このユニットでは、意思決定ツリーを構築するために使用されるさまざまなタイプの条件について説明します。
軸に沿った条件と斜めの条件
軸に沿った 条件には、1 つの特徴のみが含まれます。斜め条件には複数の特徴が関係します。たとえば、次は軸に沿った条件です。
num_legs ≥ 2
一方、次の条件は間接的な条件です。
num_legs ≥ num_fingers
多くの場合、ディシジョン ツリーは軸に沿った条件のみでトレーニングされます。ただし、斜めの分割はより複雑なパターンを表現できるため、より強力です。斜め分割では、トレーニングと推論のコストが増加する代わりに、より良い結果が得られることがあります。
split_axis="SPARSE_OBLIQUE" パラメータで有効にできます。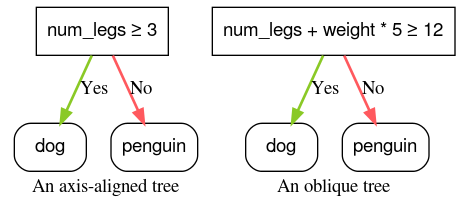
図 4. 軸に沿った条件と斜めの条件の例。
上記の 2 つの条件をグラフにすると、次の特徴空間分離が得られます。

図 5. 図 4 の条件に対する特徴空間の分離。
バイナリ条件と非バイナリ条件
結果が 2 つ(true または false など)の条件をバイナリ条件と呼びます。二値の条件のみを含むディシジョン ツリーは、二値ディシジョン ツリーと呼ばれます。
バイナリ以外の条件には、2 つ以上の結果が考えられます。したがって、バイナリ以外の条件は、バイナリ条件よりも識別力が高くなります。1 つ以上の非バイナリ条件を含む決定は、非バイナリ分類ツリーと呼ばれます。

図 6: バイナリと非バイナリのディシジョン ツリー。
パワーが多すぎる条件も、過学習する可能性が高くなります。このため、ディシジョン フォレストは通常、バイナリ ディシジョン ツリーを使用します。このコースでは、バイナリ ディシジョン ツリーに焦点を当てます。
最も一般的な条件は、次のように表されるしきい値条件です。
feature ≥ threshold
次に例を示します。
num_legs ≥ 2
他にもさまざまなタイプの条件があります。以下は、よく使用されるその他のバイナリ条件のタイプです。
表 2. 一般的なバイナリ条件のタイプ。
| 名前 | 条件 | 例 |
| しきい値条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i \geq \mathrm{threshold}$ | $\mathrm{num\_legs} \geq 2$ |
| 等式条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i = \mathrm{value}$ | $\mathrm{species} = ``cat"$ |
| セット内の条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i \in \mathrm{collection}$ | $\mathrm{species} \in \{``cat", ``dog", ``bird"\}$ |
| 斜め状態 | $\sum_{i} \mathrm{weight}_i \mathrm{feature}_i \geq \mathrm{threshold}$ | $5 \ \mathrm{num\_legs} + 2 \ \mathrm{num\_eyes} \geq 10$ |
| 機能がない | $\mathrm{feature}_i \mathrm{is} \mathrm{Missing}$ | $\mathrm{num\_legs} \mathrm{is} \mathrm{Missing}$ |