを実行し、解答を表示します。
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer)
C++
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions;
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb);
C#
// Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb);
このプログラムは、8x8 ボード用の 92 種類のソリューションを見つけます。それでは、最初の問題です。
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Solutions found: 92異なるサイズのボードの場合は、
コマンドライン引数を指定します。たとえば、プログラムの名前が queens の場合、
python nqueens_sat.py 6 は 6x6 ボードの問題を解決します。
プログラム全体
こちらが N-queens プログラムのプログラム全体です。
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() def main(board_size: int) -> None: # Creates the solver. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Creates the variables. # There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)) # Solve the model. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer) # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" conflicts : {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" wall time : {solver.wall_time} s") print(f" solutions found: {solution_printer.solution_count}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void NQueensSat(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. CpModelBuilder cp_model; // There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2); int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; })); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions; // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { if (!absl::SimpleAtoi(argv[1], &board_size)) { LOG(INFO) << "Cannot parse '" << argv[1] << "', using the default value of 8."; board_size = 8; } } operations_research::sat::NQueensSat(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; /** OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. */ public final class NQueensSat { static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; } public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Create the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2); // Create a solver and solve the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" conflicts : " + solver.numConflicts()); System.out.println(" branches : " + solver.numBranches()); System.out.println(" wall time : " + solver.wallTime() + " s"); System.out.println(" solutions : " + cb.getSolutionCount()); } private NQueensSat() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class NQueensSat { public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; } static void Main() { // Constraint programming engine CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
元の CP ソルバーを使用した解
以降のセクションでは、N クイーンを 元の CP ソルバーです。 (ただし、新しい CP-SAT ソルバーの使用をおすすめします)。
ライブラリのインポート
次のコードは、必要なライブラリをインポートします。
Python
import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
C++
#include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
解法を宣言する
次のコードは、元の CP ソルバーを宣言しています。
Python
solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens")
C++
Solver solver("N-Queens");
Java
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
C#
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
変数を作成する
解法の IntVar メソッドは、問題の変数を配列として作成する
名前は「queens」です。
Python
# The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
どのような解でも、queens[j] = i は列 j と行にクイーンが存在することを意味します。
i。
制約を作成する
以下は、問題の制約を作成するコードです。
Python
# All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)]))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2));
Java
// All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2));
C#
// All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent());
これらの制約により、N クイーン問題( 異なる行、列、対角線上のクイーンなど)が使用されます。
同じ行に 2 人のクイーンは存在しない
ソルバーの AllDifferent メソッドを queens に適用すると、
queens[j] は j ごとに異なる。つまり、すべてのクイーンが
表示されます
同じ列に 2 つのクイーンがない
この制約は、queens の定義に暗黙的に含まれています。
queens の 2 つの要素に同じインデックスを設定できないため、2 つのクイーンを
表示されます
同じ対角線上に 2 つのクイーンはない
対角線の制約は、行と列の制約よりも少し複雑です。 まず、2 つのクイーンが同じ対角線上にある場合、次のいずれかに該当する必要があります。
- 対角線が降順(左から右へ)の場合は、行番号と
2 つのクイーンの列番号は等しくなります。したがって、
queens(i) + iには 2 つの異なるインデックスiに同じ値を設定しています。 - 対角線が昇順の場合は、それぞれの行番号から列番号を引いた値
等しくなります。この場合、
queens(i) - iは同じ値になります。 (2 つの異なるインデックスiに対して)
したがって、対角線の制約は queens(i) + i の値がすべて
同じく、queens(i) - i の値もすべて異なっている必要があります。
異なる i。
上記のコードでは、この制約を追加するために、
AllDifferent
メソッドを i ごとに queens[j] + j と queens[j] - j に渡します。
意思決定者を追加する
次のステップでは、意思決定者を作成して検索戦略を設定します。 解決します検索戦略は検索時間に大きな影響を与えます。 制約の伝播によって生じる変数値の数が減るため、 解明が必要なことです。この例については、このモジュールの 4 クイーンの例
次のコードは、ソルバーの
Phase
メソッドを呼び出します。
Python
db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE)
C++
DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
Java
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
C#
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
詳細はディシジョン ビルダーを参照
入力引数を Phase メソッドに渡します。
4 クイーンのサンプルにおける意思決定者の仕組み
では、意思決定者がどのように検索を指示するのかを
4 クイーンの例
指示どおり、解は配列の最初の変数である queens[0] で始まります
作成者: CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND。解法は、queens[0] に最小値を
値(この段階では 0)を返します。
ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE。これにより、最初のクイーンがページの左上に配置され、
表示されます。
次に、ソルバーは queens[1] を選択します。これは、今度は最初の未バインドの変数です。
queens。制約を伝播すると、行が 2 つになり、
クイーンを列 1: 行 2 または行 3 に配置します。ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE オプションは、
queens[1] = 2 を割り当てます。(代わりに IntValueStrategy を
ASSIGN_MAX_VALUE の場合は、ソルバーによって queens[1] = 3 が割り当てられます)。
残りの検索が同じルールに従っていることを確認できます。
ソルバーを呼び出して結果を表示する
次のコードはソルバーを実行し、解答を表示します。
Python
# Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch()
C++
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch();
Java
int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch();
C#
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch();
8x8 ボード用のプログラムで見つかった最初の解答は次のとおりです。
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Statistics
failures: 304
branches: 790
wall time: 5 ms
Solutions found: 92異なるサイズのボードの場合は、
コマンドライン引数を指定します。たとえば、python nqueens_cp.py 6 は問題を解決します。
6x6 のボードなら
プログラム全体
完全なプログラムを以下に示します。
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp def main(board_size): # Creates the solver. solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens") # Creates the variables. # The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)])) db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE) # Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch() # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" failures: {solver.Failures()}") print(f" branches: {solver.Branches()}") print(f" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms") print(f" Solutions found: {num_solutions}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h" namespace operations_research { void NQueensCp(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver("N-Queens"); std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2)); DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << " failures: " << solver.failures(); LOG(INFO) << " branches: " << solver.branches(); LOG(INFO) << " wall time: " << solver.wall_time() << " ms"; LOG(INFO) << " Solutions found: " << num_solutions; } } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { board_size = std::atoi(argv[1]); } operations_research::NQueensCp(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver; /** N-Queens Problem. */ public final class NQueensCp { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2)); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch(); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" failures: " + solver.failures()); System.out.println(" branches: " + solver.branches()); System.out.println(" wall time: " + solver.wallTime() + "ms"); System.out.println(" Solutions found: " + solutionCount); } private NQueensCp() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver; public class NQueensCp { public static void Main(String[] args) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent()); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" failures: {solver.Failures()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches: {solver.Branches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms"); Console.WriteLine($" Solutions found: {SolutionCount}"); } }
ソリューションの数
ソリューションの数は、取締役会の規模に応じてほぼ指数関数的に増加します。
| ボードサイズ | ソリューション | すべての解を見つけるまでの時間(ミリ秒) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | 40 | 3 |
| 8 | 92 | 9 |
| 9 | 352 | 35 |
| 10 | 724 | 95 |
| 11 | 2680 | 378 |
| 12 | 14200 | 2198 |
| 13 | 73712 | 11628 |
| 14 | 365596 | 62427 |
| 15 | 2279184 | 410701 |
対称性という手法では他の解の回転が 必要な計算量を削減するために使用できます。Google が あります。上記のソリューションは高速化を意図したものではなく、シンプルです。もちろん 1 つの解決策を 1 つだけ見つけることができれば 50 までのボードサイズで数ミリ秒未満です。
