নিম্নলিখিত বিভাগে, আমরা দাবা খেলার উপর ভিত্তি করে একটি সমন্বিত সমস্যা দ্বারা সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রোগ্রামিং (CP) চিত্রিত করব। দাবায়, একজন রানী অনুভূমিকভাবে, উল্লম্বভাবে এবং তির্যকভাবে আক্রমণ করতে পারে। এন-কুইন্স সমস্যা জিজ্ঞাসা করে:
কিভাবে এন রানীদের একটি NxN চেসবোর্ডে স্থাপন করা যেতে পারে যাতে তাদের দুজন একে অপরকে আক্রমণ না করে?
নীচে, আপনি N = 4 এর জন্য N-queens সমস্যার একটি সম্ভাব্য সমাধান দেখতে পারেন।
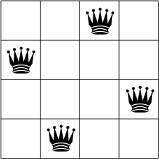
কোন দুই রানী একই সারি, কলাম বা তির্যক নয়।
মনে রাখবেন যে এটি একটি অপ্টিমাইজেশান সমস্যা নয়: আমরা একটি সর্বোত্তম সমাধানের পরিবর্তে সমস্ত সম্ভাব্য সমাধান খুঁজতে চাই, যা এটিকে সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রোগ্রামিংয়ের জন্য একটি প্রাকৃতিক প্রার্থী করে তোলে। নিম্নলিখিত বিভাগগুলি এন-কুইন্স সমস্যার CP পদ্ধতির বর্ণনা করে এবং CP-SAT সমাধানকারী এবং আসল CP সমাধানকারী উভয় ব্যবহার করে এটি সমাধান করে এমন প্রোগ্রামগুলি উপস্থাপন করে।
এন-কুইন্স সমস্যায় সিপি পন্থা
একটি CP সমাধানকারী একটি সমস্যায় ভেরিয়েবলের সমস্ত সম্ভাব্য অ্যাসাইনমেন্ট পদ্ধতিগতভাবে চেষ্টা করে, সম্ভাব্য সমাধানগুলি খুঁজে বের করার জন্য কাজ করে। 4-রানী সমস্যায়, সমাধানকারীটি বামদিকের কলাম থেকে শুরু হয় এবং পর্যায়ক্রমে প্রতিটি কলামে একটি করে রানী স্থাপন করে, এমন একটি স্থানে যা পূর্বে রাখা কোনো রানী দ্বারা আক্রান্ত হয় না।
প্রচার এবং ব্যাকট্র্যাকিং
একটি সীমাবদ্ধ প্রোগ্রামিং অনুসন্ধানের দুটি মূল উপাদান রয়েছে:
- প্রচার - প্রতিবার সমাধানকারী একটি ভেরিয়েবলের জন্য একটি মান নির্ধারণ করে, সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলি অনির্ধারিত ভেরিয়েবলের সম্ভাব্য মানগুলির উপর সীমাবদ্ধতা যুক্ত করে। এই নিষেধাজ্ঞাগুলি ভবিষ্যতের পরিবর্তনশীল অ্যাসাইনমেন্টগুলিতে প্রচারিত হয় । উদাহরণস্বরূপ, 4-রানীর সমস্যায়, প্রতিবার সমাধানকারী রাণীকে স্থাপন করলে, এটি বর্তমান রানী চালু থাকা সারি এবং তির্যকগুলিতে অন্য কোনো রানী স্থাপন করতে পারে না। সলভারের অন্বেষণ করা আবশ্যক পরিবর্তনশীল মানগুলির সেট হ্রাস করে প্রচারটি অনুসন্ধানকে উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে ত্বরান্বিত করতে পারে।
- ব্যাকট্র্যাকিং ঘটে যখন হয় সমাধানকারী পরবর্তী ভেরিয়েবলের জন্য একটি মান নির্ধারণ করতে পারে না, সীমাবদ্ধতার কারণে, বা এটি একটি সমাধান খুঁজে পায়। উভয় ক্ষেত্রেই, সমাধানকারী পূর্ববর্তী পর্যায়ে ফিরে যায় এবং সেই পর্যায়ে ভেরিয়েবলের মানকে এমন একটি মানতে পরিবর্তন করে যা ইতিমধ্যে চেষ্টা করা হয়নি। 4-রানী উদাহরণে, এর অর্থ বর্তমান কলামের একটি নতুন বর্গক্ষেত্রে একটি রানীকে সরানো৷
এরপরে, আপনি দেখতে পাবেন কিভাবে সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রোগ্রামিং 4-রানী সমস্যা সমাধানের জন্য প্রচার এবং ব্যাকট্র্যাকিং ব্যবহার করে।
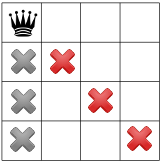
ধরুন সমাধানকারীটি ইচ্ছামত উপরের বাম কোণায় একটি রানী স্থাপন করে শুরু করে। এটা একধরনের অনুমান; সম্ভবত এটি চালু হবে যে উপরের বাম কোণে একটি রাণীর সাথে কোন সমাধান বিদ্যমান নেই।
এই অনুমান দেওয়া, আমরা কি সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রচার করতে পারি? একটি সীমাবদ্ধতা হল একটি কলামে শুধুমাত্র একটি রাণী থাকতে পারে (নীচের ধূসর Xs), এবং আরেকটি সীমাবদ্ধতা একই তির্যক (নীচে লাল Xs) দুটি রাণীকে নিষিদ্ধ করে।
আমাদের তৃতীয় সীমাবদ্ধতা একই সারিতে রাণীদের নিষিদ্ধ করে:
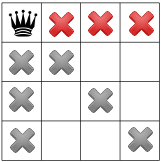
আমাদের সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রচারিত হয়েছে, আমরা অন্য একটি অনুমান পরীক্ষা করতে পারি এবং উপলব্ধ অবশিষ্ট স্কোয়ারগুলির একটিতে দ্বিতীয় রানী স্থাপন করতে পারি। আমাদের সমাধানকারী এটিতে দ্বিতীয় কলামের প্রথম উপলব্ধ বর্গক্ষেত্রটি রাখার সিদ্ধান্ত নিতে পারে:
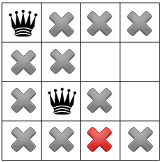
তির্যক সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রচার করার পরে, আমরা দেখতে পাচ্ছি যে এটি তৃতীয় কলাম বা শেষ সারিতে কোনও উপলব্ধ স্কোয়ার ছেড়ে যায় না:
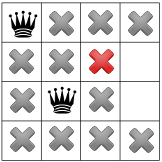
এই পর্যায়ে কোন সমাধান সম্ভব না থাকায়, আমাদের পিছিয়ে যেতে হবে। একটি বিকল্প হল সমাধানকারীর জন্য দ্বিতীয় কলামে অন্য উপলব্ধ বর্গক্ষেত্রটি বেছে নেওয়ার জন্য। যাইহোক, সীমাবদ্ধতা প্রচারের ফলে একজন রানীকে তৃতীয় কলামের দ্বিতীয় সারিতে নিয়ে যেতে বাধ্য করে, চতুর্থ রাণীর জন্য কোনো বৈধ দাগ থাকে না:
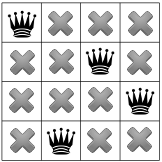
এবং তাই সমাধানকারীকে আবার পিছিয়ে যেতে হবে, এইবার প্রথম রাণীর স্থান নির্ধারণে ফিরে যেতে হবে। আমরা এখন দেখিয়েছি যে রাণী সমস্যার কোন সমাধান কোণার বর্গক্ষেত্র দখল করবে না।
যেহেতু কোণে কোন রানী থাকতে পারে না, তাই সমাধানকারী প্রথম রানীকে এক করে নিচে নিয়ে যায় এবং প্রচার করে, দ্বিতীয় রানীর জন্য শুধুমাত্র একটি স্থান রেখে দেয়:
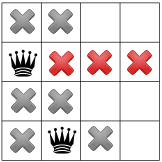
আবার প্রচার করা তৃতীয় রানীর জন্য শুধুমাত্র একটি স্থান অবশিষ্ট প্রকাশ করে:
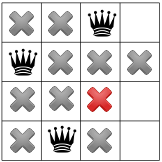
এবং চতুর্থ এবং চূড়ান্ত রানীর জন্য:
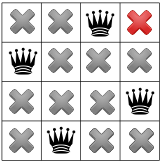
আমরা আমাদের প্রথম সমাধান আছে! যদি আমরা আমাদের সমাধানকারীকে প্রথম সমাধান খোঁজার পরে থামতে নির্দেশ দিই, তাহলে এটি এখানেই শেষ হবে। অন্যথায়, এটি আবার পিছিয়ে যাবে এবং প্রথম রাণীকে প্রথম কলামের তৃতীয় সারিতে রাখবে।
CP-SAT ব্যবহার করে সমাধান
এন-কুইন্স সমস্যাটি সীমাবদ্ধ প্রোগ্রামিংয়ের জন্য আদর্শভাবে উপযুক্ত। এই বিভাগে আমরা একটি সংক্ষিপ্ত পাইথন প্রোগ্রামের মাধ্যমে হেঁটে যাব যা সমস্যার সমস্ত সমাধান খুঁজে পেতে CP-SAT সমাধানকারী ব্যবহার করে।
লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোড প্রয়োজনীয় লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করে।
পাইথন
import sys import time from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
সি++
#include <stdlib.h> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include "absl/strings/numbers.h" #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h" #include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h" #include "ortools/sat/model.h" #include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h" #include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h"
জাভা
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver; import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback; import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr;
সি#
using System; using Google.OrTools.Sat;
মডেল ঘোষণা করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোডটি CP-SAT মডেল ঘোষণা করে।
পাইথন
model = cp_model.CpModel()
সি++
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
জাভা
CpModel model = new CpModel();
সি#
CpModel model = new CpModel();
int BoardSize = 8;
// There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each
// column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the
// queen is in.
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}");
}
// Define constraints.
// All rows must be different.
model.AddAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i);
diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i);
}
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1);
model.AddAllDifferent(diag2);
// Creates a solver and solves the model.
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver();
SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens);
// Search for all solutions.
solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true";
// And solve.
solver.Solve(model, cb);
Console.WriteLine("Statistics");
Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}");
Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}");
Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s");
Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}");
}
}
ভেরিয়েবল তৈরি করুন
সমাধানকারীরা queens নামের একটি অ্যারে হিসাবে সমস্যার জন্য ভেরিয়েবল তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
# There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column
# of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)]সি++
// There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column
// of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
std::vector<IntVar> queens;
queens.reserve(board_size);
Domain range(0, board_size - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
queens.push_back(
cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i)));
}জাভা
int boardSize = 8;
// There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The
// value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i);
}সি#
int BoardSize = 8;
// There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each
// column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the
// queen is in.
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}");
} এখানে আমরা অনুমান করি যে queens[j] হল j কলামে রানীর সারি সংখ্যা। অন্য কথায়, queens[j] = i মানে সারি i এবং কলাম j এ একজন রাণী আছে।
সীমাবদ্ধতা তৈরি করুন
এখানে কোড যা সমস্যার জন্য সীমাবদ্ধতা তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
# All rows must be different. model.add_all_different(queens) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)) model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size))
সি++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows.
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1;
diag_1.reserve(board_size);
std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2;
diag_2.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i);
diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i);
}
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1);
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2);জাভা
// All rows must be different.
model.addAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize];
LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build();
diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build();
}
model.addAllDifferent(diag1);
model.addAllDifferent(diag2);সি#
// All rows must be different.
model.AddAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i);
diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i);
}
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1);
model.AddAllDifferent(diag2); কোডটি AddAllDifferent পদ্ধতি ব্যবহার করে, যার জন্য একটি পরিবর্তনশীল অ্যারের সমস্ত উপাদান আলাদা হতে হবে।
আসুন দেখি কিভাবে এই সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলি এন-কুইন্স সমস্যার জন্য তিনটি শর্তের গ্যারান্টি দেয় (বিভিন্ন সারি, কলাম এবং তির্যকগুলিতে রাণী)।
একই সারিতে দুই রানী নেই
queens জন্য সমাধানকারীর AllDifferent পদ্ধতি প্রয়োগ করা প্রতিটি j এর জন্য queens[j] মানগুলিকে আলাদা হতে বাধ্য করে, যার মানে হল যে সমস্ত রাণীকে অবশ্যই ভিন্ন সারিতে থাকতে হবে।
একই কলামে দুই রানী নেই
এই সীমাবদ্ধতা queens সংজ্ঞায় নিহিত। যেহেতু queens কোন দুটি উপাদানের একই সূচক থাকতে পারে না, তাই কোন দুটি রাণী একই কলামে থাকতে পারে না।
একই তির্যক উপর কোন দুই রানী
তির্যক সীমাবদ্ধতা সারি এবং কলামের সীমাবদ্ধতার চেয়ে একটু জটিল। প্রথমত, যদি দুটি রাণী একই তির্যক উপর শুয়ে থাকে, তাহলে নিম্নলিখিত শর্তগুলির মধ্যে একটি সত্য হতে হবে:
- দুই রানীর প্রত্যেকের জন্য সারি সংখ্যা এবং কলাম সংখ্যা সমান। অন্য কথায়,
queens(j) + jদুটি ভিন্ন সূচকjএর জন্য একই মান রয়েছে। - দুই রানীর প্রত্যেকের জন্য সারি সংখ্যা বিয়োগ কলাম সংখ্যা সমান। এই ক্ষেত্রে,
queens(j) - jদুটি ভিন্ন সূচকjএর জন্য একই মান আছে।
এই শর্তগুলির মধ্যে একটির অর্থ হল রাণীরা একই আরোহী কর্ণের উপর শুয়ে থাকে (বাম থেকে ডানে যায়), অন্যটি মানে তারা একই অবরোহী কর্ণের উপর শুয়ে থাকে। কোন অবস্থার সাথে আরোহী এবং কোনটি অবরোহের সাথে মিল রয়েছে তা নির্ভর করে আপনি কীভাবে সারি এবং কলামগুলিকে অর্ডার করবেন তার উপর৷ পূর্ববর্তী বিভাগে উল্লিখিত হিসাবে, সমাধানের সেটের উপর অর্ডারের কোন প্রভাব নেই, আপনি কীভাবে সেগুলিকে কল্পনা করেন তার উপর।
সুতরাং তির্যক সীমাবদ্ধতা হল যে queens(j) + j এর মানগুলি অবশ্যই আলাদা হতে হবে, এবং queens(j) - j এর মানগুলি অবশ্যই আলাদা হতে হবে, বিভিন্ন j এর জন্য।
queens(j) + j এ AddAllDifferent পদ্ধতি প্রয়োগ করতে, আমরা ভেরিয়েবলের N দৃষ্টান্তগুলি রাখি, j 0 N-1 পর্যন্ত, একটি অ্যারেতে, diag1 , নিম্নরূপ:
q1 = model.NewIntVar(0, 2 * board_size, 'diag1_%i' % i) diag1.append(q1) model.Add(q1 == queens[j] + j)
তারপর আমরা diag1 এ AddAllDifferent প্রয়োগ করি।
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1)
queens(j) - j এর জন্য সীমাবদ্ধতা একইভাবে তৈরি করা হয়েছে।
একটি সমাধান প্রিন্টার তৈরি করুন
এন-কুইন্স সমস্যার সমস্ত সমাধান প্রিন্ট করতে, আপনাকে CP-SAT সমাধানকারীর কাছে একটি কলব্যাক পাস করতে হবে, যাকে একটি সমাধান প্রিন্টার বলা হয়। কলব্যাক প্রতিটি নতুন সমাধান প্রিন্ট করে যেমন সমাধানকারী এটি খুঁজে পায়। নিম্নলিখিত কোড একটি সমাধান প্রিন্টার তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
"""Print intermediate solutions."""
def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__queens = queens
self.__solution_count = 0
self.__start_time = time.time()
@property
def solution_count(self) -> int:
return self.__solution_count
def on_solution_callback(self):
current_time = time.time()
print(
f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, "
f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s"
)
self.__solution_count += 1
all_queens = range(len(self.__queens))
for i in all_queens:
for j in all_queens:
if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i:
# There is a queen in column j, row i.
print("Q", end=" ")
else:
print("_", end=" ")
print()
print()
সি++
int num_solutions = 0;
Model model;
model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) {
LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions;
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
std::stringstream ss;
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) {
if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) {
// There is a queen in column j, row i.
ss << "Q";
} else {
ss << "_";
}
if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " ";
}
LOG(INFO) << ss.str();
}
num_solutions++;
}));জাভা
static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback {
public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) {
solutionCount = 0;
queens = queensIn;
}
@Override
public void onSolutionCallback() {
System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) {
if (value(queens[j]) == i) {
System.out.print("Q");
} else {
System.out.print("_");
}
if (j != queens.length - 1) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
solutionCount++;
}
public int getSolutionCount() {
return solutionCount;
}
private int solutionCount;
private final IntVar[] queens;
}সি#
public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback
{
public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens)
{
queens_ = queens;
}
public override void OnSolutionCallback()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}");
for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j)
{
if (Value(queens_[j]) == i)
{
Console.Write("Q");
}
else
{
Console.Write("_");
}
if (j != queens_.Length - 1)
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
SolutionCount_++;
}
public int SolutionCount()
{
return SolutionCount_;
}
private int SolutionCount_;
private IntVar[] queens_;
}মনে রাখবেন যে সমাধান প্রিন্টারকে অবশ্যই পাইথন ক্লাস হিসাবে লিখতে হবে, পাইথন ইন্টারফেসের কারণে অন্তর্নিহিত C++ সমাধানকারী।
সমাধানগুলি সমাধান প্রিন্টারে নিম্নলিখিত লাইনগুলি দ্বারা মুদ্রিত হয়।
for v in self.__variables:
print('%s = %i' % (v, self.Value(v)), end = ' ') এই উদাহরণে, self.__variables হল পরিবর্তনশীল queens , এবং প্রতিটি v queens আটটি এন্ট্রির একটির সাথে মিলে যায়। এটি নিম্নলিখিত আকারে একটি সমাধান প্রিন্ট করে: x0 = queens(0) x1 = queens(1) ... x7 = queens(7) যেখানে xi হল i সারিতে থাকা রানীর কলাম নম্বর।
পরবর্তী বিভাগে সমাধানের একটি উদাহরণ দেখায়।
সমাধানকারীকে কল করুন এবং ফলাফল প্রদর্শন করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোড সমাধানকারী চালায় এবং সমাধান প্রদর্শন করে।
পাইথন
solver = cp_model.CpSolver() solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens) solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True solver.solve(model, solution_printer)
সি++
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. SatParameters parameters; parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true); model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters)); const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model); LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions;
জাভা
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions. solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true); // And solve. solver.solve(model, cb);
সি#
// Creates a solver and solves the model. CpSolver solver = new CpSolver(); SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens); // Search for all solutions. solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true"; // And solve. solver.Solve(model, cb);
প্রোগ্রামটি একটি 8x8 বোর্ডের জন্য 92টি ভিন্ন সমাধান খুঁজে পায়। এখানে প্রথম এক.
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Solutions found: 92 আপনি কমান্ড-লাইন আর্গুমেন্ট হিসাবে N পাস করে একটি ভিন্ন আকারের একটি বোর্ডের জন্য সমস্যার সমাধান করতে পারেন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, যদি প্রোগ্রামটির নাম হয় queens , python nqueens_sat.py 6 একটি 6x6 বোর্ডের সমস্যার সমাধান করে।
পুরো প্রোগ্রাম
এখানে এন-কুইন্স প্রোগ্রামের জন্য সম্পূর্ণ প্রোগ্রাম।
পাইথন
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem."""
import sys
import time
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
class NQueenSolutionPrinter(cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback):
"""Print intermediate solutions."""
def __init__(self, queens: list[cp_model.IntVar]):
cp_model.CpSolverSolutionCallback.__init__(self)
self.__queens = queens
self.__solution_count = 0
self.__start_time = time.time()
@property
def solution_count(self) -> int:
return self.__solution_count
def on_solution_callback(self):
current_time = time.time()
print(
f"Solution {self.__solution_count}, "
f"time = {current_time - self.__start_time} s"
)
self.__solution_count += 1
all_queens = range(len(self.__queens))
for i in all_queens:
for j in all_queens:
if self.value(self.__queens[j]) == i:
# There is a queen in column j, row i.
print("Q", end=" ")
else:
print("_", end=" ")
print()
print()
def main(board_size: int) -> None:
# Creates the solver.
model = cp_model.CpModel()
# Creates the variables.
# There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column
# of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
queens = [model.new_int_var(0, board_size - 1, f"x_{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
# Creates the constraints.
# All rows must be different.
model.add_all_different(queens)
# No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
model.add_all_different(queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size))
model.add_all_different(queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size))
# Solve the model.
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
solution_printer = NQueenSolutionPrinter(queens)
solver.parameters.enumerate_all_solutions = True
solver.solve(model, solution_printer)
# Statistics.
print("\nStatistics")
print(f" conflicts : {solver.num_conflicts}")
print(f" branches : {solver.num_branches}")
print(f" wall time : {solver.wall_time} s")
print(f" solutions found: {solution_printer.solution_count}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# By default, solve the 8x8 problem.
size = 8
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
size = int(sys.argv[1])
main(size)সি++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include "absl/strings/numbers.h"
#include "ortools/base/logging.h"
#include "ortools/sat/cp_model.h"
#include "ortools/sat/cp_model.pb.h"
#include "ortools/sat/cp_model_solver.h"
#include "ortools/sat/model.h"
#include "ortools/sat/sat_parameters.pb.h"
#include "ortools/util/sorted_interval_list.h"
namespace operations_research {
namespace sat {
void NQueensSat(const int board_size) {
// Instantiate the solver.
CpModelBuilder cp_model;
// There are `board_size` number of variables, one for a queen in each column
// of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
std::vector<IntVar> queens;
queens.reserve(board_size);
Domain range(0, board_size - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
queens.push_back(
cp_model.NewIntVar(range).WithName("x" + std::to_string(i)));
}
// Define constraints.
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows.
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_1;
diag_1.reserve(board_size);
std::vector<LinearExpr> diag_2;
diag_2.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
diag_1.push_back(queens[i] + i);
diag_2.push_back(queens[i] - i);
}
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_1);
cp_model.AddAllDifferent(diag_2);
int num_solutions = 0;
Model model;
model.Add(NewFeasibleSolutionObserver([&](const CpSolverResponse& response) {
LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions;
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
std::stringstream ss;
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) {
if (SolutionIntegerValue(response, queens[j]) == i) {
// There is a queen in column j, row i.
ss << "Q";
} else {
ss << "_";
}
if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " ";
}
LOG(INFO) << ss.str();
}
num_solutions++;
}));
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions.
SatParameters parameters;
parameters.set_enumerate_all_solutions(true);
model.Add(NewSatParameters(parameters));
const CpSolverResponse response = SolveCpModel(cp_model.Build(), &model);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of solutions found: " << num_solutions;
// Statistics.
LOG(INFO) << "Statistics";
LOG(INFO) << CpSolverResponseStats(response);
}
} // namespace sat
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int board_size = 8;
if (argc > 1) {
if (!absl::SimpleAtoi(argv[1], &board_size)) {
LOG(INFO) << "Cannot parse '" << argv[1]
<< "', using the default value of 8.";
board_size = 8;
}
}
operations_research::sat::NQueensSat(board_size);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}জাভা
package com.google.ortools.sat.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.sat.CpModel;
import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolver;
import com.google.ortools.sat.CpSolverSolutionCallback;
import com.google.ortools.sat.IntVar;
import com.google.ortools.sat.LinearExpr;
/** OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem. */
public final class NQueensSat {
static class SolutionPrinter extends CpSolverSolutionCallback {
public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queensIn) {
solutionCount = 0;
queens = queensIn;
}
@Override
public void onSolutionCallback() {
System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < queens.length; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < queens.length; ++j) {
if (value(queens[j]) == i) {
System.out.print("Q");
} else {
System.out.print("_");
}
if (j != queens.length - 1) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
solutionCount++;
}
public int getSolutionCount() {
return solutionCount;
}
private int solutionCount;
private final IntVar[] queens;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Create the model.
CpModel model = new CpModel();
int boardSize = 8;
// There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each column of the board. The
// value of each variable is the row that the queen is in.
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
queens[i] = model.newIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i);
}
// Define constraints.
// All rows must be different.
model.addAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[boardSize];
LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
diag1[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(i).build();
diag2[i] = LinearExpr.newBuilder().add(queens[i]).add(-i).build();
}
model.addAllDifferent(diag1);
model.addAllDifferent(diag2);
// Create a solver and solve the model.
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver();
SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens);
// Tell the solver to enumerate all solutions.
solver.getParameters().setEnumerateAllSolutions(true);
// And solve.
solver.solve(model, cb);
// Statistics.
System.out.println("Statistics");
System.out.println(" conflicts : " + solver.numConflicts());
System.out.println(" branches : " + solver.numBranches());
System.out.println(" wall time : " + solver.wallTime() + " s");
System.out.println(" solutions : " + cb.getSolutionCount());
}
private NQueensSat() {}
}সি#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.
using System;
using Google.OrTools.Sat;
public class NQueensSat
{
public class SolutionPrinter : CpSolverSolutionCallback
{
public SolutionPrinter(IntVar[] queens)
{
queens_ = queens;
}
public override void OnSolutionCallback()
{
Console.WriteLine($"Solution {SolutionCount_}");
for (int i = 0; i < queens_.Length; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < queens_.Length; ++j)
{
if (Value(queens_[j]) == i)
{
Console.Write("Q");
}
else
{
Console.Write("_");
}
if (j != queens_.Length - 1)
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
SolutionCount_++;
}
public int SolutionCount()
{
return SolutionCount_;
}
private int SolutionCount_;
private IntVar[] queens_;
}
static void Main()
{
// Constraint programming engine
CpModel model = new CpModel();
int BoardSize = 8;
// There are `BoardSize` number of variables, one for a queen in each
// column of the board. The value of each variable is the row that the
// queen is in.
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
queens[i] = model.NewIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}");
}
// Define constraints.
// All rows must be different.
model.AddAllDifferent(queens);
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
LinearExpr[] diag1 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
LinearExpr[] diag2 = new LinearExpr[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
diag1[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/i);
diag2[i] = LinearExpr.Affine(queens[i], /*coeff=*/1, /*offset=*/-i);
}
model.AddAllDifferent(diag1);
model.AddAllDifferent(diag2);
// Creates a solver and solves the model.
CpSolver solver = new CpSolver();
SolutionPrinter cb = new SolutionPrinter(queens);
// Search for all solutions.
solver.StringParameters = "enumerate_all_solutions:true";
// And solve.
solver.Solve(model, cb);
Console.WriteLine("Statistics");
Console.WriteLine($" conflicts : {solver.NumConflicts()}");
Console.WriteLine($" branches : {solver.NumBranches()}");
Console.WriteLine($" wall time : {solver.WallTime()} s");
Console.WriteLine($" number of solutions found: {cb.SolutionCount()}");
}
}মূল CP সল্ভার ব্যবহার করে সমাধান
নিম্নলিখিত বিভাগগুলি একটি পাইথন প্রোগ্রাম উপস্থাপন করে যা মূল CP সল্ভার ব্যবহার করে N-queens সমাধান করে। (তবে, আমরা নতুন CP-SAT সমাধানকারী ব্যবহার করার পরামর্শ দিই)
লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোড প্রয়োজনীয় লাইব্রেরি আমদানি করে।
পাইথন
import sys from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
সি++
#include <cstdint> #include <cstdlib> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include "ortools/base/logging.h" #include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h"
জাভা
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar; import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver;
সি#
using System; using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
সমাধানকারী ঘোষণা করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোডটি মূল CP সমাধানকারী ঘোষণা করে।
পাইথন
solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens")সি++
Solver solver("N-Queens");জাভা
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");সি#
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");ভেরিয়েবল তৈরি করুন
সমাধানকারীর IntVar পদ্ধতিটি queens নামের একটি অ্যারে হিসাবে সমস্যার জন্য ভেরিয়েবল তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
# The array index is the column, and the value is the row.
queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)]সি++
std::vector<IntVar*> queens;
queens.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
queens.push_back(
solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i)));
}জাভা
int boardSize = 8;
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i);
}সি#
const int BoardSize = 8;
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}");
} যেকোনো সমাধানের জন্য, queens[j] = i মানে j এবং রো i কলামে একটি রানী আছে।
সীমাবদ্ধতা তৈরি করুন
এখানে কোড যা সমস্যার জন্য সীমাবদ্ধতা তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
# All rows must be different. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens)) # No two queens can be on the same diagonal. solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)])) solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)]))
সি++
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows.
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens));
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all
// different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1;
diag_1.reserve(board_size);
std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2;
diag_2.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var());
diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var());
}
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1));
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2));জাভা
// All rows must be different.
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens));
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different.
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize];
IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var();
diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var();
}
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1));
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2));সি#
// All rows must be different.
solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent());
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different.
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize];
IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var();
diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var();
}
solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent());
solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent());এই সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলি এন-কুইন্স সমস্যার জন্য তিনটি শর্তের গ্যারান্টি দেয় (বিভিন্ন সারি, কলাম এবং কর্ণের রাণী)।
একই সারিতে দুই রানী নেই
queens জন্য সমাধানকারীর AllDifferent পদ্ধতি প্রয়োগ করা প্রতিটি j এর জন্য queens[j] মানগুলিকে আলাদা হতে বাধ্য করে, যার মানে হল যে সমস্ত রাণীকে অবশ্যই ভিন্ন সারিতে থাকতে হবে।
একই কলামে দুই রানী নেই
এই সীমাবদ্ধতা queens সংজ্ঞায় নিহিত। যেহেতু queens কোন দুটি উপাদানের একই সূচক থাকতে পারে না, তাই কোন দুটি রাণী একই কলামে থাকতে পারে না।
একই তির্যক উপর কোন দুই রানী
তির্যক সীমাবদ্ধতা সারি এবং কলামের সীমাবদ্ধতার চেয়ে একটু জটিল। প্রথমত, যদি দুটি রাণী একই তির্যকের উপর শুয়ে থাকে, তাহলে নিম্নলিখিতগুলির একটি সত্য হতে হবে:
- যদি তির্যকটি অবতরণ করা হয় (বাম থেকে ডানে যাচ্ছে), দুটি রানীর প্রত্যেকটির জন্য সারি সংখ্যা এবং কলাম সংখ্যা সমান। সুতরাং
queens(i) + iদুটি ভিন্ন সূচকের জন্য একই মান আছেi। - যদি তির্যকটি আরোহী হয়, তাহলে দুই রানীর প্রত্যেকটির জন্য সারি সংখ্যা বিয়োগ কলাম সংখ্যা সমান। এই ক্ষেত্রে,
queens(i) - iদুটি ভিন্ন সূচকের জন্য একই মান আছেi।
সুতরাং তির্যক সীমাবদ্ধতা হল যে queens(i) + i এর মানগুলি অবশ্যই আলাদা হতে হবে, এবং একইভাবে queens(i) - i এর মানগুলিও আলাদা হতে হবে, বিভিন্ন i এর জন্য।
উপরের কোডটি queens[j] + j এবং queens[j] - j , প্রতিটি i এর জন্য AllDifferent পদ্ধতি প্রয়োগ করে এই সীমাবদ্ধতা যোগ করে।
সিদ্ধান্ত নির্মাতা যোগ করুন
পরবর্তী পদক্ষেপ হল একটি সিদ্ধান্ত নির্মাতা তৈরি করা, যা সমস্যার জন্য অনুসন্ধান কৌশল নির্ধারণ করে। সীমাবদ্ধতার প্রচারের কারণে অনুসন্ধানের কৌশলটি অনুসন্ধানের সময়ের উপর একটি বড় প্রভাব ফেলতে পারে, যা সমাধানকারীকে অন্বেষণ করতে হয় এমন পরিবর্তনশীল মানগুলির সংখ্যা হ্রাস করে। আপনি ইতিমধ্যে 4-রাণী উদাহরণে এর একটি উদাহরণ দেখেছেন।
নিম্নলিখিত কোড সমাধানকারীর Phase পদ্ধতি ব্যবহার করে একটি সিদ্ধান্ত নির্মাতা তৈরি করে।
পাইথন
db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE)
সি++
DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase(
queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);জাভা
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions.
final DecisionBuilder db =
solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);সি#
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions. DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
Phase পদ্ধতিতে ইনপুট আর্গুমেন্টের বিস্তারিত জানার জন্য ডিসিশন বিল্ডার দেখুন।
সিদ্ধান্ত নির্মাতা কিভাবে 4-রানী উদাহরণে কাজ করে
চলুন এক নজরে দেখে নেওয়া যাক কিভাবে সিদ্ধান্ত নির্মাতা 4-কুইন্স উদাহরণে অনুসন্ধান পরিচালনা করেন। CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND দ্বারা নির্দেশিত অ্যারের প্রথম ভেরিয়েবল queens[0] দিয়ে সলভার শুরু হয়। সমাধানকারী তারপর queens[0] ক্ষুদ্রতম মান বরাদ্দ করে যা ইতিমধ্যেই চেষ্টা করা হয়নি, যা এই পর্যায়ে 0, ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE দ্বারা নির্দেশিত। এটি বোর্ডের উপরের বাম কোণে প্রথম রানীকে রাখে।
এর পরে, সমাধানকারী queens[1] , যা এখন queens মধ্যে প্রথম আনবাউন্ড পরিবর্তনশীল। সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলি প্রচার করার পরে, কলাম 1-এ রাণীর জন্য দুটি সম্ভাব্য সারি রয়েছে: সারি 2 বা সারি 3৷ ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE বিকল্পটি সমাধানকারীকে queens[1] = 2 ৷ (যদি পরিবর্তে, আপনি ASSIGN_MAX_VALUE এ IntValueStrategy সেট করেন, তাহলে সমাধানকারী queens[1] = 3 )
আপনি দেখতে পারেন যে বাকি অনুসন্ধান একই নিয়ম অনুসরণ করে।
সমাধানকারীকে কল করুন এবং ফলাফল প্রদর্শন করুন
নিম্নলিখিত কোড সমাধানকারী চালায় এবং সমাধান প্রদর্শন করে।
পাইথন
# Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
num_solutions = 0
solver.NewSearch(db)
while solver.NextSolution():
# Displays the solution just computed.
for i in range(board_size):
for j in range(board_size):
if queens[j].Value() == i:
# There is a queen in column j, row i.
print("Q", end=" ")
else:
print("_", end=" ")
print()
print()
num_solutions += 1
solver.EndSearch()সি++
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
int num_solutions = 0;
solver.NewSearch(db);
while (solver.NextSolution()) {
// Displays the solution just computed.
LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions;
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
std::stringstream ss;
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) {
if (queens[j]->Value() == i) {
// There is a queen in column j, row i.
ss << "Q";
} else {
ss << "_";
}
if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " ";
}
LOG(INFO) << ss.str();
}
num_solutions++;
}
solver.EndSearch();জাভা
int solutionCount = 0;
solver.newSearch(db);
while (solver.nextSolution()) {
System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) {
if (queens[j].value() == i) {
System.out.print("Q");
} else {
System.out.print("_");
}
if (j != boardSize - 1) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
solutionCount++;
}
solver.endSearch();সি#
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
int SolutionCount = 0;
solver.NewSearch(db);
while (solver.NextSolution())
{
Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j)
{
if (queens[j].Value() == i)
{
Console.Write("Q");
}
else
{
Console.Write("_");
}
if (j != BoardSize - 1)
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
SolutionCount++;
}
solver.EndSearch();এখানে একটি 8x8 বোর্ডের জন্য প্রোগ্রাম দ্বারা পাওয়া প্রথম সমাধান।
Q _ _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ Q _
_ _ _ _ Q _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ Q
_ Q _ _ _ _ _ _
_ _ _ Q _ _ _ _
_ _ _ _ _ Q _ _
_ _ Q _ _ _ _ _
...91 other solutions displayed...
Statistics
failures: 304
branches: 790
wall time: 5 ms
Solutions found: 92 আপনি কমান্ড-লাইন আর্গুমেন্ট হিসাবে N পাস করে একটি ভিন্ন আকারের একটি বোর্ডের জন্য সমস্যার সমাধান করতে পারেন। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, python nqueens_cp.py 6 একটি 6x6 বোর্ডের সমস্যার সমাধান করে।
পুরো প্রোগ্রাম
সম্পূর্ণ প্রোগ্রাম নীচে দেখানো হয়.
পাইথন
"""OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem."""
import sys
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
def main(board_size):
# Creates the solver.
solver = pywrapcp.Solver("n-queens")
# Creates the variables.
# The array index is the column, and the value is the row.
queens = [solver.IntVar(0, board_size - 1, f"x{i}") for i in range(board_size)]
# Creates the constraints.
# All rows must be different.
solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent(queens))
# No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] + i for i in range(board_size)]))
solver.Add(solver.AllDifferent([queens[i] - i for i in range(board_size)]))
db = solver.Phase(queens, solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE)
# Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
num_solutions = 0
solver.NewSearch(db)
while solver.NextSolution():
# Displays the solution just computed.
for i in range(board_size):
for j in range(board_size):
if queens[j].Value() == i:
# There is a queen in column j, row i.
print("Q", end=" ")
else:
print("_", end=" ")
print()
print()
num_solutions += 1
solver.EndSearch()
# Statistics.
print("\nStatistics")
print(f" failures: {solver.Failures()}")
print(f" branches: {solver.Branches()}")
print(f" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms")
print(f" Solutions found: {num_solutions}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# By default, solve the 8x8 problem.
size = 8
if len(sys.argv) > 1:
size = int(sys.argv[1])
main(size)সি++
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include "ortools/base/logging.h"
#include "ortools/constraint_solver/constraint_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void NQueensCp(const int board_size) {
// Instantiate the solver.
Solver solver("N-Queens");
std::vector<IntVar*> queens;
queens.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
queens.push_back(
solver.MakeIntVar(0, board_size - 1, absl::StrCat("x", i)));
}
// Define constraints.
// The following sets the constraint that all queens are in different rows.
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(queens));
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all
// different. No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
std::vector<IntVar*> diag_1;
diag_1.reserve(board_size);
std::vector<IntVar*> diag_2;
diag_2.reserve(board_size);
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
diag_1.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i)->Var());
diag_2.push_back(solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i)->Var());
}
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_1));
solver.AddConstraint(solver.MakeAllDifferent(diag_2));
DecisionBuilder* const db = solver.MakePhase(
queens, Solver::CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver::ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
int num_solutions = 0;
solver.NewSearch(db);
while (solver.NextSolution()) {
// Displays the solution just computed.
LOG(INFO) << "Solution " << num_solutions;
for (int i = 0; i < board_size; ++i) {
std::stringstream ss;
for (int j = 0; j < board_size; ++j) {
if (queens[j]->Value() == i) {
// There is a queen in column j, row i.
ss << "Q";
} else {
ss << "_";
}
if (j != board_size - 1) ss << " ";
}
LOG(INFO) << ss.str();
}
num_solutions++;
}
solver.EndSearch();
// Statistics.
LOG(INFO) << "Statistics";
LOG(INFO) << " failures: " << solver.failures();
LOG(INFO) << " branches: " << solver.branches();
LOG(INFO) << " wall time: " << solver.wall_time() << " ms";
LOG(INFO) << " Solutions found: " << num_solutions;
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int board_size = 8;
if (argc > 1) {
board_size = std::atoi(argv[1]);
}
operations_research::NQueensCp(board_size);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}জাভা
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.
package com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.DecisionBuilder;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.IntVar;
import com.google.ortools.constraintsolver.Solver;
/** N-Queens Problem. */
public final class NQueensCp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
// Instantiate the solver.
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
int boardSize = 8;
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
queens[i] = solver.makeIntVar(0, boardSize - 1, "x" + i);
}
// Define constraints.
// All rows must be different.
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(queens));
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different.
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[boardSize];
IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[boardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
diag1[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], i).var();
diag2[i] = solver.makeSum(queens[i], -i).var();
}
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag1));
solver.addConstraint(solver.makeAllDifferent(diag2));
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions.
final DecisionBuilder db =
solver.makePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
int solutionCount = 0;
solver.newSearch(db);
while (solver.nextSolution()) {
System.out.println("Solution " + solutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < boardSize; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < boardSize; ++j) {
if (queens[j].value() == i) {
System.out.print("Q");
} else {
System.out.print("_");
}
if (j != boardSize - 1) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
solutionCount++;
}
solver.endSearch();
// Statistics.
System.out.println("Statistics");
System.out.println(" failures: " + solver.failures());
System.out.println(" branches: " + solver.branches());
System.out.println(" wall time: " + solver.wallTime() + "ms");
System.out.println(" Solutions found: " + solutionCount);
}
private NQueensCp() {}
}সি#
// OR-Tools solution to the N-queens problem.
using System;
using Google.OrTools.ConstraintSolver;
public class NQueensCp
{
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Instantiate the solver.
Solver solver = new Solver("N-Queens");
const int BoardSize = 8;
IntVar[] queens = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
queens[i] = solver.MakeIntVar(0, BoardSize - 1, $"x{i}");
}
// Define constraints.
// All rows must be different.
solver.Add(queens.AllDifferent());
// All columns must be different because the indices of queens are all different.
// No two queens can be on the same diagonal.
IntVar[] diag1 = new IntVar[BoardSize];
IntVar[] diag2 = new IntVar[BoardSize];
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
diag1[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], i).Var();
diag2[i] = solver.MakeSum(queens[i], -i).Var();
}
solver.Add(diag1.AllDifferent());
solver.Add(diag2.AllDifferent());
// Create the decision builder to search for solutions.
DecisionBuilder db = solver.MakePhase(queens, Solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND, Solver.ASSIGN_MIN_VALUE);
// Iterates through the solutions, displaying each.
int SolutionCount = 0;
solver.NewSearch(db);
while (solver.NextSolution())
{
Console.WriteLine("Solution " + SolutionCount);
for (int i = 0; i < BoardSize; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < BoardSize; ++j)
{
if (queens[j].Value() == i)
{
Console.Write("Q");
}
else
{
Console.Write("_");
}
if (j != BoardSize - 1)
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
SolutionCount++;
}
solver.EndSearch();
// Statistics.
Console.WriteLine("Statistics");
Console.WriteLine($" failures: {solver.Failures()}");
Console.WriteLine($" branches: {solver.Branches()}");
Console.WriteLine($" wall time: {solver.WallTime()} ms");
Console.WriteLine($" Solutions found: {SolutionCount}");
}
}সমাধানের সংখ্যা
বোর্ডের আকারের সাথে সমাধানের সংখ্যা মোটামুটিভাবে বেড়ে যায়:
| বোর্ডের আকার | সমাধান | সব সমাধান খুঁজে বের করার সময় (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 10 | 0 |
| 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 7 | 40 | 3 |
| 8 | 92 | 9 |
| 9 | 352 | 35 |
| 10 | 724 | 95 |
| 11 | 2680 | 378 |
| 12 | 14200 | 2198 |
| 13 | 73712 | 11628 |
| 14 | 365596 | 62427 |
| 15 | 2279184 | 410701 |
অনেক সমাধান হল অন্যের ঘূর্ণন মাত্র, এবং সিমেট্রি ব্রেকিং নামক একটি কৌশল ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে গণনার পরিমাণ কমাতে। আমরা এখানে এটি ব্যবহার করি না; উপরের আমাদের সমাধানটি দ্রুত হওয়ার উদ্দেশ্যে নয়, শুধু সহজ। অবশ্যই, আমরা এটিকে আরও দ্রুত করতে পারি যদি আমরা তাদের সবগুলির পরিবর্তে শুধুমাত্র একটি সমাধান খুঁজে পেতে চাই: 50 পর্যন্ত বোর্ডের আকারের জন্য কয়েক মিলিসেকেন্ডের বেশি নয়।

