Page Summary
-
The Autocomplete (New) service for iOS provides real-time place suggestions based on user input and customizable search criteria like location and place type.
-
Developers can refine search results using parameters like location restriction/bias, place type filters, and country limitations.
-
The API handles billing through session tokens and allows retrieval of detailed place information via a separate Place Details (New) request.
-
Autocomplete with Filter Comprehension demonstrates how to use filters like location restriction, bias, and place types to refine autocomplete suggestions, with code examples provided in Swift and Objective-C.
-
When using Autocomplete, attributions are required, including the Google logo, even if a map is not displayed alongside the suggestions.
The Autocomplete (New) service is an iOS API that returns place suggestions in response to a request. In the request, specify a text search string and geographic bounds that control the search area.
The Autocomplete (New) service can match on full words and substrings of the input, resolving place names, addresses, and plus codes. Applications can therefore send queries as the user types, to provide on-the-fly place suggestions.
Place suggestions are places, such as businesses, addresses, and points of interest, based on the specified input text string and search area.
For example, you call the API using as input a string that contains a partial user input, "Spagh", with the search area limited to New York City. The response then contains a list of place suggestions that match the search string and search area, such as the restaurant named "Cafe Spaghetti", along with details about the place.
The returned place suggestions are designed to be presented to the user so that they can select the desired place. You can make a Place Details (New) request to get more information about any of the returned place suggestions.
You can integrate Autocomplete (New) functionality into your app in two main ways:
- Get place predictions programmatically: Call the API directly to retrieve predictions and display them in a custom user interface.
- Add the Place Autocomplete widget: Provides a ready-to-use search autocomplete experience that displays predictions as the user types.
Get place predictions programmatically
Autocomplete (New) requests
Create an autocomplete request by calling a method on the
GMSPlacesClient.
You can pass parameters in the
GMSAutocompleteRequest
object. The response provides Autocomplete suggestions within a
GMSAutocompletePlaceSuggestion
object.
The API key and
query
parameters are required. You can also include
GMSAutocompleteSessionToken
to associate requests with a billing session and
GMSAutocompleteFilter
to apply to the results.
Places Swift SDK version
Create an autocomplete request by calling a method on the
PlacesClient.
You can pass parameters in the
AutocompleteRequest
object. The response provides Autocomplete suggestions within a
AutocompletePlaceSuggestion
object.
The API key and query parameters are required. You can also include
AutocompleteSessionToken
to associate requests with a billing session and
AutocompleteFilter
to apply to the results.
For more information about required and optional parameters, see the parameters section of this document.
Places Swift SDK
let center = (37.3913916, -122.0879074) let northEast = (37.388162, -122.088137) let southWest = (37.395804, -122.077023) let bias = RectangularCoordinateRegion(northEast: northEast, southWest: southWest) let filter = AutocompleteFilter(types: [ .restaurant ], origin: center, coordinateRegionBias: bias) let autocompleteRequest = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Sicilian piz", filter: filter) switch await placesClient.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(with: autocompleteRequest) { case .success(let autocompleteSuggestions): // Handle suggestions. case .failure(let placesError): // Handle error. }
Swift
let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken() let northWestBounds = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.921628, -73.700051) let southEastBounds = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.477398, -74.259087) let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.types = [kGMSPlaceTypeRestaurant] filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption(northWestBounds, southEastBounds) let request = GMSAutocompleteRequest(query:"Spagh") request.filter = filter request.sessionToken = token GMSPlacesClient.shared().fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(from: request, callback: { ( results, error ) in if let error = error { print("Autocomplete error: \(error)") return } if let autocompleteResults = results { for result in autocompleteResults { print("Result \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.placeID)) with \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.attributedFullText))") } } })
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D northEast = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.388162, -122.088137); CLLocationCoordinate2D southWest = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.395804, -122.077023); GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.types = @[ kGMSPlaceTypeRestaurant ]; filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption(northEast, southWest); GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Sicilian piz"]; request.sessionToken = token; request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> * results, NSError * error){ // Handle response for (GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *suggestion in results) { if (suggestion.placeSuggestion) { // Show place suggestion data. } } }];
Autocomplete (New) responses
Autocomplete returns an array of up to five
GMSAutocompleteSuggestion instances. The array contains:
placeIDtypes: Types that apply to this place.distanceMeters: Distance from origin.attributedFullText: Full human-readable text of a suggestion.attributedPrimaryText: Human-readable primary text of a suggestion.attributedSecondaryText: Human-readable secondary text of a suggestion.structuredFormat: The specific name and disambiguating text, like city or region.
Required parameters
query
The text string on which to search. Specify full words and substrings, place names, addresses, and plus codes. The Autocomplete (New) service returns candidate matches based on this string and orders results based on their perceived relevance.
Optional parameters
sessionToken
Session tokens are user-generated strings that track Autocomplete (New) calls—both calls made through the widget and programmatic calls—as "sessions." Autocomplete (New) uses session tokens to group the query and selection phases of a user autocomplete search into a discrete session for billing purposes.
You can expose your Places Autocomplete session token in order to pass it to other services that are not a part of the Places SDK for iOS, such as to Address Validation:
Places Swift SDK
let token = AutocompleteSessionToken() let filter = AutocompleteFilter(origin: CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(39.7, -94.5)) let request = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Piz", sessionToken: token, filter: filter) PlacesClient.shared.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(request: request) { case .success(let suggestions): ... case .failure(let placesError): print(placesError) } // pass token's string format to use with a service that is not a part of iOS SDK. print("token: \(token)")
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Piz"]; GMSAutocompleteSessionToken *token = [[GMSAutocompleteSessionToken alloc] init]; request.sessionToken = token; GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.origin = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:39.7 longitude:-94.5]; filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption(topLocation, bottomLocation); request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> *_Nullable results, NSError *_Nullable error) { ... }]; // pass token's string format to use with a service that is not a part of iOS SDK. NSLog(@"%@", token.description);
See Session tokens for more information.
Optional AutocompleteFilter parameters
types
A place can only have a single primary type from types Table
A or Table
B associated with it.
For example, the primary type might be mexican_restaurant or steak_house.
By default, the API returns all places based on the input parameter,
regardless of the primary type value associated with the place. Restrict results
to be of a certain primary type or primary types by passing the types
parameter.
Use this parameter to specify up to five type values from Table A or Table B. A place must match one of the specified primary type values to be included in the response.
The request is rejected with an INVALID_REQUEST error if:
- More than five types are specified.
- Any unrecognized types are specified.
For example, to limit results to sporting goods stores, specify that type in
your AutocompleteFilter:
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter(types: [ PlaceType(rawValue: "sporting_goods_store") ])
Swift
let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.types = ["sporting_goods_store"]
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.types = @[ "sporting_goods_store" ];
countries
Only include results from the list of specified regions, specified as an array of up to 15 ccTLD ("top-level domain") two-character values. If omitted, no restrictions are applied to the response. For example, to limit the regions to Germany and France:
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter(countries: ["DE", "FR"])
Swift
let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.countries = ["DE", "FR"]
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.countries = @[ @"DE", @"FR" ];
If you specify both locationRestriction and countries, the results are
located in the area of intersection of the two settings.
inputOffset
The zero-based Unicode character offset indicating the cursor position in
input. The cursor position can influence what predictions are returned. If
empty, it defaults to the length of input.
locationBias or locationRestriction
You can specify locationBias or locationRestriction, but not both, to define
the search area. Think of locationRestriction as specifying the region which
the results must be within, and locationBias as specifying the region that the
results must be near but can be outside of the area.
locationBiasspecifies an area to search. This location serves as a bias, which means results around the specified location can be returned, including results outside the specified area.locationRestrictionspecifies an area to search. Results outside the specified area are not returned.
Specify the locationBias or locationRestriction region as a rectangular
viewport or as a circle.
A circle is defined by center point and radius in meters. The radius must be
between 0.0 and 50000.0, inclusive. The default value is 0.0. For
locationRestriction, you must set the radius to a value greater than 0.0.
Otherwise, the request returns no results.
For example:
Places Swift SDK
let center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.477398, -74.259087) let bias = CircularCoordinateRegion(center: center, radius: 1000.0) let filter = AutocompleteFilter(coordinateRegionBias: bias)
Swift
let center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.730610, -73.935242) let radius = 1000.0 filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius)
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.730610, -73.935242); radius = 1000.0; GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius);
A rectangle is a latitude-longitude viewport, represented as two diagonally
opposite low and high points. A viewport is considered a closed region,
meaning it includes its boundary. The latitude bounds must range between -90 to
90 degrees inclusive, and the longitude bounds must range between -180 to 180
degrees inclusive:
- If
low=high, the viewport consists of that single point. - If
low.longitude>high.longitude, the longitude range is inverted (the viewport crosses the 180 degree longitude line). - If
low.longitude= -180 degrees andhigh.longitude= 180 degrees, the viewport includes all longitudes. - If
low.longitude= 180 degrees andhigh.longitude= -180 degrees, the longitude range is empty.
Both low and high must be populated, and the represented box cannot be
empty. An empty viewport results in an error.
For example, this viewport fully encloses New York City:
Places Swift SDK
let northEast = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.477398, -74.259087) let southWest = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.921628, -73.700051) let filter = AutocompleteFilter(coordinateRegionBias: bias)
Swift
let high = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.921628, -73.700051) let low = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.477398, -74.259087) let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption(high, low)
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D high = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(40.477398, -74.259087); CLLocationCoordinate2D low = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(440.921628, -73.700051); GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceRectangularLocationOption(high, low);
origin
The origin point from which to calculate straight-line distance to the
destination (returned as distanceMeters). If this value is omitted,
straight-line distance won't be returned. Must be specified as latitude and
longitude coordinates:
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter(origin: CLLocation(latitude: 37.395804, longitude: -122.077023))
Swift
let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.origin = CLLocation(latitude: 37.395804, longitude: -122.077023)
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.origin = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:37.395804 longitude: -122.077023];
regionCode
The region code used to format the response, specified as a ccTLD ("top-level domain") two-character value. Most ccTLD codes are identical to ISO 3166-1 codes, with some notable exceptions. For example, the United Kingdom's ccTLD is "uk" (.co.uk) while its ISO 3166-1 code is "gb" (technically for the entity of "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland").
If you specify an invalid region code, the API returns an INVALID_ARGUMENT
error. The parameter can affect results based on applicable law.
shouldIncludePureServiceAreaBusinesses
If true, returns pure service area businesses in the response array. A pure
service area business is a business that visits or delivers to customers
directly, but does not serve customers at their business address.
For example:
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter() filter.shouldIncludePureServiceAreaBusinesses = true
Swift
let filter = AutocompleteFilter() filter.shouldIncludePureServiceAreaBusinesses = true
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.shouldIncludePureServiceAreaBusinesses = YES;
Add the Place Autocomplete widget
To more easily provide a consistent place autocomplete experience, you can add
the Place Autocomplete widget to your app. The widget provides a dedicated,
full-screen interface that handles user input and displays place predictions to
the user while returning
AutocompletePlaceSuggestion
objects to the app. You can then make a Place Details
(New) request to get
additional information about any of the place predictions.
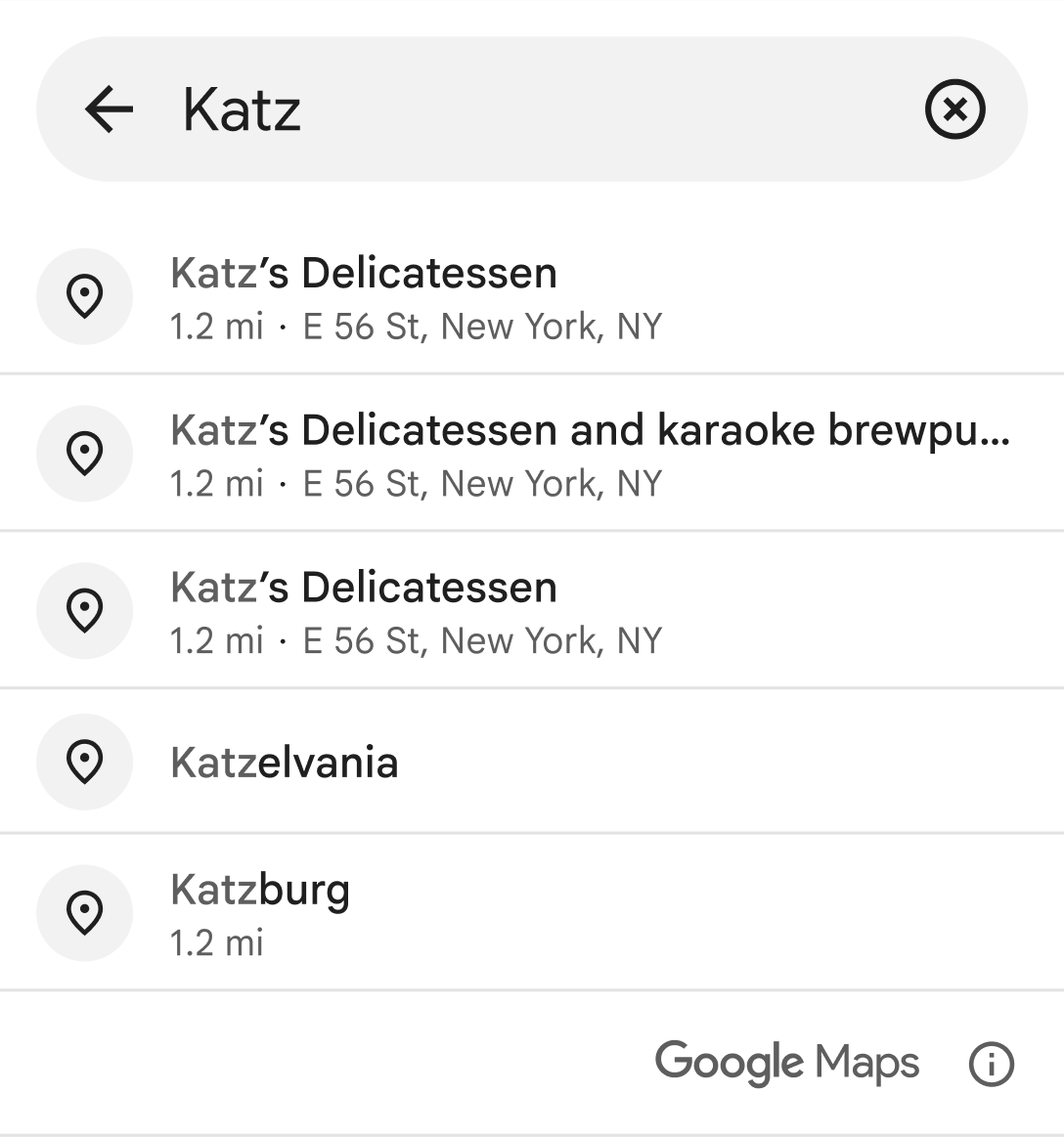
Like when getting place predictions programmatically,
the Place Autocomplete widget lets you use session
tokens to
group autocomplete requests into session for billing purposes. You can pass a
session token by calling
AutocompleteSessionToken().
If you don't provide a session token, the widget will create an Autocomplete
session token for you, which can then be obtained from the onSelection
callback. For more information on using session tokens, see About session
tokens.
When the show binding value is set to true, the user will be brought to a
full screen view where they can select a place. As the user types, the widget
returns suggestions for places such as businesses, addresses, and points of
interest. When the user selects a place, the widget calls the onSelection
handler with the selected place, and closes the fullscreen view.
Place Autocomplete widget parameters
In addition to the parameters available programmatically, the Place Autocomplete widget also offers the following parameters.
show
show specifies whether the widget is shown.
onSelection
The closure to run when a place is selected.
onError
The closure to run when an error occurs. A
PlacesError
will be passed if an error occurs.
Content and theme customization
The
AutocompleteUICustomization
parameters specify the UI cusomizations to apply to the widget. The
customization options are:
AutocompleteListDensity. This parameter lets you choose the density of the suggestion list, eithermultiLineortwoLine.AutocompleteUIIcon. This parameter lets you choose whether to show the default icon for each list item.theme. This parameter specifies a custom theme that overrides any of the default style attributes. You can customize the colors, typography, spacing, borders, and corners of your Place Autocomplete component. The default isPlacesMaterialTheme. Any theme attributes that are not overridden use the default styles.
Autocomplete (New) examples
Use locationRestriction and locationBias
Autocomplete (New) uses IP biasing by default to
control the search area. With IP biasing, the API uses the IP address of the
device to bias the results. You can optionally use locationRestriction or
locationBias, but not both, to specify
an area to search.
Location restriction specifies the area to search. Results outside the specified area are not returned. The following example uses location restriction to limit the request to a circular location restriction with a 5000-meter radius centered on San Francisco:
Places Swift SDK
let center = (37.775061, -122.419400) let radius = 5000.0 let restriction = CircularCoordinateRegion(center: center, radius: radius) let filter = AutocompleteFilter(coordinateRegionRestriction: restriction) let token = AutocompleteSessionToken() let autocompleteRequest = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Sicilian piz", sessionToken: token, filter: filter) switch await placesClient.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(with: autocompleteRequest) { case .success(let autocompleteSuggestions): for suggestion in autocompleteSuggestions { switch suggestion { case .place: // Show place suggestion data. } } case .failure(let placesError): // Handle error. }
Swift
let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken() let center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.775061, -122.419400) let radius = 5000.0 let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.locationRestriction = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius) let request = GMSAutocompleteRequest(query:"Piz") request.filter = filter request.sessionToken = token GMSPlacesClient.shared().fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(from: request, callback: { ( results, error ) in if let error = error { print("Autocomplete error: \(error)") return } if let autocompleteResults = results { for result in autocompleteResults { print("Result \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.placeID)) with \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.attributedFullText))") } } })
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.775061, -122.419400); radius = 5000.0; GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.locationRestriction = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius); GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Sicilian piz"]; request.sessionToken = token; request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> * results, NSError * error){ // Handle response for (GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *suggestion in results) { if (suggestion.placeSuggestion) { // Show place suggestion data. } } }];
With location bias, the location serves as a bias, which means results around the specified location can be returned, including results outside the specified area. The next example changes the previous request to use location bias:
Places Swift SDK
let center = (37.775061, -122.419400) let radius = 5000.0 let bias = CircularCoordinateRegion(center: center, radius: radius) let filter = AutocompleteFilter(coordinateRegionBias: bias) let token = AutocompleteSessionToken() let autocompleteRequest = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Sicilian piz", sessionToken: token, filter: filter) switch await placesClient.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(with: autocompleteRequest) { case .success(let autocompleteSuggestions): for suggestion in autocompleteSuggestions { switch suggestion { case .place: // Show place suggestion data. } } case .failure(let placesError): // Handle error. }
Swift
let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken() let center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.775061, -122.419400) let radius = 5000.0 let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius) let request = GMSAutocompleteRequest(query:"Piz") request.filter = filter request.sessionToken = token GMSPlacesClient.shared().fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(from: request, callback: { ( results, error ) in if let error = error { print("Autocomplete error: \(error)") return } if let autocompleteResults = results { for result in autocompleteResults { print("Result \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.placeID)) with \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.attributedFullText))") } } })
Objective-C
CLLocationCoordinate2D center = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(37.775061, -122.419400); radius = 5000.0; GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.locationBias = GMSPlaceCircularLocationOption(center, radius); GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Sicilian piz"]; request.sessionToken = token; request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> * results, NSError * error){ // Handle response for (GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *suggestion in results) { if (suggestion.placeSuggestion) { // Show place suggestion data. } } }];
Use types
Use the types parameter to restrict results from a request to be of a certain type as listed in Table A and Table B. You can specify an array of up to five values. If omitted, all types are returned.
The following example specifies a query string of "Soccer" and uses the types
parameter to restrict results to establishments of type
"sporting_goods_store":
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter(types: [ PlaceType(rawValue: "sporting_goods_store") ]) let token = AutocompleteSessionToken() let autocompleteRequest = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Soccer", sessionToken: token, filter: filter) switch await placesClient.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(with: autocompleteRequest) { case .success(let autocompleteSuggestions): for suggestion in autocompleteSuggestions { switch suggestion { case .place: // Show place suggestion data. } } case .failure(let placesError): // Handle error. }
Swift
let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken() let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.types = ["sporting_goods_store"] let request = GMSAutocompleteRequest(query:"Soccer") request.filter = filter request.sessionToken = token GMSPlacesClient.shared().fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(from: request, callback: { ( results, error ) in if let error = error { print("Autocomplete error: \(error)") return } if let autocompleteResults = results { for result in autocompleteResults { print("Result \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.placeID)) with \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.attributedFullText))") } } })
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.types = @[ "sporting_goods_store" ]; GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Soccer"]; request.sessionToken = token; request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> * results, NSError * error){ // Handle response for (GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *suggestion in results) { if (suggestion.placeSuggestion) { // Show place suggestion data. } } }];
Use origin
When you include the origin parameter in the request, specified as
latitude and longitude coordinates, the API includes the straight-line distance
from the origin to the destination in the response. The response returns the
distance as distanceMeters.
This example sets the origin to the center of San Francisco:
Places Swift SDK
let filter = AutocompleteFilter(origin: CLLocation(latitude: 37.7749, longitude: -122.4194)) let token = AutocompleteSessionToken() let autocompleteRequest = AutocompleteRequest(query: "Amoeba", sessionToken: token, filter: filter) switch await placesClient.fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(with: autocompleteRequest) { case .success(let autocompleteSuggestions): for suggestion in autocompleteSuggestions { switch suggestion { case .place: // Show place suggestion data. } } case .failure(let placesError): // Handle error. }
Swift
let token = GMSAutocompleteSessionToken() let origin = CLLocation(latitude: 37.7749, longitude: -122.4194) let filter = GMSAutocompleteFilter() filter.origin = origin let request = GMSAutocompleteRequest(query:"Amoeba") request.filter = filter request.sessionToken = token GMSPlacesClient.shared().fetchAutocompleteSuggestions(from: request, callback: { ( results, error ) in if let error = error { print("Autocomplete error: \(error)") return } if let autocompleteResults = results { for result in autocompleteResults { print("Result \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.placeID)) with \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.attributedFullText)) and distance: \(String(describing: result.placeSuggestion?.distanceMeters))") } } })
Objective-C
GMSAutocompleteFilter *filter = [[GMSAutocompleteFilter alloc] init]; filter.origin = [[CLLocation alloc] initWithLatitude:37.395804 longitude:-122.077023]; GMSAutocompleteRequest *request = [[GMSAutocompleteRequest alloc] initWithQuery:@"Amoeba"]; request.sessionToken = token; request.filter = filter; [[GMSPlacesClient sharedClient] fetchAutocompleteSuggestionsFromRequest:request callback:^(NSArray<GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *> * results, NSError * error){ // Handle response for (GMSAutocompleteSuggestion *suggestion in results) { if (suggestion.placeSuggestion) { // Show place suggestion data. } } }];
Customize content and theme
Swift
let uiCustomization = AutocompleteUICustomization( listDensity: .multiLine, listItemIcon: .noIcon, theme: PlacesMaterialTheme() )
Add a Places Autocomplete widget (full code)
Places Swift SDK
struct PlaceAutocompleteDemoView: View { @State private var fetchedPlace: Place? @State private var placesError: PlacesError? @State private var showWidget = false public var body: some View { VStack { Button("Search for a place") { showWidget.toggle() } .placeAutocomplete( show: $showWidget, onSelection: { (autocompletePlaceSuggestion, autocompleteSessionToken) in Task { let placesClient = await PlacesClient.shared let fetchPlaceRequest = FetchPlaceRequest( placeID: autocompletePlaceSuggestion.placeID, placeProperties: [.displayName, .formattedAddress], sessionToken: autocompleteSessionToken ) switch await placesClient.fetchPlace(with: fetchPlaceRequest) { case .success(let place): print("Fetched place: \(place)") self.fetchedPlace = place case .failure(let placesError): print("Failed to fetch place: \(placesError)") self.placesError = placesError } } }, onError: { placesError in self.placesError = placesError } ) } } }
Autocomplete (New) optimization
This section describes best practices to help you make the most of the Autocomplete (New) service.
Here are some general guidelines:
- The quickest way to develop a working user interface is to use the Maps JavaScript API Autocomplete (New) widget, Places SDK for Android Autocomplete (New) widget, or Places SDK for iOS Autocomplete (New) widget.
- Understand essential Autocomplete (New) data fields from the start.
- Location biasing and location restriction fields are optional but can have a significant impact on autocomplete performance.
- Use error handling to make sure your app degrades gracefully if the API returns an error.
- Make sure your app handles when there is no selection and offers users a way to continue.
Cost optimization best practices
Basic cost optimization
To optimize the cost of using the Autocomplete (New) service, use field masks in Place Details (New) and Autocomplete (New) widgets to return only the Autocomplete (New) data fields you need.
Advanced cost optimization
Consider programmatic implementation of Autocomplete (New) in order to access SKU: Autocomplete Request pricing and request Geocoding API results about the selected place instead of Place Details (New). Per-request pricing paired with Geocoding API is more cost-effective than per-session (session-based) pricing if both of the following conditions are met:
- If you only need the latitude/longitude or address of the user's selected place, the Geocoding API delivers this information for less than a Place Details (New) call.
- If users select an autocomplete prediction within an average of four Autocomplete (New) predictions requests or fewer, per-request pricing may be more cost-effective than per-session pricing.
Does your application require any information other than the address and latitude/longitude of the selected prediction?
Yes, needs more details
Use session-based Autocomplete (New) with Place Details (New).
Since your application requires Place Details (New), such as the place name, business status,
or opening hours, your implementation of Autocomplete (New) should use a session token
(programmatically or built into the
JavaScript,
Android,
or iOS
widgets)
per session plus applicable Places SKUs,
depending on which place data fields you request.1
Widget implementation
Session management is automatically built into the
JavaScript,
Android,
or iOS
widgets. This includes both the Autocomplete (New) requests and the Place Details (New) request
on the selected prediction. Be sure to specify the fields parameter in order to
ensure you are only requesting the
Autocomplete (New) data fields
you need.
Programmatic implementation
Use a
session token
with your Autocomplete (New) requests. When requesting Place Details (New) about the selected prediction, include the following parameters:
- The place ID from the Autocomplete (New) response
- The session token used in the Autocomplete (New) request
- The
fieldsparameter specifying the Autocomplete (New) data fields you need
No, needs only address and location
Geocoding API could be a more cost-effective option than Place Details (New) for your application, depending on the performance of your Autocomplete (New) usage. Every application's Autocomplete (New) efficiency varies depending on what users are entering, where the application is being used, and whether performance optimization best practices have been implemented.
In order to answer the following question, analyze how many characters a user types on average before selecting a Autocomplete (New) prediction in your application.
Do your users select a Autocomplete (New) prediction in four or fewer requests, on average?
Yes
Implement Autocomplete (New) programmatically without session tokens and call Geocoding API on the selected place prediction.
Geocoding API delivers addresses and latitude/longitude coordinates.
Making four
Autocomplete Requests
requests plus a Geocoding API
call about the selected place prediction is less than the per-session Autocomplete (New)
cost per session.1
Consider employing performance best practices to help your users get the prediction they're looking for in even fewer characters.
No
Use session-based Autocomplete (New) with Place Details (New).
Since the average number of requests you expect to make before a user selects a
Autocomplete (New) prediction exceeds the cost of per-session pricing, your implementation
of Autocomplete (New) should use a session token for both the Autocomplete (New) requests
and the associated Place Details (New) request
per session.
1
Widget implementation
Session management is automatically built into the
JavaScript,
Android,
or iOS
widgets. This includes both the Autocomplete (New) requests and the Place Details (New)
request on the selected prediction. Be sure to specify the fields parameter
in order to ensure you are only requesting the fields you need.
Programmatic implementation
Use a
session token
with your Autocomplete (New) requests.
When requesting Place Details (New) about the selected prediction,
include the following parameters:
- The place ID from the Autocomplete (New) response
- The session token used in the Autocomplete (New) request
- The
fieldsparameter specifying fields such as address and geometry
Consider delaying Autocomplete (New) requests
You can employ strategies such as delaying a Autocomplete (New) request until the user has typed in the first three or four characters so that your application makes fewer requests. For example, making Autocomplete (New) requests for each character after the user has typed the third character means that if the user types seven characters then selects a prediction for which you make one Geocoding API request, the total cost would be for 4 Autocomplete (New) Per Request + Geocoding.1
If delaying requests can get your average programmatic request below four, you can follow the guidance for performant Autocomplete (New) with Geocoding API implementation. Note that delaying requests can be perceived as latency by the user who might be expecting to see predictions with every new keystroke.
Consider employing performance best practices to help your users get the prediction they're looking for in fewer characters.
-
For costs, see Google Maps Platform pricing lists.
Performance best practices
The following guidelines describe ways to optimize Autocomplete (New) performance:
- Add country restrictions, location biasing, and (for programmatic implementations) language preference to your Autocomplete (New) implementation. Language preference is not needed with widgets since they pick language preferences from the user's browser or mobile device.
- If Autocomplete (New) is accompanied by a map, you can bias location by map viewport.
- In situations when a user does not choose one of the Autocomplete (New) predictions, generally
because none of those predictions are the result-address wanted, you can reuse the original
user input to attempt to get more relevant results:
- If you expect the user to enter only address information, reuse the original user input in a call to the Geocoding API.
- If you expect the user to enter queries for a specific place by name or address, use a Place Details (New) request. If results are only expected in a specific region, use location biasing.
- Users inputting subpremise addresses, such as addresses for specific units or apartments within a building. For example, the Czech address "Stroupežnického 3191/17, Praha" yields a partial prediction in Autocomplete (New).
- Users inputting addresses with road-segment prefixes like "23-30 29th St, Queens" in New York City or "47-380 Kamehameha Hwy, Kaneohe" on the island of Kauai in Hawai'i.
Location biasing
Bias results to a specified area by passing a location parameter and a radius
parameter. This instructs Autocomplete (New) to prefer showing results
within the defined area. Results outside of the defined area may still be
displayed. You can use the includedRegionCodes parameter to filter results
to show only those places within a specified country.
Location restricting
Restrict results to a specified area by passing a locationRestriction parameter.
You may also restrict results to the region defined by location
and a radius parameter, by adding the
locationRestriction
parameter. This instructs Autocomplete (New) to return only
results within that region.
