Aşağıdaki bölümlerde LP sorunlarına bir örnek ve nasıl çözüleceği anlatılmaktadır. Sorun şudur:
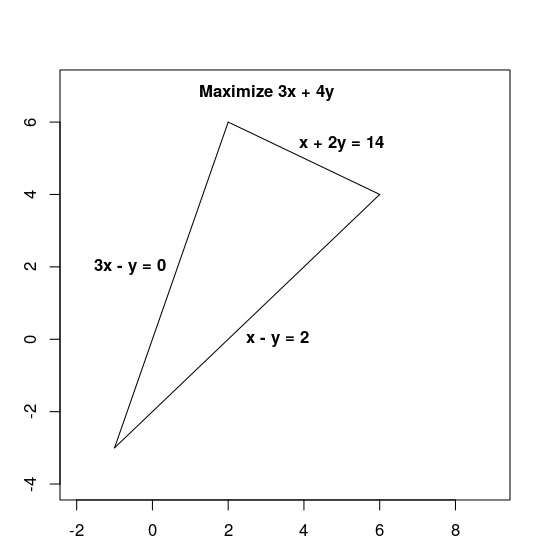
3x + 4y değerini aşağıdaki kısıtlamalara tabi olarak en üst düzeye çıkarın:
x + 2y≤ 143x - y≥ 0x - y≤ 2
Hem hedef fonksiyon hem de 3x + 4y ve kısıtlamalar, doğrusal ifadelerle verildiği için bu problemi doğrusal bir problemdir.
Kısıtlamalar, iç kısmı da dahil olmak üzere aşağıda gösterilen üçgen olan uygun bölgeyi tanımlar.
Bir açılış sayfası sorununu çözmeye yönelik temel adımlar
Bir LP sorununu çözmek için programınız aşağıdaki adımları içermelidir:
- Doğrusal çözücü sarmalayıcısını içe aktarın.
- LP çözücüyü tanımlayın.
- değişkenleri tanımlayın,
- kısıtları tanımlamanız,
- hedefi tanımlayın
- LP çözücüyü arayın ve
- çözümü göster
MPSolver kullanan çözüm
Aşağıdaki bölümde, MPSolver sarmalayıcısı ve bir LP çözücü kullanarak problemi çözen bir program sunulmaktadır.
Not: Aşağıdaki programı çalıştırmak için OR-Tools'u yüklemeniz gerekir.
VEYA araçlarındaki birincil doğrusal optimizasyon çözücü, Google'ın şirket içi doğrusal programlama çözücü olan Glop'tur. Hızlı, bellek açısından verimli ve sayısal açıdan kararlıdır.
Doğrusal çözücü sarmalayıcıyı içe aktarma
Aşağıda gösterildiği gibi, MIP çözücüler ve doğrusal çözücülere yönelik bir arayüz olan VEYA Araçları doğrusal çözücü sarmalayıcısını içe aktarın (veya dahil edin).
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
C++
#include <iostream> #include <memory> #include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
Java
import com.google.ortools.Loader; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver; import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
C#
using System; using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
LP çözücüyü tanımlama
MPsolver, Glop dahil birçok farklı çözücü için bir sarmalayıcıdır. Aşağıdaki kod, GLOP çözücüyü tanımlar.
Python
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
C++
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
Java
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
C#
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
Not: Alternatif bir LP çözücü kullanmak için GLOP yerine PDLP yazın. Çözücü seçimi hakkında daha fazla bilgi için gelişmiş LP çözme bölümüne bakın. Üçüncü taraf çözücülerin kurulumu için de kurulum kılavuzuna bakın.
Değişkenleri oluşturma
Öncelikle, değerleri 0 ile sonsuz arasında olan x ve y değişkenlerini oluşturun.
Python
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
C++
const double infinity = solver->infinity(); // x and y are non-negative variables. MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x"); MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y"); LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
Java
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
C#
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
Kısıtlamaları tanımlama
Ardından, değişkenlerdeki kısıtlamaları tanımlayın. Her kısıta benzersiz bir ad (constraint0 gibi) verin ve ardından kısıtlamanın katsayılarını tanımlayın.
Python
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
C++
// x + 2*y <= 14. MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0); c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2); // 3*x - y >= 0. MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity); c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3); c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1); // x - y <= 2. MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0); c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1); c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1); LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
Java
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
C#
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
Hedef işlevini tanımlama
Aşağıdaki kod, 3x + 4y hedef işlevini tanımlar ve bunun bir maksimizasyon problemi olduğunu belirtir.
Python
# Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
C++
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective(); objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3); objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4); objective->SetMaximization();
Java
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y. MPObjective objective = solver.objective(); objective.setCoefficient(x, 3); objective.setCoefficient(y, 4); objective.setMaximization();
C#
// Objective function: 3x + 4y. solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
Çözücüyü çağır
Aşağıdaki kod çözücüyü çağırır.
Python
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
C++
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
Java
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
C#
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
Çözümü görüntüleyin
Aşağıdaki kod çözümü gösterir.
Python
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
C++
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:"; LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value(); LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value(); LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
Java
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
C#
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Programların tamamı
Programların tamamı aşağıda gösterilmektedir.
Python
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def LinearProgrammingExample():
"""Linear programming sample."""
# Instantiate a Glop solver, naming it LinearExample.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
if not solver:
return
# Create the two variables and let them take on any non-negative value.
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
print("Number of variables =", solver.NumVariables())
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
# Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
# Solve the system.
print(f"Solving with {solver.SolverVersion()}")
status = solver.Solve()
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print(f"Objective value = {solver.Objective().Value():0.1f}")
print(f"x = {x.solution_value():0.1f}")
print(f"y = {y.solution_value():0.1f}")
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
print("\nAdvanced usage:")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.wall_time():d} milliseconds")
print(f"Problem solved in {solver.iterations():d} iterations")
LinearProgrammingExample()
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include "ortools/linear_solver/linear_solver.h"
namespace operations_research {
void LinearProgrammingExample() {
std::unique_ptr<MPSolver> solver(MPSolver::CreateSolver("SCIP"));
if (!solver) {
LOG(WARNING) << "SCIP solver unavailable.";
return;
}
const double infinity = solver->infinity();
// x and y are non-negative variables.
MPVariable* const x = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable* const y = solver->MakeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
LOG(INFO) << "Number of variables = " << solver->NumVariables();
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint* const c0 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 14.0);
c0->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c0->SetCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint* const c1 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(0.0, infinity);
c1->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
c1->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint* const c2 = solver->MakeRowConstraint(-infinity, 2.0);
c2->SetCoefficient(x, 1);
c2->SetCoefficient(y, -1);
LOG(INFO) << "Number of constraints = " << solver->NumConstraints();
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
MPObjective* const objective = solver->MutableObjective();
objective->SetCoefficient(x, 3);
objective->SetCoefficient(y, 4);
objective->SetMaximization();
const MPSolver::ResultStatus result_status = solver->Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (result_status != MPSolver::OPTIMAL) {
LOG(FATAL) << "The problem does not have an optimal solution!";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Solution:";
LOG(INFO) << "Optimal objective value = " << objective->Value();
LOG(INFO) << x->name() << " = " << x->solution_value();
LOG(INFO) << y->name() << " = " << y->solution_value();
}
} // namespace operations_research
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
operations_research::LinearProgrammingExample();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Java
package com.google.ortools.linearsolver.samples;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/** Simple linear programming example. */
public final class LinearProgrammingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 3);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 4);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");
}
private LinearProgrammingExample() {}
}
C#
using System;
using Google.OrTools.LinearSolver;
public class LinearProgrammingExample
{
static void Main()
{
Solver solver = Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP");
if (solver is null)
{
return;
}
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
Variable x = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "x");
Variable y = solver.MakeNumVar(0.0, double.PositiveInfinity, "y");
Console.WriteLine("Number of variables = " + solver.NumVariables());
// x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0);
// 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0);
// x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0);
Console.WriteLine("Number of constraints = " + solver.NumConstraints());
// Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y);
Solver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.Solve();
// Check that the problem has an optimal solution.
if (resultStatus != Solver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL)
{
Console.WriteLine("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Solution:");
Console.WriteLine("Objective value = " + solver.Objective().Value());
Console.WriteLine("x = " + x.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("y = " + y.SolutionValue());
Console.WriteLine("\nAdvanced usage:");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.WallTime() + " milliseconds");
Console.WriteLine("Problem solved in " + solver.Iterations() + " iterations");
}
}
Optimum çözüm
Program, aşağıda gösterildiği gibi, soruna en uygun çözümü döndürür.
Number of variables = 2
Number of constraints = 3
Solution:
x = 6.0
y = 4.0
Optimal objective value = 34.0
Çözümü gösteren bir grafik aşağıda verilmiştir:
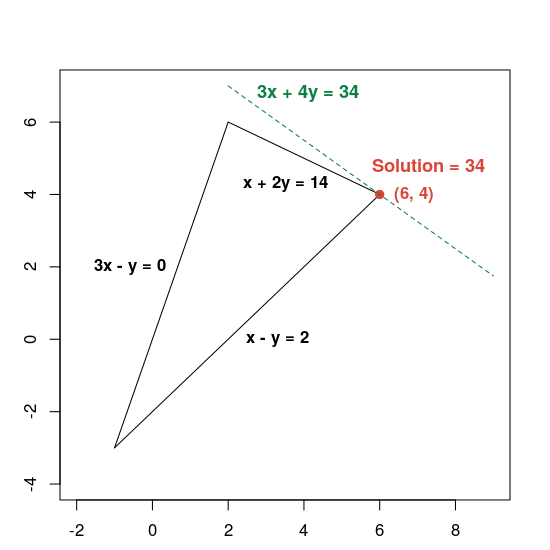
Kesikli yeşil çizgi, hedef işlevinin optimum değeri 34'e eşit olarak ayarlanmasıyla tanımlanır. Denklemi 3x + 4y = c biçiminde olan herhangi bir doğru, kesikli çizgiye paraleldir. 34 ise çizginin uygun bölgeyle kesiştiği en büyük c değeridir.
Doğrusal optimizasyon problemlerini çözme hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinmek için gelişmiş LP çözme bölümünü inceleyin.
