Trong những phần sau, chúng tôi sẽ minh hoạ quy trình lập trình ràng buộc (CP) bằng bài toán tổ hợp dựa trên ván cờ. Trong cờ vua, hoàng hậu có thể tấn công theo chiều ngang, chiều dọc và đường chéo. Bài toán N-queens hỏi:
Làm thế nào để đặt N quân hậu lên bàn cờ NxN để không có hai quân nào tấn công với nhau?
Dưới đây, bạn có thể thấy một giải pháp khả thi cho bài toán N-queens với N = 4.
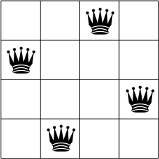
Không có hai que đánh dấu làm hoàng hậu nằm trên cùng một hàng, cột hoặc đường chéo.
Lưu ý rằng đây không phải là vấn đề tối ưu hoá: chúng tôi muốn tìm tất cả các giải pháp thay vì một giải pháp tối ưu, khiến nó trở thành một ứng viên tự nhiên để lập trình ràng buộc. Các phần sau đây mô tả phương pháp CP đối với vấn đề N-queens, và trình bày các chương trình giải quyết vấn đề đó bằng cả trình giải quyết CP-SAT và CP gốc của Google.
Phương pháp CP đối với bài toán N-queens
Công cụ giải quyết CP hoạt động bằng cách thử tất cả những gì một cách có hệ thống cách chỉ định giá trị có thể có cho các biến trong một bài toán, để tìm ra các giải pháp khả thi. Trong bài toán 4 nữ hoàng, trình giải bắt đầu ở điểm ngoài cùng bên trái và đặt lần lượt một ngả vào mỗi cột tại vị trí không bị bất kỳ quân hậu nào từng đặt trước đó tấn công.
Truyền phát và theo dõi ngược
Có hai phần tử chính trong việc tìm kiếm khi lập trình ràng buộc:
- Nhân bản – Mỗi lần trình giải chỉ định một giá trị cho một biến, các quy tắc ràng buộc bổ sung các hạn chế về các giá trị có thể có của các trạng thái chưa được chỉ định biến. Những hạn chế này sẽ áp dụng cho các lượt chỉ định biến trong tương lai. Ví dụ: trong bài toán 4 nữ hoàng, mỗi khi người giải đặt một hoàng hậu, không thể đặt bất kỳ quân hậu nào khác lên hàng và các đường chéo mà hoàng hậu hiện tại đang bật. Việc truyền tải có thể tăng tốc đáng kể quá trình tìm kiếm bằng cách giảm tập hợp các giá trị biến thiên mà trình giải phải khám phá.
- Theo dõi ngược xảy ra khi trình giải không thể chỉ định giá trị cho câu tiếp theo biến, do các hạn chế hoặc tìm được một nghiệm. Trong cả hai trường hợp, trình giải toán quay lại giai đoạn trước và thay đổi giá trị của biến tại giai đoạn đó thành một giá trị chưa được thử. Trong ví dụ về 4 nữ hoàng, điều này có nghĩa là di chuyển một quân hậu sang một hình vuông mới trên cột hiện tại.
Tiếp theo, bạn sẽ thấy cách lập trình ràng buộc sử dụng phổ biến và theo dõi ngược để để giải bài toán 4 cặp đôi.
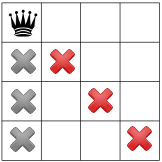
Giả sử trình giải bắt đầu bằng cách tuỳ ý đặt một nữ hoàng ở phía trên bên trái góc. Đó là một giả thuyết; có thể sẽ không có giải pháp có một hậu cảnh ở góc trên bên trái.
Với giả thuyết này, chúng ta có thể phổ biến những ràng buộc nào? Một hạn chế là chỉ có thể có một nữ hoàng trong một cột (dấu X màu xám bên dưới) và một nữ khác quy tắc ràng buộc cấm hai hoàng hậu trên cùng một đường chéo (dấu X màu đỏ bên dưới).
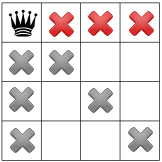
Quy tắc ràng buộc thứ ba của chúng tôi cấm các hậu tố trên cùng một hàng:
Các điều kiện ràng buộc của chúng ta được lan truyền, chúng ta có thể kiểm định một giả thuyết khác và đặt một nữ hoàng thứ hai trên một trong các ô còn lại. Trình giải quyết của chúng tôi có thể quyết định để đặt vào đó hình vuông có sẵn đầu tiên trong cột thứ hai:
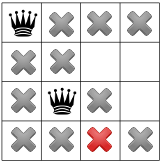
Sau khi áp dụng hạn chế đường chéo, chúng ta có thể thấy rằng hạn chế đó không các ô vuông sẵn có trong cột thứ ba hoặc hàng cuối cùng:
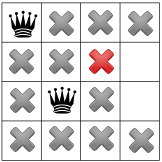
Vì không có giải pháp ở giai đoạn này nên chúng ta cần xem lại. Có một lựa chọn là để người giải chọn hình vuông khác có sẵn trong cột thứ hai. Tuy nhiên, cơ chế lan truyền ràng buộc buộc một nữ hoàng vào hàng thứ hai của cột thứ ba, không để lại chỗ hợp lệ cho nữ hoàng thứ tư:
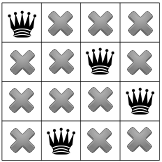
Do đó, người giải quyết phải theo dõi lại lần nữa, lần này hãy quay lại vị trí của hoàng hậu thứ nhất. Chúng ta hiện đã chỉ ra rằng không có giải pháp nào cho vấn đề bài toán sẽ chiếm một hình vuông góc.
Vì không có nữ hoàng nào ở góc, nên người giải đã di chuyển nữ hoàng đầu tiên xuống một vị trí và nhân bản, chỉ để lại một vị trí cho nữ hoàng thứ hai:
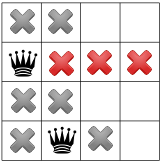
Tiếp tục truyền tải lại chỉ còn lại một vị trí cho nữ hoàng thứ ba:
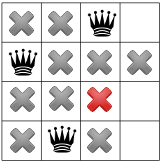
Còn với Nữ hoàng thứ tư và cũng là Nữ hoàng cuối cùng:
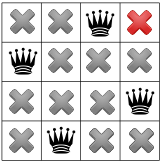
Chúng tôi đã có giải pháp đầu tiên! Nếu chúng ta hướng dẫn trình giải toán dừng lại sau khi tìm được giải pháp đầu tiên, nó sẽ kết thúc ở đây. Nếu không, nó sẽ theo dõi lại và đặt nữ hoàng đầu tiên vào hàng thứ ba của cột đầu tiên.
Giải pháp sử dụng CP-SAT
Bài toán N-queens rất phù hợp với quy trình lập trình ràng buộc. Trong phần này chúng tôi sẽ hướng dẫn bạn về một chương trình Python ngắn sử dụng trình giải quyết CP-SAT để tìm mọi giải pháp cho vấn đề.
Nhập thư viện
Mã sau đây nhập thư viện bắt buộc.
Python
import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
Khai báo mô hình
Mã sau đây khai báo mô hình CP-SAT.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
Tạo biến
Trình giải toán sẽ tạo các biến cho bài toán dưới dạng một mảng có tên là queens.
Python
# There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
// There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
Ở đây, chúng tôi giả định rằng queens[j] là số hàng của nữ hoàng trong cột j.
Nói cách khác, queens[j] = i có nghĩa là có một nữ hoàng ở hàng i và cột j.
Tạo các quy tắc ràng buộc
Dưới đây là mã tạo ra các quy tắc ràng buộc cho bài toán này.
Python
# All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2);
Java
// All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2);
C#
// All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2);
Mã này sử dụng phương thức AddAllDifferent, phương thức này yêu cầu tất cả các phần tử của một
mảng biến khác nhau.
Hãy xem những quy tắc ràng buộc này đảm bảo ba điều kiện cho N-queens như thế nào bài toán (ques trên các hàng, cột và đường chéo khác nhau).
Không có hai nữ hoàng ở cùng một hàng
Áp dụng phương thức AllDifferent của trình giải cho queens buộc giá trị của
queens[j] phải khác nhau cho mỗi j, nghĩa là tất cả các hoàng hậu phải ở trong
hàng khác nhau.
Không có hai nữ hoàng trên cùng một cột
Quy tắc ràng buộc này được ngầm định trong định nghĩa của queens.
Vì không có hai phần tử nào của queens có thể có cùng chỉ mục nên không thể có hai hậu tố
trong cùng một cột.
Không có hai góc 2 phía trên cùng một đường chéo
Quy tắc ràng buộc về đường chéo phức tạp hơn một chút so với quy tắc ràng buộc đối với hàng và cột. Trước tiên, nếu hai hoàng hậu nằm trên cùng một đường chéo thì một trong các điều kiện sau sẽ xảy ra phải đúng:
- Số hàng cộng với số cột của mỗi 2 nữ hoàng bằng nhau.
Nói cách khác,
queens(j) + jcó cùng giá trị đối với hai chỉ mục khác nhauj - Số hàng trừ đi số cột của mỗi 2 nữ hoàng bằng nhau.
Trong trường hợp này,
queens(j) - jcó cùng giá trị cho hai chỉ mụcjkhác nhau.
Một trong các điều kiện này có nghĩa là ong nằm trên cùng một đường chéo tăng dần ( đi từ trái sang phải), còn giá trị còn lại có nghĩa là chúng nằm trên cùng một phương diện giảm dần đường chéo. Điều kiện nào tương ứng với tăng dần và điều kiện nào tương ứng với giảm dần tuỳ thuộc vào cách bạn sắp xếp các hàng và cột. Như đã đề cập trong phần trước, thứ tự không ảnh hưởng đến tập hợp giải pháp, chỉ là cách bạn trực quan hoá chúng.
Vì vậy, điều kiện ràng buộc về đường chéo là tất cả giá trị của queens(j) + j phải bằng
khác nhau và giá trị của queens(j) - j phải khác nhau, đối với
j khác.
Để áp dụng phương thức AddAllDifferent cho queens(j) + j, chúng ta đặt N thực thể
của biến cho j từ 0 đến N-1 thành một mảng diag1 như sau:
q1 = model.NewIntVar(0, 2 * board_size, 'diag1_%i' % i) diag1.append(q1) model.Add(q1 == queens[j] + j)
Sau đó, chúng tôi áp dụng AddAllDifferent cho diag1.
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1)
Quy tắc ràng buộc cho queens(j) - j được tạo tương tự.
Tạo máy in giải pháp
Để in tất cả đáp án cho bài toán N-queens, bạn cần truyền một lệnh gọi lại, có tên là máy in giải pháp cho trình giải CP-SAT. Lệnh gọi lại in mỗi một giải pháp mới khi người giải tìm ra phương án đó. Đoạn mã sau đây tạo ra một giải pháp .
Python
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print()
C++
int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; }));
Java
static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; }
C#
public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; }
Lưu ý rằng máy in giải pháp phải được viết dưới dạng lớp Python, do Giao diện Python đến trình giải quyết C++ cơ bản.
Giải pháp được in bằng các dòng sau trong máy in giải pháp.
for v in self.__variables: print('%s = %i' % (v, self.Value(v)), end = ' ')
Trong ví dụ này, self.__variables là biến queens và mỗi v
tương ứng với một trong tám mục của queens. Thao tác này sẽ in một giải pháp trong
biểu mẫu sau: x0 = queens(0) x1 = queens(1) ... x7 = queens(7) trong đó
xi là số cột của hoàng hậu trong hàng i.
Phần tiếp theo trình bày một ví dụ về một giải pháp.
Gọi trình giải và hiện kết quả
Mã sau đây chạy trình giải và cho thấy đáp án.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer)
C++
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions;
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb);
C#
// Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb);
Chương trình tìm 92 giải pháp khác nhau cho một bảng 8x8. Đây là sự kiện đầu tiên.
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Solutions found: 92Bạn có thể giải bài toán cho một bảng có kích thước khác bằng cách truyền N dưới dạng một
đối số dòng lệnh. Ví dụ: nếu chương trình có tên là queens,
python nqueens_sat.py 6 giải bài toán cho một bảng 6x6.
Toàn bộ chương trình
Dưới đây là toàn bộ chương trình dành cho chương trình N-queens.
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() def main(board_size: int) -> None: # Creates the solver. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Creates the variables. # There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)) # Solve the model. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer) # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" conflicts : {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" wall time : {solver.wall_time} s") print(f" solutions found: {solution_printer.solution_count}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void NQueensSat(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. CpModelBuilder cp_model; // There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2); int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; })); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions; // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { if (!absl::SimpleAtoi(argv[1], &board_size)) { LOG(INFO) << "Cannot parse '" << argv[1] << "', using the default value of 8."; board_size = 8; } } operations_research::sat::NQueensSat(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; /** OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. */ public final class NQueensSat { static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; } public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Create the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2); // Create a solver and solve the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" conflicts : " + solver.numConflicts()); System.out.println(" branches : " + solver.numBranches()); System.out.println(" wall time : " + solver.wallTime() + " s"); System.out.println(" solutions : " + cb.getSolutionCount()); } private NQueensSat() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class NQueensSat { public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; } static void Main() { // Constraint programming engine CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
Giải pháp bằng trình giải quyết CP ban đầu
Các phần sau đây trình bày một chương trình Python để giải quyết N-queens bằng cách sử dụng công cụ giải quyết CP đầu tiên. (Tuy nhiên, bạn nên dùng trình giải CP-SAT mới hơn)
Nhập thư viện
Mã sau đây nhập thư viện bắt buộc.
Python
import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
C++
#include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
Khai báo trình giải
Mã sau đây khai báo trình giải quyết CP ban đầu.
Python
solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens")
C++
Solver solver("N-Queens");
Java
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
C#
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
Tạo biến
Phương thức IntVar của trình giải tạo các biến cho bài toán dưới dạng một mảng
có tên là queens.
Python
# The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
Đối với mọi giải pháp, queens[j] = i có nghĩa là có một nữ hoàng trong cột j và hàng
i.
Tạo các quy tắc ràng buộc
Dưới đây là mã tạo ra các quy tắc ràng buộc cho bài toán này.
Python
# All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)]))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2));
Java
// All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2));
C#
// All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent());
Những ràng buộc này đảm bảo ba điều kiện cho bài toán N-queens ( ông hoàng trên các hàng, cột và đường chéo khác nhau).
Không có hai nữ hoàng ở cùng một hàng
Áp dụng phương thức AllDifferent của trình giải cho queens buộc giá trị của
queens[j] phải khác nhau cho mỗi j, nghĩa là tất cả các hoàng hậu phải ở trong
hàng khác nhau.
Không có hai nữ hoàng trên cùng một cột
Quy tắc ràng buộc này được ngầm định trong định nghĩa của queens.
Vì không có hai phần tử nào của queens có thể có cùng chỉ mục nên không thể có hai hậu tố
trong cùng một cột.
Không có hai góc 2 phía trên cùng một đường chéo
Quy tắc ràng buộc về đường chéo phức tạp hơn một chút so với quy tắc ràng buộc đối với hàng và cột. Trước tiên, nếu hai hai cái nằm trên cùng một đường chéo thì một trong các điều kiện sau phải đúng:
- Nếu đường chéo giảm dần (từ trái sang phải), số hàng cộng với
số cột của mỗi quốc gia bằng nhau. Vì vậy,
queens(i) + icó cùng giá trị cho hai chỉ mục khác nhaui. - Nếu đường chéo tăng dần, số hàng trừ đi số cột của mỗi hàng
giữa hai hoàng hậu bằng nhau. Trong trường hợp này,
queens(i) - icó cùng giá trị cho hai chỉ mục khác nhaui.
Vì vậy, điều kiện ràng buộc về đường chéo là tất cả giá trị của queens(i) + i phải bằng
khác nhau và tương tự, giá trị của queens(i) - i phải khác nhau, đối với
i khác.
Mã trên thêm điều kiện ràng buộc này bằng cách áp dụng phương thức
AllDifferent
sang queens[j] + j và queens[j] - j cho từng i.
Thêm trình tạo quyết định
Bước tiếp theo là tạo một trình tạo quyết định để đặt chiến lược tìm kiếm cho sự cố. Chiến lược tìm kiếm có thể có tác động lớn đến thời gian tìm kiếm, do các hạn chế lan truyền, giúp làm giảm số lượng giá trị biến mà người giải phải khám phá. Bạn đã xem ví dụ về thành phần này trong Ví dụ về 4-queens.
Mã sau đây tạo một trình tạo quyết định bằng cách sử dụng trình giải quyết
Phase
.
Python
db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE)
C++
DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
Java
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
C#
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
Xem Trình tạo quyết định để biết thông tin chi tiết về
các đối số đầu vào cho phương thức Phase.
Cách hoạt động của trình tạo quyết định trong ví dụ 4-queens
Hãy xem cách trình tạo quyết định hướng dẫn tìm kiếm trong
Ví dụ về 4-queens.
Trình giải bắt đầu bằng queens[0], biến đầu tiên trong mảng, theo hướng dẫn
của CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND. Sau đó, trình giải sẽ chỉ định queens[0] giá trị nhỏ nhất
giá trị chưa được thử, là 0 ở giai đoạn này, theo chỉ dẫn của
ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE Thao tác này sẽ đặt hoàng hậu thứ nhất vào góc trên bên trái của
bảng.
Tiếp theo, trình giải quyết chọn queens[1], hiện là biến không liên kết đầu tiên trong
queens Sau khi áp dụng các điều kiện ràng buộc, có hai hàng cho một
nữ hoàng ở cột 1: hàng 2 hoặc hàng 3. Tùy chọn ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE chuyển hướng
để giao queens[1] = 2. (Nếu thay vào đó, bạn đặt IntValueStrategy thành
ASSIGN_MAX_VALUE, người giải sẽ chỉ định queens[1] = 3.)
Bạn có thể kiểm tra xem phần còn lại của nội dung tìm kiếm có tuân thủ các quy tắc tương tự không.
Gọi trình giải và hiện kết quả
Mã sau đây chạy trình giải và hiển thị đáp án.
Python
# Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch()
C++
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch();
Java
int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch();
C#
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch();
Đây là giải pháp đầu tiên mà chương trình này tìm ra cho bảng 8x8.
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Statistics
failures: 304
branches: 790
wall time: 5 ms
Solutions found: 92Bạn có thể giải bài toán cho một bảng có kích thước khác bằng cách truyền N dưới dạng
đối số dòng lệnh. Ví dụ: python nqueens_cp.py 6 giải bài toán này
cho bảng 6x6.
Toàn bộ chương trình
Chương trình hoàn chỉnh được trình bày dưới đây.
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp def main(board_size): # Creates the solver. solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens") # Creates the variables. # The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)])) db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE) # Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch() # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" failures: {solver.Failures()}") print(f" branches: {solver.Branches()}") print(f" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms") print(f" Solutions found: {num_solutions}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h" namespace operations_research { void NQueensCp(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver("N-Queens"); std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2)); DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << " failures: " << solver.failures(); LOG(INFO) << " branches: " << solver.branches(); LOG(INFO) << " wall time: " << solver.wall_time() << " ms"; LOG(INFO) << " Solutions found: " << num_solutions; } } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { board_size = std::atoi(argv[1]); } operations_research::NQueensCp(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver; /** N-Queens Problem. */ public final class NQueensCp { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2)); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch(); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" failures: " + solver.failures()); System.out.println(" branches: " + solver.branches()); System.out.println(" wall time: " + solver.wallTime() + "ms"); System.out.println(" Solutions found: " + solutionCount); } private NQueensCp() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver; public class NQueensCp { public static void Main(String[] args) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent()); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" failures: {solver.Failures()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches: {solver.Branches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms"); Console.WriteLine($" Solutions found: {SolutionCount}"); } }
Số giải pháp
Số lượng nghiệm tăng gần như theo cấp số nhân theo kích thước của bảng:
| Kích thước bảng | Giải pháp | Thời gian tìm tất cả đáp án (mili giây) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | 40 | 3 |
| 8 | 92 | 9 |
| 9 | 352 | 35 |
| 10 | 724 | 95 |
| 11 | 2680 | 378 |
| 12 | 14200 | 2198 |
| 13 | 73712 | 11628 |
| 14 | 365596 | 62427 |
| 15 | 2279184 | 410701 |
Nhiều nghiệm chỉ là phép quay khác và một kỹ thuật gọi là đối xứng có thể được sử dụng để giảm lượng phép tính cần thiết. Chúng tôi không sử dụng ở đây; giải pháp của chúng tôi ở trên không nhằm mục đích nhanh chóng, chỉ đơn giản. Tất nhiên, chúng tôi có thể làm cho trang web đó nhanh hơn nhiều nếu chỉ muốn tìm một giải pháp thay vì tất cả các báo cáo: không quá vài mili giây cho các kích thước bảng lên tới 50.
