Page Summary
-
Actions on Google communicates with your fulfillment service via a webhook using a specific JSON format.
-
Your fulfillment needs to implement a webhook to respond to HTTP requests from Actions on Google.
-
Your fulfillment receives user requests as HTTP POST with a JSON payload and responds with a JSON formatted response.
-
There are two main webhook formats: Dialogflow webhook format and Conversation webhook format (for Actions SDK).
-
Webhooks can receive different request types including Invocation, Conversation, and Helper results.
This document describes the webhook format for communicating between Actions on Google and a fulfillment service that defines a custom conversational user interface.
It's important to understand how Actions on Google and your fulfillment communicate through the Actions on Google webhook formats:
- To participate in conversations with Actions on Google, your fulfillment implements a webhook that can respond to HTTP requests from Actions on Google.
- When users invoke your Action, your fulfillment receives an
HTTP POSTwith a JSON payload that describes the user's request. - In turn, your fulfillment is responsible for reading the parameters from the request payload, generating an appropriate JSON formatted response, and sending a reply to the Assistant with this response.
Request types
This table summarizes the types of requests that your webhook might receive from the Assistant:
| Type | Description | JSON Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Invocation requests | User utterances that initiate the conversation with your fulfillment or
trigger deep-link Actions (for example, "Talk to Personal Chef to find
dinner recipes").
|
|
| Conversation requests | Utterances by users in the same session once the conversation with your
fulfillment has started. In the conversation webhook format, these are the
raw text responses from the user corresponding to actions.intent.TEXT
intents that your fulfillment requested in the previous turn. |
|
| Helper results | Requests sent by the Assistant to your fulfillment when your webhook has
requested a helper intent
in the previous turn of the conversation to handle parts of the
conversation (for example, actions.intent.OPTION and
actions.intent.PERMISSION). |
Conversation requests and responses
In a typical Actions on Google interaction scenario, users utter a phrase to invoke an Action. To provide a response, Actions on Google finds the fulfillment that matches the Action invoked by the user and sends the request there.
Once Actions on Google establishes that your fulfillment is a suitable match for the user's invocation, it starts a conversation session by sending an HTTP request that contains a JSON payload with the user's request information to your fulfillment endpoint. Your fulfillment parses the request and returns a response that contains a JSON payload. Actions on Google then converts the payload into rendered speech and multimedia output for users.
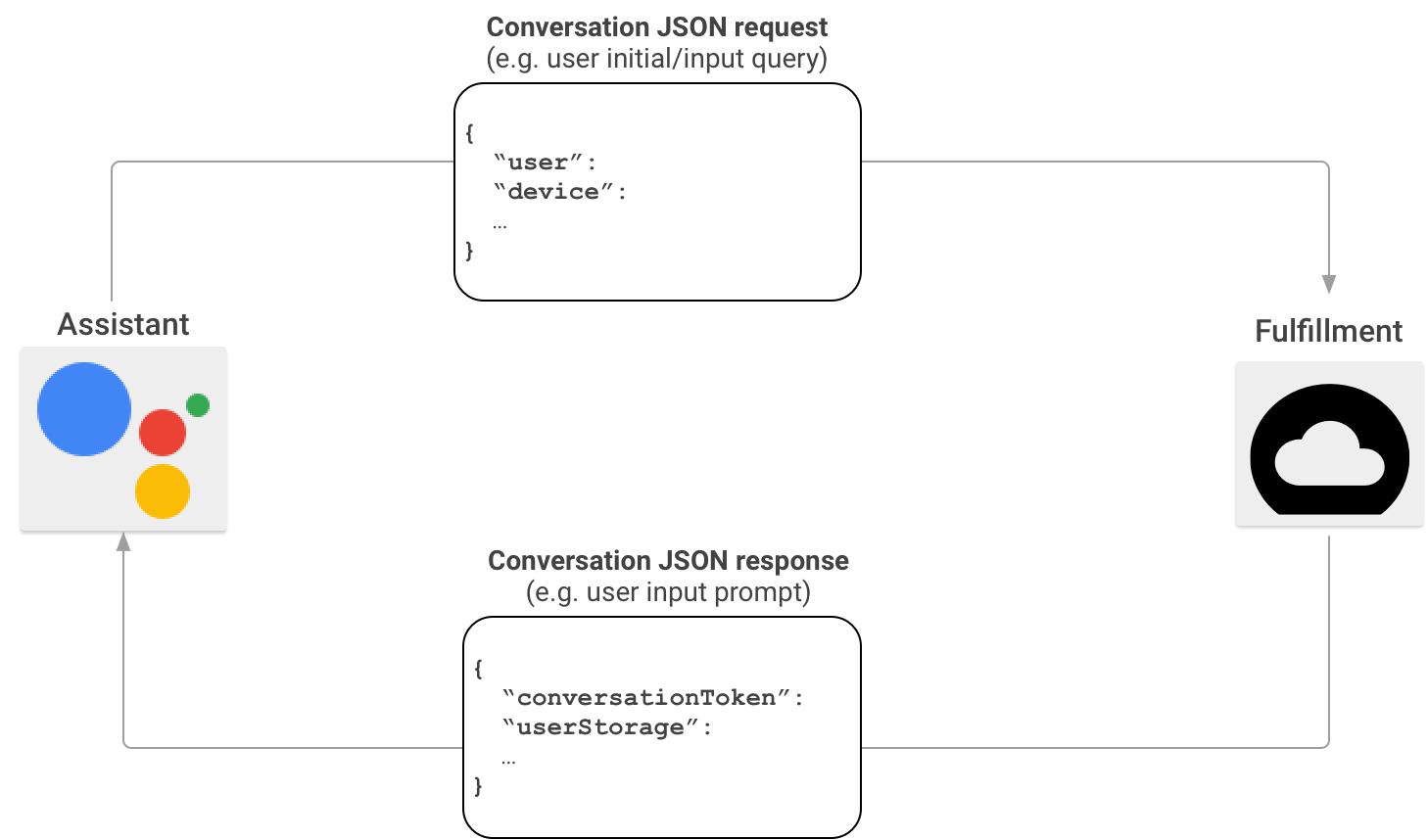
To learn more about the format of the JSON payload when Actions on Google invokes your fulfillment through the Actions SDK, see Conversation webhook format.
Dialogflow requests and responses
When you create Actions, you can optionally use Dialogflow to simplify the task of building conversational interfaces. In this scenario, Dialogflow acts as a proxy between Actions on Google and your fulfillment. Instead of sending the HTTP/JSON request directly to your fulfillment endpoint, Actions on Google sends it to Dialogflow.
Dialogflow wraps the JSON payload contained in the original request into the Dialogflow webhook format, and forwards the resulting request to your Dialogflow fulfillment.
Conversely, when your fulfillment sends a response to Dialogflow, the JSON payload of the response must comply with the Dialogflow webhook format. Your fulfillment parses the parameters from the Dialogflow JSON request, and generates a response in the Dialogflow webhook format. Dialogflow then converts the response from your fulfillment into a response message that the Assistant understands.
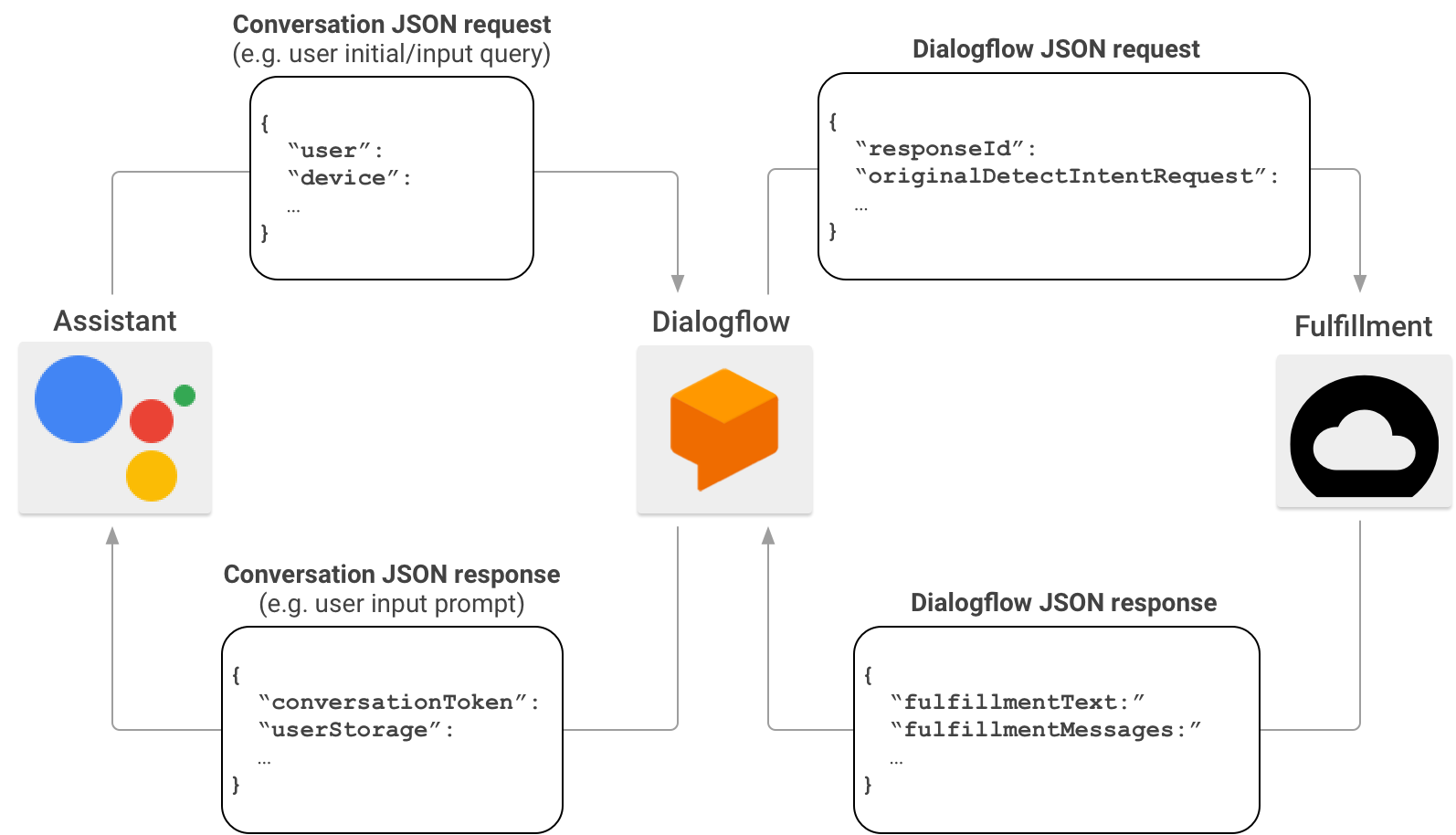
To learn more about the format of the JSON payload when Actions on Google invokes your fulfillment through Dialogflow, see Dialogflow webhook format.