Page Summary
-
Google Maps Platform secures its products by requiring API keys for authentication and billing purposes.
-
API keys can be created and managed through the Google Cloud Console or the Cloud SDK.
-
Restricting API keys to specific websites and APIs enhances security by limiting unauthorized usage.
-
All Maps Embed API requests must include your API key as a parameter for authentication.
This document describes the steps needed to start using the Maps Embed API.
|
Ensure that you meet the prerequisites. |
Enable the API in your Google Cloud project. |
Configure an API key to make an authenticated API request. |
Google Maps Platform products are secured from unauthorized use by requiring API calls to include an API key.
Get an API key for use with Maps Embed API
An API key is a unique alphanumeric string that associates your Cloud Billing account and Google Cloud project with the request your application makes to a Google Maps Platform API or SDK.
To add Maps Embed API to an API key:
Console
-
Go to the Google Maps Platform > Keys & Credentials page.
- If prompted, select an existing project.
The list of available keys appears under API Keys.
If you don't have an API key, or you want to create an API key for use with the Maps Embed API, create a new API key:
On the Keys & Credentials page, click + Create credentials > API key.
The API key created dialog displays your newly created API key.
- Click the Name of an API key to edit the key.
On the edit page, under Key restrictions:
- Under Application restrictions, if any option other than None is selected, only requests originating from those sources are permitted. For more information, see Restrict your API keys.
Under API restrictions:
- If Restrict key is selected, select the drop-down box to add the Maps Embed API to the API key.
- If Don't restrict key is selected, then you can use the API key to make requests to Maps Embed API.
Remember to restrict the API key before using it in production.
- Select Save.
- Select Show key for the key you edited to display the key's alphanumeric string. Pass that string to the example request shown in the next section.
gcloud
-
Get the ID of the key that you want to update.
The ID is not the same as the display name or the key string. You can get the ID by using the following
gcloudcommand to list the keys in your project.gcloud services api-keys list
The ID is part of the
namefield of the response for each key:name: projects/PROJECT_ID/locations/global/keys/KEY_ID
If you don't have an API key, or you want to create an API key for use with the Maps Embed API, create a new API key:
gcloud services api-keys create \ --project "PROJECT" \ --display-name "DISPLAY_NAME"
Read more about the Google Cloud SDK , Cloud SDK installation , and the following commands:
-
Use the
gcloud services api-keys updatecommand to specify which services an API key can be used to authenticate to.Replace the following values:
- KEY_ID: The ID of the key that you want to restrict.
SERVICE_1, SERVICE_2...:
The service names of the APIs that the key can be used to access. You must provide all service names with the update command; the service names provided replace any existing services on the key.
You can find the service name by searching for the API on the API dashboard. For the Maps Embed API, the service names
maps-embed-backend.googleapis.com.gcloud services api-keys update KEY_ID \ --api-target=service=maps-embed-backend.googleapis.com \ --api-target=service=SERVICE_1 --api-target=service=SERVICE_2
Make an API request
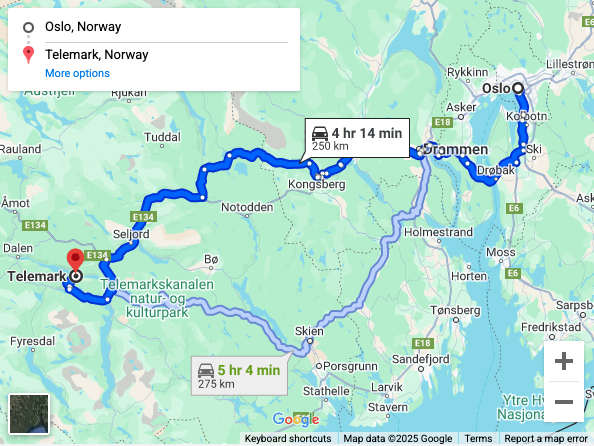
Make a Maps Embed API request to display the path between Oslow and Telemark, Norway, the distance, and travel time avoiding tolls and highways. You must include your API key's alphanumeric string with every request and use HTTPS for requests that include the API key.
Click API_KEY in the code below to insert the key's alphanumeric string:
<iframe class="map-top" width="598" height="450" src="https://www.google.com/maps/embed/v1/directions?key=YOUR_API_KEY &origin=Oslo+Norway&destination=Telemark+Norway&avoid=tolls|highways" allowfullscreen></iframe>- Open your default text editor.
- Create an HTML file and name it
index.html. - Add the following code with the iframe you generated above:
<html> <!-- Replace this code comment with your iframe. --> </html>
- Save your
index.htmlHTML file. - Load the HTML file in a web browser by dragging it from your desktop onto your browser; alternatively, double-clicking the file works on most operating systems.
The embedded map appears as:
Apply API key restrictions
Google strongly recommends that you restrict your API keys by limiting their usage to those only APIs needed for your application. Restricting API keys adds security to your application by protecting it from unwarranted requests. You are financially responsible for charges caused by abuse of unrestricted API keys. For more information, see Google Maps Platform security guidance.
API keys support two types of restrictions:
- API restrictions specify which SDKs and APIs can be called using the API key.
- Application restrictions specify which websites, IP addresses, or apps can use an API key.
For more information on applying restrictions, see Restrict your API keys.
What's next
Now that you have enabled Maps Embed API and made a successful request, see Embedding a map to learn more about using the API.
