Un problème de planification courant est l'atelier d'offres d'emploi, dans lequel plusieurs emplois sont traitées sur plusieurs machines.
Chaque tâche consiste en une séquence de tâches, qui doivent être effectuées dans un
et chaque tâche doit être traitée
sur une machine spécifique.
Par exemple, il peut s'agir de la fabrication d'un seul article de consommation :
une automobile.
Le problème est de planifier les tâches sur les machines
length de la planification : temps nécessaire pour exécuter toutes les tâches.
Il existe plusieurs contraintes pour le problème des magasins d'emploi:
- Aucune tâche d'un job ne peut être lancée tant que la tâche précédente de ce job n'est pas terminé.
- Une machine ne peut travailler que sur une tâche à la fois.
- Une tâche, une fois lancée, doit s'exécuter jusqu'à la fin.
Exemple de problème
Vous trouverez ci-dessous un exemple simple de problème lié à un magasin d'emploi, dans lequel chaque tâche est étiquetée par une paire de nombres (m, p), où "m" représente le numéro de la machine doit être traitée, et "p" correspond au temps de traitement de la tâche, le temps nécessaire. (La numérotation des tâches et des machines commence à 0.)
- job 0 = [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)]
- job 1 = [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)]
- job 2 = [(1, 4), (2, 3)]
Dans cet exemple, la tâche 0 comporte trois tâches. La première, (0, 3), doit être traitée sur la machine 0 en 3 unités de temps. La seconde, (1, 2), doit être traitée machine 1 sur 2 unités de temps, et ainsi de suite. Au total, il y a huit tâches.
Une solution au problème
Une solution au problème de l'atelier d'emploi consiste à attribuer une heure de début à chaque
qui répond aux contraintes indiquées ci-dessus.
Le diagramme ci-dessous présente une solution possible au problème:
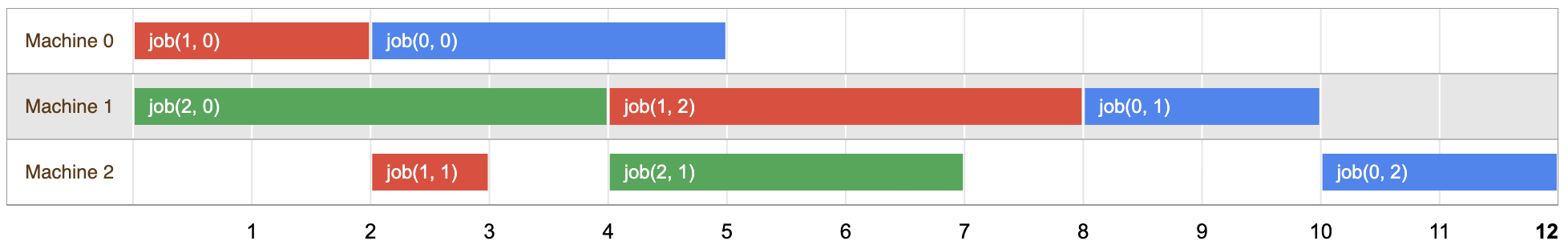
Vous pouvez vérifier que les tâches de chaque job sont planifiées à des heures qui ne se chevauchent pas. dans l'ordre indiqué par le problème.
La longueur de cette solution est de 12, ce qui est la première fois que les trois jobs sont terminés. Toutefois, comme vous le verrez ci-dessous, ce n'est pas la solution optimale pour le problème.
Variables et contraintes pour le problème
Cette section décrit comment configurer les variables et les contraintes pour
problème.
Tout d'abord, supposons que task(i, j) désigne la jième tâche de la séquence correspondant à la tâche i. Pour
exemple, task(0, 2) désigne la deuxième tâche de la tâche 0, qui correspond à
la paire (1, 2) dans la description du problème.
Définissez ensuite ti, j comme heure de début de task(i, j). La
ti, j sont les variables du problème de l'atelier d'offres d'emploi. Trouver un
la solution implique de déterminer pour ces variables des valeurs qui répondent aux
exigence du problème.
Il existe deux types de contraintes pour le problème de l’atelier d’emploi:
- Contraintes de priorité : elles découlent de la condition selon laquelle, pour toute
deux tâches consécutives dans le même job, la première doit être terminée avant
peut être lancée. Par exemple,
task(0, 2)ettask(0, 3)sont tâches consécutives pour la tâche 0. Comme le temps de traitement pourtask(0, 2)est de 2, l'heure de début de La valeur detask(0, 3)doit être postérieure d'au moins deux unités de temps à l'heure de début de la tâche 2. (Peut-être que la tâche 2 consiste à peindre une porte et qu'il faut deux heures pour peindre dry.) Par conséquent, vous obtenez la contrainte suivante: <ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">- </ph>
t0, 2 + 2 <=t0, 3
- Aucune contrainte de chevauchement : ces contraintes découlent de la restriction qu'un
machine ne peut pas travailler sur
deux tâches en même temps.
Par exemple, les tâches task(0, 2) et task(2, 1) sont toutes deux traitées sur la machine 1.
Puisque leurs temps de traitement sont respectivement de 2 et 4, l'une des valeurs suivantes
doivent contenir:
<ph type="x-smartling-placeholder">
- </ph>
t0, 2 + 2 <=t2, 1 (sitask(0, 2)est programmé) avant letask(2, 1)) out2, 1 + 4 <=t0, 2 (sitask(2, 1)est programmé) avant letask(0, 2)).
Objectif du problème
L'objectif du problème de l'atelier d'offres d'emploi est de minimiser la makespan: la durée comprise entre l'heure de début la plus proche et l'heure de fin la plus proche.
Une solution de programme
Les sections suivantes décrivent les principaux éléments d'un programme qui résout le de l'atelier d'emploi.
Importer les bibliothèques
Le code suivant importe la bibliothèque requise.
Python
import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
Java
import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream;
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
Définir les données
Ensuite, le programme définit les données du problème.
Python
jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job)
C++
using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } }
Java
class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
C#
var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } }
Déclarer le modèle
Le code suivant déclare le modèle pour le problème.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
Définir les variables
Le code suivant définit les variables du problème.
Python
# Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var)
C++
struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } }
Java
class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } }
C#
Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } }
Pour chaque tâche et tâche, le programme utilise l'API
NewIntVar/new_int_var/newIntVar pour créer les variables:
start_var: heure de début de la tâche.end_var: heure de fin de la tâche.
La limite supérieure pour start_var et end_var est horizon, ce qui correspond à la somme des
de temps de traitement pour toutes les tâches.
horizon est suffisamment volumineux pour effectuer toutes les tâches pour la raison suivante:
si vous planifiez les tâches à des intervalles de temps qui ne se chevauchent pas (une
solution), la durée totale de la planification est exactement de horizon. Ainsi,
la durée de la solution optimale ne peut pas être supérieure à horizon.
Ensuite, le programme utilise le NewIntervalVar/new_interval_var/newIntervalVar
pour créer une variable d'intervalle, dont la valeur est une heure variable
pour la tâche. Les entrées de cette méthode sont les suivantes:
- Heure de début de la tâche.
- Durée de l'intervalle de temps de la tâche.
- Heure de fin de la tâche.
- Nom de la variable d'intervalle.
Quelle que soit la solution, end_var moins start_var doit être égal à duration.
Définir les contraintes
Le code suivant définit les contraintes du problème.
Python
# Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end )
C++
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } }
Java
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } }
C#
// Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } }
Le programme utilise la méthode AddNoOverlap/add_no_overlap/addNoOverlap du modèle
pour créer des contraintes d'absence de chevauchement, ce qui empêche les tâches
la même machine de
chevauchement dans le temps.
Ensuite, le programme ajoute les contraintes de priorité qui empêchent des tâches consécutives pour un même emploi de se chevaucher dans le temps. Pour chaque tâche et chaque tâche de la tâche, une contrainte linéaire est ajoutée pour spécifier que la valeur l'heure d'exécution d'une tâche avant l'heure de début de la tâche suivante du job.
Définir l’objectif
Le code suivant définit l'objectif du problème.
Python
# Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var)
C++
// Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var);
Java
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar);
C#
// Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar);
Ce code crée une variable d'objectif et la contraint à correspondre au maximum à la fin de tous les jobs.
Appeler le résolveur
Le code suivant appelle le résolveur.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model)
C++
const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build());
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model);
C#
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}");
Afficher les résultats
Le code suivant affiche les résultats, y compris la planification et la tâche optimales à intervalles réguliers.
Python
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.")
C++
if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; }
Java
if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); }
C#
if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); }
La programmation optimale est indiquée ci-dessous:
Optimal Schedule Length: 11
Machine 0: job_0_0 job_1_0
[0,3] [3,5]
Machine 1: job_2_0 job_0_1 job_1_2
[0,4] [4,6] [7,11]
Machine 2: job_1_1 job_0_2 job_2_1
[5,6] [6,8] [8,11]

Les lecteurs à l'œil de lynx examinant la machine 1 pourraient se demander pourquoi le job_1_2 était programmé pour l'heure 7 au lieu de l'heure 6. Les deux sont des solutions valides, mais n’oubliez pas: l’objectif est de minimiser le makespan. Déplacer la tâche_1_2 précédemment ne réduit pas le délai de création , les deux solutions sont donc égales du point de vue du résolveur.
Intégralité du programme
Enfin, voici l'ensemble du programme pour le problème des magasins d'emploi.
Python
"""Minimal jobshop example.""" import collections from ortools.sat.python import cp_model def main() -> None: """Minimal jobshop problem.""" # Data. jobs_data = [ # task = (machine_id, processing_time). [(0, 3), (1, 2), (2, 2)], # Job0 [(0, 2), (2, 1), (1, 4)], # Job1 [(1, 4), (2, 3)], # Job2 ] machines_count = 1 + max(task[0] for job in jobs_data for task in job) all_machines = range(machines_count) # Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. horizon = sum(task[1] for job in jobs_data for task in job) # Create the model. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Named tuple to store information about created variables. task_type = collections.namedtuple("task_type", "start end interval") # Named tuple to manipulate solution information. assigned_task_type = collections.namedtuple( "assigned_task_type", "start job index duration" ) # Creates job intervals and add to the corresponding machine lists. all_tasks = {} machine_to_intervals = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine, duration = task suffix = f"_{job_id}_{task_id}" start_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "start" + suffix) end_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "end" + suffix) interval_var = model.new_interval_var( start_var, duration, end_var, "interval" + suffix ) all_tasks[job_id, task_id] = task_type( start=start_var, end=end_var, interval=interval_var ) machine_to_intervals[machine].append(interval_var) # Create and add disjunctive constraints. for machine in all_machines: model.add_no_overlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]) # Precedences inside a job. for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id in range(len(job) - 1): model.add( all_tasks[job_id, task_id + 1].start >= all_tasks[job_id, task_id].end ) # Makespan objective. obj_var = model.new_int_var(0, horizon, "makespan") model.add_max_equality( obj_var, [all_tasks[job_id, len(job) - 1].end for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data)], ) model.minimize(obj_var) # Creates the solver and solve. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() status = solver.solve(model) if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL or status == cp_model.FEASIBLE: print("Solution:") # Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. assigned_jobs = collections.defaultdict(list) for job_id, job in enumerate(jobs_data): for task_id, task in enumerate(job): machine = task[0] assigned_jobs[machine].append( assigned_task_type( start=solver.value(all_tasks[job_id, task_id].start), job=job_id, index=task_id, duration=task[1], ) ) # Create per machine output lines. output = "" for machine in all_machines: # Sort by starting time. assigned_jobs[machine].sort() sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + str(machine) + ": " sol_line = " " for assigned_task in assigned_jobs[machine]: name = f"job_{assigned_task.job}_task_{assigned_task.index}" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += f"{name:15}" start = assigned_task.start duration = assigned_task.duration sol_tmp = f"[{start},{start + duration}]" # add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += f"{sol_tmp:15}" sol_line += "\n" sol_line_tasks += "\n" output += sol_line_tasks output += sol_line # Finally print the solution found. print(f"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.objective_value}") print(output) else: print("No solution found.") # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" - conflicts: {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" - branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" - wall time: {solver.wall_time}s") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
C++
// Nurse scheduling problem with shift requests. #include <stdlib.h> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdint> #include <map> #include <numeric> #include <string> #include <tuple> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/str_format.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void MinimalJobshopSat() { using Task = std::tuple<int64_t, int64_t>; // (machine_id, processing_time) using Job = std::vector<Task>; std::vector<Job> jobs_data = { {{0, 3}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}}, // Job_0: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{0, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}}, // Job_1: Task_0 Task_1 Task_2 {{1, 4}, {2, 3}}, // Job_2: Task_0 Task_1 }; int64_t num_machines = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [machine, _] : job) { num_machines = std::max(num_machines, 1 + machine); } } std::vector<int> all_machines(num_machines); std::iota(all_machines.begin(), all_machines.end(), 0); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int64_t horizon = 0; for (const auto& job : jobs_data) { for (const auto& [_, time] : job) { horizon += time; } } // Creates the model. CpModelBuilder cp_model; struct TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; }; using TaskID = std::tuple<int, int>; // (job_id, task_id) std::map<TaskID, TaskType> all_tasks; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<IntervalVar>> machine_to_intervals; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; std::string suffix = absl::StrFormat("_%d_%d", job_id, task_id); IntVar start = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("start") + suffix); IntVar end = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}) .WithName(std::string("end") + suffix); IntervalVar interval = cp_model.NewIntervalVar(start, duration, end) .WithName(std::string("interval") + suffix); TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); all_tasks.emplace(key, TaskType{/*.start=*/start, /*.end=*/end, /*.interval=*/interval}); machine_to_intervals[machine].push_back(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (const auto machine : all_machines) { cp_model.AddNoOverlap(machine_to_intervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size() - 1; ++task_id) { TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); TaskID next_key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id + 1); cp_model.AddGreaterOrEqual(all_tasks[next_key].start, all_tasks[key].end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar obj_var = cp_model.NewIntVar({0, horizon}).WithName("makespan"); std::vector<IntVar> ends; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, job.size() - 1); ends.push_back(all_tasks[key].end); } cp_model.AddMaxEquality(obj_var, ends); cp_model.Minimize(obj_var); const CpSolverResponse response = Solve(cp_model.Build()); if (response.status() == CpSolverStatus::OPTIMAL || response.status() == CpSolverStatus::FEASIBLE) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; // create one list of assigned tasks per machine. struct AssignedTaskType { int job_id; int task_id; int64_t start; int64_t duration; bool operator<(const AssignedTaskType& rhs) const { return std::tie(this->start, this->duration) < std::tie(rhs.start, rhs.duration); } }; std::map<int64_t, std::vector<AssignedTaskType>> assigned_jobs; for (int job_id = 0; job_id < jobs_data.size(); ++job_id) { const auto& job = jobs_data[job_id]; for (int task_id = 0; task_id < job.size(); ++task_id) { const auto [machine, duration] = job[task_id]; TaskID key = std::make_tuple(job_id, task_id); int64_t start = SolutionIntegerValue(response, all_tasks[key].start); assigned_jobs[machine].push_back( AssignedTaskType{/*.job_id=*/job_id, /*.task_id=*/task_id, /*.start=*/start, /*.duration=*/duration}); } } // Create per machine output lines. std::string output = ""; for (const auto machine : all_machines) { // Sort by starting time. std::sort(assigned_jobs[machine].begin(), assigned_jobs[machine].end()); std::string sol_line_tasks = "Machine " + std::to_string(machine) + ": "; std::string sol_line = " "; for (const auto& assigned_task : assigned_jobs[machine]) { std::string name = absl::StrFormat( "job_%d_task_%d", assigned_task.job_id, assigned_task.task_id); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line_tasks += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", name); int64_t start = assigned_task.start; int64_t duration = assigned_task.duration; std::string sol_tmp = absl::StrFormat("[%i,%i]", start, start + duration); // Add spaces to output to align columns. sol_line += absl::StrFormat("%-15s", sol_tmp); } output += sol_line_tasks + "\n"; output += sol_line + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. LOG(INFO) << "Optimal Schedule Length: " << response.objective_value(); LOG(INFO) << "\n" << output; } else { LOG(INFO) << "No solution found."; } // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main() { operations_research::sat::MinimalJobshopSat(); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import static java.lang.Math.max; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverStatus; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntervalVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.IntStream; /** Minimal Jobshop problem. */ public class MinimalJobshopSat { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); class Task { int machine; int duration; Task(int machine, int duration) { this.machine = machine; this.duration = duration; } } final List<List<Task>> allJobs = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 3), new Task(1, 2), new Task(2, 2)), // Job0 Arrays.asList(new Task(0, 2), new Task(2, 1), new Task(1, 4)), // Job1 Arrays.asList(new Task(1, 4), new Task(2, 3)) // Job2 ); int numMachines = 1; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { numMachines = max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } final int[] allMachines = IntStream.range(0, numMachines).toArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; for (List<Task> job : allJobs) { for (Task task : job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); class TaskType { IntVar start; IntVar end; IntervalVar interval; } Map<List<Integer>, TaskType> allTasks = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); String suffix = "_" + jobID + "_" + taskID; TaskType taskType = new TaskType(); taskType.start = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); taskType.end = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); taskType.interval = model.newIntervalVar( taskType.start, LinearExpr.constant(task.duration), taskType.end, "interval" + suffix); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); allTasks.put(key, taskType); machineToIntervals.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); machineToIntervals.get(task.machine).add(taskType.interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. for (int machine : allMachines) { List<IntervalVar> list = machineToIntervals.get(machine); model.addNoOverlap(list); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size() - 1; ++taskID) { List<Integer> prevKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); List<Integer> nextKey = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID + 1); model.addGreaterOrEqual(allTasks.get(nextKey).start, allTasks.get(prevKey).end); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.newIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new ArrayList<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, job.size() - 1); ends.add(allTasks.get(key).end); } model.addMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.minimize(objVar); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.solve(model); if (status == CpSolverStatus.OPTIMAL || status == CpSolverStatus.FEASIBLE) { class AssignedTask { int jobID; int taskID; int start; int duration; // Ctor AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } } class SortTasks implements Comparator<AssignedTask> { @Override public int compare(AssignedTask a, AssignedTask b) { if (a.start != b.start) { return a.start - b.start; } else { return a.duration - b.duration; } } } System.out.println("Solution:"); // Create one list of assigned tasks per machine. Map<Integer, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new HashMap<>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.size(); ++jobID) { List<Task> job = allJobs.get(jobID); for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.size(); ++taskID) { Task task = job.get(taskID); List<Integer> key = Arrays.asList(jobID, taskID); AssignedTask assignedTask = new AssignedTask( jobID, taskID, (int) solver.value(allTasks.get(key).start), task.duration); assignedJobs.computeIfAbsent(task.machine, (Integer k) -> new ArrayList<>()); assignedJobs.get(task.machine).add(assignedTask); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; for (int machine : allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. Collections.sort(assignedJobs.get(machine), new SortTasks()); String solLineTasks = "Machine " + machine + ": "; String solLine = " "; for (AssignedTask assignedTask : assignedJobs.get(machine)) { String name = "job_" + assignedTask.jobID + "_task_" + assignedTask.taskID; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += String.format("%-15s", name); String solTmp = "[" + assignedTask.start + "," + (assignedTask.start + assignedTask.duration) + "]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += String.format("%-15s", solTmp); } output += solLineTasks + "%n"; output += solLine + "%n"; } System.out.printf("Optimal Schedule Length: %f%n", solver.objectiveValue()); System.out.printf(output); } else { System.out.println("No solution found."); } // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.printf(" conflicts: %d%n", solver.numConflicts()); System.out.printf(" branches : %d%n", solver.numBranches()); System.out.printf(" wall time: %f s%n", solver.wallTime()); } private MinimalJobshopSat() {} }
C#
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class ScheduleRequestsSat { private class AssignedTask : IComparable { public int jobID; public int taskID; public int start; public int duration; public AssignedTask(int jobID, int taskID, int start, int duration) { this.jobID = jobID; this.taskID = taskID; this.start = start; this.duration = duration; } public int CompareTo(object obj) { if (obj == null) return 1; AssignedTask otherTask = obj as AssignedTask; if (otherTask != null) { if (this.start != otherTask.start) return this.start.CompareTo(otherTask.start); else return this.duration.CompareTo(otherTask.duration); } else throw new ArgumentException("Object is not a Temperature"); } } public static void Main(String[] args) { var allJobs = new[] { new[] { // job0 new { machine = 0, duration = 3 }, // task0 new { machine = 1, duration = 2 }, // task1 new { machine = 2, duration = 2 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job1 new { machine = 0, duration = 2 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 1 }, // task1 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task2 } .ToList(), new[] { // job2 new { machine = 1, duration = 4 }, // task0 new { machine = 2, duration = 3 }, // task1 } .ToList(), } .ToList(); int numMachines = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { numMachines = Math.Max(numMachines, 1 + task.machine); } } int[] allMachines = Enumerable.Range(0, numMachines).ToArray(); // Computes horizon dynamically as the sum of all durations. int horizon = 0; foreach (var job in allJobs) { foreach (var task in job) { horizon += task.duration; } } // Creates the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>> allTasks = new Dictionary<Tuple<int, int>, Tuple<IntVar, IntVar, IntervalVar>>(); // (start, end, duration) Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>> machineToIntervals = new Dictionary<int, List<IntervalVar>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; String suffix = $"_{jobID}_{taskID}"; IntVar start = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "start" + suffix); IntVar end = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "end" + suffix); IntervalVar interval = model.NewIntervalVar(start, task.duration, end, "interval" + suffix); var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); allTasks[key] = Tuple.Create(start, end, interval); if (!machineToIntervals.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { machineToIntervals.Add(task.machine, new List<IntervalVar>()); } machineToIntervals[task.machine].Add(interval); } } // Create and add disjunctive constraints. foreach (int machine in allMachines) { model.AddNoOverlap(machineToIntervals[machine]); } // Precedences inside a job. for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count() - 1; ++taskID) { var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); var nextKey = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID + 1); model.Add(allTasks[nextKey].Item1 >= allTasks[key].Item2); } } // Makespan objective. IntVar objVar = model.NewIntVar(0, horizon, "makespan"); List<IntVar> ends = new List<IntVar>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, job.Count() - 1); ends.Add(allTasks[key].Item2); } model.AddMaxEquality(objVar, ends); model.Minimize(objVar); // Solve CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); CpSolverStatus status = solver.Solve(model); Console.WriteLine($"Solve status: {status}"); if (status == CpSolverStatus.Optimal || status == CpSolverStatus.Feasible) { Console.WriteLine("Solution:"); Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>> assignedJobs = new Dictionary<int, List<AssignedTask>>(); for (int jobID = 0; jobID < allJobs.Count(); ++jobID) { var job = allJobs[jobID]; for (int taskID = 0; taskID < job.Count(); ++taskID) { var task = job[taskID]; var key = Tuple.Create(jobID, taskID); int start = (int)solver.Value(allTasks[key].Item1); if (!assignedJobs.ContainsKey(task.machine)) { assignedJobs.Add(task.machine, new List<AssignedTask>()); } assignedJobs[task.machine].Add(new AssignedTask(jobID, taskID, start, task.duration)); } } // Create per machine output lines. String output = ""; foreach (int machine in allMachines) { // Sort by starting time. assignedJobs[machine].Sort(); String solLineTasks = $"Machine {machine}: "; String solLine = " "; foreach (var assignedTask in assignedJobs[machine]) { String name = $"job_{assignedTask.jobID}_task_{assignedTask.taskID}"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLineTasks += $"{name,-15}"; String solTmp = $"[{assignedTask.start},{assignedTask.start+assignedTask.duration}]"; // Add spaces to output to align columns. solLine += $"{solTmp,-15}"; } output += solLineTasks + "\n"; output += solLine + "\n"; } // Finally print the solution found. Console.WriteLine($"Optimal Schedule Length: {solver.ObjectiveValue}"); Console.WriteLine($"\n{output}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("No solution found."); } Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts: {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()}s"); } }
