कॉम्पोनेंट: कॉन्सेप्ट
संग्रह की मदद से व्यवस्थित रहें
अपनी प्राथमिकताओं के आधार पर, कॉन्टेंट को सेव करें और कैटगरी में बांटें.
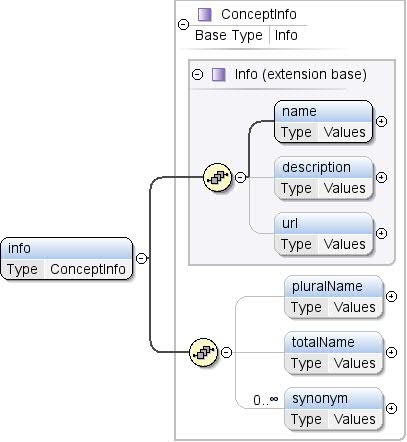
एलिमेंट: कॉन्सेप्ट / जानकारी
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| एनोटेशन |
टेक्स्ट पर दी जाने वाली जानकारी, जैसे कि
कॉन्सेप्ट को समझने की कोशिश करते हैं. |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| टाइप |
ConceptInfo |
| टाइप हैरारकी |
|
| प्रॉपर्टी |
|
| मॉडल |
name , description{0,1} , url{0,1} , pluralName{0,1} , totalName{0,1} , समानार्थी शब्द* |
| बच्चे |
ब्यौरा, नाम, pluralName,
समानार्थी शब्द, totalName, url |
| इंस्टेंस |
<info>
<name>{1,1}</name>
<description>{0,1}</description>
<url>{0,1}</url>
</info>
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
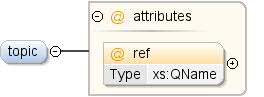
| एनोटेशन |
ऐसा विषय जिससे जुड़ा कॉन्सेप्ट जुड़ा हो. |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
अनबाउंड |
|
| विशेषताएं |
| QName |
टाइप |
तय |
डिफ़ॉल्ट |
इस्तेमाल करें |
टिप्पणी |
| रेफ़रंस |
xs:QName |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
इस कॉन्सेप्ट से जुड़े विषय का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर
के साथ संबद्ध. यह मुमकिन है कि रेफ़रंस के तौर पर दिए गए विषय,
डेटासेट या बाहरी डेटासेट में, जैसे कि किसी दूसरे डेटासेट में.
बाहरी विषय इस रूप में होना चाहिए
"prefix:other_topic_id", जहां "prefix" क्या
बाहरी डेटासेट के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला प्रीफ़िक्स (एक्सएमएल देखें
नेमस्पेस). |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
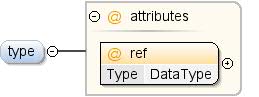
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत का डेटा टाइप. कॉन्सेप्ट में एक टाइप होना चाहिए
एलान या किसी दूसरे कॉन्सेप्ट को शामिल करने के बारे में नहीं है. ऐसे मामले में जहां यह है
साथ ही, इसमें एक टाइप का एलान भी दिया जा सकता है. किस तरह का है
एक्सटेंडेड कॉन्सेप्ट,
साथ ही, उससे जुड़े सिद्धांतों को बढ़ा सकते हैं. "इससे कम पाबंदी" (एलआरटी) एक ऐसी
आंशिक क्रम इस तरह परिभाषित किया गया है: स्ट्रिंग LRT फ़्लोट फ़्लोट LRT पूर्णांक
स्ट्रिंग LRT तारीख स्ट्रिंग LRT बूलियन |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
|
| विशेषताएं |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
|
एलिमेंट: कॉन्सेप्ट / एट्रिब्यूट
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
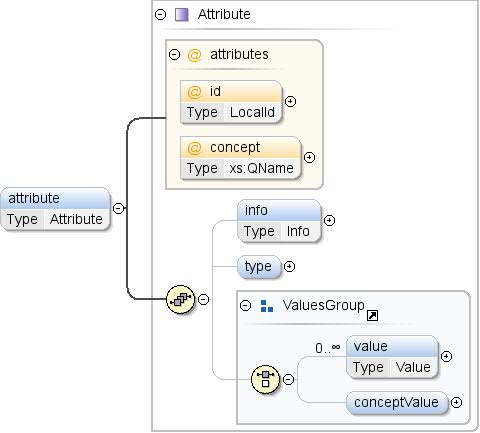
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत की एक विशेषता. एट्रिब्यूट अतिरिक्त जानकारी दिखाते हैं
जानकारी (उदाहरण के लिए, GDP एक प्रतिशत है). |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| टाइप |
एट्रिब्यूट |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
अनबाउंड |
|
| मॉडल |
info{0,1} , टाइप{0,1} , (वैल्यू*
| conceptValue{0,1}) |
| बच्चे |
conceptValue, info, type,
वैल्यू |
| इंस्टेंस |
<attribute concept="" id="">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type format="" ref="">{0,1}</type>
</attribute>
|
| विशेषताएं |
| QName |
टाइप |
तय |
डिफ़ॉल्ट |
इस्तेमाल करें |
टिप्पणी |
| सिद्धांत |
xs:QName |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
वैल्यू से मेल खाने वाले कॉन्सेप्ट का रेफ़रंस
एट्रिब्यूट की वैल्यू डालें. अगर विशेषता किसी प्रकार के बारे में बताती है, तो
दिए गए कॉन्सेप्ट के टाइप से मेल खाना चाहिए.
बाहरी सिद्धांत इस रूप में होना चाहिए
"prefix:other_Concept_id", जहां "prefix" इससे मेल खाता है
बाहरी डेटासेट के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया गया प्रीफ़िक्स (एक्सएमएल देखें
नेमस्पेस). |
| आईडी |
LocalId |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
सिद्धांत विशेषता का आईडी. यह पहचानकर्ता होना चाहिए
यूनीक होनी चाहिए. (एट्रिब्यूट और प्रॉपर्टी में). कॉन्टेंट बनाने
अगर सिद्धांत एट्रिब्यूट दिया गया है, तो आईडी को छोड़ा जा सकता है. इसमें
केस, एक आईडी में आसानी से
में बताया गया है. उदाहरण के लिए <attribute
concept="unit:currency"/> इसके बराबर है
<एट्रिब्यूट आईडी="मुद्रा"
concept="unit:currency"/> |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
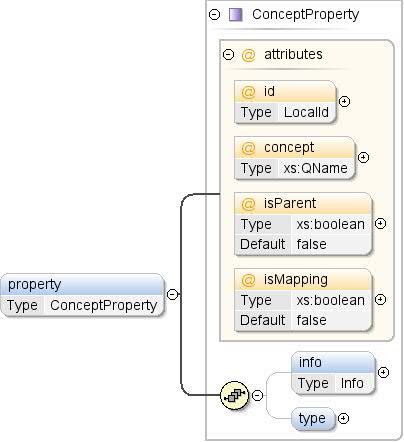
एलिमेंट: Concept / प्रॉपर्टी
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत की प्रॉपर्टी. प्रॉपर्टी अतिरिक्त जानकारी दिखाती हैं
कॉन्सेप्ट के इंस्टेंस के बारे में जानकारी (जैसे, कोई कॉन्सेप्ट
"शहर" शायद "country" प्रॉपर्टी भी शामिल हो. |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| टाइप |
ConceptProperty |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
| maxOccurs: |
अनबाउंड |
|
| मॉडल |
जानकारी{0,1} , टाइप{0,1} |
| बच्चे |
जानकारी, टाइप |
| इंस्टेंस |
<property concept="" id="" isMapping="false" isParent="false">
<info>{0,1}</info>
<type ref="">{0,1}</type>
</property>
|
| विशेषताएं |
| QName |
टाइप |
तय |
डिफ़ॉल्ट |
इस्तेमाल करें |
टिप्पणी |
| सिद्धांत |
xs:QName |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
वैल्यू से मेल खाने वाले कॉन्सेप्ट का रेफ़रंस
प्रॉपर्टी का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. अगर प्रॉपर्टी किसी प्रकार के बारे में बताती है, तो
दिए गए कॉन्सेप्ट के टाइप से मेल खाना चाहिए.
बाहरी सिद्धांत इस रूप में होना चाहिए
"prefix:other_Concept_id", जहां "prefix" इससे मेल खाता है
बाहरी डेटासेट के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया गया प्रीफ़िक्स (एक्सएमएल देखें
नेमस्पेस). |
| आईडी |
LocalId |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
कॉन्सेप्ट प्रॉपर्टी का आईडी. यह पहचानकर्ता होना चाहिए
यूनीक होनी चाहिए. (एट्रिब्यूट और प्रॉपर्टी में). कॉन्टेंट बनाने
अगर कॉन्सेप्ट प्रॉपर्टी दी गई है, तो आईडी को हटाया जा सकता है. इसमें
केस, एक आईडी स्पष्ट रूप से
में बताया गया है. उदाहरण के लिए <property
concept="geo:country"/> <property
id="country"
concept="geo:country"/> |
| isMapping |
xs:boolean |
|
गलत |
ज़रूरी नहीं |
अगर सही है, तो इस प्रॉपर्टी में किसी कॉन्सेप्ट का रेफ़रंस होना चाहिए, और
यह प्रॉपर्टी
दिया गया है. रेफ़र की गई सभी फ़ाइलों का हर इंस्टेंस
इस कॉन्सेप्ट का संदर्भ इस
कॉन्सेप्ट शामिल है. |
| isParent |
xs:boolean |
|
गलत |
ज़रूरी नहीं |
अगर सही है, तो इस प्रॉपर्टी में किसी कॉन्सेप्ट का रेफ़रंस होना चाहिए, और
यह प्रॉपर्टी
के साथ-साथ कॉन्सेप्ट और कॉन्सेप्ट (उदाहरण के लिए, किसी महाद्वीप)
देश के हिसाब से). |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
एलिमेंट: Concept / defaultValue
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत के लिए एक डिफ़ॉल्ट वैल्यू, जिसका इस्तेमाल ऐप्लिकेशन में किया जाएगा
जब उन्हें इनमें से किसी एक संभावित वैल्यू को चुनना होता है
कॉन्सेप्ट को समझने की कोशिश करते हैं. |
| डायग्राम |
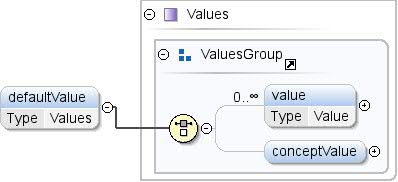 |
| टाइप |
वैल्यू |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
|
| मॉडल |
मान* | conceptValue{0,1} |
| बच्चे |
conceptValue, value |
| इंस्टेंस |
<defaultValue>
<value lang="">{0,unbounded}</value>
<conceptValue concept="">{0,1}</conceptValue>
</defaultValue>
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| एनोटेशन |
ऐसी टेबल का रेफ़रंस जिसमें सभी संभावित वैल्यू मौजूद हैं
. |
| डायग्राम |
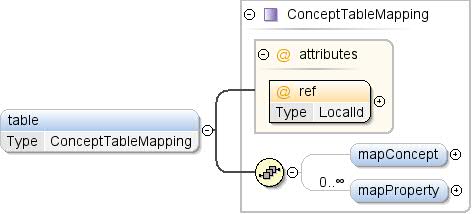 |
| टाइप |
ConceptTableMapping |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| सामग्री: |
जटिल |
| मिनट समय: |
0 |
|
| मॉडल |
mapConcept{0,1} , mapProperty* |
| बच्चे |
mapConcept, mapProperty |
| इंस्टेंस |
<table ref="">
<mapConcept toColumn="">{0,1}</mapConcept>
<mapProperty lang="" ref="" toColumn="">{0,unbounded}</mapProperty>
</table>
|
| विशेषताएं |
| QName |
टाइप |
तय |
डिफ़ॉल्ट |
इस्तेमाल करें |
टिप्पणी |
| रेफ़रंस |
LocalId |
|
|
ज़रूरी है |
उस तालिका की आईडी जिसमें
कॉन्सेप्ट को समझने की कोशिश करते हैं. |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
|
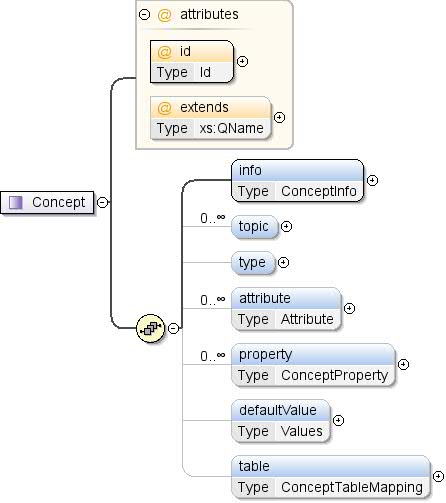
कॉम्प्लेक्स टाइप: कॉन्सेप्ट
| नाम-स्थान |
http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010 |
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत ऐसे डेटा की परिभाषा है जो
डेटासेट (उदाहरण के लिए, "जीडीपी" या "काउंटी"). एक कॉन्सेप्ट
सभी संभावित वैल्यू की गिनती के साथ जुड़ा हुआ है या नहीं. ऐप्लिकेशन
कुछ डेटासेट में बताए गए सिद्धांत का दूसरे
डेटासेट में जोड़ दिया जाएगा. |
| डायग्राम |
 |
| इस्तेमाल करने वाले |
|
| मॉडल |
जानकारी , विषय* , टाइप{0,1} ,
attribute* , प्रॉपर्टी* , defaultValue{0,1} , टेबल{0,1} |
| बच्चे |
attribute, defaultValue, info,
प्रॉपर्टी, टेबल, विषय,
टाइप |
| विशेषताएं |
| QName |
टाइप |
तय |
डिफ़ॉल्ट |
इस्तेमाल करें |
टिप्पणी |
| बढ़ावा देता है |
xs:QName |
|
|
ज़रूरी नहीं |
इस कॉन्सेप्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर
विस्तार. इस कॉन्सेप्ट के बारे में एक ही डेटासेट में बताया जा सकता है
या बाहरी डेटासेट में मौजूद है. किसी बाहरी सोर्स का रेफ़रंस
सिद्धांत "prefix:other_Concept_id" के रूप में होना चाहिए,
जहां "prefix" के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला प्रीफ़िक्स है
बाहरी डेटासेट (एक्सएमएल नेमस्पेस देखें). |
| आईडी |
आईडी |
|
|
ज़रूरी है |
सिद्धांत का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर, जिसे
यूनीक होता है. |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:complexType name="Concept">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A concept is a definition of a type of data that appears in the
dataset (e.g., "GDP" or "County"). A concept may be associated with
an enumeration of all its possible values or not. A concept defined in
some dataset may be referenced in other datasets.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="info" type="ConceptInfo">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>Textual information, such as the name and description of
the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="topic" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A topic the concept is associated with.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="type" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The data type of the concept. A concept must provide a type declaration or extend
another concept. In the case where it's extending a concept, it may also
provide a type declaration. The type of the extended concept must be less restrictive
than the type of the concept extending it.
"Less restrictive than" (LRT) is a partial order defined as follows:
string LRT float
float LRT integer
string LRT date
string LRT boolean</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="attribute" type="Attribute" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An attribute of the concept. Attributes represent additional
information about the concept (e.g., GDP is a percentage).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="property" type="ConceptProperty" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A property of the concept. Properties represent additional
information about instances of the concept (e.g., a concept
"city" may have a property "country").</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="defaultValue" type="Values" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A default value for the concept, to be used by
applications when they need to pick one of the possible
values of the concept.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="table" type="ConceptTableMapping" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>A reference to a table that contains all the
possible values for the concept and its non-constant
properties.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
<xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
</xs:complexType>
|
| नाम-स्थान |
कोई नेमस्पेस नहीं |
| एनोटेशन |
इस कॉन्सेप्ट से जुड़े विषय का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर
के साथ. रेफ़र किए गए विषय को उसी डेटासेट में बताया जा सकता है या
यानी, किसी दूसरे डेटासेट में. किसी बाहरी विषय का रेफ़रंस
यह "prefix:other_topic_id" के रूप में होना चाहिए, जहां
"प्रीफ़िक्स" बाहरी के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला प्रीफ़िक्स है
डेटासेट (एक्सएमएल नेमस्पेस देखें). |
| टाइप |
xs:QName |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
|
| इस्तेमाल करने वाले |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="xs:QName">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the topic this concept is
associated with.
The referenced topic may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external topic must be of the form
"prefix:other_topic_id", where "prefix" is the prefix
used for the namespace of the external dataset (see
XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
| नाम-स्थान |
कोई नेमस्पेस नहीं |
| टाइप |
DataType |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
|
| Facets |
| गिनती |
स्ट्रिंग |
|
| गिनती |
फ़्लोट |
|
| गिनती |
पूर्णांक |
|
| गिनती |
बूलियन |
|
| गिनती |
तारीख |
|
| गिनती |
सिद्धान्त |
|
|
| इस्तेमाल करने वाले |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:attribute name="ref" type="DataType" use="required"/>
|
एट्रिब्यूट: Concept / @id
| नाम-स्थान |
कोई नेमस्पेस नहीं |
| एनोटेशन |
सिद्धांत का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर, जो दुनिया भर में मौजूद होना चाहिए
यूनीक होनी चाहिए. |
| टाइप |
आईडी |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
|
| Facets |
|
| इस्तेमाल करने वाले |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:attribute name="id" type="Id" use="required">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of the concept, which must be globally
unique within the dataset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
एट्रिब्यूट: Concept / @ex सर्टिफ़िकेशन
| नाम-स्थान |
कोई नेमस्पेस नहीं |
| एनोटेशन |
किसी ऐसे कॉन्सेप्ट का यूनीक आइडेंटिफ़ायर जिसका दायरा भी बढ़ जाता है.
बताए गए कॉन्सेप्ट को उसी डेटासेट में या बाहरी तौर पर,
उदाहरण के लिए, किसी दूसरे डेटासेट में. किसी बाहरी कॉन्सेप्ट का रेफ़रंस ऐसा होना चाहिए
फ़ॉर्म "prefix:other_Concept_id", जहां "prefix" इससे मेल खाता है
बाहरी डेटासेट के नेमस्पेस के लिए इस्तेमाल किया गया प्रीफ़िक्स (एक्सएमएल देखें
नेमस्पेस). |
| टाइप |
xs:QName |
| प्रॉपर्टी |
| इस्तेमाल करें: |
ज़रूरी नहीं |
|
| इस्तेमाल करने वाले |
|
| स्रोत |
<xs:attribute name="extends" type="xs:QName" use="optional">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>The unique identifier of a concept that this
concept extends.
The referenced concept may be defined in the same
dataset or externally, i.e., in another dataset. A
reference to an external concept must be of the form
"prefix:other_concept_id", where "prefix" is the
prefix used for the namespace of the external
dataset (see XML namespaces).</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:attribute>
|
इसका इस्तेमाल करके बनाया गया
oXygen का एक्सएमएल एडिटर.
जब तक कुछ अलग से न बताया जाए, तब तक इस पेज की सामग्री को Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License के तहत और कोड के नमूनों को Apache 2.0 License के तहत लाइसेंस मिला है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, Google Developers साइट नीतियां देखें. Oracle और/या इससे जुड़ी हुई कंपनियों का, Java एक रजिस्टर किया हुआ ट्रेडमार्क है.
आखिरी बार 2025-07-25 (UTC) को अपडेट किया गया.
[[["समझने में आसान है","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["मेरी समस्या हल हो गई","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["अन्य","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["वह जानकारी मौजूद नहीं है जो मुझे चाहिए","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["बहुत मुश्किल है / बहुत सारे चरण हैं","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["पुराना","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["अनुवाद से जुड़ी समस्या","translationIssue","thumb-down"],["सैंपल / कोड से जुड़ी समस्या","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["अन्य","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["आखिरी बार 2025-07-25 (UTC) को अपडेट किया गया."],[],["Concepts, within a dataset (namespace: `http://schemas.google.com/dspl/2010`), define data types and are globally unique. Concepts can extend others, using `prefix:other_concept_id` for external references. They include `info` (textual details), `topic` (associated topics via `ref`), `type` (data type, `ref`), `attribute` (additional information), `property` (instance information), `defaultValue`, and `table` (data source, `ref`). Key concept attributes are `id` (unique), and `extends` (referencing another concept). External references are in `prefix:identifier` format. A concept must have a `type` or `extends`.\n"]]







