Page Summary
-
Google Chat apps can use either user or app authentication to interact with the Chat API.
-
User authentication requires user consent for specific data access, while app authentication utilizes service accounts.
-
Different Chat API methods require specific authentication types and authorization scopes.
-
The document provides detailed tables outlining supported authentication and authorization for various API functionalities.
-
Developers should carefully consider the authentication and authorization requirements for their specific app's functionality.
Authentication and authorization are mechanisms used to verify identity and access to resources, respectively. This document outlines how authentication and authorization work for Chat apps and Chat API requests.
Process overview
The following diagram shows the high-level steps of authentication and authorization for Google Chat:
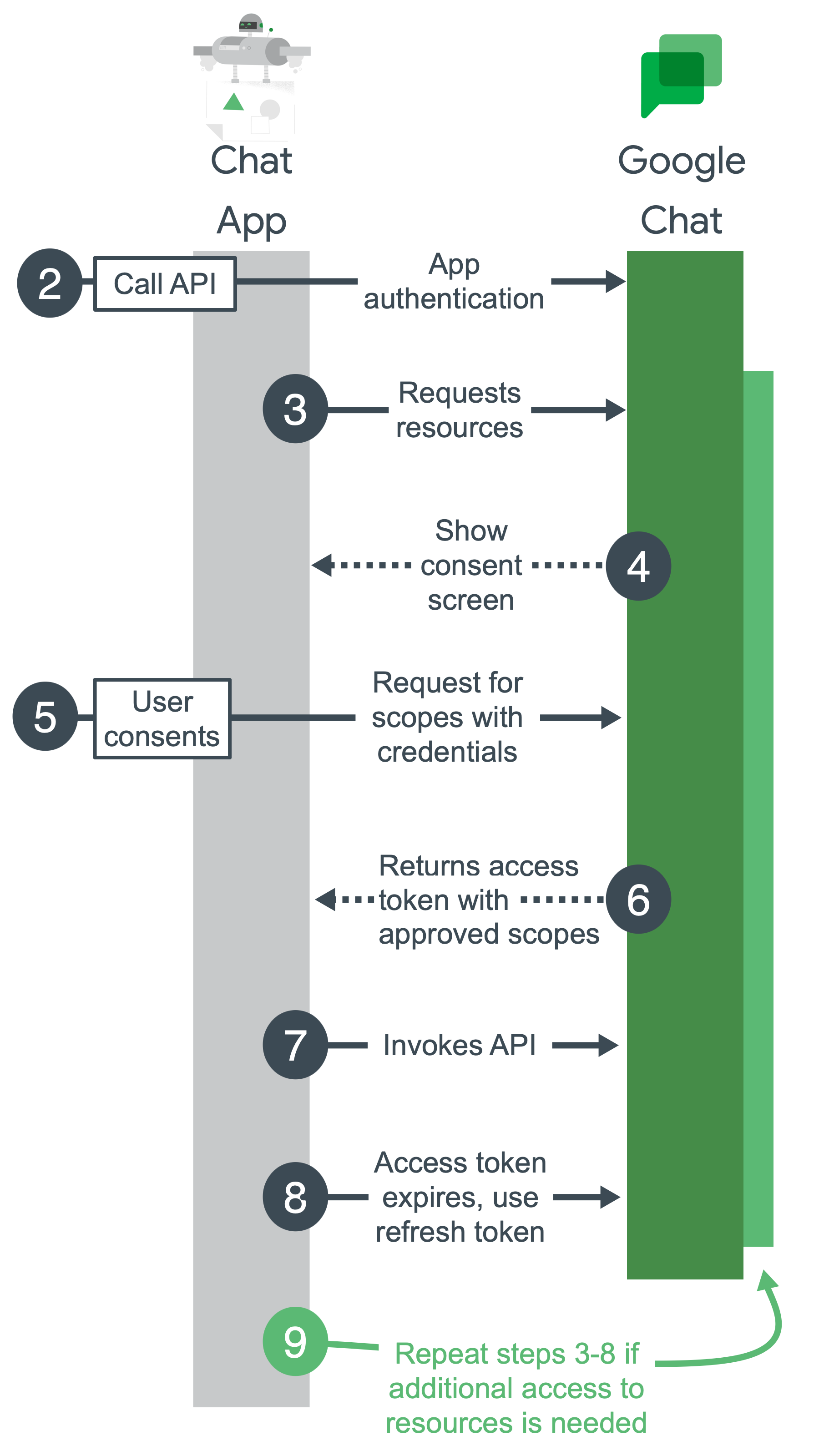

Configure a Google Cloud project, enable Chat API, and configure your Chat app: During development, you create a Google Cloud project. In the Google Cloud project, you enable Chat API, configure your Chat app, and set up authentication. For more information, see Develop on Google Workspace and Build a Chat app.
Call Chat API: When your app calls the Chat API, it sends authentication credentials to the Chat API. If your app authenticates with a service account, the credentials are sent as part of your app's code. If your app requires calling Chat API using a user's authentication that hasn't yet been granted, it prompts the user to sign in.
Request resources: Your app asks for access with scopes that you specify while setting up authentication.
Ask for consent: If your app is authenticating as a user, Google displays an OAuth consent screen so the user can decide whether to grant your app access to the requested data. Authentication with a service account doesn't require user consent.
Send approved request for resources: If the user consents to the authorization scopes, your app bundles the credentials and the user-approved scopes into a request. The request is sent to the Google authorization server to obtain an access token.
Google returns an access token: The access token contains a list of granted scopes. If the returned list of scopes is more restrictive than the requested scopes, your app turns off any features limited by the token.
Access requested resources: Your app uses the access token from Google to invoke the Chat API and access Chat API resources.
Get a refresh token (optional): If your app must access the Google Chat API beyond the lifetime of a single access token, it can get a refresh token. For more information, see Use OAuth 2.0 to access Google APIs.
Request more resources: If your app needs more access, it asks the user to grant new scopes, resulting in a new request to get an access token (steps 3-6).
When Chat apps require authentication
Chat apps can send messages in response to a user interaction, or asynchronously. They can also complete tasks on a user's behalf, such as creating a Chat space or getting a list of people in a Chat space.
Chat apps don't require authentication to respond to a user interaction, unless the Chat app calls the Chat API or another Google API while processing a response.
To send asynchronous messages or perform tasks on a user's behalf, Chat apps make RESTful requests to the Chat API, which require authentication and authorization.
Responses to user interactions don't require authentication
Google Chat apps don't need to authenticate as a user or Chat app to receive and respond synchronously to interaction events.
Google Chat apps receive interaction events whenever a user interacts or invokes a Chat app, including the following:
- A user sends a message to a Chat app.
- A user @mentions a Chat app.
- A user invokes one of the Chat app's commands.
The following diagram shows a request-response sequence between a Chat user and Chat app:
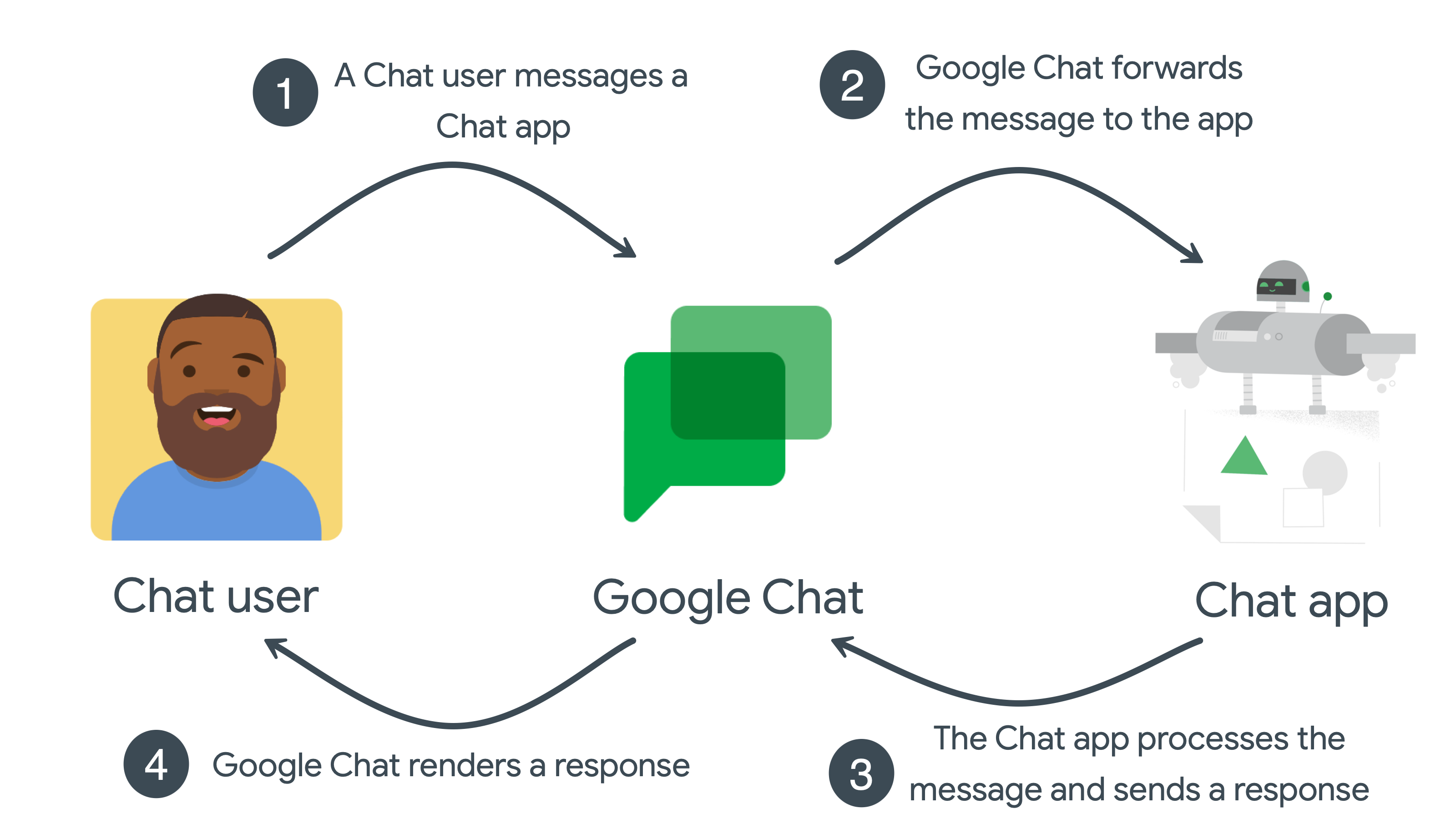

- The user sends a message to the Chat app in Google Chat.
- Google Chat forwards the message to the app.
- The app receives the message, processes it, and returns a response to Google Chat.
- Google Chat renders the response for the user, or in a space.
This sequence repeats for each Chat app interaction event.
Asynchronous messages require authentication
Asynchronous messages occur when a Chat app makes a request to the Chat API, which requires authentication and authorization.
By calling the Chat API, Chat apps can post messages to Google Chat or complete tasks and access data on a user's behalf. For example, after detecting a server outage, a Chat app can call the Chat API to:
- Create a Chat space dedicated to investigating and fixing the outage.
- Add people to the Chat space.
- Post a message to the Chat space to give details about the outage.
The following diagram shows an asynchronous message sequence between a Chat app and a Chat space:
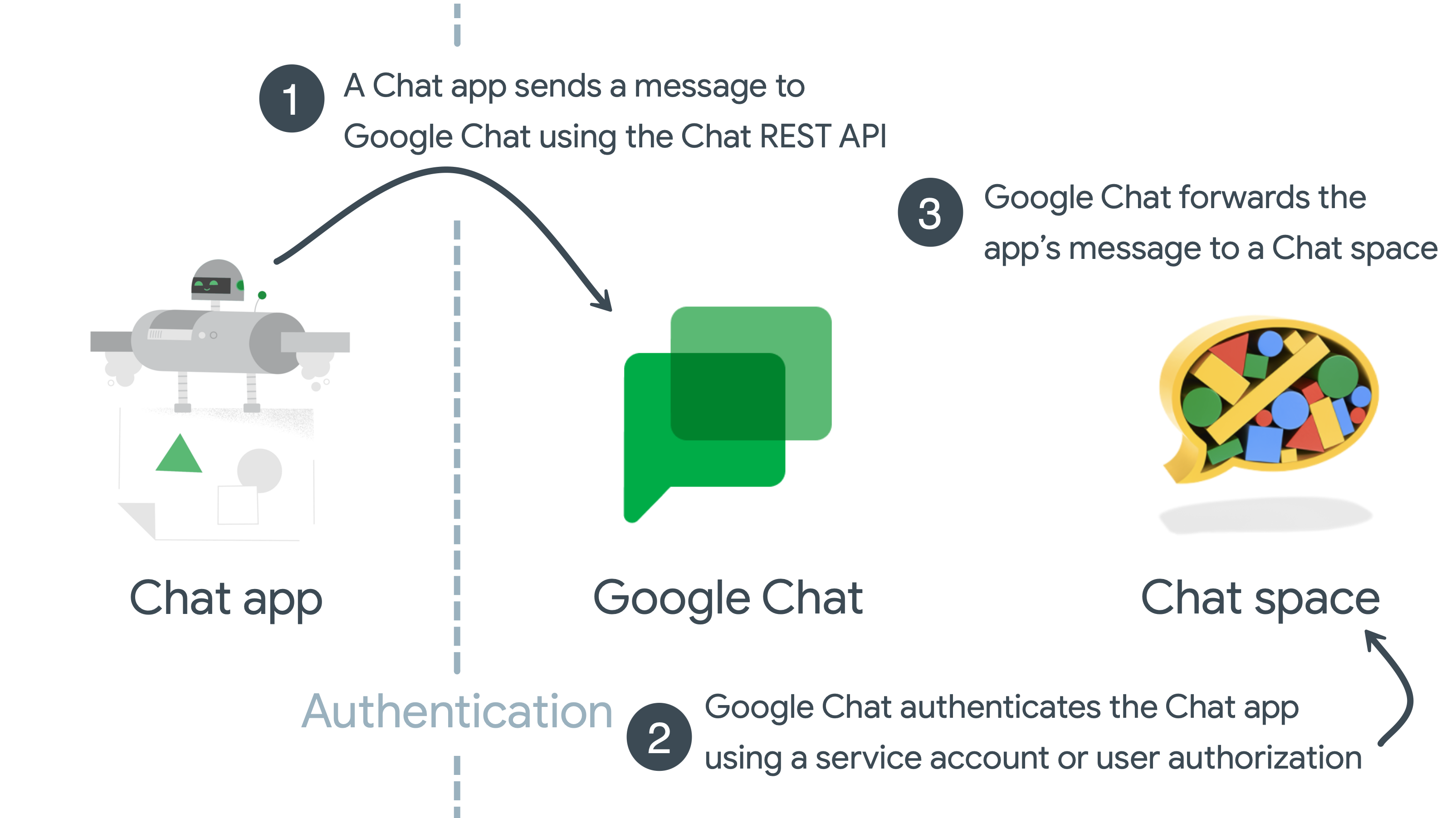

- A Chat app creates a message by calling the
Chat API using the
spaces.messages.createmethod, and includes user credentials in the HTTP request. - Google Chat authenticates the Chat app with service account or user credentials.
- Google Chat renders the app's message to a specified Chat space.
Chat API scopes
Configure the OAuth consent screen and choose scopes to define what information is displayed to users and app reviewers, and register your app so that you can publish it later.
To define the level of access granted to your app, you need to identify and declare authorization scopes. An authorization scope is an OAuth 2.0 URI string that contains the Google Workspace app name, what kind of data it accesses, and the level of access.
Non-sensitive scopes
| Scope code | Description |
|---|---|
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.bot
|
Lets Chat apps view chats and send messages. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
Sensitive scopes
| Scope code | Description |
|---|---|
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.spaces
|
Create conversations and spaces and see or edit metadata (including history settings and access settings) in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.spaces.create
|
Create new conversations in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.spaces.readonly
|
View chat and spaces in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.memberships
|
View, add, update, and remove members from conversations in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.memberships.app
|
Add and remove itself from conversations in Google Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.memberships.readonly
|
View members in Chat conversations. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.create
|
Compose and send messages in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.reactions
|
View, add, and delete reactions to messages in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.reactions.create
|
Add reactions to a message in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.reactions.readonly
|
View reactions to a message in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.users.readstate
|
View and modify last read time for Chat conversations. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.users.readstate.readonly
|
View last read time for Chat conversations. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.admin.spaces.readonly
|
View chat and spaces owned by the administrator's domain in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.admin.spaces
|
View or edit chat and spaces owned by the administrator's domain in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.admin.memberships.readonly
|
View members and managers in conversations owned by the administrator's domain in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.admin.memberships
|
View, add, update and remove members and managers in conversations owned by the administrator's domain in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.spaces
|
Create conversations and spaces and see or update metadata (including history settings and access settings) in Chat as a Chat app. Requires administrator approval. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.spaces.create
|
Create new conversations and spaces in Chat as a Chat app. Requires administrator approval. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.memberships
|
See, add, update, and remove members from conversations and spaces in Chat as a Chat app. Requires administrator approval. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.customemojis
|
View, create, and delete custom emoji in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.customemojis.readonly
|
View custom emoji in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.users.spacesettings
|
View and update Chat user space settings. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.users.sections
|
View, create, update, and delete your sections in Chat; move and list your section items in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.users.sections.readonly
|
View your sections and their section items in Chat. |
Restricted scopes
| Scope code | Description |
|---|---|
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.delete
|
Delete conversations and spaces, and remove access to associated files in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.import
|
Import spaces, messages, and memberships into Chat. For more information, see Authorize Chat apps to import data |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages
|
View, compose, send, update, and delete messages, and add, view, and delete reactions to messages. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.messages.readonly
|
View messages and reactions in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.messages.readonly
|
View messages and reactions in Chat as a Chat app. Requires administrator approval. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.admin.delete
|
Delete conversations and spaces owned by the administrator's domain, and remove access to associated files in Chat. |
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.delete
|
Delete conversations and spaces and remove access to associated files in Chat as a Chat app. Requires administrator approval. This scope only supports app authentication with service accounts. You can't authenticate with user credentials or with domain-wide delegation using this scope. |
The scopes in the preceding tables indicate their sensitivity, according to the following definitions:
Non-sensitive—These scopes provide the smallest sphere of authorization access and only require basic app verification. For information about this requirement, see Steps to prepare for verification.
Sensitive—These scopes provide your app access to a specific user's Google data after receiving authorization from the user. It requires you to go through additional app verification. For information about this requirement, see Steps for apps requesting sensitive scopes.
Restricted—These scopes provide wide access to Google user data and require you to go through the restricted scope verification process. For information about this requirement, see Google API Services: User Data Policy and Additional Requirements for Specific API Scopes. See also Steps for apps requesting restricted scopes.
If your app requires access to any other Google APIs, you can add those scopes as well. For more information about Google API scopes, see Using OAuth 2.0 to Access Google APIs.
To learn more about scopes for Google Workspace APIs, see Configure the OAuth consent screen and choose scopes.
Types of required authentication
There are two ways Chat apps can authenticate and authorize with the Chat API:
- User authentication
- User authentication lets a Chat app access user data and complete actions on a user's behalf. OAuth scopes specify the authorized data and actions. Unless the Chat app was admin installed or given domain-wide delegation, the first time the Chat app performs an action on a user's behalf, the user must authorize the Chat app using the OAuth consent screen.
- App authentication
App authentication lets a Chat app use service account credentials and access data and complete actions as itself. Because the Chat app uses its own credentials to access and work with resources, end users don't need to approve the Chat app's API calls, and you can't add OAuth authorization scopes that support app authorization to the OAuth consent screen.
Two types of OAuth authorization scopes support app authentication:
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.bot: Your Chat app can call Google Chat API methods that support this authorization scope to create, update, get, list, or delete resources that it has access to, like messages in spaces that end users add your Chat app to. Your Chat app can self-grant this authorization scope, no administrator or end user authorization required.https://www.googleapis.com/auth/chat.app.*: Using these scopes requires one-time administrator approval. To receive administrator approval, you prepare the Chat app's service account to receive administrator approval by creating a Google Workspace Marketplace-compatible OAuth client and configuring the app in Google Workspace Marketplace SDK. These scopes allow your Chat app to call specific Google Chat API methods. For example,chat.app.spaces.createpermits apps to create Chat spaces.
If a method supports both user or app authentication, the Chat API returns different results based on the authentication type that you use:
- With app authentication, the methods only return resources that the Chat app can access.
- With user authentication, the methods only return resources that the user can access.
For example, calling the spaces.list() method with app authorization returns
the list of spaces that the Chat app is a member of.
Calling spaces.list() with
user authorization returns the list of spaces that the user is a member of. In
practice, you might use both types of
authentication when calling the Chat API, depending on the design
and features of your Chat app.
For asynchronous Chat API calls
The following table lists the Chat API methods and their supported authorization scopes:
| Method | User authentication supported | App authentication supported | Authorization scopes supported | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spaces | ||||
| Create a space |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Set up a space | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Get a space |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| List spaces |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Search spaces | — |
With User authentication using administrator privileges:
|
||
| Update a space |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Delete a space |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Complete the import process for a space | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Find a direct message |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Members | ||||
| Create a member |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Get a member |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| List members |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Delete a member |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Update a member |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Messages | ||||
| Create a message |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Get a message |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| List messages |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Update a message |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Delete a message |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Reactions | ||||
| Create a reaction | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| List reactions | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Delete a reaction | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Custom emoji | ||||
| Create a custom emoji | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Delete a custom emoji | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Get a custom emoji | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| List custom emoji | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Media & attachments | ||||
| Upload media as a file attachment | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Download media |
With User authentication:
|
|||
| Get a message attachment | — |
With App authentication:
|
||
| User read states | ||||
| Get a user's space read state | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Update a user's space read state | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Get a user's thread read state | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| User space settings | ||||
| Get a user's space notification setting | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Update a user's space notification setting | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Space events | ||||
| Get space events | — |
With User authentication,
you must use a scope based on the
event type:
|
||
| List space events | — |
With User authentication,
you must use a scope for each
event type included in the request:
|
||
| Sections | ||||
| Create a section | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Delete a section | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| List sections | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Update a section | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Position a section | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| Section Items | ||||
| Move a section item | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
| List section items | — |
With User authentication:
|
||
For Chat app interaction events
The following table lists common ways that users interact with Chat apps and whether authentication is required or supported:
| Scenario | No authentication required | User authentication supported | App authentication supported | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receive messages from: |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Respond to messages: |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Send new messages: |
|
|||||||||||||||
Related topics
- For an overview of authentication and authorization in Google Workspace, see Learn about authentication & authorization.
- For an overview of authentication and authorization in Google Cloud, see Authentication overview.
- To learn more about service accounts, see Service accounts.
- To learn more about how Google APIs use OAuth 2.0, see Using OAuth 2.0 to Access Google APIs.
- Set up authentication and authorization with user credentials or a service account.
- To manage granular OAuth permissions, see Manage granular OAuth permissions for Google Chat apps.