উপাদান: ধারণা
সেভ করা পৃষ্ঠা গুছিয়ে রাখতে 'সংগ্রহ' ব্যবহার করুন
আপনার পছন্দ অনুযায়ী কন্টেন্ট সেভ করুন ও সঠিক বিভাগে রাখুন।
উপাদান: ধারণা / তথ্য
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | টেক্সচুয়াল তথ্য, যেমন ধারণার নাম এবং বর্ণনা। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 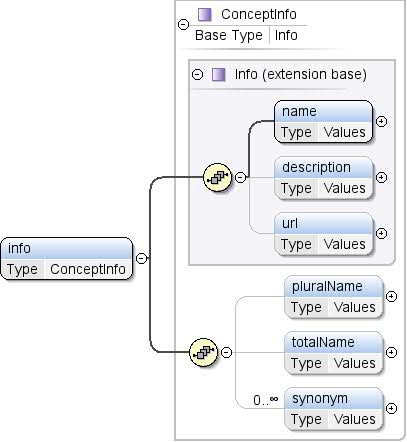 |
|---|
| টাইপ | ধারণার তথ্য |
|---|
| শ্রেণিবিন্যাস টাইপ করুন | |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | |
|---|
| মডেল | নাম , বর্ণনা{0,1} , url{0,1} , pluralName{0,1} , totalName{0,1} , সমার্থক* |
|---|
| শিশুরা | বর্ণনা , নাম , বহুবচন নাম , প্রতিশব্দ , মোট নাম , url৷ |
|---|
| দৃষ্টান্ত | <info>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</info> |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / বিষয়
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | একটি বিষয় যার সাথে ধারণাটি যুক্ত। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 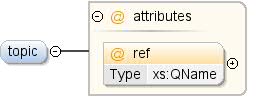 |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
| সর্বাধিক ঘটনা: | সীমাহীন |
|---|
|
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| রেফ | xs:QName | | | ঐচ্ছিক | এই ধারণাটি যে বিষয়ের সাথে যুক্ত তার অনন্য শনাক্তকারী। উল্লেখিত বিষয় একই ডেটাসেটে বা বাহ্যিকভাবে, অর্থাৎ, অন্য ডেটাসেটে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা যেতে পারে। একটি বাহ্যিক বিষয়ের একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_topic_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / প্রকার
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | ধারণার ডেটা প্রকার। একটি ধারণা একটি প্রকার ঘোষণা প্রদান করতে হবে বা অন্য ধারণা প্রসারিত করতে হবে। যে ক্ষেত্রে এটি একটি ধারণাকে প্রসারিত করছে, এটি একটি প্রকার ঘোষণাও প্রদান করতে পারে। বর্ধিত ধারণার ধরনটি অবশ্যই প্রসারিত ধারণার ধরণ থেকে কম সীমাবদ্ধ হতে হবে। "এর চেয়ে কম সীমাবদ্ধ" (LRT) হল একটি আংশিক ক্রম যা নিম্নরূপ সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়েছে: স্ট্রিং LRT float float LRT পূর্ণসংখ্যা স্ট্রিং LRT তারিখ স্ট্রিং LRT বুলিয়ান |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 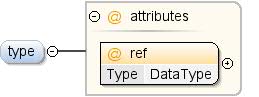 |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
|
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| রেফ | ডেটা টাইপ | | | প্রয়োজনীয় | |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / বৈশিষ্ট্য
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | ধারণার একটি বৈশিষ্ট্য। বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ধারণা সম্পর্কে অতিরিক্ত তথ্য উপস্থাপন করে (যেমন, জিডিপি একটি শতাংশ)। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 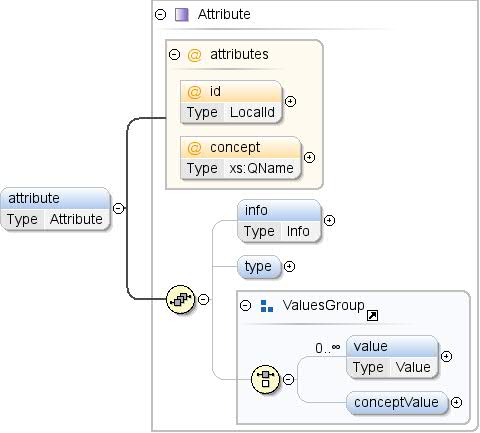 |
|---|
| টাইপ | বৈশিষ্ট্য |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
| সর্বাধিক ঘটনা: | সীমাহীন |
|---|
|
|---|
| মডেল | তথ্য{0,1} , টাইপ{0,1} , ( মান* | ধারণামূল্য{0,1} ) |
|---|
| শিশুরা | ধারণামূল্য , তথ্য , প্রকার , মান |
|---|
| দৃষ্টান্ত | <attribute concept="" id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type format="" ref="">{0,1}</type>
</attribute> |
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| ধারণা | xs:QName | | | ঐচ্ছিক | বৈশিষ্ট্যের মানগুলির সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ একটি ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স৷ যদি অ্যাট্রিবিউটটি একটি টাইপ নির্দিষ্ট করে, তাহলে টাইপটি অবশ্যই উল্লেখিত ধারণার ধরনের সাথে মিলবে। একটি বাহ্যিক ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_concept_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
| আইডি | স্থানীয় আইডি | | | ঐচ্ছিক | ধারণা বৈশিষ্ট্যের আইডি। এই শনাক্তকারীকে অবশ্যই ধারণার মধ্যে অনন্য হতে হবে (গুণাবলী এবং বৈশিষ্ট্য জুড়ে)। ধারণা বৈশিষ্ট্য নির্দিষ্ট করা থাকলে আইডিটি বাদ দেওয়া হতে পারে। সেক্ষেত্রে, একটি আইডি হল রেফারেন্সকৃত ধারণার স্থানীয় নামের মান দিয়ে তৈরি করা অন্তর্নিহিততা। উদাহরণস্বরূপ <attribute concept="unit:currency"/> হল <attribute id="currency" concept="unit:currency"/> এর সমতুল্য |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / সম্পত্তি
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | ধারণার একটি সম্পত্তি। বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি ধারণার উদাহরণ সম্পর্কে অতিরিক্ত তথ্য উপস্থাপন করে (যেমন, একটি ধারণা "শহর" এর একটি সম্পত্তি "দেশ" থাকতে পারে)। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 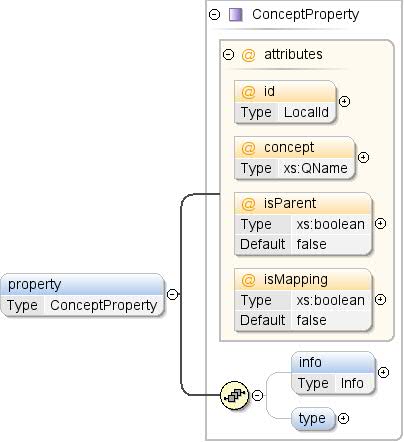 |
|---|
| টাইপ | কনসেপ্ট প্রপার্টি |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
| সর্বাধিক ঘটনা: | সীমাহীন |
|---|
|
|---|
| মডেল | তথ্য{0,1} , টাইপ{0,1} |
|---|
| শিশুরা | তথ্য , টাইপ |
|---|
| দৃষ্টান্ত | <property concept="" id="" isMapping="false" isParent="false">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type ref="">{0,1}</type>
</property> |
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| ধারণা | xs:QName | | | ঐচ্ছিক | সম্পত্তির মানগুলির সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ একটি ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স৷ যদি সম্পত্তি একটি প্রকার নির্দিষ্ট করে, তাহলে টাইপটি অবশ্যই উল্লেখিত ধারণার প্রকারের সাথে মিলবে। একটি বাহ্যিক ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_concept_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
| আইডি | স্থানীয় আইডি | | | ঐচ্ছিক | ধারণা সম্পত্তির আইডি। এই শনাক্তকারীকে অবশ্যই ধারণার মধ্যে অনন্য হতে হবে (গুণাবলী এবং বৈশিষ্ট্য জুড়ে)। ধারণা সম্পত্তি নির্দিষ্ট করা থাকলে আইডিটি বাদ দেওয়া যেতে পারে। সেক্ষেত্রে, রেফারেন্সকৃত ধারণার স্থানীয় নামের মান দিয়ে একটি আইডি অন্তর্নিহিতভাবে তৈরি করা হয়। উদাহরণস্বরূপ <property concept="geo:country"/> হল <property id="country" concept="geo:country"/> এর সমতুল্য |
|---|
| ম্যাপিং | xs: বুলিয়ান | | মিথ্যা | ঐচ্ছিক | যদি সত্য হয়, তাহলে এই সম্পত্তিটিকে অবশ্যই একটি ধারণার উল্লেখ করতে হবে এবং এই বৈশিষ্ট্যটি এই ধারণা এবং উল্লেখিত ধারণার মধ্যে একটি ম্যাপিং (1-থেকে-1) সম্পর্ককে নির্দেশ করে। উল্লেখিত ধারণার প্রতিটি উদাহরণ এই ধারণার সর্বাধিক একটি উদাহরণ দ্বারা উল্লেখ করা হয়। |
|---|
| পিতামাতা | xs: বুলিয়ান | | মিথ্যা | ঐচ্ছিক | যদি সত্য হয়, তাহলে এই সম্পত্তিটিকে অবশ্যই একটি ধারণার উল্লেখ করতে হবে, এবং এই সম্পত্তিটি এই ধারণা এবং উল্লেখিত ধারণার (যেমন, একটি দেশের মহাদেশ) মধ্যে একটি শ্রেণিবদ্ধ সম্পর্ককে নির্দেশ করে। |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / ডিফল্ট ভ্যালু
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | ধারণার জন্য একটি ডিফল্ট মান, যখন অ্যাপ্লিকেশনগুলিকে ধারণার সম্ভাব্য মানগুলির একটি বেছে নিতে হবে তখন ব্যবহার করা হবে৷ |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 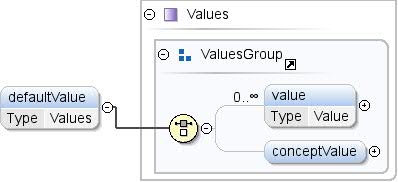 |
|---|
| টাইপ | মূল্যবোধ |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
|
|---|
| মডেল | মান* | ধারণার মান{0,1} |
|---|
| শিশুরা | ধারণামূল্য , মান |
|---|
| দৃষ্টান্ত | <defaultValue>
<value lang="">{0,unbounded}</value>
<conceptValue concept="">{0,1}</conceptValue>
</defaultValue> |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |
|---|
উপাদান: ধারণা / টেবিল
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | একটি টেবিলের একটি রেফারেন্স যেখানে ধারণার জন্য সম্ভাব্য সমস্ত মান এবং এর অ-স্থির বৈশিষ্ট্য রয়েছে। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 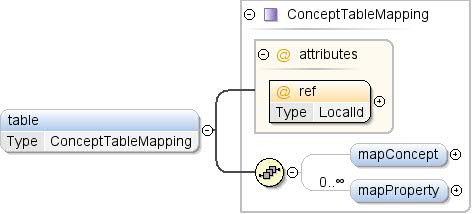 |
|---|
| টাইপ | ConceptTableMapping |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | বিষয়বস্তু: | জটিল |
|---|
| সামান্য ঘটনা: | 0 |
|---|
|
|---|
| মডেল | mapConcept{0,1} , mapProperty* |
|---|
| শিশুরা | mapConcept , mapProperty |
|---|
| দৃষ্টান্ত | <table ref="">
<mapConcept toColumn="">{0,1}</mapConcept>
<mapProperty lang="" ref="" toColumn="">{0,unbounded}</mapProperty>
</table> |
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| রেফ | স্থানীয় আইডি | | | প্রয়োজনীয় | সারণীর আইডি যেটিতে ধারণার ডেটা রয়েছে। |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |
|---|
জটিল প্রকার: ধারণা
| নামস্থান | http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
|---|
| টীকা | একটি ধারণা হল এক ধরনের ডেটার একটি সংজ্ঞা যা ডেটাসেটে প্রদর্শিত হয় (যেমন, "GDP" বা "কাউন্টি")। একটি ধারণা তার সমস্ত সম্ভাব্য মানগুলির একটি গণনার সাথে যুক্ত হতে পারে বা না। কিছু ডেটাসেটে সংজ্ঞায়িত একটি ধারণা অন্য ডেটাসেটে উল্লেখ করা যেতে পারে। |
|---|
| ডায়াগ্রাম | 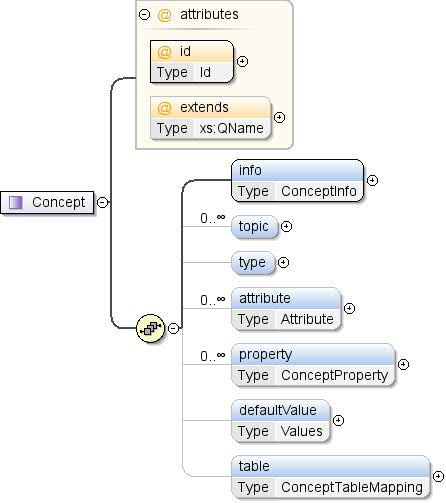 |
|---|
| দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত | |
|---|
| মডেল | তথ্য , বিষয়* , প্রকার{0,1} , বৈশিষ্ট্য* , সম্পত্তি* , ডিফল্ট মান{0,1} , টেবিল{0,1} |
|---|
| শিশুরা | বৈশিষ্ট্য , ডিফল্ট মান , তথ্য , সম্পত্তি , টেবিল , বিষয় , প্রকার |
|---|
| গুণাবলী | | QName | টাইপ | স্থির | ডিফল্ট | ব্যবহার করুন | টীকা |
|---|
| প্রসারিত | xs:QName | | | ঐচ্ছিক | একটি ধারণার অনন্য শনাক্তকারী যা এই ধারণাটি প্রসারিত করে। উল্লেখিত ধারণা একই ডেটাসেটে বা বাহ্যিকভাবে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা যেতে পারে, অর্থাৎ, অন্য ডেটাসেটে। একটি বাহ্যিক ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_concept_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
| আইডি | আইডি | | | প্রয়োজনীয় | ধারণাটির অনন্য শনাক্তকারী, যা ডেটাসেটের মধ্যে বিশ্বব্যাপী অনন্য হতে হবে। |
|---|
|
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:complexType name="Concept">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A concept is a definition of a type of data that appears in the
dataset (e.g., "GDP" or "County"). A concept may be associated with
an enumeration of all its possible values or not. A concept defined in
some dataset may be referenced in other datasets.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType> |
|---|
বৈশিষ্ট্য: ধারণা / বিষয় / @ রেফ
| নামস্থান | কোনো নামস্থান নেই |
|---|
| টীকা | এই ধারণাটি যে বিষয়ের সাথে যুক্ত তার অনন্য শনাক্তকারী। উল্লেখিত বিষয় একই ডেটাসেটে বা বাহ্যিকভাবে, অর্থাৎ, অন্য ডেটাসেটে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা যেতে পারে। একটি বাহ্যিক বিষয়ের একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_topic_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
| টাইপ | xs:QName |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | |
|---|
| দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত | |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute> |
|---|
| নামস্থান | কোনো নামস্থান নেই |
|---|
| টাইপ | ডেটা টাইপ |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | ব্যবহার করুন: | প্রয়োজনীয় |
|---|
|
|---|
| দিক | | গণনা | স্ট্রিং | |
|---|
| গণনা | ভাসা | |
|---|
| গণনা | পূর্ণসংখ্যা | |
|---|
| গণনা | বুলিয়ান | |
|---|
| গণনা | তারিখ | |
|---|
| গণনা | ধারণা | |
|---|
|
|---|
| দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত | |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/> |
|---|
বৈশিষ্ট্য: ধারণা / @id
| নামস্থান | কোনো নামস্থান নেই |
|---|
| টীকা | ধারণাটির অনন্য শনাক্তকারী, যা ডেটাসেটের মধ্যে বিশ্বব্যাপী অনন্য হতে হবে। |
|---|
| টাইপ | আইডি |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | | ব্যবহার করুন: | প্রয়োজনীয় |
|---|
|
|---|
| দিক | |
|---|
| দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত | |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute> |
|---|
বৈশিষ্ট্য: ধারণা / @extends
| নামস্থান | কোনো নামস্থান নেই |
|---|
| টীকা | একটি ধারণার অনন্য শনাক্তকারী যা এই ধারণাটি প্রসারিত করে। উল্লেখিত ধারণা একই ডেটাসেটে বা বাহ্যিকভাবে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা যেতে পারে, অর্থাৎ, অন্য ডেটাসেটে। একটি বাহ্যিক ধারণার একটি রেফারেন্স অবশ্যই "উপসর্গ:other_concept_id" ফর্মের হতে হবে, যেখানে "উপসর্গ" বহিরাগত ডেটাসেটের নামস্থানের জন্য ব্যবহৃত উপসর্গ (এক্সএমএল নেমস্পেস দেখুন)। |
|---|
| টাইপ | xs:QName |
|---|
| বৈশিষ্ট্য | |
|---|
| দ্বারা ব্যবহৃত | |
|---|
| উৎস | <xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute> |
|---|
অক্সিজেন এক্সএমএল এডিটর ব্যবহার করে তৈরি করা হয়েছে।
অন্য কিছু উল্লেখ না করা থাকলে, এই পৃষ্ঠার কন্টেন্ট Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License-এর অধীনে এবং কোডের নমুনাগুলি Apache 2.0 License-এর অধীনে লাইসেন্স প্রাপ্ত। আরও জানতে, Google Developers সাইট নীতি দেখুন। Java হল Oracle এবং/অথবা তার অ্যাফিলিয়েট সংস্থার রেজিস্টার্ড ট্রেডমার্ক।
2025-07-25 UTC-তে শেষবার আপডেট করা হয়েছে।
[[["সহজে বোঝা যায়","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["আমার সমস্যার সমাধান হয়েছে","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["অন্যান্য","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["এতে আমার প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য নেই","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["খুব জটিল / অনেক ধাপ","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["পুরনো","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["অনুবাদ সংক্রান্ত সমস্যা","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["নমুনা / কোড সংক্রান্ত সমস্যা","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["অন্যান্য","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["2025-07-25 UTC-তে শেষবার আপডেট করা হয়েছে।"],[],["Concepts, within a dataset (namespace: `http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010`), define data types and are globally unique. Concepts can extend others, using `prefix:other_concept_id` for external references. They include `info` (textual details), `topic` (associated topics via `ref`), `type` (data type, `ref`), `attribute` (additional information), `property` (instance information), `defaultValue`, and `table` (data source, `ref`). Key concept attributes are `id` (unique), and `extends` (referencing another concept). External references are in `prefix:identifier` format. A concept must have a `type` or `extends`.\n"]]








