Nível de programação: intermediário
Duração: 20 minutos
Tipo de projeto: automação com um menu personalizado
Objetivos
- Entenda o que a solução faz.
- Entenda o que os serviços do Apps Script fazem na solução.
- Prepare o ambiente.
- Configure o script.
- Execute o script.
Sobre esta solução
É possível analisar dados de texto, como feedback aberto, em escala. Para realizar análises de entidade e sentimento nas Planilhas Google, essa solução usa o serviço UrlFetch para se conectar à API Cloud Natural Language.
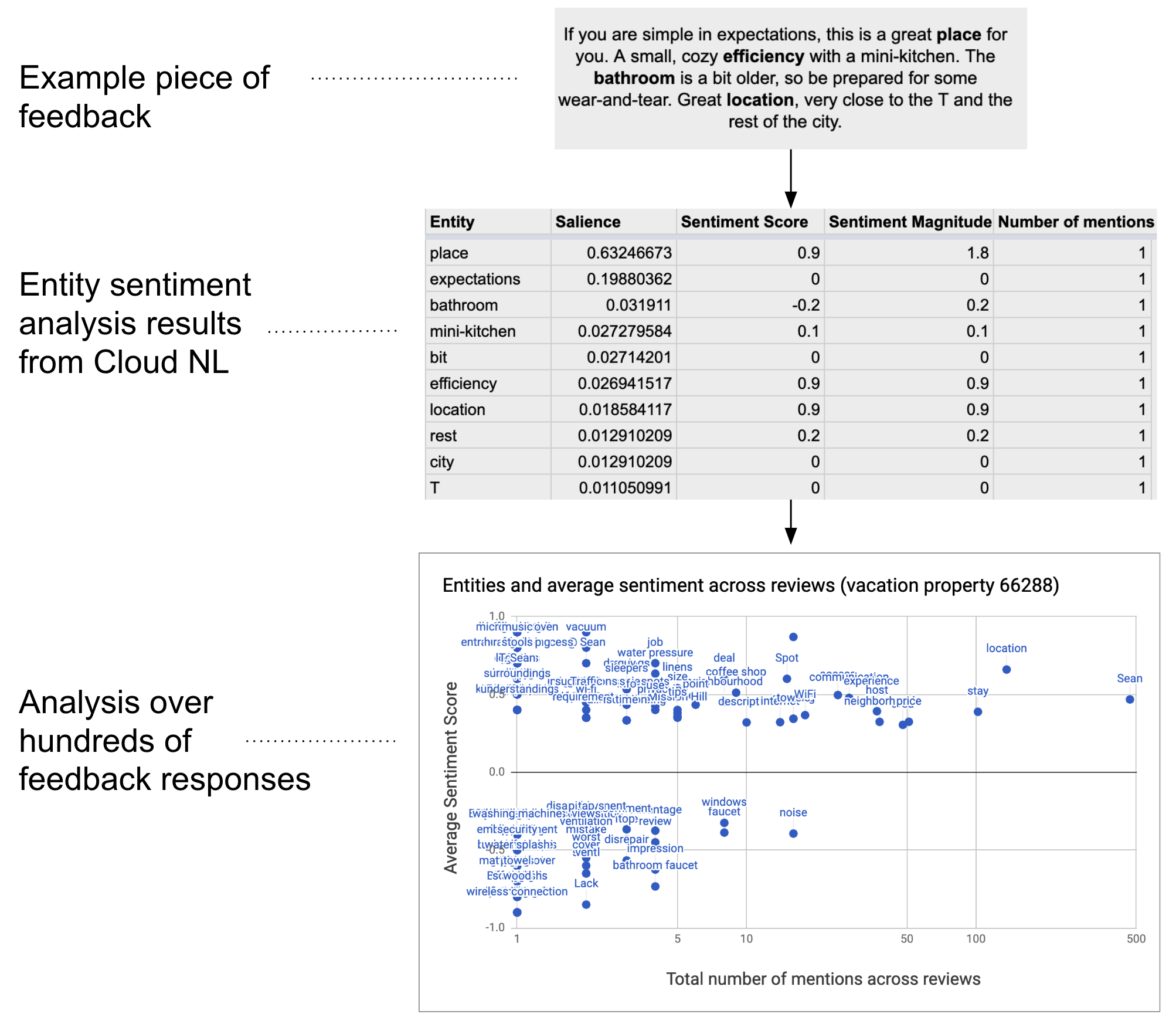

Como funciona
O script coleta texto da planilha e se conecta à API Natural Language do Google Cloud para analisar entidades e sentimentos presentes na string. Uma tabela dinâmica resume a pontuação média de sentimento para cada entidade mencionada em todas as linhas de dados de texto.
Serviços do Apps Script
Esta solução usa os seguintes serviços:
- Serviço de planilha: envia os dados de texto para a API Cloud Natural Language do Google Cloud e marca cada linha como "Concluída" depois que o sentimento é analisado.
- Serviço UrlFetch: se conecta à API Google Cloud Natural Language para realizar análises de entidade e sentimento no texto.
Pré-requisitos
Para usar esta amostra, você precisa atender aos seguintes pré-requisitos:
- Uma Conta do Google (as contas do Google Workspace podem exigir a aprovação do administrador).
Um navegador da Web com acesso à Internet.
Um projeto do Google Cloud com uma conta de faturamento associada. Consulte Ativar o faturamento de um projeto.
Configurar o ambiente
Abra seu projeto do Cloud no console do Google Cloud.
Se ele ainda não estiver aberto, abra o projeto do Google Cloud que você pretende usar para esta amostra:
- No console do Google Cloud, acesse a página Selecionar um projeto.
- Selecione o projeto do Google Cloud que você quer usar. Ou clique em Criar projeto e siga as instruções na tela. Se você criar um projeto do Google Cloud, talvez seja necessário ativar o faturamento dele.
Ativar a API Cloud Natural Language
Essa solução se conecta à API Cloud Natural Language do Google Cloud. Antes de usar as APIs do Google, é necessário ativá-las em um projeto do Google Cloud. É possível ativar uma ou mais APIs em um único projeto do Google Cloud.
No seu projeto do Cloud, ative a API Google Cloud Natural Language.
Configurar a tela de permissão OAuth
Essa solução exige um projeto do Cloud com uma tela de consentimento configurada. A configuração da tela de permissão OAuth define o que o Google mostra aos usuários e registra seu app para que você possa publicá-lo mais tarde.
- No console do Google Cloud, acesse Menu > Google Auth platform > Branding.
- Se você já tiver configurado o Google Auth platform, poderá configurar as seguintes opções da tela de permissão do OAuth em Branding, Público-alvo e Acesso a dados. Se você receber uma mensagem informando que Google Auth platform ainda não foi configurado, clique em Começar:
- Em Informações do app, no campo Nome do app, insira um nome para o app.
- Em E-mail para suporte do usuário, escolha um endereço de e-mail de suporte para que os usuários possam entrar em contato com você se tiverem dúvidas sobre o consentimento deles.
- Clique em Próxima.
- Em Público-alvo, selecione Interno.
- Clique em Próxima.
- Em Informações de contato, insira um Endereço de e-mail para receber notificações sobre mudanças no seu projeto.
- Clique em Próxima.
- Em Concluir, leia a Política de dados do usuário dos serviços de API do Google e, se concordar, selecione Concordo com a Política de dados do usuário dos serviços de API do Google.
- Clique em Continuar.
- Clique em Criar.
- Por enquanto, você pode pular a adição de escopos. No futuro, quando você criar um app para uso fora da sua organização do Google Workspace, mude o Tipo de usuário para Externo. Em seguida, adicione os escopos de autorização necessários para o app. Para saber mais, consulte o guia completo Configurar a permissão OAuth.
Receber uma chave de API para a API Google Cloud Natural Language
- Acesse o Console do Google Cloud. Verifique se o projeto com faturamento ativado está aberto.
No console do Google Cloud, acesse Menu > APIs e serviços > Credenciais.
Clique em Criar credenciais > Chave de API.
Anote a chave de API para usar em uma etapa posterior.
Configurar o script
Criar o projeto do Apps Script
- Clique no botão abaixo para fazer uma cópia da planilha de exemplo Análise de sentimento para feedback. O projeto do Apps Script
para essa solução está anexado à planilha.
Fazer uma cópia - Clique em Extensões > Apps Script.
- Atualize a seguinte variável no arquivo de script com sua chave de API:
const myApiKey = 'YOUR_API_KEY'; // Replace with your API key.
- Clique em Salvar
.
Adicionar dados de texto
- Volte para a planilha.
- Adicione dados de texto às colunas id e comments. Você pode usar amostras de avaliações de imóveis para férias do Kaggle ou seus próprios dados. Você pode adicionar mais colunas, se necessário, mas para ser executado com sucesso, o script precisa ter dados nas colunas id e comments.
Executar o script
- Na parte de cima da planilha, clique em Ferramentas de análise de sentimento > Marcar entidades e sentimento. Talvez seja necessário atualizar a página para que esse menu personalizado apareça.
Quando solicitado, autorize o script. Se a tela de permissão OAuth mostrar o aviso Este app não foi verificado, selecione Avançado > Acessar {Nome do projeto} (não seguro).
Clique em Ferramentas de análise de sentimento > Marcar entidades e sentimento novamente.
Quando o script terminar, mude para a planilha Tabela dinâmica para conferir os resultados.
Revisar o código
Para revisar o código do Apps Script dessa solução, clique em Ver código-fonte abaixo:
Acessar o código-fonte
Code.gs
Colaboradores
Esta amostra é mantida pelo Google com a ajuda de especialistas em desenvolvimento do Google.
Próximas etapas
- Blog: como analisar textos nas Planilhas Google usando a API Cloud Natural Language e o Apps Script
- Documentação da API Google Cloud Natural Language