בקטעים הבאים נמחיש את תכנות אילוצים (CP) באמצעות בעיה קומבינטורית שמבוססת על משחק השחמט. בשחמט, מלכה יכולה לתקוף לרוחב, לאורך ובאלכסון. בעיית מלכות ה-N שואלת:
איך אפשר למקם N מלכות על לוח שחמט של NxN כך שאף אחת מהן לא תוקפים זה את זה?
בהמשך מוצג פתרון אפשרי לבעיית ה-N-queens עבור N = 4.
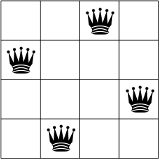
אין שתי מלכות באותה שורה, עמודה או אלכסון.
חשוב לזכור שזו לא בעיית אופטימיזציה: אנחנו רוצים למצוא את כל האפשרויות במקום פתרון אופטימלי אחד, וזה הופך אותו למועמד טבעי לתכנות אילוצים. בקטעים הבאים מתוארת גישת ה-CP לגבי בעיית ה-N- Quens. להציג תוכנות שפותרות אותו באמצעות פותר ה-CP-SAT וה-CP המקורי לפתור בעיות.
גישת CP לפתרון בעיית ה-N-queens
פותר בעיות שקשורות ל-CP פועל באופן שיטתי על ידי ניסיון של כל הקצאות אפשריות של ערכים למשתנים בבעיה, כדי למצוא לפתרונות אפשריים. בבעיה של 4 מלכות, הפותר מתחיל בפינה השמאלית ביותר ולאחר מכן מציבה מלכה אחת בכל עמודה, במיקום לא מותקף על ידי מלכות שהוצבו בעבר.
הפצה ומעקב לאחור
בחיפוש תכנות אילוצים יש שני אלמנטים מרכזיים:
- הפצה — בכל פעם שהפותר מקצה ערך למשתנה, האילוצים מוסיפים הגבלות על הערכים האפשריים של משתנים. ההגבלות האלה מופצות בהקצאות עתידיות של משתנים. לדוגמה, בבעיה של 4 מלכות, בכל פעם שהפותר מניח מלכה, היא לא יכולה למקם מלכות אחרות על השורה ואלכסונים שבהם מוצגת המלכה הנוכחית. ההפצה יכולה להאיץ את החיפוש באופן משמעותי על ידי צמצום משתנים שהפותר צריך לחקור.
- מעקב לאחור מתרחש כשהפותר לא יכול להקצות ערך לצד הבא עקב המגבלות, או שהוא מוצא פתרון. בכל מקרה, הפותר חוזר לשלב קודם ומשנה את ערך המשתנה את השלב הזה לערך שעדיין לא ניסה. בדוגמה של 4 מלכות, כלומר, העברה של מלכה לריבוע חדש בעמודה הנוכחית.
בשלב הבא נראה איך תכנות אילוצים משתמש בהפצה ובמעקב לאחור כדי פותרים את בעיית 4 המלכות.
נניח שהפותר מתחיל בהצבת מלכה באופן שרירותי בפינה השמאלית העליונה בפינה הימנית העליונה. זו השערה מסוג מסוים; אולי יתברר שאין פתרון קיים עם מלכה בפינה השמאלית העליונה.
בהתאם להשערה הזו, אילו אילוצים אנחנו יכולים להפיץ? אילוץ אחד הוא יכולה להיות רק מלכה אחת בעמודה (ה-X האפורים שלמטה), ועוד האילוץ אוסר על שתי מלכות על אותו אלכסון (ה-X האדומים בהמשך).
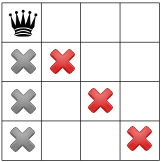
האילוץ השלישי שלנו אוסר על מלכות באותה שורה:
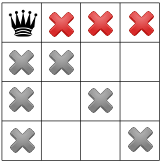
האילוצים שלנו הופצו, אנחנו יכולים לבדוק השערה נוספת, המלכה השנייה באחד מהריבועים הזמינים שנותרו. הפותר שלנו עשוי להחליט כדי להציב אותו בריבוע הזמין הראשון בעמודה השנייה:
לאחר הפצת האילוץ באלכסון, ניתן לראות שהוא לא הריבועים הזמינים בעמודה השלישית או בשורה האחרונה:
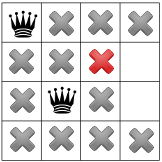
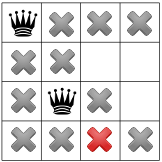
אין פתרונות אפשריים בשלב הזה, לכן עלינו לחזור אחורה. אפשרות אחת היא לפותר לבחור בריבוע הזמין האחר בעמודה השנייה. עם זאת, הפצת אילוצים מאלצת מלכה לעבור לשורה השנייה של את העמודה השלישית, כך שלא יהיו מקומות מתאימים למלכה הרביעית:
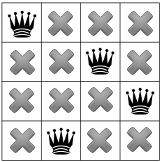
ולכן הפותר חייב לחזור אחורה, הפעם, עד של המלכה הראשונה. ראינו עכשיו שאין פתרון למלכות של הבעיה תתפוס ריבוע פינתי.
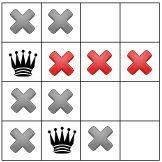
בגלל שאי אפשר של מלכה בפינה, הפותר מזיז את המלכה הראשונה בנפרד, ומופצת, כך שלמלכה השנייה נשארת רק מקום אחד:
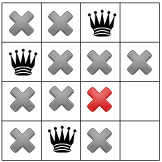
הפצה חוזרת תחשוף רק מקום אחד למלכה השלישית:
ולמלכה הרביעית והאחרונה:
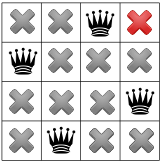
יש לנו את הפתרון הראשון שלנו! אם מורים לפותר שלנו להפסיק את התהליך אחרי שמוצאים בפתרון הראשון, הוא יסתיים כאן. אחרת, הוא יבצע שוב מעקב להציב את המלכה הראשונה בשורה השלישית של העמודה הראשונה.
פתרון באמצעות CP-SAT
בעיית ה-N-queens מתאימה אידיאלית לאילוץ בתכנות. כאן אני אעבור על תוכנית Python קצרה שמשתמשת בפותר CP-SAT כדי למצוא את כל הפתרונות לבעיה.
ייבוא הספריות
הקוד הבא מייבא את הספרייה הנדרשת.
Python
import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
C++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
להצהיר על המודל
הקוד הבא מציין את מודל CP-SAT.
Python
model = cp_model.CpModel()
C++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
Java
CpModel model = new CpModel();
C#
CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
יצירת המשתנים
הפותר יוצר את המשתנים של הבעיה כמערך בשם queens.
Python
# There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
// There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
כאן אנחנו מניחים ש-queens[j] הוא מספר השורה של המלכה בעמודה j.
במילים אחרות, המשמעות של queens[j] = i היא שיש מלכה בשורה i ובעמודה j.
יצירת האילוצים
זהו הקוד שיוצר את המגבלות לבעיה.
Python
# All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2);
Java
// All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2);
C#
// All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2);
הקוד משתמש בשיטה AddAllDifferent, שדורשת את כל הרכיבים של
של מערך המשתנים.
בואו נראה איך המגבלות האלה מבטיחים את שלושת התנאים למלכות ה-N (מלכות בשורות, בעמודות ובאלכסונים שונים).
אין שתי מלכות באותה שורה
החלת שיטת AllDifferent של הפתרון על queens מאלצת את הערכים של
queens[j] יהיה שונה לכל j, כלומר כל המלכות חייבות להיות
שורות שונות.
אין שתי מלכות באותה עמודה
האילוץ הזה משתמע מההגדרה של queens.
מכיוון שלשני יסודות של queens לא יכול להיות אותו אינדקס, אי אפשר להגדיר שתי מלכות
באותה עמודה.
אין שתי מלכות באותו אלכסון
מגבלת האלכסון קצת יותר מורכבת ממגבלות השורות והעמודות. ראשית, אם שתי מלכות נמצאות באותו אלכסון, אחד מהתנאים הבאים חייב להיות True:
- מספר השורה ומספר העמודה של כל אחת משתי המלכות שווים.
במילים אחרות, ל-
queens(j) + jיש ערך זהה בשני אינדקסים שוניםj. - מספר השורה פחות מספר העמודה של כל אחת משתי המלכות שווה.
במקרה הזה, ל-
queens(j) - jיש ערך זהה בשני אינדקסים שוניםj.
אחד מהתנאים האלה פירושו שהמלכות שוכנות באותו אלכסון עולה ( משמאל לימין), והשני פירושו שהם נמצאים באותו סדר באלכסון. איזה תנאי תואם לסדר עולה ואילו לתנאי יורד לסידור השורות והעמודות. כפי שצוין הקטע הקודם, לסדר אין השפעה על של העסק, רק באופן שבו אתם ממחישים אותם.
לכן האילוץ האלכסון הוא שהערכים של queens(j) + j חייבים להיות
שונה, והערכים של queens(j) - j חייבים להיות שונים,
j שונה.
כדי להחיל את השיטה AddAllDifferent על queens(j) + j, הוספנו את N מכונות
של המשתנה, עבור j מ-0 עד N-1, למערך, diag1, באופן הבא:
q1 = model.NewIntVar(0, 2 * board_size, 'diag1_%i' % i) diag1.append(q1) model.Add(q1 == queens[j] + j)
לאחר מכן נחיל את AddAllDifferent על diag1.
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1)
האילוץ עבור queens(j) - j נוצר באופן דומה.
יצירת מדפסת פתרונות
כדי להדפיס את כל הפתרונות לבעיית ה-N-queens, אתם צריכים להעביר קריאה חוזרת, שנקרא מדפסת פתרונות, לפותר הבעיות של CP-SAT. הקריאה החוזרת מדפיסה והפתרון החדש, הקוד הבא יוצר פתרון למדפסת.
Python
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print()
C++
int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; }));
Java
static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; }
C#
public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; }
הערה: צריך לכתוב את מדפסת הפתרון כמחלקה של Python, בגלל בממשק Python אל פותר C++ הבסיסי.
הפתרונות מודפסים לפי השורות הבאות במדפסת הפתרונות.
for v in self.__variables: print('%s = %i' % (v, self.Value(v)), end = ' ')
בדוגמה הזו, self.__variables הוא המשתנה queens, וכל v
תואם לאחת משמונה הערכים של queens. הפעולה הזו מדפיסה את הפתרון
בצורה הבאה: x0 = queens(0) x1 = queens(1) ... x7 = queens(7) כאשר
xi הוא מספר העמודה של המלכה בשורה i.
בקטע הבא מוצגת דוגמה לפתרון.
התקשרות לפותר והצגת התוצאות
הקוד הבא מפעיל את הפותר ומציג את הפתרונות.
Python
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer)
C++
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions;
Java
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb);
C#
// Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb);
התוכנית מוצאת 92 פתרונות שונים ללוח בגודל 8x8. הנה הראשון.
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Solutions found: 92ניתן לפתור את הבעיה עבור לוח בגודל אחר על ידי העברת N בתור
של הארגומנט בשורת הפקודה. לדוגמה, אם השם של התוכנה הוא queens,
python nqueens_sat.py 6 פותר את הבעיה עבור לוח בגודל 6x6.
התוכנית כולה
הנה התוכנית המלאה של תוכנית ה-N- Quens.
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback): """Print intermediate solutions.""" def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]): cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self) self.__queens = queens self.__solution_count = 0 self.__start_time = time.time() @property def solution_count(self) -> int: return self.__solution_count def on_solution_callback(self): current_time = time.time() print( f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, " f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s" ) self.__solution_count += 1 all_queens = range(len(self.__queens)) for i in all_queens: for j in all_queens: if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() def main(board_size: int) -> None: # Creates the solver. model = cp_model.CpModel() # Creates the variables. # There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column # of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)) # Solve the model. solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer) # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" conflicts : {solver.num_conflicts}") print(f" branches : {solver.num_branches}") print(f" wall time : {solver.wall_time} s") print(f" solutions found: {solution_printer.solution_count}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h" namespace operations_research { namespace sat { void NQueensSat(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. CpModelBuilder cp_model; // There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column // of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. std::vector<IntVar> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); Domain range(0, board_size - 1); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i); diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i); } cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1); cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2); int num_solutions = 0; Model model; model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) { LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; })); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions; // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response); } } // namespace sat } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { if (!absl::SimpleAtoi(argv[1], &board_size)) { LOG(INFO) << "Cannot parse '" << argv[1] << "', using the default value of 8."; board_size = 8; } } operations_research::sat::NQueensSat(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr; /** OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. */ public final class NQueensSat { static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) { solutionCount = 0; queens = queensIn; } @Override public void onSolutionCallback() { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) { if (value(queens[j]) == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != queens.length - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } public int getSolutionCount() { return solutionCount; } private int solutionCount; private final IntVar[] queens; } public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Create the model. CpModel model = new CpModel(); int boardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The // value of each variable is the row that the queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.addAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build(); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build(); } model.addAllDifferent(diag1); model.addAllDifferent(diag2); // Create a solver and solve the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" conflicts : " + solver.numConflicts()); System.out.println(" branches : " + solver.numBranches()); System.out.println(" wall time : " + solver.wallTime() + " s"); System.out.println(" solutions : " + cb.getSolutionCount()); } private NQueensSat() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat; public class NQueensSat { public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback { public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens) { queens_ = queens; } public override void OnSolutionCallback() { Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}"); for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j) { if (Value(queens_[j]) == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != queens_.Length - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount_++; } public int SolutionCount() { return SolutionCount_; } private int SolutionCount_; private IntVar[] queens_; } static void Main() { // Constraint programming engine CpModel model = new CpModel(); int BoardSize = 8; // There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each // column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the // queen is in. IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. model.AddAllDifferent(queens); // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i); diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i); } model.AddAllDifferent(diag1); model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); // Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb); Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s"); Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}"); } }
פתרון באמצעות פותר ה-CP המקורי
בקטעים הבאים מוצגת תוכנית Python שפותרת N- Quens באמצעות פותר ה-CP המקורי. (עם זאת, אנחנו ממליצים להשתמש בפותר CP-SAT החדש יותר)
ייבוא הספריות
הקוד הבא מייבא את הספרייה הנדרשת.
Python
import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
C++
#include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
להצהיר על הפתרון
הקוד הבא מצהיר על פותר ה-CP המקורי.
Python
solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens")
C++
Solver solver("N-Queens");
Java
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
C#
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
יצירת המשתנים
שיטת IntVar של הפתרון יוצרת את המשתנים של הבעיה כמערך
בשם queens.
Python
# The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
C++
std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); }
Java
int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); }
C#
const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); }
לכל פתרון, המשמעות של queens[j] = i היא שיש מלכה בעמודה j ובשורה
i.
יצירת האילוצים
זהו הקוד שיוצר את המגבלות לבעיה.
Python
# All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)]))
C++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2));
Java
// All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2));
C#
// All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent());
האילוצים האלה מבטיחים את שלושת התנאים לבעיית ה-N-Quens ( מלכות בשורות, בעמודות ובאלכסונים שונים).
אין שתי מלכות באותה שורה
החלת שיטת AllDifferent של הפתרון על queens מאלצת את הערכים של
queens[j] יהיה שונה לכל j, כלומר כל המלכות חייבות להיות
שורות שונות.
אין שתי מלכות באותה עמודה
האילוץ הזה משתמע מההגדרה של queens.
מכיוון שלשני יסודות של queens לא יכול להיות אותו אינדקס, אי אפשר להגדיר שתי מלכות
באותה עמודה.
אין שתי מלכות באותו אלכסון
מגבלת האלכסון קצת יותר מורכבת ממגבלות השורות והעמודות. ראשית, אם שתי מלכות נמצאות באותו אלכסון, צריך להתקיים אחד מהתנאים הבאים:
- אם האלכסון יורד (משמאל לימין), מספר השורה בתוספת
של כל אחת משתי המלכות שווה ערך. כלומר, ב-
queens(i) + iיש את אותו ערך לשני מדדים שוניםi. - אם האלכסון עולה, מספר השורה בניכוי מספר העמודה של כל אחת מהשורות
של שתי המלכות שוות. במקרה הזה, ל-
queens(i) - iיש אותו הערך לשני אינדקסים שוניםi.
לכן האילוץ האלכסון הוא שהערכים של queens(i) + i חייבים להיות
שונה, וכך גם הערכים של queens(i) - i צריכים להיות שונים,
i שונה.
הקוד שלמעלה מוסיף את האילוץ הזה על ידי החלת
AllDifferent
שיטה queens[j] + j ו-queens[j] - j לכל i.
הוספה של הכלי ליצירת החלטות
בשלב הבא יוצרים כלי ליצירת החלטות, שמגדיר את אסטרטגיית החיפוש. לבעיה. לאסטרטגיית החיפוש יכולה להיות השפעה משמעותית על זמן החיפוש, עקב הפצת מגבלות, שמפחיתה את מספר ערכי המשתנים שהפותר צריך לחקור. כבר ראית דוגמה לזה דוגמה של 4 מלכות.
הקוד הבא יוצר בונה החלטות באמצעות
Phase
.
Python
db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE)
C++
DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
Java
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
C#
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
לפרטים על
קלט ארגומנטים ל-method Phase.
איך פועל הכלי ליצירת החלטות בדוגמה של 4 מלכות
בואו נראה איך הכלי ליצירת החלטות מפנה את החיפוש
דוגמה של 4 מלכות.
הפותר מתחיל ב-queens[0], המשתנה הראשון במערך, כפי שמוסבר
מאת CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND. לאחר מכן, הפתרון מקצה את הערך הקטן ביותר של queens[0]
שעדיין לא נוסה, שהוא 0 בשלב זה, כפי שנקבע על ידי
ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE. היא מניחה את המלכה הראשונה בפינה השמאלית העליונה של
לוח.
בשלב הבא, הפותר בוחר את queens[1], שהוא עכשיו המשתנה הלא-מקושר הראשון
queens. לאחר הפצת המגבלות, יש שתי שורות אפשריות
מלכה בעמודה 1: שורה 2 או שורה 3. האפשרות ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE קובעת
פותר כדי להקצות את queens[1] = 2. (אם במקום זאת, צריך להגדיר את IntValueStrategy לערך
ASSIGN_MAX_VALUE, הפתרון יקצה queens[1] = 3.)
תוכלו לוודא ששאר הכללים של החיפוש עומדים באותם הכללים.
התקשרות לפותר והצגת התוצאות
הקוד הבא מפעיל את הפותר ומציג את הפתרון.
Python
# Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch()
C++
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch();
Java
int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch();
C#
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch();
זה הפתרון הראשון שתוכנה מצאה ללוח בגודל 8x8.
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Statistics
failures: 304
branches: 790
wall time: 5 ms
Solutions found: 92ניתן לפתור את הבעיה עבור לוח בגודל אחר על ידי העברת N בתור
של הארגומנט בשורת הפקודה. לדוגמה, python nqueens_cp.py 6 פותר את הבעיה
ללוח בגודל 6x6.
התוכנית כולה
התוכנית המלאה מוצגת למטה.
Python
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.""" import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp def main(board_size): # Creates the solver. solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens") # Creates the variables. # The array index is the column, and the value is the row. queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)] # Creates the constraints. # All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)])) db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE) # Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. num_solutions = 0 solver.NewSearch(db) while solver.NextSolution(): # Displays the solution just computed. for i in range(board_size): for j in range(board_size): if queens[j].Value() == i: # There is a queen in column j, row i. print("Q", end=" ") else: print("_", end=" ") print() print() num_solutions += 1 solver.EndSearch() # Statistics. print("\nStatistics") print(f" failures: {solver.Failures()}") print(f" branches: {solver.Branches()}") print(f" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms") print(f" Solutions found: {num_solutions}") if __name__ == "__main__": # By default, solve the 8x8 problem. size = 8 if len(sys.argv) > 1: size = int(sys.argv[1]) main(size)
C++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. #include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h" namespace operations_research { void NQueensCp(const int board_size) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver("N-Queens"); std::vector<IntVar*> queens; queens.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { queens.push_back( solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i))); } // Define constraints. // The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows. solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all // different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal. std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1; diag_1.reserve(board_size); std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2; diag_2.reserve(board_size); for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var()); diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var()); } solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1)); solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2)); DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase( queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int num_solutions = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { // Displays the solution just computed. LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions; for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) { std::stringstream ss; for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) { if (queens[j]->Value() == i) { // There is a queen in column j, row i. ss << "Q"; } else { ss << "_"; } if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " "; } LOG(INFO) << ss.str(); } num_solutions++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. LOG(INFO) << "Statistics"; LOG(INFO) << " failures: " << solver.failures(); LOG(INFO) << " branches: " << solver.branches(); LOG(INFO) << " wall time: " << solver.wall_time() << " ms"; LOG(INFO) << " Solutions found: " << num_solutions; } } // namespace operations_research int main(int argc, char** argv) { int board_size = 8; if (argc > 1) { board_size = std::atoi(argv[1]); } operations_research::NQueensCp(board_size); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
Java
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples; import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver; /** N-Queens Problem. */ public final class NQueensCp { public static void main(String[] args) { Loader.loadNativeLibraries(); // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); int boardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens)); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var(); diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var(); } solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1)); solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2)); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. final DecisionBuilder db = solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); int solutionCount = 0; solver.newSearch(db); while (solver.nextSolution()) { System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].value() == i) { System.out.print("Q"); } else { System.out.print("_"); } if (j != boardSize - 1) { System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } solutionCount++; } solver.endSearch(); // Statistics. System.out.println("Statistics"); System.out.println(" failures: " + solver.failures()); System.out.println(" branches: " + solver.branches()); System.out.println(" wall time: " + solver.wallTime() + "ms"); System.out.println(" Solutions found: " + solutionCount); } private NQueensCp() {} }
C#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver; public class NQueensCp { public static void Main(String[] args) { // Instantiate the solver. Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens"); const int BoardSize = 8; IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}"); } // Define constraints. // All rows must be different. solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent()); // All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different. // No two queens can be on the same diagonal. IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize]; for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var(); diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var(); } solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent()); solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent()); // Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE); // Iterates through the solutions, displaying each. int SolutionCount = 0; solver.NewSearch(db); while (solver.NextSolution()) { Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount); for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j) { if (queens[j].Value() == i) { Console.Write("Q"); } else { Console.Write("_"); } if (j != BoardSize - 1) Console.Write(" "); } Console.WriteLine(""); } SolutionCount++; } solver.EndSearch(); // Statistics. Console.WriteLine("Statistics"); Console.WriteLine($" failures: {solver.Failures()}"); Console.WriteLine($" branches: {solver.Branches()}"); Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms"); Console.WriteLine($" Solutions found: {SolutionCount}"); } }
מספר הפתרונות
מספר הפתרונות גדל בצורה אקספוננציאלית, בקירוב, בהתאם לגודל הלוח:
| גודל הלוחות | פתרונות | זמן למציאת כל הפתרונות (באלפיות השנייה) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | 40 | 3 |
| 8 | 92 | 9 |
| 9 | 352 | 35 |
| 10 | 724 | 95 |
| 11 | 2680 | 378 |
| 12 | 14200 | 2198 |
| 13 | 73712 | 11628 |
| 14 | 365596 | 62427 |
| 15 | 2279184 | 410701 |
פתרונות רבים הם פשוט סיבובים של אחרים, ושיטה שנקראת סימטריה יכולה לשמש להפחתת כמות החישובים שנדרשים. אנחנו לא משתמשים שכאן, הפתרון שלנו שלמעלה לא נועד להיות מהיר, פשוט פשוט. כמובן, נוכל להאיץ הרבה יותר אם נרצה למצוא רק פתרון אחד במקום את כולם: מספר אלפיות השנייה לכל היותר עבור גודל של עד 50 לוח.
