The PLACES_COUNT function returns a single count value of places based on the
specified search area and search filters. You must specify the search area to
the PLACES_COUNT function and can optionally specify additional filter
parameters, such as place type, operating status, price level, and more.
Because the PLACES_COUNT function returns a single value, call it using
a SELECT clause.
Input parameters:
Required: The
geographyfilter parameter that specifies the search area. Thegeographyparameter takes a value defined by the BigQueryGEOGRAPHYdata type, which supports points, linestrings, and polygons.Optional: Additional filter parameters to refine your search.
Returns:
- A single
countvalue as anINT64.
- A single
Example: Calculate the number of places in a search radius
The simplest PLACES_COUNT function call returns a single count of all places
in a geographical area. In this example, you return the count of all operational
places within 1000 meters of the Empire State building.
This example uses the BigQuery
ST_GEOGPOINT
function to return a GEOGRAPHY value from a point.
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000 -- Radius in meters ) ) as count;
The response contains a single count:
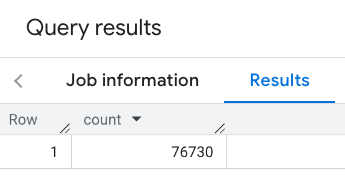
A more typical call applies filters to the search area. The next example uses filters to limit the search to only return a count of:
- Places of type
restaurantwith the minimum rating of 3 - A price level of inexpensive or medium
- Currently operational
- Allows dogs
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 3, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
The filtered response:

Remember that place dataset queries enforce a minimum count threshold of 5. One of the advantages of the place count functions is that they can return any counts, including 0. For example, the following call returns a count of 1:
SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 500, -- Radius in meters 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 4.0, 'free_parking_lot', TRUE, 'good_for_watching_sports', TRUE ) ) as count;
Example: Calculate the number of restaurants using a polygon
You can use a polygon to specify the search area. When using a polygon, the points of the polygon must define a closed loop where the first point in the polygon is the same as the last point.
This example uses the BigQuery
ST_GEOGFROMTEXT
function to return a GEOGRAPHY value from a polygon.
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('''POLYGON((-73.985708 40.75773,-73.993324 40.750298, -73.9857 40.7484,-73.9785 40.7575, -73.985708 40.75773))'''); -- NYC viewport SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- viewport 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
The response for the viewport:
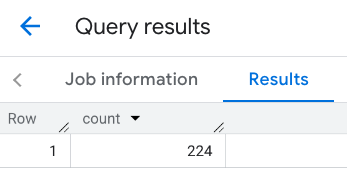
Example: Calculate the number of restaurants using a line
In the next example, you define the search area using a line of connected points with a search radius of 100 meters around the line. The line is similar to a travel route calculated by the Routes API. The route might be for a vehicle, a bicycle, or for a pedestrian:
DECLARE geo GEOGRAPHY; SET geo = ST_GEOGFROMTEXT('LINESTRING(-73.98903537033028 40.73655649223003,-73.93580216278471 40.80955538843361)'); -- NYC line SELECT `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'geography',geo, -- line 'geography_radius', 100, -- Radius around line 'types', ["restaurant"], 'min_rating', 1.0, 'max_rating', 4.5, 'min_user_rating_count', 1, 'max_user_rating_count', 10000, 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE', 'PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'], 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'allows_dogs', TRUE ) ) as count;
The response for the line:
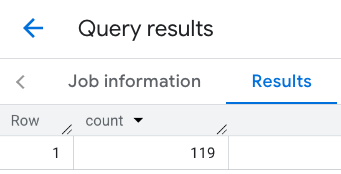
Example: Combine the results of multiple calls
You can combine the results of multiple calls to the PLACES_COUNT function.
For example, you want a single result showing the number of restaurants for
the following price levels within a specific area:
PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_MODERATEPRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVEPRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"
In this example, you create a loop to call the PLACES_COUNT function for each
price level, and insert the results of each call to a temporary table. You then
query the temporary table to display the results:
-- Create a temp table to hold the results. CREATE TEMP TABLE results (type STRING, count INT64); -- Create a loop that calls PLACES_COUNT for each price level. FOR types IN (SELECT type FROM UNNEST(["PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE", "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE", "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE"]) as type) DO INSERT INTO results VALUES (types.type, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', [types.type] ))); END FOR; -- Query the table of results. SELECT * FROM results;
The combined response:
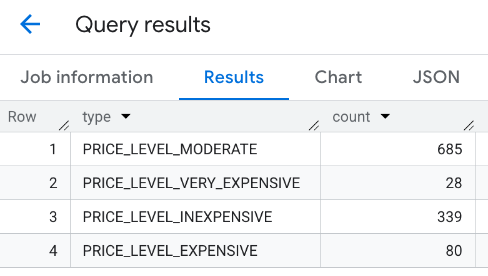
Another option is to use the UNION ALL command to combine the results of
multiple SELECT statements. The following example shows the same results as
from the previous example:
SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_INEXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_MODERATE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count UNION ALL SELECT "PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE" as price_level, `PROJECT_NAME.places_insights___us.PLACES_COUNT`( JSON_OBJECT( 'types', ["restaurant"], 'geography', ST_GEOGPOINT(-73.9857, 40.7484), -- Empire State Building 'geography_radius', 1000, -- Radius in meters 'business_status', ['OPERATIONAL'], 'price_level', ['PRICE_LEVEL_VERY_EXPENSIVE'] ) ) as count
