本单元将重点介绍用于构建决策树的不同类型的条件。
轴心对齐条件与倾斜条件
轴对齐 条件仅涉及单个地图项。斜向条件涉及多个地图项。例如,以下是轴对齐的条件:
num_legs ≥ 2
而以下是斜线条件:
num_legs ≥ num_fingers
通常,决策树仅使用与轴对齐的条件进行训练。但是,斜分块更强大,因为它们可以表达更复杂的模式。斜向拆分有时可以产生更好的结果,但代价是训练和推理费用更高。
YDF 代码
在 YDF 中,决策树默认使用轴对齐条件进行训练。您可以使用 split_axis="SPARSE_OBLIQUE" 参数启用决策斜向树。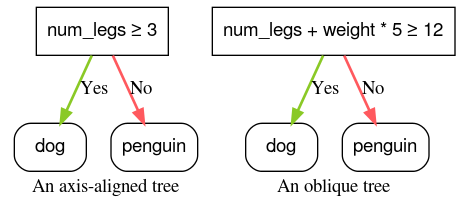
图 4. 轴对齐条件和倾斜条件示例。
将上述两个条件绘制到图表中,可得出以下特征空间分离:

图 5. 图 4 中各个条件的特征空间分离。
二元条件与非二元条件
具有两个可能结果(例如 true 或 false)的条件称为二元条件。仅包含二元条件的决策树称为二元决策树。
非二元条件有两种以上的可能结果。因此,非二元条件比二元条件具有更强的区分能力。包含一个或多个非二元条件的决策称为非二元决策树。

图 6:二元决策树与非二元决策树。
过于强大的条件也更容易过拟合。因此,决策森林通常使用二元决策树,因此本课程将重点介绍二元决策树。
最常见的条件类型是阈值条件,表示为:
feature ≥ threshold
例如:
num_legs ≥ 2
还有其他类型的条件。以下是其他常用的二元条件类型:
表 2. 常见的二进制条件类型。
| 名称 | 条件 | 示例 |
| 阈值条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i \geq \mathrm{threshold}$ | $\mathrm{num\_legs} \geq 2$ |
| 等式条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i = \mathrm{value}$ | $\mathrm{species} = ``cat"$ |
| 在组合中的条件 | $\mathrm{feature}_i \in \mathrm{collection}$ | $\mathrm{species} \in \{``cat", ``dog", ``bird"\}$ |
| 斜视 | $\sum_{i} \mathrm{weight}_i \mathrm{feature}_i \geq \mathrm{threshold}$ | $5 \ \mathrm{num\_legs} + 2 \ \mathrm{num\_eyes} \geq 10$ |
| 缺少功能 | $\mathrm{feature}_i \mathrm{is} \mathrm{Missing}$ | $\mathrm{num\_legs} \mathrm{is} \mathrm{Missing}$ |