При заполнении адреса доставки, платёжной информации или информации о мероприятии включение функции автозаполнения мест Place Autocomplete помогает пользователям сократить количество нажатий клавиш и количество ошибок при вводе адресной информации. В этом руководстве подробно описываются шаги, необходимые для включения функции автозаполнения мест Place Autocomplete в поле ввода, заполнения полей формы адреса компонентами адреса, выбранного пользователем, и отображения выбранного адреса на карте для визуального подтверждения.
Видео: Улучшите формы адресов с помощью функции автозаполнения Place
Формы адресов
Андроид
iOS
Интернет
Платформа Google Карт предоставляет виджет автозаполнения мест для мобильных платформ и веб-сайтов. Виджет, показанный на предыдущих рисунках, представляет собой диалоговое окно поиска со встроенной функцией автозаполнения, которую можно оптимизировать даже для поиска по местоположению.
Получить код
Клонируйте или загрузите репозиторий Google Places SDK для Android Demos из GitHub.
Просмотреть версию упражнения на Java:
/* * Copyright 2022 Google LLC * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package com.example.placesdemo; import android.annotation.SuppressLint; import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.pm.PackageManager; import android.content.res.Resources; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewStub; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.CheckBox; import android.widget.Toast; import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher; import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts; import androidx.annotation.NonNull; import androidx.annotation.Nullable; import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat; import com.example.placesdemo.databinding.AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding; import com.google.android.gms.location.FusedLocationProviderClient; import com.google.android.gms.location.LocationServices; import com.google.android.gms.maps.CameraUpdateFactory; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMap; import com.google.android.gms.maps.GoogleMapOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.OnMapReadyCallback; import com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.LatLng; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MapStyleOptions; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.Marker; import com.google.android.gms.maps.model.MarkerOptions; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.Places; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.AddressComponent; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.AddressComponents; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.Place; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.model.PlaceTypes; import com.google.android.libraries.places.api.net.PlacesClient; import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.Autocomplete; import com.google.android.libraries.places.widget.model.AutocompleteActivityMode; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import static android.Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION; import static com.google.maps.android.SphericalUtil.computeDistanceBetween; import androidx.activity.EdgeToEdge; /** * Activity for using Place Autocomplete to assist filling out an address form. */ @SuppressWarnings("FieldCanBeLocal") public class AutocompleteAddressActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements OnMapReadyCallback { private static final String TAG = "ADDRESS_AUTOCOMPLETE"; private static final String MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG = "MAP"; private LatLng coordinates; private boolean checkProximity = false; private SupportMapFragment mapFragment; private GoogleMap map; private Marker marker; private PlacesClient placesClient; private View mapPanel; private LatLng deviceLocation; private static final double acceptedProximity = 150; private AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding binding; View.OnClickListener startAutocompleteIntentListener = view -> { view.setOnClickListener(null); startAutocompleteIntent(); }; private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } }); @Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent intent) { super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, intent); binding.autocompleteAddress1.setOnClickListener(startAutocompleteIntentListener); } @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Enable edge-to-edge display. This must be called before calling super.onCreate(). EdgeToEdge.enable(this); super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); binding = AutocompleteAddressActivityBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater()); setContentView(binding.getRoot()); // Retrieve a PlacesClient (previously initialized - see MainActivity) placesClient = Places.createClient(this); // Attach an Autocomplete intent to the Address 1 EditText field binding.autocompleteAddress1.setOnClickListener(startAutocompleteIntentListener); // Update checkProximity when user checks the checkbox CheckBox checkProximityBox = findViewById(R.id.checkbox_proximity); checkProximityBox.setOnCheckedChangeListener((view, isChecked) -> { // Set the boolean to match user preference for when the Submit button is clicked checkProximity = isChecked; }); // Submit and optionally check proximity Button saveButton = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_save_button); saveButton.setOnClickListener(v -> saveForm()); // Reset the form Button resetButton = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_reset_button); resetButton.setOnClickListener(v -> clearForm()); } private void startAutocompleteIntent() { // Set the fields to specify which types of place data to // return after the user has made a selection. List<Place.Field> fields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.ADDRESS_COMPONENTS, Place.Field.LOCATION, Place.Field.VIEWPORT); // Build the autocomplete intent with field, country, and type filters applied Intent intent = new Autocomplete.IntentBuilder(AutocompleteActivityMode.OVERLAY, fields) .setCountries(List.of("US")) .setTypesFilter(List.of("establishment")) .build(this); startAutocomplete.launch(intent); } @Override public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) { map = googleMap; try { // Customise the styling of the base map using a JSON object defined // in a string resource. boolean success = map.setMapStyle( MapStyleOptions.loadRawResourceStyle(this, R.raw.style_json)); if (!success) { Log.e(TAG, "Style parsing failed."); } } catch (Resources.NotFoundException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Can't find style. Error: ", e); } map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(coordinates, 15f)); marker = map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(coordinates)); } private void fillInAddress(Place place) { AddressComponents components = place.getAddressComponents(); StringBuilder address1 = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder postcode = new StringBuilder(); // Get each component of the address from the place details, // and then fill-in the corresponding field on the form. // Possible AddressComponent types are documented at https://goo.gle/32SJPM1 if (components != null) { for (AddressComponent component : components.asList()) { String type = component.getTypes().get(0); switch (type) { case "street_number": { address1.insert(0, component.getName()); break; } case "route": { address1.append(" "); address1.append(component.getShortName()); break; } case "postal_code": { postcode.insert(0, component.getName()); break; } case "postal_code_suffix": { postcode.append("-").append(component.getName()); break; } case "locality": binding.autocompleteCity.setText(component.getName()); break; case "administrative_area_level_1": { binding.autocompleteState.setText(component.getShortName()); break; } case "country": binding.autocompleteCountry.setText(component.getName()); break; } } } binding.autocompleteAddress1.setText(address1.toString()); binding.autocompletePostal.setText(postcode.toString()); // After filling the form with address components from the Autocomplete // prediction, set cursor focus on the second address line to encourage // entry of sub-premise information such as apartment, unit, or floor number. binding.autocompleteAddress2.requestFocus(); // Add a map for visual confirmation of the address showMap(place); } private void showMap(Place place) { coordinates = place.getLocation(); // It isn't possible to set a fragment's id programmatically so we set a tag instead and // search for it using that. mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG); // We only create a fragment if it doesn't already exist. if (mapFragment == null) { mapPanel = ((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_map)).inflate(); GoogleMapOptions mapOptions = new GoogleMapOptions(); mapOptions.mapToolbarEnabled(false); // To programmatically add the map, we first create a SupportMapFragment. mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions); // Then we add it using a FragmentTransaction. getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .add(R.id.confirmation_map, mapFragment, MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG) .commit(); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this); } else { updateMap(coordinates); } } private void updateMap(LatLng latLng) { marker.setPosition(latLng); map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(latLng, 15f)); if (mapPanel.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { mapPanel.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); } } private void saveForm() { Log.d(TAG, "checkProximity = " + checkProximity); if (checkProximity) { checkLocationPermissions(); } else { Toast.makeText( this, R.string.autocomplete_skipped_message, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT) .show(); } } private void clearForm() { binding.autocompleteAddress1.setText(""); binding.autocompleteAddress2.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteCity.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteState.getText().clear(); binding.autocompletePostal.getText().clear(); binding.autocompleteCountry.getText().clear(); if (mapPanel != null) { mapPanel.setVisibility(View.GONE); } binding.autocompleteAddress1.requestFocus(); } // Register the permissions callback, which handles the user's response to the // system permissions dialog. Save the return value, an instance of // ActivityResultLauncher, as an instance variable. private final ActivityResultLauncher<String> requestPermissionLauncher = registerForActivityResult(new ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission(), isGranted -> { if (isGranted) { // Since ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION is the only permission in this sample, // run the location comparison task once permission is granted. // Otherwise, check which permission is granted. getAndCompareLocations(); } else { // Fallback behavior if user denies permission Log.d(TAG, "User denied permission"); } }); private void checkLocationPermissions() { if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION) == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) { getAndCompareLocations(); } else { requestPermissionLauncher.launch( ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION); } } @SuppressLint("MissingPermission") private void getAndCompareLocations() { // TODO: Detect and handle if user has entered or modified the address manually and update // the coordinates variable to the Lat/Lng of the manually entered address. May use // Geocoding API to convert the manually entered address to a Lat/Lng. LatLng enteredLocation = coordinates; map.setMyLocationEnabled(true); FusedLocationProviderClient fusedLocationClient = LocationServices.getFusedLocationProviderClient(this); fusedLocationClient.getLastLocation() .addOnSuccessListener(this, location -> { // Got last known location. In some rare situations this can be null. if (location == null) { return; } deviceLocation = new LatLng(location.getLatitude(), location.getLongitude()); Log.d(TAG, "device location = " + deviceLocation); Log.d(TAG, "entered location = " + enteredLocation.toString()); // Use the computeDistanceBetween function in the Maps SDK for Android Utility Library // to use spherical geometry to compute the distance between two Lat/Lng points. double distanceInMeters = computeDistanceBetween(deviceLocation, enteredLocation); if (distanceInMeters <= acceptedProximity) { Log.d(TAG, "location matched"); // TODO: Display UI based on the locations matching } else { Log.d(TAG, "location not matched"); // TODO: Display UI based on the locations not matching } }); } }
Включение API
Для реализации этих рекомендаций необходимо включить следующие API в консоли Google Cloud:
- Maps SDK для Android (или API для выбранной вами платформы)
- API мест
Дополнительную информацию о настройке см. в разделе Настройка проекта Google Cloud .
Добавление автозаполнения в поля ввода
В этом разделе описывается, как добавить функцию автозаполнения места в форму адреса.
Добавление виджета автозаполнения мест
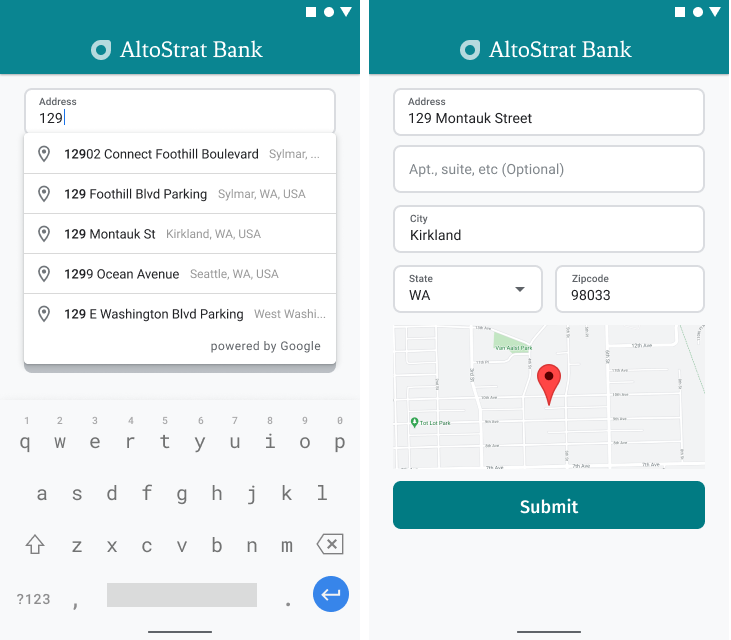
В Android вы можете добавить виджет автозаполнения с помощью намерения Autocomplete , которое запускает Place Autocomplete из поля ввода «Адресная строка 1», где пользователь начинает вводить свой адрес. Начав вводить адрес, пользователь сможет выбрать его из списка подсказок Autocomplete.
Сначала подготовьте средство запуска активности с помощью ActivityResultLauncher , которое будет ожидать результат от запущенной активности. Обратный вызов результата будет содержать объект Place, соответствующий адресу, выбранному пользователем из подсказок автозаполнения.
private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } });
Затем определите поля, местоположение и свойства типа намерения Place Autocomplete и создайте его с помощью Autocomplete.IntentBuilder . Наконец, запустите намерение с помощью ActivityResultLauncher определённого в предыдущем примере кода.
private void startAutocompleteIntent() { // Set the fields to specify which types of place data to // return after the user has made a selection. List<Place.Field> fields = Arrays.asList(Place.Field.ADDRESS_COMPONENTS, Place.Field.LOCATION, Place.Field.VIEWPORT); // Build the autocomplete intent with field, country, and type filters applied Intent intent = new Autocomplete.IntentBuilder(AutocompleteActivityMode.OVERLAY, fields) .setCountries(List.of("US")) .setTypesFilter(List.of("establishment")) .build(this); startAutocomplete.launch(intent); }
Обработка адреса, возвращаемого Place Autocomplete
Определение ActivityResultLauncher ранее также определяло, что должно происходить при возврате результата активности в обратном вызове. Если пользователь выбрал прогноз, он будет передан в намерении, содержащемся в объекте результата. Поскольку намерение было создано с помощью Autocomplete.IntentBuilder , метод Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent() может извлечь из него объект Place.
private final ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> startAutocomplete = registerForActivityResult( new ActivityResultContracts.StartActivityForResult(), result -> { if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_OK) { Intent intent = result.getData(); if (intent != null) { Place place = Autocomplete.getPlaceFromIntent(intent); // Write a method to read the address components from the Place // and populate the form with the address components Log.d(TAG, "Place: " + place.getAddressComponents()); fillInAddress(place); } } else if (result.getResultCode() == Activity.RESULT_CANCELED) { // The user canceled the operation. Log.i(TAG, "User canceled autocomplete"); } });
Далее вызовите Place.getAddressComponents() и сопоставьте каждый компонент адреса с соответствующим полем ввода в форме адреса, заполнив поле значением из выбранного пользователем места.
Пример реализации заполнения полей формы адреса приведен в методе fillInAddress примера кода, приведенного в разделе «Получить код» на этой странице.
Получение адресных данных из прогноза вместо ручного ввода адреса помогает обеспечить точность адреса, гарантирует, что адрес известен и может быть доставлен, а также сокращает количество нажатий клавиш пользователем.
Что следует учитывать при внедрении функции автозаполнения мест
Place Autocomplete имеет ряд опций, которые обеспечивают гибкость его реализации, если вы хотите использовать не только виджет. Вы можете комбинировать сервисы, чтобы получить именно то, что вам нужно для корректного сопоставления местоположения.
Для формы ADDRESS установите параметр types на
address, чтобы ограничить совпадения полными адресами. Подробнее о типах, поддерживаемых в запросах Place Autocomplete .Если вам не нужно искать по всему миру, установите соответствующие ограничения и смещения . Существует ряд параметров, которые можно использовать для смещения или ограничения результатов поиска только определёнными регионами.
Используйте
RectangularBoundsдля установки прямоугольных границ для ограничения области, используйтеsetLocationRestriction()чтобы убедиться, что возвращаются только адреса в этих областях.Используйте
setCountries(), чтобы ограничить ответы определенным набором стран.
Оставьте поля редактируемыми на случай, если какие-либо поля будут пропущены при сопоставлении, и дайте клиентам возможность обновить адрес при необходимости. Поскольку большинство адресов, возвращаемых Place Autocomplete, не содержат номера помещений, таких как номера квартир, офисов или корпусов, вы можете переместить фокус на строку адреса 2, чтобы побудить пользователя заполнить эту информацию при необходимости.
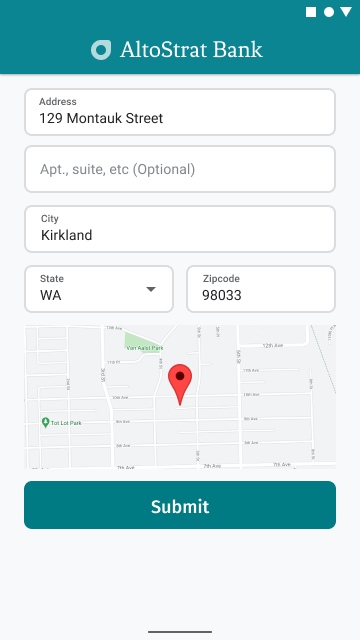
Предоставление визуального подтверждения адреса
При вводе адреса предоставьте пользователям визуальное подтверждение адреса на карте. Это даст им дополнительную уверенность в его правильности.
На следующем рисунке показана карта под адресом с булавкой на введенном адресе.
В следующем примере показаны основные шаги по добавлению карты в Android. Подробнее см. в документации.
- Добавление
SupportMapFragment(в данном случае динамическое добавление фрагмента) - Получение дескриптора фрагмента и регистрация обратного вызова
- Стилизация и добавление маркера на карту
- Отключение управления картой
Добавление SupportMapFragment
Сначала добавьте фрагмент SupportMapFragment в XML-файл макета .
<fragment
android:name="com.google.android.gms.maps.SupportMapFragment"
android:id="@+id/confirmation_map"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>Затем программно добавьте фрагмент, если его еще нет.
private void showMap(Place place) {
coordinates = place.getLocation();
// It isn't possible to set a fragment's id programmatically so we set a tag instead and
// search for it using that.
mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment)
getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentByTag(MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG);
// We only create a fragment if it doesn't already exist.
if (mapFragment == null) {
mapPanel = ((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_map)).inflate();
GoogleMapOptions mapOptions = new GoogleMapOptions();
mapOptions.mapToolbarEnabled(false);
// To programmatically add the map, we first create a SupportMapFragment.
mapFragment = SupportMapFragment.newInstance(mapOptions);
// Then we add it using a FragmentTransaction.
getSupportFragmentManager()
.beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.confirmation_map, mapFragment, MAP_FRAGMENT_TAG)
.commit();
mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
} else {
updateMap(coordinates);
}
}Получение дескриптора фрагмента и регистрация обратного вызова
Чтобы получить дескриптор фрагмента, вызовите метод
FragmentManager.findFragmentByIdи передайте ему идентификатор ресурса фрагмента в файле макета. Если фрагмент был добавлен динамически , пропустите этот шаг, так как дескриптор уже получен.Вызовите метод
getMapAsync, чтобы установить обратный вызов для фрагмента.
Например, если вы добавили фрагмент статически:
Котлин
val mapFragment = supportFragmentManager .findFragmentById(R.id.map) as SupportMapFragment mapFragment.getMapAsync(this)
Ява
SupportMapFragment mapFragment = (SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.map); mapFragment.getMapAsync(this);
Стилизация и добавление маркера на карту
Когда карта будет готова, задайте стиль, отцентрируйте камеру и добавьте маркер в точке с координатами введённого адреса. Следующий код использует стиль, определённый в JSON-объекте, или вы можете загрузить идентификатор карты, определённый с помощью облачного стиля карт .
@Override public void onMapReady(@NonNull GoogleMap googleMap) { map = googleMap; try { // Customise the styling of the base map using a JSON object defined // in a string resource. boolean success = map.setMapStyle( MapStyleOptions.loadRawResourceStyle(this, R.raw.style_json)); if (!success) { Log.e(TAG, "Style parsing failed."); } } catch (Resources.NotFoundException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Can't find style. Error: ", e); } map.moveCamera(CameraUpdateFactory.newLatLngZoom(coordinates, 15f)); marker = map.addMarker(new MarkerOptions().position(coordinates)); }
Отключение управления картой
Чтобы карта была простой и отображала местоположение без дополнительных элементов управления (таких как компас, панель инструментов или другие встроенные функции), попробуйте отключить ненужные элементы управления . На Android также можно включить облегченный режим , обеспечивающий ограниченную интерактивность.

