The MediaPipe Framework Android Archive (AAR) library is a convenient way to use MediaPipe Framework with Android Studio and Gradle. MediaPipe Framework doesn't publish a general AAR that can be used by all projects. Instead, developers need to create a mediapipe_aar() target to generate a custom AAR file for their own projects. This is necessary in order to include specific resources such as MediaPipe calculators needed for each project.
Steps to build a MediaPipe Framework AAR
Create a mediapipe_aar() target.
In the MediaPipe directory, create a new mediapipe_aar() target in a BUILD file. You need to figure out what calculators are used in the graph and provide the calculator dependencies to the mediapipe_aar(). For example, to build an AAR for a face detection graph, you can put the following code into mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example/BUILD.
load("//mediapipe/java/com/google/mediapipe:mediapipe_aar.bzl", "mediapipe_aar") mediapipe_aar( name = "mediapipe_face_detection", calculators = ["//mediapipe/graphs/face_detection:mobile_calculators"], )Run the Bazel build command to generate the AAR.
bazel build -c opt --strip=ALWAYS \ --host_crosstool_top=@bazel_tools//tools/cpp:toolchain \ --fat_apk_cpu=arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a \ --legacy_whole_archive=0 \ --features=-legacy_whole_archive \ --copt=-fvisibility=hidden \ --copt=-ffunction-sections \ --copt=-fdata-sections \ --copt=-fstack-protector \ --copt=-Oz \ --copt=-fomit-frame-pointer \ --copt=-DABSL_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=2 \ --linkopt=-Wl,--gc-sections,--strip-all \ //path/to/the/aar/build/file:aar_name.aarFor the face detection AAR target we made in step 1, run:
bazel build -c opt --strip=ALWAYS \ --host_crosstool_top=@bazel_tools//tools/cpp:toolchain \ --fat_apk_cpu=arm64-v8a,armeabi-v7a \ --legacy_whole_archive=0 \ --features=-legacy_whole_archive \ --copt=-fvisibility=hidden \ --copt=-ffunction-sections \ --copt=-fdata-sections \ --copt=-fstack-protector \ --copt=-Oz \ --copt=-fomit-frame-pointer \ --copt=-DABSL_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=2 \ --linkopt=-Wl,--gc-sections,--strip-all \ //mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example:mediapipe_face_detection.aar # It should print: # Target //mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example:mediapipe_face_detection.aar up-to-date: # bazel-bin/mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example/mediapipe_face_detection.aar(Optional) Save the AAR to your preferred location.
cp bazel-bin/mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example/mediapipe_face_detection.aar /absolute/path/to/your/preferred/location
Steps to use a MediaPipe Framework AAR in Android Studio with Gradle
Start Android Studio and go to your project.
Copy the AAR into app/libs.
cp bazel-bin/mediapipe/examples/android/src/java/com/google/mediapipe/apps/aar_example/mediapipe_face_detection.aar /path/to/your/app/libs/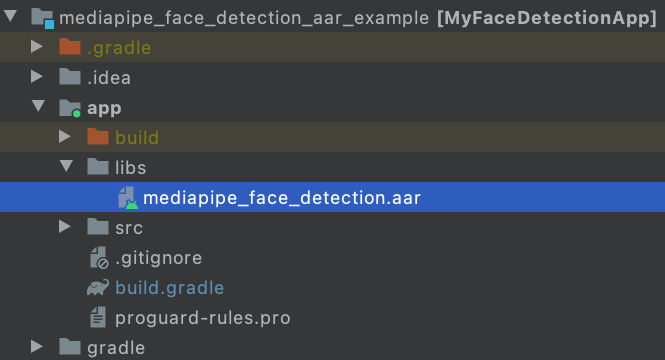
Make app/src/main/assets and copy assets (graph, model, and etc) into app/src/main/assets.
Build the MediaPipe binary graph and copy the assets into app/src/main/assets, e.g., for the face detection graph, you need to build and copy the binary graph and the face detection tflite model.
bazel build -c opt mediapipe/graphs/face_detection:face_detection_mobile_gpu_binary_graph cp bazel-bin/mediapipe/graphs/face_detection/face_detection_mobile_gpu.binarypb /path/to/your/app/src/main/assets/ cp mediapipe/modules/face_detection/face_detection_short_range.tflite /path/to/your/app/src/main/assets/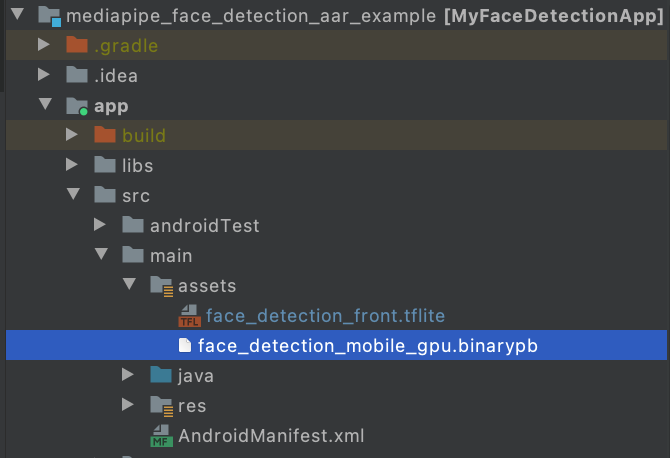
Modify app/build.gradle to add MediaPipe dependencies and MediaPipe AAR.
dependencies { implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar', '*.aar']) implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.0.2' implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:1.1.3' testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.12' androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.0' androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.1.1' // MediaPipe deps implementation 'com.google.flogger:flogger:latest.release' implementation 'com.google.flogger:flogger-system-backend:latest.release' implementation 'com.google.code.findbugs:jsr305:latest.release' implementation 'com.google.guava:guava:27.0.1-android' implementation 'com.google.protobuf:protobuf-javalite:3.19.1' // CameraX core library def camerax_version = "1.0.0-beta10" implementation "androidx.camera:camera-core:$camerax_version" implementation "androidx.camera:camera-camera2:$camerax_version" implementation "androidx.camera:camera-lifecycle:$camerax_version" // AutoValue def auto_value_version = "1.8.1" implementation "com.google.auto.value:auto-value-annotations:$auto_value_version" annotationProcessor "com.google.auto.value:auto-value:$auto_value_version" }Follow our Android app examples to use MediaPipe in Android Studio for your use case. If you are looking for an example, a face detection example can be found here and a multi-hand tracking example can be found here.
