Teslimat adresi, fatura bilgileri veya etkinlik bilgileri doldurulurken Yer Otomatik Doldurma'nın etkinleştirildiği formlar, kullanıcıların adres bilgilerini girerken tuş vuruşlarını ve hataları azaltmasına yardımcı olur. Bu eğitimde, yer otomatik tamamlama özelliğini içeren bir giriş alanını etkinleştirmek, adres formu alanlarını kullanıcı tarafından seçilen adresteki adres bileşenleriyle doldurmak ve görsel onay için seçilen adresi haritada göstermek üzere gereken adımlar açıklanmaktadır.
Videolar: Yer Otomatik Tamamlama ile adres formlarını geliştirme
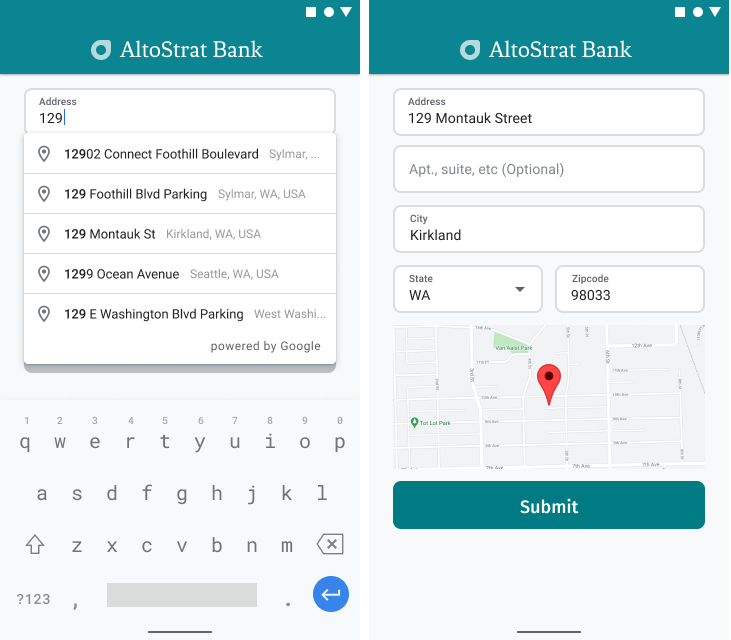
Adres formları
Android
iOS
Web
Google Haritalar Platformu, mobil platformlar ve web için Yer Otomatik Tamamlama widget'ı sağlar. Önceki şekillerde gösterilen widget, yerel kapsamlı arama için bile optimize edebileceğiniz yerleşik otomatik tamamlama işlevine sahip bir arama iletişim kutusu sağlar.
Kodu alın
GitHub'dan Android için Google Yerler SDK'sı Demoları deposunu klonlayın veya indirin.
Etkinliğin Java sürümünü görüntüleme:
/* * Copyright 2022 Google LLC * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package com.example.placesdemo; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android.content.res.Resources; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewStub; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.CheckBox; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher; import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat; import com.example.placesdemo.databinding.AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding; import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient; import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMapOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MapStyleOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.AddressComponent; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.AddressComponents; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.PlaceTypes; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.PlacesClient; import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.Autocomplete; import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.AutocompleteActivityMode; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import static android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION; import static com.google.maps.android.SphericalUtil.computeDistanceBetween; import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge; /** * Activity for using Place Autocomplete to assist filling out an address form. */ @SuppressWarnings("FieldCanBeLocal") public class AutocompleteAddressActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { private static final String TAG = "ADDRESS_AUTOCOMPLETE"; private static final String MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG = "MAP"; private LatLng coordinates; private boolean checkProximity = false; private SupportMapFragment mapFragment; private GoogleMap map; private Marker marker; private PlacesClient placesClient; private View mapPanel; private LatLng deviceLocation; private static final double acceptedProximity = 150; private AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding binding; View.OnClickListener startAutocompleteIntentListener = view -> { view.setOnClickListener(null); startAutocompleteIntent(); }; private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } }); @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent intent) { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, intent); binding.autocompleteAddress1.setOnClickListener(startAutocompleteIntentListener); } @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Enable edge-to-edge display. This must be called before calling super.onCreate(). EdgeToEdge.enable(this); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); binding = AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); // Retrieve a PlacesClient (previously initialized - see MainActivity) placesClient = Places.createClient(this); // Attach an Autocomplete intent to the Address 1 EditText field binding.autocompleteAddress1.setOnClickListener(startAutocompleteIntentListener); // Update checkProximity when user checks the checkbox CheckBox checkProximityBox = findViewById(R.id.checkbox_proximity); checkProximityBox.setOnCheckedChangeListener((view, isChecked) -> { // Set the boolean to match user preference for when the Submit button is clicked checkProximity = isChecked; }); // Submit and optionally check proximity Button saveButton = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_save_button); saveButton.setOnClickListener(v -> saveForm()); // Reset the form Button resetButton = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_reset_button); resetButton.setOnClickListener(v -> clearForm()); } private void startAutocompleteIntent() { // Set the fields to specify which types of place data to // return after the user has made a selection. List<Place.Field> fields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.ADDRESS_COMPONENTS, Place.Field.LOCATION, Place.Field.VIEWPORT); // Build the autocomplete intent with field, country, and type filters applied Intent intent = new Autocomplete.IntentBuilder(AutocompleteActivityMode.OVERLAY, fields) .setCountries(List.of("US")) .setTypesFilter(List.of("establishment")) .build(this); startAutocomplete.launch(intent); } @Override public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) { map = googleMap; try { // Customise the styling of the base map using a JSON object defined // in a string resource. boolean success = map.setMapStyle( MapStyleOptions.loadRawResourceStyle(this, R.raw.style_json)); if (!success) { Log.e(TAG, "Style parsing failed."); } } catch (Resources.NotFoundException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Can't find style. Error: ", e); } map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(coordinates, 15f)); marker = map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(coordinates)); } private void fillInAddress(Place place) { AddressComponents components = place.getAddressComponents(); StringBuilder address1 = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder postcode = new StringBuilder(); // Get each component of the address from the place details, // and then fill-in the corresponding field on the form. // Possible AddressComponent types are documented at https://goo.gle/32SJPM1 if (components != null) { for (AddressComponent component : components.asList()) { String type = component.getTypes().get(0); switch (type) { case "street_number": { address1.insert(0, component.getName()); break; } case "route": { address1.append(" "); address1.append(component.getShortName()); break; } case "postal_code": { postcode.insert(0, component.getName()); break; } case "postal_code_suffix": { postcode.append("-").append(component.getName()); break; } case "locality": binding.autocompleteCity.setText(component.getName()); break; case "administrative_area_level_1": { binding.autocompleteState.setText(component.getShortName()); break; } case "country": binding.autocompleteCountry.setText(component.getName()); break; } } } binding.autocompleteAddress1.setText(address1.toString()); binding.autocompletePostal.setText(postcode.toString()); // After filling the form with address components from the Autocomplete // prediction, set cursor focus on the second address line to encourage // entry of sub-premise information such as apartment, unit, or floor number. binding.autocompleteAddress2.requestFocus(); // Add a map for visual confirmation of the address showMap(place); } private void showMap(Place place) { coordinates = place.getLocation(); // It isn't possible to set a fragment's id programmatically so we set a tag instead and // search for it using that. mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG); // We only create a fragment if it doesn't already exist. if (mapFragment == null) { mapPanel = ((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_map)).inflate(); GoogleMapOptions mapOptions = new GoogleMapOptions(); mapOptions.mapToolbarEnabled(false); // To programmatically add the map, we first create a SupportMapFragment. mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions); // Then we add it using a FragmentTransaction. getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.confirmation_map, mapFragment, MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG) .commit(); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } else { updateMap(coordinates); } } private void updateMap(LatLng latLng) { marker.setPosition(latLng); map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(latLng, 15f)); if (mapPanel.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { mapPanel.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } } private void saveForm() { Log.d(TAG, "checkProximity = " + checkProximity); if (checkProximity) { checkLocationPermissions(); } else { Toast.makeText( this, R.string.autocomplete_skipped_message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT) .show(); } } private void clearForm() { binding.autocompleteAddress1.setText(""); binding.autocompleteAddress2.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteCity.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteState.getText().clear(); binding.autocompletePostal.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteCountry.getText().clear(); if (mapPanel != null) { mapPanel.setVisibility(View.GONE); } binding.autocompleteAddress1.requestFocus(); } // Register the permissions callback, which handles the user's response to the // system permissions dialog. Save the return value, an instance of // ActivityResultLauncher, as an instance variable. private final ActivityResultLauncher<String> requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(new ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission(), isGranted -> { if (isGranted) { // Since ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION is the only permission in this sample, // run the location comparison task once permission is granted. // Otherwise, check which permission is granted. getAndCompareLocations(); } else { // Fallback behavior if user denies permission Log.d(TAG, "User denied permission"); } }); private void checkLocationPermissions() { if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { getAndCompareLocations(); } else { requestPermissionLauncher.launch( ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION); } } @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private void getAndCompareLocations() { // TODO: Detect and handle if user has entered or modified the address manually and update // the coordinates variable to the Lat/Lng of the manually entered address. May use // Geocoding API to convert the manually entered address to a Lat/Lng. LatLng enteredLocation = coordinates; map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); FusedLocationProviderClient fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this); fusedLocationClient.getLastLocation() .addOnSuccessListener(this, location -> { // Got last known location. In some rare situations this can be null. if (location == null) { return; } deviceLocation = new LatLng(location.getLatitude(), location.getLongitude()); Log.d(TAG, "device location = " + deviceLocation); Log.d(TAG, "entered location = " + enteredLocation.toString()); // Use the computeDistanceBetween function in the Maps SDK for Android Utility Library // to use spherical geometry to compute the distance between two Lat/Lng points. double distanceInMeters = computeDistanceBetween(deviceLocation, enteredLocation); if (distanceInMeters <= acceptedProximity) { Log.d(TAG, "location matched"); // TODO: Display UI based on the locations matching } else { Log.d(TAG, "location not matched"); // TODO: Display UI based on the locations not matching } }); } }
API'ler etkinleştiriliyor
Bu önerileri uygulamak için Google Cloud Console'da aşağıdaki API'leri etkinleştirmeniz gerekir:
- Android için Haritalar SDK'sı (veya seçtiğiniz platformun API'si)
- Places API
Kurulum hakkında daha fazla bilgi için Google Cloud projenizi ayarlama başlıklı makaleyi inceleyin.
Giriş alanlarına otomatik tamamlama ekleme
Bu bölümde, adres formuna yer otomatik tamamlama özelliğinin nasıl ekleneceği açıklanmaktadır.
Yer Adı Otomatik Tamamlama widget'ını ekleme
Android'de, kullanıcının adresini girmeye başlayacağı Adres Satırı 1 giriş alanından Yer Adı Otomatik Tamamlama'yı başlatan bir otomatik tamamlama amaçlı kullanarak otomatik tamamlama widget'ını ekleyebilirsiniz. Kullanıcılar yazmaya başladığında, otomatik tamamlama tahminleri listesinden adreslerini seçebilir.
İlk olarak, başlatılan etkinlikten sonuç dinleyecek bir etkinlik başlatıcıyı ActivityResultLauncher kullanarak hazırlayın. Sonuç geri çağırması, kullanıcının Otomatik Tamamlama tahminlerinden seçtiği adrese karşılık gelen bir Yer nesnesi içerir.
private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } });
Ardından, Yer Otomatik Tamamlama amacının alanlarını, konumunu ve tür özelliklerini tanımlayın ve bu amacı Autocomplete.IntentBuilder ile oluşturun.
Son olarak, önceki kod örneğinde tanımlanan ActivityResultLauncher kullanarak amacı başlatın.
private void startAutocompleteIntent() { // Set the fields to specify which types of place data to // return after the user has made a selection. List<Place.Field> fields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.ADDRESS_COMPONENTS, Place.Field.LOCATION, Place.Field.VIEWPORT); // Build the autocomplete intent with field, country, and type filters applied Intent intent = new Autocomplete.IntentBuilder(AutocompleteActivityMode.OVERLAY, fields) .setCountries(List.of("US")) .setTypesFilter(List.of("establishment")) .build(this); startAutocomplete.launch(intent); }
Yer otomatik tamamlama tarafından döndürülen adresi işleme
ActivityResultLauncher öğesini daha önce tanımlamak, etkinlik sonucu geri çağırmada döndürüldüğünde ne yapılması gerektiğini de tanımlıyordu. Kullanıcı bir tahmini seçtiyse bu tahmin, sonuç nesnesinde yer alan amaçla birlikte sunulur. Intent Autocomplete.IntentBuilder tarafından oluşturulduğundan Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent() yöntemi, Place nesnesini intentten çıkarabilir.
private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } });
Buradan Place.getAddressComponents() işlevini çağırın ve her adres bileşenini adres formundaki ilgili giriş alanıyla eşleştirerek alanı, kullanıcının seçtiği yerin değeriyle doldurun.
Adres formu alanlarını doldurmaya yönelik örnek bir uygulama, bu sayfanın Kodu edinme bölümünde sağlanan fillInAddress örnek kod yönteminde paylaşılmıştır.
Adres verilerinin manuel olarak girilen bir adres yerine tahminden alınması, adresin doğruluğunu ve bilinen bir adres olmasını sağlar, adrese teslimat yapılabilmesini sağlar ve kullanıcıların tuş vuruşlarını azaltır.
Yer otomatik tamamlama özelliğini uygularken dikkat edilmesi gereken noktalar
Yalnızca widget'ı kullanmak istemiyorsanız Yer Otomatik Tamamlama'nın, uygulanması konusunda esneklik sağlayan çeşitli seçenekleri vardır. Bir konumu doğru şekilde eşleştirmek için ihtiyacınız olan bilgileri almak üzere hizmetleri birlikte kullanabilirsiniz.
BİR ADRES formu için, eşleşmeleri tam açık adreslerle sınırlamak üzere türler parametresini
addressolarak ayarlayın. Yer Otomatik Tamamlama isteklerinde desteklenen türler hakkında daha fazla bilgi edinin.Dünya çapında arama yapmanız gerekmiyorsa uygun kısıtlamaları ve önyargıları ayarlayın. Eşleşmeleri yalnızca belirli bölgelerle sınırlamak veya eşleşmelere belirli bir yön vermek için kullanılabilecek çeşitli parametreler vardır.
Bir alanı sınırlamak için dikdörtgen sınırları ayarlamak üzere
RectangularBoundssimgesini, yalnızca bu alanlardaki adreslerin döndürülmesini sağlamak içinsetLocationRestriction()simgesini kullanın.Yanıtları belirli bir ülke grubuyla sınırlamak için
setCountries()kullanın.
Eşleşmede belirli alanlar atlanırsa alanların düzenlenebilir kalmasını sağlayın ve gerekirse müşterilerin adresi güncellemesine izin verin. Yer Otomatik Tamamlama tarafından döndürülen adreslerin çoğu, daire, süit veya birim numaraları gibi alt bina numaraları içermediğinden, gerekirse kullanıcının bu bilgileri doldurmasını sağlamak için odağı 2. Adres Satırı'na taşıyabilirsiniz.
Adresin görsel onayını sağlama
Adres girişi kapsamında, kullanıcılara haritada adresin görsel onayını sağlayın. Bu sayede kullanıcılar, adresin doğru olduğundan daha fazla emin olabilir.
Aşağıdaki şekilde, girilen adresin altında, adrese eklenmiş bir raptiye simgesi içeren bir harita gösterilmektedir.

Aşağıdaki örnekte, Android'de harita eklemeyle ilgili temel adımlar uygulanmaktadır. Daha fazla bilgi için belgelere bakın.
- Ekleme
SupportMapFragment(bu örnekte, bir parçayı dinamik olarak ekleme) - Parçanın tutamacını alma ve geri çağırmayı kaydetme
- Haritaya işaretçi ekleme ve işaretçiyi stilize etme
- Harita kontrollerini devre dışı bırakma
SupportMapFragment ekleniyor
Öncelikle layout XML dosyasına bir SupportMapFragment parçası ekleyin.
<fragment
android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment"
android:id="@+id/confirmation_map"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>Ardından, henüz mevcut değilse parçayı programatik olarak ekleyin.
private void showMap(Place place) {
coordinates = place.getLocation();
// It isn't possible to set a fragment's id programmatically so we set a tag instead and
// search for it using that.
mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment)
getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG);
// We only create a fragment if it doesn't already exist.
if (mapFragment == null) {
mapPanel = ((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_map)).inflate();
GoogleMapOptions mapOptions = new GoogleMapOptions();
mapOptions.mapToolbarEnabled(false);
// To programmatically add the map, we first create a SupportMapFragment.
mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions);
// Then we add it using a FragmentTransaction.
getSupportFragmentManager()
.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.confirmation_map, mapFragment, MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG)
.commit();
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
} else {
updateMap(coordinates);
}
}Parçanın işleyicisini alma ve geri çağırmayı kaydetme
Parçanın tutamacını almak için
FragmentManager.findFragmentByIdyöntemini çağırın ve düzen dosyanızdaki parçanın kaynak kimliğini iletin. Parçayı dinamik olarak eklediyseniz bu adımı atlayın. Çünkü tutma yerini zaten aldınız.Parçadaki geri çağırmayı ayarlamak için
getMapAsyncyöntemini çağırın.
Örneğin, parçayı statik olarak eklediyseniz:
Kotlin
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
Java
SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
Haritayı stilize etme ve haritaya işaretçi ekleme
Harita hazır olduğunda stili ayarlayın, kamerayı ortalayın ve girilen adresin koordinatlarına bir işaretçi ekleyin. Aşağıdaki kod, bir JSON nesnesinde tanımlanan stili kullanır. Alternatif olarak, bulut tabanlı harita stili ile tanımlanmış bir harita kimliği de yükleyebilirsiniz.
@Override public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) { map = googleMap; try { // Customise the styling of the base map using a JSON object defined // in a string resource. boolean success = map.setMapStyle( MapStyleOptions.loadRawResourceStyle(this, R.raw.style_json)); if (!success) { Log.e(TAG, "Style parsing failed."); } } catch (Resources.NotFoundException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Can't find style. Error: ", e); } map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(coordinates, 15f)); marker = map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(coordinates)); }
Harita kontrollerini devre dışı bırakma
Konumu ek harita kontrolleri (ör. pusula, araç çubuğu veya diğer yerleşik özellikler) olmadan göstererek haritayı basit tutmak için gerekli görmediğiniz kontrolleri devre dışı bırakabilirsiniz. Android'de, sınırlı etkileşim sağlamak için lite modunu etkinleştirebilirsiniz.
