Bagian ini menampilkan contoh yang menunjukkan cara menyelesaikan Masalah Staf Penjualan Perjalanan (TSP) untuk lokasi yang ditampilkan pada peta di bawah.
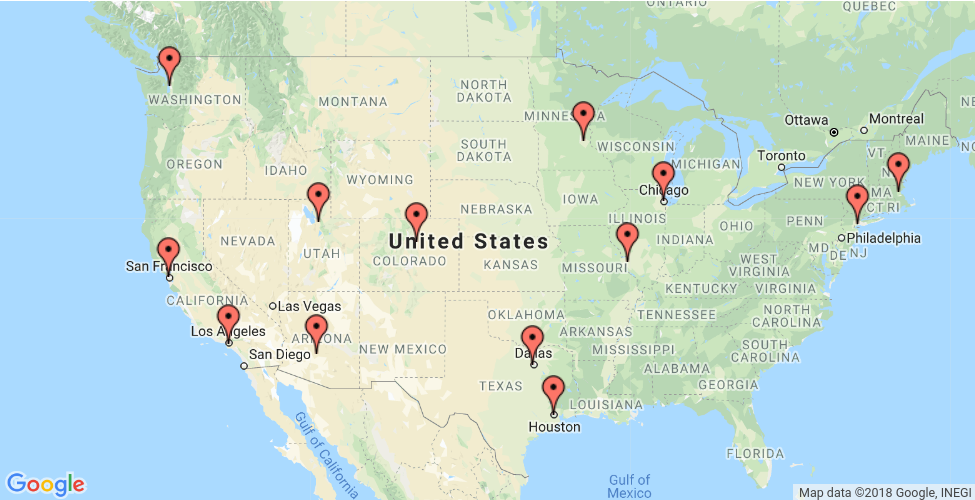
Bagian berikut menampilkan program dalam Python, C++, Java, dan C# yang menyelesaikan TSP menggunakan OR-Tools
Membuat data
Kode di bawah membuat data untuk masalah.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
Matriks jarak adalah array yang entri i dan j-nya adalah jarak dari lokasi i ke lokasi j dalam mil, dengan indeks array sesuai dengan lokasi dalam urutan berikut:
0. New York - 1. Los Angeles - 2. Chicago - 3. Minneapolis - 4. Denver - 5. Dallas
- 6. Seattle - 7. Boston - 8. San Francisco - 9. St. Louis - 10. Houston - 11. Phoenix - 12. Salt Lake City
Data tersebut juga mencakup:
- Jumlah kendaraan yang bermasalah, yaitu 1 karena ini adalah TSP. (Untuk masalah pemilihan rute kendaraan (VRP), jumlah kendaraan dapat lebih besar dari 1.)
- Depot: lokasi awal dan akhir untuk rute. Dalam hal ini, depotnya adalah 0, yang sesuai dengan New York.
Cara lain untuk membuat matriks jarak
Dalam contoh ini, matriks jarak didefinisikan secara eksplisit dalam program. Anda juga dapat menggunakan fungsi untuk menghitung jarak antarlokasi: misalnya, rumus Euclidean untuk jarak antara titik di bidang. Namun, masih lebih efisien untuk menghitung terlebih dahulu semua jarak antara lokasi dan menyimpannya dalam matriks, daripada menghitungnya pada saat runtime. Lihat Contoh: pengeboran papan sirkuit untuk mengetahui contoh yang membuat matriks jarak dengan cara ini.
Alternatif lain adalah menggunakan Google Maps Distance Matrix API untuk membuat matriks jarak (atau waktu perjalanan) secara dinamis untuk masalah pemilihan rute.
Membuat model perutean
Kode berikut di bagian utama program membuat pengelola indeks (manager) dan model pemilihan rute (routing). Metode manager.IndexToNode mengonversi indeks internal pemecah soal (yang dapat Anda abaikan dengan aman) menjadi angka untuk lokasi. Nomor lokasi sesuai dengan indeks untuk matriks jarak.
Python
data = create_data_model()
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
C++
DataModel data;
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
RoutingModel routing(manager);
Java
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
C#
DataModel data = new DataModel();
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
Input untuk RoutingIndexManager adalah:
- Jumlah baris matriks jarak, yang merupakan jumlah lokasi (termasuk depot).
- Jumlah kendaraan yang bermasalah.
- Node yang sesuai dengan depot.
Membuat callback jarak
Untuk menggunakan pemecah masalah perutean, Anda perlu membuat callback jarak (atau transit): fungsi yang mengambil pasangan lokasi apa pun dan menampilkan jarak di antara keduanya. Cara termudah untuk melakukannya adalah menggunakan matriks jarak.
Fungsi berikut membuat callback dan mendaftarkannya ke pemecah masalah sebagai
transit_callback_index.
Python
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
C++
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
Java
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
C#
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
The callback accepts two indices, from_index and to_index, and returns the
corresponding entry of the distance matrix.
Set the cost of travel
The arc cost evaluator tells the solver how to calculate the cost of travel between any two locations — in other words, the cost of the edge (or arc) joining them in the graph for the problem. The following code sets the arc cost evaluator.
Python
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
Dalam contoh ini, evaluator biaya busur adalah transit_callback_index, yang merupakan referensi internal pemecah masalah untuk callback jarak. Artinya, biaya perjalanan antara dua lokasi hanya berjarak di antara keduanya.
Namun, secara umum biaya juga dapat melibatkan faktor lain.
Anda juga dapat menentukan beberapa evaluator biaya busur yang bergantung pada kendaraan yang
melakukan perjalanan antarlokasi, menggunakan metode routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfVehicle().
Misalnya, jika kendaraan memiliki kecepatan yang berbeda, Anda dapat menentukan biaya
perjalanan antarlokasi menjadi jarak dibagi dengan kecepatan kendaraan
— dengan kata lain, waktu perjalanan.
Tetapkan parameter penelusuran
Kode berikut menetapkan parameter penelusuran default dan metode heuristik untuk menemukan solusi pertama:
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
Java
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
C#
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
Kode tersebut menetapkan strategi solusi pertama ke PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC, yang membuat rute awal untuk pemecah soal dengan berulang kali menambahkan tepi dengan bobot paling kecil yang tidak mengarah ke node yang dikunjungi sebelumnya (selain depot). Untuk opsi lainnya, lihat Strategi solusi pertama.
Menambahkan printer solusi
Fungsi yang menampilkan solusi yang ditampilkan oleh pemecah soal ditunjukkan di bawah ini. Fungsi tersebut mengekstrak rute dari solusi dan mencetaknya ke konsol.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
Fungsi ini menampilkan rute yang optimal dan jaraknya, yang diberikan oleh ObjectiveValue().
Selesaikan dan cetak solusi
Terakhir, Anda dapat memanggil pemecah masalah dan mencetak solusinya:
Python
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
C++
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
Java
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters); printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
C#
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters); PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
Tindakan ini akan menampilkan solusi dan menampilkan rute optimal.
Menjalankan program
Saat Anda menjalankan program, program akan menampilkan output berikut.
Objective: 7293 miles Route for vehicle 0: 0 -> 7 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 12 -> 6 -> 8 -> 1 -> 11 -> 10 -> 5 -> 9 -> 0
Dalam contoh ini, hanya ada satu rute karena TSP-nya. Namun, dalam masalah pemilihan rute kendaraan yang lebih umum, solusi ini berisi beberapa rute.
Menyimpan rute ke daftar atau array
Sebagai alternatif untuk mencetak solusi secara langsung, Anda dapat menyimpan rute (atau rute, untuk VRP) ke daftar atau array. Opsi ini memberikan keuntungan jika rute tersedia jika Anda ingin melakukan sesuatu dengannya nanti. Misalnya, Anda dapat menjalankan program beberapa kali dengan parameter yang berbeda dan menyimpan rute dalam solusi yang ditampilkan ke file untuk perbandingan.
Fungsi berikut menyimpan rute dalam solusi ke VRP (mungkin dengan beberapa kendaraan) sebagai daftar (Python) atau array (C++).
Python
def get_routes(solution, routing, manager):
"""Get vehicle routes from a solution and store them in an array."""
# Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array whose
# i,j entry is the jth location visited by vehicle i along its route.
routes = []
for route_nbr in range(routing.vehicles()):
index = routing.Start(route_nbr)
route = [manager.IndexToNode(index)]
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route.append(manager.IndexToNode(index))
routes.append(route)
return routes
C++
std::vector<std::vector<int>> GetRoutes(const Assignment& solution,
const RoutingModel& routing,
const RoutingIndexManager& manager) {
// Get vehicle routes and store them in a two dimensional array, whose
// i, j entry is the node for the jth visit of vehicle i.
std::vector<std::vector<int>> routes(manager.num_vehicles());
// Get routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < manager.num_vehicles(); ++vehicle_id) {
int64_t index = routing.Start(vehicle_id);
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routes[vehicle_id].push_back(manager.IndexToNode(index).value());
}
}
return routes;
}
Anda dapat menggunakan fungsi ini untuk mendapatkan rute di salah satu contoh VRP di bagian Pemilihan rute.
Kode berikut menampilkan rute.
Python
routes = get_routes(solution, routing, manager)
# Display the routes.
for i, route in enumerate(routes):
print('Route', i, route)
C++
const std::vector⟨std::vector⟨int⟩⟩
routes = GetRoutes(*solution,
routing,
manager);
// Display the routes.
for (int vehicle_id = 0; vehicle_id < routes.size(); ++vehicle_id) {
LOG(INFO) << "Route " << vehicle_id;
for (int j = 1; j < routes[vehicle_id].size(); ++j) {
LOG(INFO) << routes[vehicle_id][j];
}
}
Untuk contoh saat ini, kode ini menampilkan rute berikut:
Route 0 [0, 7, 2, 3, 4, 12, 6, 8, 1, 11, 10, 5, 9, 0]
Sebagai latihan, ubah kode di atas untuk memformat output dengan cara yang sama seperti printer solusi untuk program.
Selesaikan program
Program TSP lengkap ditampilkan di bawah ini.
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) between cities."""
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
data["distance_matrix"] = [
[0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972],
[2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579],
[713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260],
[1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987],
[1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371],
[1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999],
[2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701],
[213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099],
[2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600],
[875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162],
[1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200],
[2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504],
[1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0],
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()} miles")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route for vehicle 0:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Route distance: {route_distance}miles\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["distance_matrix"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return data["distance_matrix"][from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distance_matrix{
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
//! @brief Print the solution.
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
// Inspect solution.
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue() << " miles";
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.distance_matrix.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&data, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return data.distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP using distance matrix. */
public class TspCities {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCities.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final long[][] distanceMatrix = {
{0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972},
{2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579},
{713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260},
{1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987},
{1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371},
{1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999},
{2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701},
{213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099},
{2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600},
{875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162},
{1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200},
{2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504},
{1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0},
};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue() + "miles");
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance + "miles");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.distanceMatrix.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return data.distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP using distance matrix.
/// </summary>
public class TspCities
{
class DataModel
{
public long[,] DistanceMatrix = {
{ 0, 2451, 713, 1018, 1631, 1374, 2408, 213, 2571, 875, 1420, 2145, 1972 },
{ 2451, 0, 1745, 1524, 831, 1240, 959, 2596, 403, 1589, 1374, 357, 579 },
{ 713, 1745, 0, 355, 920, 803, 1737, 851, 1858, 262, 940, 1453, 1260 },
{ 1018, 1524, 355, 0, 700, 862, 1395, 1123, 1584, 466, 1056, 1280, 987 },
{ 1631, 831, 920, 700, 0, 663, 1021, 1769, 949, 796, 879, 586, 371 },
{ 1374, 1240, 803, 862, 663, 0, 1681, 1551, 1765, 547, 225, 887, 999 },
{ 2408, 959, 1737, 1395, 1021, 1681, 0, 2493, 678, 1724, 1891, 1114, 701 },
{ 213, 2596, 851, 1123, 1769, 1551, 2493, 0, 2699, 1038, 1605, 2300, 2099 },
{ 2571, 403, 1858, 1584, 949, 1765, 678, 2699, 0, 1744, 1645, 653, 600 },
{ 875, 1589, 262, 466, 796, 547, 1724, 1038, 1744, 0, 679, 1272, 1162 },
{ 1420, 1374, 940, 1056, 879, 225, 1891, 1605, 1645, 679, 0, 1017, 1200 },
{ 2145, 357, 1453, 1280, 586, 887, 1114, 2300, 653, 1272, 1017, 0, 504 },
{ 1972, 579, 1260, 987, 371, 999, 701, 2099, 600, 1162, 1200, 504, 0 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0} miles", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}miles", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.DistanceMatrix.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return data.DistanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
Contoh: mengebor papan sirkuit
Contoh berikutnya adalah mengebor lubang di papan sirkuit dengan bor otomatis. Masalahnya adalah menemukan rute terpendek untuk latihan bor yang dilakukan di papan untuk mengebor semua lubang yang diperlukan. Contoh ini diambil dari TSPLIB, sebuah library masalah TSP.
Berikut adalah diagram sebar lokasi untuk lubang:
Bagian berikut menampilkan program yang menemukan solusi yang baik untuk soal papan sirkuit, menggunakan parameter penelusuran default pemecah masalah. Setelah itu, kami akan menunjukkan cara untuk menemukan solusi yang lebih baik dengan mengubah strategi penelusuran.
Membuat data
Data untuk masalah tersebut terdiri dari 280 titik pada bidang, yang ditunjukkan dalam diagram sebar di atas. Program ini membuat data dalam array pasangan yang diurutkan sesuai dengan titik-titik pada bidang, seperti yang ditunjukkan di bawah ini.
Python
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
C++
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
Java
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
C#
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
Menghitung matriks jarak
Fungsi di bawah ini menghitung jarak Euclidean antara dua titik dalam data dan menyimpannya dalam array. Karena pemecah masalah perutean bekerja pada bilangan bulat, fungsi membulatkan jarak yang dihitung ke bilangan bulat. Pembulatan tidak memengaruhi solusi dalam contoh ini, tetapi mungkin memengaruhi kasus lainnya. Lihat Menskalakan matriks jarak untuk mengetahui cara menghindari masalah pembulatan yang mungkin terjadi.
Python
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
C++
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
Java
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
Menambahkan callback jarak
Kode yang membuat callback jarak hampir sama seperti pada contoh sebelumnya. Namun, dalam hal ini program memanggil fungsi yang menghitung matriks jarak sebelum menambahkan callback.
Python
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
C++
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
Java
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
C#
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
Printer solusi
Fungsi berikut mencetak solusi ke konsol. Agar output lebih ringkas, fungsi tersebut hanya menampilkan indeks lokasi di rute.
Python
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
C++
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
Java
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
C#
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
Fungsi utama
Fungsi utama pada dasarnya sama dengan yang ada di contoh sebelumnya, tetapi juga menyertakan panggilan ke fungsi yang membuat matriks jarak.
Menjalankan program
Program lengkap akan ditampilkan di bagian berikutnya. Saat Anda menjalankan program, program akan menampilkan rute berikut:
Total distance: 2790 Route of vehicle 0: 0 -> 1 -> 279 -> 2 -> 278 -> 277 -> 247 -> 248 -> 249 -> 246 -> 244 -> 243 -> 242 -> 241 -> 240 -> 239 -> 238 -> 237 -> 236 -> 235 -> 234 -> 233 -> 232 -> 231 -> 230 -> 245 -> 250 -> 229 -> 228 -> 227 -> 226 -> 225 -> 224 -> 223 -> 222 -> 221 -> 220 -> 219 -> 218 -> 217 -> 216 -> 215 -> 214 -> 213 -> 212 -> 211 -> 210 -> 209 -> 208 -> 251 -> 254 -> 255 -> 257 -> 256 -> 253 -> 252 -> 207 -> 206 -> 205 -> 204 -> 203 -> 202 -> 142 -> 141 -> 146 -> 147 -> 140 -> 139 -> 265 -> 136 -> 137 -> 138 -> 148 -> 149 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 178 -> 179 -> 180 -> 181 -> 182 -> 183 -> 184 -> 186 -> 185 -> 192 -> 196 -> 197 -> 198 -> 144 -> 145 -> 143 -> 199 -> 201 -> 200 -> 195 -> 194 -> 193 -> 191 -> 190 -> 189 -> 188 -> 187 -> 163 -> 164 -> 165 -> 166 -> 167 -> 168 -> 169 -> 171 -> 170 -> 172 -> 105 -> 106 -> 104 -> 103 -> 107 -> 109 -> 110 -> 113 -> 114 -> 116 -> 117 -> 61 -> 62 -> 63 -> 65 -> 64 -> 84 -> 85 -> 115 -> 112 -> 86 -> 83 -> 82 -> 87 -> 111 -> 108 -> 89 -> 90 -> 91 -> 102 -> 101 -> 100 -> 99 -> 98 -> 97 -> 96 -> 95 -> 94 -> 93 -> 92 -> 79 -> 88 -> 81 -> 80 -> 78 -> 77 -> 76 -> 74 -> 75 -> 73 -> 72 -> 71 -> 70 -> 69 -> 66 -> 68 -> 67 -> 57 -> 56 -> 55 -> 54 -> 53 -> 52 -> 51 -> 50 -> 49 -> 48 -> 47 -> 46 -> 45 -> 44 -> 43 -> 58 -> 60 -> 59 -> 42 -> 41 -> 40 -> 39 -> 38 -> 37 -> 36 -> 35 -> 34 -> 33 -> 32 -> 31 -> 30 -> 29 -> 124 -> 123 -> 122 -> 121 -> 120 -> 119 -> 118 -> 156 -> 157 -> 158 -> 173 -> 162 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 150 -> 151 -> 155 -> 152 -> 154 -> 153 -> 128 -> 129 -> 130 -> 131 -> 18 -> 19 -> 20 -> 127 -> 126 -> 125 -> 28 -> 27 -> 26 -> 25 -> 21 -> 24 -> 22 -> 23 -> 13 -> 12 -> 14 -> 11 -> 10 -> 9 -> 7 -> 8 -> 6 -> 5 -> 275 -> 274 -> 273 -> 272 -> 271 -> 270 -> 15 -> 16 -> 17 -> 132 -> 133 -> 269 -> 268 -> 134 -> 135 -> 267 -> 266 -> 264 -> 263 -> 262 -> 261 -> 260 -> 258 -> 259 -> 276 -> 3 -> 4 -> 0
Berikut adalah grafik untuk rute yang sesuai:
Library OR-Tools menemukan tur di atas dengan sangat cepat: dalam waktu kurang dari satu detik di komputer biasa. Panjang total tur di atas adalah 2790.
Selesaikan program
Berikut adalah program lengkap untuk contoh papan sirkuit.
Python
"""Simple Travelling Salesperson Problem (TSP) on a circuit board."""
import math
from ortools.constraint_solver import routing_enums_pb2
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def create_data_model():
"""Stores the data for the problem."""
data = {}
# Locations in block units
data["locations"] = [
# fmt: off
(288, 149), (288, 129), (270, 133), (256, 141), (256, 157), (246, 157),
(236, 169), (228, 169), (228, 161), (220, 169), (212, 169), (204, 169),
(196, 169), (188, 169), (196, 161), (188, 145), (172, 145), (164, 145),
(156, 145), (148, 145), (140, 145), (148, 169), (164, 169), (172, 169),
(156, 169), (140, 169), (132, 169), (124, 169), (116, 161), (104, 153),
(104, 161), (104, 169), (90, 165), (80, 157), (64, 157), (64, 165),
(56, 169), (56, 161), (56, 153), (56, 145), (56, 137), (56, 129),
(56, 121), (40, 121), (40, 129), (40, 137), (40, 145), (40, 153),
(40, 161), (40, 169), (32, 169), (32, 161), (32, 153), (32, 145),
(32, 137), (32, 129), (32, 121), (32, 113), (40, 113), (56, 113),
(56, 105), (48, 99), (40, 99), (32, 97), (32, 89), (24, 89),
(16, 97), (16, 109), (8, 109), (8, 97), (8, 89), (8, 81),
(8, 73), (8, 65), (8, 57), (16, 57), (8, 49), (8, 41),
(24, 45), (32, 41), (32, 49), (32, 57), (32, 65), (32, 73),
(32, 81), (40, 83), (40, 73), (40, 63), (40, 51), (44, 43),
(44, 35), (44, 27), (32, 25), (24, 25), (16, 25), (16, 17),
(24, 17), (32, 17), (44, 11), (56, 9), (56, 17), (56, 25),
(56, 33), (56, 41), (64, 41), (72, 41), (72, 49), (56, 49),
(48, 51), (56, 57), (56, 65), (48, 63), (48, 73), (56, 73),
(56, 81), (48, 83), (56, 89), (56, 97), (104, 97), (104, 105),
(104, 113), (104, 121), (104, 129), (104, 137), (104, 145), (116, 145),
(124, 145), (132, 145), (132, 137), (140, 137), (148, 137), (156, 137),
(164, 137), (172, 125), (172, 117), (172, 109), (172, 101), (172, 93),
(172, 85), (180, 85), (180, 77), (180, 69), (180, 61), (180, 53),
(172, 53), (172, 61), (172, 69), (172, 77), (164, 81), (148, 85),
(124, 85), (124, 93), (124, 109), (124, 125), (124, 117), (124, 101),
(104, 89), (104, 81), (104, 73), (104, 65), (104, 49), (104, 41),
(104, 33), (104, 25), (104, 17), (92, 9), (80, 9), (72, 9),
(64, 21), (72, 25), (80, 25), (80, 25), (80, 41), (88, 49),
(104, 57), (124, 69), (124, 77), (132, 81), (140, 65), (132, 61),
(124, 61), (124, 53), (124, 45), (124, 37), (124, 29), (132, 21),
(124, 21), (120, 9), (128, 9), (136, 9), (148, 9), (162, 9),
(156, 25), (172, 21), (180, 21), (180, 29), (172, 29), (172, 37),
(172, 45), (180, 45), (180, 37), (188, 41), (196, 49), (204, 57),
(212, 65), (220, 73), (228, 69), (228, 77), (236, 77), (236, 69),
(236, 61), (228, 61), (228, 53), (236, 53), (236, 45), (228, 45),
(228, 37), (236, 37), (236, 29), (228, 29), (228, 21), (236, 21),
(252, 21), (260, 29), (260, 37), (260, 45), (260, 53), (260, 61),
(260, 69), (260, 77), (276, 77), (276, 69), (276, 61), (276, 53),
(284, 53), (284, 61), (284, 69), (284, 77), (284, 85), (284, 93),
(284, 101), (288, 109), (280, 109), (276, 101), (276, 93), (276, 85),
(268, 97), (260, 109), (252, 101), (260, 93), (260, 85), (236, 85),
(228, 85), (228, 93), (236, 93), (236, 101), (228, 101), (228, 109),
(228, 117), (228, 125), (220, 125), (212, 117), (204, 109), (196, 101),
(188, 93), (180, 93), (180, 101), (180, 109), (180, 117), (180, 125),
(196, 145), (204, 145), (212, 145), (220, 145), (228, 145), (236, 145),
(246, 141), (252, 125), (260, 129), (280, 133)
# fmt: on
]
data["num_vehicles"] = 1
data["depot"] = 0
return data
def compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(locations):
"""Creates callback to return distance between points."""
distances = {}
for from_counter, from_node in enumerate(locations):
distances[from_counter] = {}
for to_counter, to_node in enumerate(locations):
if from_counter == to_counter:
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = 0
else:
# Euclidean distance
distances[from_counter][to_counter] = int(
math.hypot((from_node[0] - to_node[0]), (from_node[1] - to_node[1]))
)
return distances
def print_solution(manager, routing, solution):
"""Prints solution on console."""
print(f"Objective: {solution.ObjectiveValue()}")
index = routing.Start(0)
plan_output = "Route:\n"
route_distance = 0
while not routing.IsEnd(index):
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)} ->"
previous_index = index
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index))
route_distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, 0)
plan_output += f" {manager.IndexToNode(index)}\n"
print(plan_output)
plan_output += f"Objective: {route_distance}m\n"
def main():
"""Entry point of the program."""
# Instantiate the data problem.
data = create_data_model()
# Create the routing index manager.
manager = pywrapcp.RoutingIndexManager(
len(data["locations"]), data["num_vehicles"], data["depot"]
)
# Create Routing Model.
routing = pywrapcp.RoutingModel(manager)
distance_matrix = compute_euclidean_distance_matrix(data["locations"])
def distance_callback(from_index, to_index):
"""Returns the distance between the two nodes."""
# Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index)
to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index)
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node]
transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(distance_callback)
# Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index)
# Setting first solution heuristic.
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.first_solution_strategy = (
routing_enums_pb2.FirstSolutionStrategy.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC
)
# Solve the problem.
solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(search_parameters)
# Print solution on console.
if solution:
print_solution(manager, routing, solution)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdint>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_enums.pb.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_index_manager.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/routing_parameters.h"
namespace operations_research {
struct DataModel {
const std::vector<std::vector<int>> locations{
{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157}, {246, 157},
{236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145},
{156, 145}, {148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169},
{156, 169}, {140, 169}, {132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153},
{104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165}, {80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165},
{56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137}, {56, 129},
{56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153},
{40, 161}, {40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145},
{32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121}, {32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113},
{56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89}, {24, 89},
{16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81},
{8, 73}, {8, 65}, {8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41},
{24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65}, {32, 73},
{32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43},
{44, 35}, {44, 27}, {32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17},
{24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17}, {56, 25},
{56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49},
{48, 51}, {56, 57}, {56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73},
{56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97}, {104, 105},
{104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137},
{164, 137}, {172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93},
{172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77}, {180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53},
{172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81}, {148, 85},
{124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101},
{104, 89}, {104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41},
{104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17}, {92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9},
{64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61},
{124, 61}, {124, 53}, {124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21},
{124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9}, {148, 9}, {162, 9},
{156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57},
{212, 65}, {220, 73}, {228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69},
{236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53}, {236, 45}, {228, 45},
{228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61},
{260, 69}, {260, 77}, {276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53},
{284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77}, {284, 85}, {284, 93},
{284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85},
{228, 85}, {228, 93}, {236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109},
{228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125}, {212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101},
{188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109}, {180, 117}, {180, 125},
{196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145}, {236, 145},
{246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133},
};
const int num_vehicles = 1;
const RoutingIndexManager::NodeIndex depot{0};
};
// @brief Generate distance matrix.
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(
const std::vector<std::vector<int>>& locations) {
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> distances =
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>>(
locations.size(), std::vector<int64_t>(locations.size(), int64_t{0}));
for (int from_node = 0; from_node < locations.size(); from_node++) {
for (int to_node = 0; to_node < locations.size(); to_node++) {
if (from_node != to_node)
distances[from_node][to_node] = static_cast<int64_t>(
std::hypot((locations[to_node][0] - locations[from_node][0]),
(locations[to_node][1] - locations[from_node][1])));
}
}
return distances;
}
//! @brief Print the solution
//! @param[in] manager Index manager used.
//! @param[in] routing Routing solver used.
//! @param[in] solution Solution found by the solver.
void PrintSolution(const RoutingIndexManager& manager,
const RoutingModel& routing, const Assignment& solution) {
LOG(INFO) << "Objective: " << solution.ObjectiveValue();
// Inspect solution.
int64_t index = routing.Start(0);
LOG(INFO) << "Route:";
int64_t distance{0};
std::stringstream route;
while (!routing.IsEnd(index)) {
route << manager.IndexToNode(index).value() << " -> ";
const int64_t previous_index = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
distance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previous_index, index, int64_t{0});
}
LOG(INFO) << route.str() << manager.IndexToNode(index).value();
LOG(INFO) << "Route distance: " << distance << "miles";
LOG(INFO) << "";
LOG(INFO) << "Advanced usage:";
LOG(INFO) << "Problem solved in " << routing.solver()->wall_time() << "ms";
}
void Tsp() {
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data;
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager(data.locations.size(), data.num_vehicles,
data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing(manager);
const auto distance_matrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
const int transit_callback_index = routing.RegisterTransitCallback(
[&distance_matrix, &manager](const int64_t from_index,
const int64_t to_index) -> int64_t {
// Convert from routing variable Index to distance matrix NodeIndex.
const int from_node = manager.IndexToNode(from_index).value();
const int to_node = manager.IndexToNode(to_index).value();
return distance_matrix[from_node][to_node];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transit_callback_index);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_first_solution_strategy(
FirstSolutionStrategy::PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC);
// Solve the problem.
const Assignment* solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(manager, routing, *solution);
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int /*argc*/, char* /*argv*/[]) {
operations_research::Tsp();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Assignment;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.FirstSolutionStrategy;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingIndexManager;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingModel;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.RoutingSearchParameters;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.main;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/** Minimal TSP. */
public class TspCircuitBoard {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(TspCircuitBoard.class.getName());
static class DataModel {
public final int[][] locations = {{288, 149}, {288, 129}, {270, 133}, {256, 141}, {256, 157},
{246, 157}, {236, 169}, {228, 169}, {228, 161}, {220, 169}, {212, 169}, {204, 169},
{196, 169}, {188, 169}, {196, 161}, {188, 145}, {172, 145}, {164, 145}, {156, 145},
{148, 145}, {140, 145}, {148, 169}, {164, 169}, {172, 169}, {156, 169}, {140, 169},
{132, 169}, {124, 169}, {116, 161}, {104, 153}, {104, 161}, {104, 169}, {90, 165},
{80, 157}, {64, 157}, {64, 165}, {56, 169}, {56, 161}, {56, 153}, {56, 145}, {56, 137},
{56, 129}, {56, 121}, {40, 121}, {40, 129}, {40, 137}, {40, 145}, {40, 153}, {40, 161},
{40, 169}, {32, 169}, {32, 161}, {32, 153}, {32, 145}, {32, 137}, {32, 129}, {32, 121},
{32, 113}, {40, 113}, {56, 113}, {56, 105}, {48, 99}, {40, 99}, {32, 97}, {32, 89},
{24, 89}, {16, 97}, {16, 109}, {8, 109}, {8, 97}, {8, 89}, {8, 81}, {8, 73}, {8, 65},
{8, 57}, {16, 57}, {8, 49}, {8, 41}, {24, 45}, {32, 41}, {32, 49}, {32, 57}, {32, 65},
{32, 73}, {32, 81}, {40, 83}, {40, 73}, {40, 63}, {40, 51}, {44, 43}, {44, 35}, {44, 27},
{32, 25}, {24, 25}, {16, 25}, {16, 17}, {24, 17}, {32, 17}, {44, 11}, {56, 9}, {56, 17},
{56, 25}, {56, 33}, {56, 41}, {64, 41}, {72, 41}, {72, 49}, {56, 49}, {48, 51}, {56, 57},
{56, 65}, {48, 63}, {48, 73}, {56, 73}, {56, 81}, {48, 83}, {56, 89}, {56, 97}, {104, 97},
{104, 105}, {104, 113}, {104, 121}, {104, 129}, {104, 137}, {104, 145}, {116, 145},
{124, 145}, {132, 145}, {132, 137}, {140, 137}, {148, 137}, {156, 137}, {164, 137},
{172, 125}, {172, 117}, {172, 109}, {172, 101}, {172, 93}, {172, 85}, {180, 85}, {180, 77},
{180, 69}, {180, 61}, {180, 53}, {172, 53}, {172, 61}, {172, 69}, {172, 77}, {164, 81},
{148, 85}, {124, 85}, {124, 93}, {124, 109}, {124, 125}, {124, 117}, {124, 101}, {104, 89},
{104, 81}, {104, 73}, {104, 65}, {104, 49}, {104, 41}, {104, 33}, {104, 25}, {104, 17},
{92, 9}, {80, 9}, {72, 9}, {64, 21}, {72, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 25}, {80, 41}, {88, 49},
{104, 57}, {124, 69}, {124, 77}, {132, 81}, {140, 65}, {132, 61}, {124, 61}, {124, 53},
{124, 45}, {124, 37}, {124, 29}, {132, 21}, {124, 21}, {120, 9}, {128, 9}, {136, 9},
{148, 9}, {162, 9}, {156, 25}, {172, 21}, {180, 21}, {180, 29}, {172, 29}, {172, 37},
{172, 45}, {180, 45}, {180, 37}, {188, 41}, {196, 49}, {204, 57}, {212, 65}, {220, 73},
{228, 69}, {228, 77}, {236, 77}, {236, 69}, {236, 61}, {228, 61}, {228, 53}, {236, 53},
{236, 45}, {228, 45}, {228, 37}, {236, 37}, {236, 29}, {228, 29}, {228, 21}, {236, 21},
{252, 21}, {260, 29}, {260, 37}, {260, 45}, {260, 53}, {260, 61}, {260, 69}, {260, 77},
{276, 77}, {276, 69}, {276, 61}, {276, 53}, {284, 53}, {284, 61}, {284, 69}, {284, 77},
{284, 85}, {284, 93}, {284, 101}, {288, 109}, {280, 109}, {276, 101}, {276, 93}, {276, 85},
{268, 97}, {260, 109}, {252, 101}, {260, 93}, {260, 85}, {236, 85}, {228, 85}, {228, 93},
{236, 93}, {236, 101}, {228, 101}, {228, 109}, {228, 117}, {228, 125}, {220, 125},
{212, 117}, {204, 109}, {196, 101}, {188, 93}, {180, 93}, {180, 101}, {180, 109},
{180, 117}, {180, 125}, {196, 145}, {204, 145}, {212, 145}, {220, 145}, {228, 145},
{236, 145}, {246, 141}, {252, 125}, {260, 129}, {280, 133}};
public final int vehicleNumber = 1;
public final int depot = 0;
}
/// @brief Compute Euclidean distance matrix from locations array.
/// @details It uses an array of locations and computes
/// the Euclidean distance between any two locations.
private static long[][] computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(int[][] locations) {
// Calculate distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
long[][] distanceMatrix = new long[locations.length][locations.length];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locations.length; ++fromNode) {
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locations.length; ++toNode) {
if (fromNode == toNode) {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] = 0;
} else {
distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode] =
(long) Math.hypot(locations[toNode][0] - locations[fromNode][0],
locations[toNode][1] - locations[fromNode][1]);
}
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// @brief Print the solution.
static void printSolution(
RoutingModel routing, RoutingIndexManager manager, Assignment solution) {
// Solution cost.
logger.info("Objective: " + solution.objectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
logger.info("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
String route = "";
long index = routing.start(0);
while (!routing.isEnd(index)) {
route += manager.indexToNode(index) + " -> ";
long previousIndex = index;
index = solution.value(routing.nextVar(index));
routing.getArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
route += manager.indexToNode(routing.end(0));
logger.info(route);
logger.info("Route distance: " + routeDistance);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the data problem.
final DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.locations.length, data.vehicleNumber, data.depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Create and register a transit callback.
final long[][] distanceMatrix = computeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.locations);
final int transitCallbackIndex =
routing.registerTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) -> {
// Convert from routing variable Index to user NodeIndex.
int fromNode = manager.indexToNode(fromIndex);
int toNode = manager.indexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode][toNode];
});
// Define cost of each arc.
routing.setArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.build();
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.solveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
printSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
/// <summary>
/// Minimal TSP.
/// A description of the problem can be found here:
/// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Travelling_salesperson_problem.
/// </summary>
public class TspCircuitBoard
{
class DataModel
{
public int[,] Locations = {
{ 288, 149 }, { 288, 129 }, { 270, 133 }, { 256, 141 }, { 256, 157 }, { 246, 157 }, { 236, 169 },
{ 228, 169 }, { 228, 161 }, { 220, 169 }, { 212, 169 }, { 204, 169 }, { 196, 169 }, { 188, 169 },
{ 196, 161 }, { 188, 145 }, { 172, 145 }, { 164, 145 }, { 156, 145 }, { 148, 145 }, { 140, 145 },
{ 148, 169 }, { 164, 169 }, { 172, 169 }, { 156, 169 }, { 140, 169 }, { 132, 169 }, { 124, 169 },
{ 116, 161 }, { 104, 153 }, { 104, 161 }, { 104, 169 }, { 90, 165 }, { 80, 157 }, { 64, 157 },
{ 64, 165 }, { 56, 169 }, { 56, 161 }, { 56, 153 }, { 56, 145 }, { 56, 137 }, { 56, 129 },
{ 56, 121 }, { 40, 121 }, { 40, 129 }, { 40, 137 }, { 40, 145 }, { 40, 153 }, { 40, 161 },
{ 40, 169 }, { 32, 169 }, { 32, 161 }, { 32, 153 }, { 32, 145 }, { 32, 137 }, { 32, 129 },
{ 32, 121 }, { 32, 113 }, { 40, 113 }, { 56, 113 }, { 56, 105 }, { 48, 99 }, { 40, 99 },
{ 32, 97 }, { 32, 89 }, { 24, 89 }, { 16, 97 }, { 16, 109 }, { 8, 109 }, { 8, 97 },
{ 8, 89 }, { 8, 81 }, { 8, 73 }, { 8, 65 }, { 8, 57 }, { 16, 57 }, { 8, 49 },
{ 8, 41 }, { 24, 45 }, { 32, 41 }, { 32, 49 }, { 32, 57 }, { 32, 65 }, { 32, 73 },
{ 32, 81 }, { 40, 83 }, { 40, 73 }, { 40, 63 }, { 40, 51 }, { 44, 43 }, { 44, 35 },
{ 44, 27 }, { 32, 25 }, { 24, 25 }, { 16, 25 }, { 16, 17 }, { 24, 17 }, { 32, 17 },
{ 44, 11 }, { 56, 9 }, { 56, 17 }, { 56, 25 }, { 56, 33 }, { 56, 41 }, { 64, 41 },
{ 72, 41 }, { 72, 49 }, { 56, 49 }, { 48, 51 }, { 56, 57 }, { 56, 65 }, { 48, 63 },
{ 48, 73 }, { 56, 73 }, { 56, 81 }, { 48, 83 }, { 56, 89 }, { 56, 97 }, { 104, 97 },
{ 104, 105 }, { 104, 113 }, { 104, 121 }, { 104, 129 }, { 104, 137 }, { 104, 145 }, { 116, 145 },
{ 124, 145 }, { 132, 145 }, { 132, 137 }, { 140, 137 }, { 148, 137 }, { 156, 137 }, { 164, 137 },
{ 172, 125 }, { 172, 117 }, { 172, 109 }, { 172, 101 }, { 172, 93 }, { 172, 85 }, { 180, 85 },
{ 180, 77 }, { 180, 69 }, { 180, 61 }, { 180, 53 }, { 172, 53 }, { 172, 61 }, { 172, 69 },
{ 172, 77 }, { 164, 81 }, { 148, 85 }, { 124, 85 }, { 124, 93 }, { 124, 109 }, { 124, 125 },
{ 124, 117 }, { 124, 101 }, { 104, 89 }, { 104, 81 }, { 104, 73 }, { 104, 65 }, { 104, 49 },
{ 104, 41 }, { 104, 33 }, { 104, 25 }, { 104, 17 }, { 92, 9 }, { 80, 9 }, { 72, 9 },
{ 64, 21 }, { 72, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 25 }, { 80, 41 }, { 88, 49 }, { 104, 57 },
{ 124, 69 }, { 124, 77 }, { 132, 81 }, { 140, 65 }, { 132, 61 }, { 124, 61 }, { 124, 53 },
{ 124, 45 }, { 124, 37 }, { 124, 29 }, { 132, 21 }, { 124, 21 }, { 120, 9 }, { 128, 9 },
{ 136, 9 }, { 148, 9 }, { 162, 9 }, { 156, 25 }, { 172, 21 }, { 180, 21 }, { 180, 29 },
{ 172, 29 }, { 172, 37 }, { 172, 45 }, { 180, 45 }, { 180, 37 }, { 188, 41 }, { 196, 49 },
{ 204, 57 }, { 212, 65 }, { 220, 73 }, { 228, 69 }, { 228, 77 }, { 236, 77 }, { 236, 69 },
{ 236, 61 }, { 228, 61 }, { 228, 53 }, { 236, 53 }, { 236, 45 }, { 228, 45 }, { 228, 37 },
{ 236, 37 }, { 236, 29 }, { 228, 29 }, { 228, 21 }, { 236, 21 }, { 252, 21 }, { 260, 29 },
{ 260, 37 }, { 260, 45 }, { 260, 53 }, { 260, 61 }, { 260, 69 }, { 260, 77 }, { 276, 77 },
{ 276, 69 }, { 276, 61 }, { 276, 53 }, { 284, 53 }, { 284, 61 }, { 284, 69 }, { 284, 77 },
{ 284, 85 }, { 284, 93 }, { 284, 101 }, { 288, 109 }, { 280, 109 }, { 276, 101 }, { 276, 93 },
{ 276, 85 }, { 268, 97 }, { 260, 109 }, { 252, 101 }, { 260, 93 }, { 260, 85 }, { 236, 85 },
{ 228, 85 }, { 228, 93 }, { 236, 93 }, { 236, 101 }, { 228, 101 }, { 228, 109 }, { 228, 117 },
{ 228, 125 }, { 220, 125 }, { 212, 117 }, { 204, 109 }, { 196, 101 }, { 188, 93 }, { 180, 93 },
{ 180, 101 }, { 180, 109 }, { 180, 117 }, { 180, 125 }, { 196, 145 }, { 204, 145 }, { 212, 145 },
{ 220, 145 }, { 228, 145 }, { 236, 145 }, { 246, 141 }, { 252, 125 }, { 260, 129 }, { 280, 133 },
};
public int VehicleNumber = 1;
public int Depot = 0;
};
/// <summary>
/// Euclidean distance implemented as a callback. It uses an array of
/// positions and computes the Euclidean distance between the two
/// positions of two different indices.
/// </summary>
static long[,] ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(in int[,] locations)
{
// Calculate the distance matrix using Euclidean distance.
int locationNumber = locations.GetLength(0);
long[,] distanceMatrix = new long[locationNumber, locationNumber];
for (int fromNode = 0; fromNode < locationNumber; fromNode++)
{
for (int toNode = 0; toNode < locationNumber; toNode++)
{
if (fromNode == toNode)
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] = 0;
else
distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode] =
(long)Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 0] - locations[fromNode, 0], 2) +
Math.Pow(locations[toNode, 1] - locations[fromNode, 1], 2));
}
}
return distanceMatrix;
}
/// <summary>
/// Print the solution.
/// </summary>
static void PrintSolution(in RoutingModel routing, in RoutingIndexManager manager, in Assignment solution)
{
Console.WriteLine("Objective: {0}", solution.ObjectiveValue());
// Inspect solution.
Console.WriteLine("Route:");
long routeDistance = 0;
var index = routing.Start(0);
while (routing.IsEnd(index) == false)
{
Console.Write("{0} -> ", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
var previousIndex = index;
index = solution.Value(routing.NextVar(index));
routeDistance += routing.GetArcCostForVehicle(previousIndex, index, 0);
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}", manager.IndexToNode((int)index));
Console.WriteLine("Route distance: {0}m", routeDistance);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the data problem.
DataModel data = new DataModel();
// Create Routing Index Manager
RoutingIndexManager manager =
new RoutingIndexManager(data.Locations.GetLength(0), data.VehicleNumber, data.Depot);
// Create Routing Model.
RoutingModel routing = new RoutingModel(manager);
// Define cost of each arc.
long[,] distanceMatrix = ComputeEuclideanDistanceMatrix(data.Locations);
int transitCallbackIndex = routing.RegisterTransitCallback((long fromIndex, long toIndex) =>
{
// Convert from routing variable Index to
// distance matrix NodeIndex.
var fromNode = manager.IndexToNode(fromIndex);
var toNode = manager.IndexToNode(toIndex);
return distanceMatrix[fromNode, toNode];
});
routing.SetArcCostEvaluatorOfAllVehicles(transitCallbackIndex);
// Setting first solution heuristic.
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
// Solve the problem.
Assignment solution = routing.SolveWithParameters(searchParameters);
// Print solution on console.
PrintSolution(routing, manager, solution);
}
}
Mengubah strategi penelusuran
Pemecah masalah perutean tidak selalu mengembalikan solusi optimal ke TSP, karena masalah perutean tidak dapat ditangani dengan komputasi. Misalnya, solusi yang ditampilkan dalam contoh sebelumnya bukanlah rute yang optimal.
Untuk menemukan solusi yang lebih baik, Anda dapat menggunakan strategi penelusuran yang lebih canggih, yang disebut penelusuran lokal terpandu, yang memungkinkan pemecah masalah meng-escape minimum lokal — solusi yang lebih pendek dari semua rute terdekat, tetapi bukan minimum global. Setelah beralih dari nilai minimum lokal, pemecah soal melanjutkan penelusuran.
Contoh di bawah menunjukkan cara menetapkan penelusuran lokal terpandu untuk contoh papan sirkuit.
Python
search_parameters = pywrapcp.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters()
search_parameters.local_search_metaheuristic = (
routing_enums_pb2.LocalSearchMetaheuristic.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
search_parameters.time_limit.seconds = 30
search_parameters.log_search = True
C++
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters = DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.set_local_search_metaheuristic(
LocalSearchMetaheuristic::GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH);
searchParameters.mutable_time_limit()->set_seconds(30);
search_parameters.set_log_search(true);
Java
Tambahkan pernyataan `import` berikut di awal program:import com.google.protobuf.Duration;Lalu, tetapkan parameter penelusuran sebagai berikut:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
main.defaultRoutingSearchParameters()
.toBuilder()
.setFirstSolutionStrategy(FirstSolutionStrategy.Value.PATH_CHEAPEST_ARC)
.setLocalSearchMetaheuristic(LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Value.GUIDED_LOCAL_SEARCH)
.setTimeLimit(Duration.newBuilder().setSeconds(30).build())
.setLogSearch(true)
.build();
C#
Tambahkan baris berikut di awal program:using Google.Protobuf.WellKnownTypes; // DurationKemudian, tetapkan parameter penelusuran sebagai berikut:
RoutingSearchParameters searchParameters =
operations_research_constraint_solver.DefaultRoutingSearchParameters();
searchParameters.FirstSolutionStrategy = FirstSolutionStrategy.Types.Value.PathCheapestArc;
searchParameters.LocalSearchMetaheuristic = LocalSearchMetaheuristic.Types.Value.GuidedLocalSearch;
searchParameters.TimeLimit = new Duration { Seconds = 30 };
searchParameters.LogSearch = true;
Untuk strategi penelusuran lokal lainnya, lihat Opsi penelusuran lokal.
Contoh di atas juga mengaktifkan logging untuk penelusuran. Meskipun tidak diperlukan, logging dapat berguna untuk proses debug.
Saat menjalankan program setelah membuat perubahan yang ditunjukkan di atas, Anda akan mendapatkan solusi berikut, yang lebih singkat dari solusi yang ditampilkan di bagian sebelumnya.
Objective: 2672 Route: 0 -> 3 -> 276 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 8 -> 7 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11 -> 14 -> 12 -> 13 -> 23 -> 22 -> 24 -> 21 -> 25 -> 26 -> 27 -> 28 -> 125 -> 126 -> 127 -> 20 -> 19 -> 130 -> 129 -> 128 -> 153 -> 154 -> 152 -> 155 -> 151 -> 150 -> 177 -> 176 -> 175 -> 180 -> 161 -> 160 -> 174 -> 159 -> 158 -> 157 -> 156 -> 118 -> 119 -> 120 -> 121 -> 122 -> 123 -> 124 -> 29 -> 30 -> 31 -> 32 -> 33 -> 34 -> 35 -> 36 -> 37 -> 38 -> 39 -> 40 -> 41 -> 42 -> 59 -> 60 -> 58 -> 43 -> 44 -> 45 -> 46 -> 47 -> 48 -> 49 -> 50 -> 51 -> 52 -> 53 -> 54 -> 55 -> 56 -> 57 -> 67 -> 68 -> 66 -> 69 -> 70 -> 71 -> 72 -> 73 -> 75 -> 74 -> 76 -> 77 -> 78 -> 80 -> 81 -> 88 -> 79 -> 92 -> 93 -> 94 -> 95 -> 96 -> 97 -> 98 -> 99 -> 100 -> 101 -> 102 -> 91 -> 90 -> 89 -> 108 -> 111 -> 87 -> 82 -> 83 -> 86 -> 112 -> 115 -> 85 -> 84 -> 64 -> 65 -> 63 -> 62 -> 61 -> 117 -> 116 -> 114 -> 113 -> 110 -> 109 -> 107 -> 103 -> 104 -> 105 -> 106 -> 173 -> 172 -> 171 -> 170 -> 169 -> 168 -> 167 -> 166 -> 165 -> 164 -> 163 -> 162 -> 187 -> 188 -> 189 -> 190 -> 191 -> 192 -> 185 -> 186 -> 184 -> 183 -> 182 -> 181 -> 179 -> 178 -> 149 -> 148 -> 138 -> 137 -> 136 -> 266 -> 267 -> 135 -> 134 -> 268 -> 269 -> 133 -> 132 -> 131 -> 18 -> 17 -> 16 -> 15 -> 270 -> 271 -> 272 -> 273 -> 274 -> 275 -> 259 -> 258 -> 260 -> 261 -> 262 -> 263 -> 264 -> 265 -> 139 -> 140 -> 147 -> 146 -> 141 -> 142 -> 145 -> 144 -> 198 -> 197 -> 196 -> 193 -> 194 -> 195 -> 200 -> 201 -> 199 -> 143 -> 202 -> 203 -> 204 -> 205 -> 206 -> 207 -> 252 -> 253 -> 256 -> 257 -> 255 -> 254 -> 251 -> 208 -> 209 -> 210 -> 211 -> 212 -> 213 -> 214 -> 215 -> 216 -> 217 -> 218 -> 219 -> 220 -> 221 -> 222 -> 223 -> 224 -> 225 -> 226 -> 227 -> 232 -> 233 -> 234 -> 235 -> 236 -> 237 -> 230 -> 231 -> 228 -> 229 -> 250 -> 245 -> 238 -> 239 -> 240 -> 241 -> 242 -> 243 -> 244 -> 246 -> 249 -> 248 -> 247 -> 277 -> 278 -> 2 -> 279 -> 1 -> 0
Untuk opsi penelusuran lainnya, lihat Opsi Perutean.
Algoritme terbaik kini dapat menyelesaikan instance TSP secara rutin dengan puluhan ribu node. (Data pada saat penulisan adalah instance pla85900 di TSPLIB, sebuah aplikasi VLSI dengan 85.900 node. Untuk instance tertentu dengan jutaan node, solusi telah ditemukan dijamin dalam 1% dari tur yang optimal.)
Menskalakan matriks jarak
Karena pemecah masalah perutean bekerja pada bilangan bulat, jika matriks jarak Anda memiliki entri non-bilangan bulat, Anda harus membulatkan jarak ke bilangan bulat. Jika beberapa jarak kecil, pembulatan dapat memengaruhi solusi.
Untuk menghindari masalah pembulatan, Anda dapat melakukan scale pada matriks jarak: kalikan semua entri matriks dengan jumlah besar, misalnya 100. Ini mengalikan panjang rute dengan faktor 100, tetapi tidak mengubah solusinya. Keuntungannya adalah sekarang saat Anda membulatkan entri matriks, jumlah pembulatan (yang paling besar 0,5), sangat kecil dibandingkan dengan jarak, sehingga tidak akan memengaruhi solusi secara signifikan.
Jika Anda menskalakan matriks jarak, Anda juga perlu mengubah printer solusi untuk membagi panjang rute yang diskalakan dengan faktor penskalaan, sehingga printer tersebut menampilkan jarak rute yang tidak diskalakan.

