Page Summary
-
Rotating barcodes enhance security by changing periodically, mitigating risks associated with ticket theft or unauthorized resale.
-
They serve as a fallback for devices lacking NFC support, ensuring accessibility for all users.
-
Google Wallet prioritizes Smart Tap, followed by rotating barcodes, and lastly static barcodes for pass redemption.
-
For optimal security, it is recommended to save pass objects to the Google Wallet server and reference them by ID in JWTs, avoiding exposure of the rotating barcode's secret key.
-
Each pass should ideally have a unique OTP secret key, remaining valid throughout the pass's lifespan.
Introduction
Rotating barcodes look just like regular barcodes but change periodically, typically every minute, and the terminal/reader is programmed to only accept the most recent one. This security measure reduces the risks associated with barcode screenshotting, in particular ticket theft or unauthorized ticket resale. Rotating barcodes can also act as a fallback for devices that can’t take advantage of Smart Tap, due to not supporting NFC (lack of hardware, or software disabled).
API reference
For technical details about Rotating Barcodes, see the
RotatingBarcode type.
Example payload
| JSON | |
|---|---|
{ "rotatingBarcode": { "type": "QR_CODE", "valuePattern": "MyRotatingBarcode-{totp_timestamp_seconds}-{totp_value_0}", "alternateText": "Ticket#: 1234567890", "totpDetails": { "algorithm": "TOTP_SHA1", "periodMillis": "3000", "parameters": [ { "key": "3132333435363738393031323334353637383930", "valueLength": "8" } ] } } } |
|
Fallback Mechanisms
On the user device, only one redemption mechanism is used at a given time, depending on how the pass is configured and on the capabilities of the device. In the order of priority, the following redemption types are used:
-
Smart Tap: If a smart-tap payload is specified and if the device supports
NFC/HCE
- Note, this can be overridden by the user by clicking “Show code,” which will force the display of the rotating barcode/static barcode.
- Rotating barcode: If a rotating barcode payload is specified
- Static barcode: If a barcode payload is specified
Specifying multiple redemption payloads can ensure all users are supported but may have security implications. In particular, using a static barcode as a fallback for a rotating barcode negates most of the security benefits of using rotating barcodes. A static barcode fallback will only be shown in web views or on clients that do not support rotating barcodes. As of today, we expect all Google Wallet clients to support rotating barcodes.
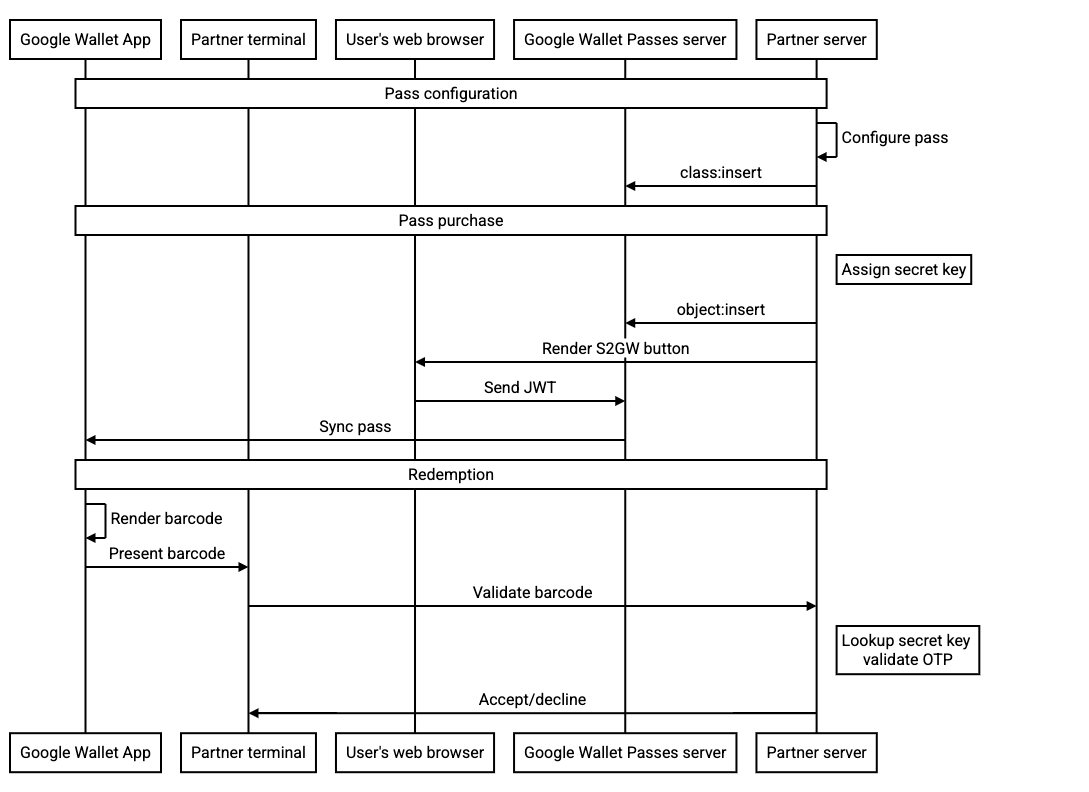
Save Flow
The Google Wallet API offers several flows, including:
- Creating the transit classes at save time, or ahead of time
- Sending the complete objects in your JWT, or saving the objects ahead of time then referencing them by ID in your JWT
- Updating the objects after they have been saved
The proposed rotatingBarcode field is compatible with all these flows, however, in order to improve security, we suggest the following:
-
Call the
object:insertAPI to insert the pass to the Google Wallet server and configure the Add to Google Wallet button to reference the specific object by ID in your JWT. This ensures that the resulting JWT does not include the secret key of the rotating barcode. - Use an OTP secret key that is scoped to a single pass
- The key, unless it is updated, is expected to be valid for the lifespan of the pass. We do not expect this key to be updated on any frequency during the course of normal operation.
The following sequence diagram illustrates the flow between the various actors for a typical integration: