Page Summary
-
Topographic diversity represents the variety of temperature and moisture conditions available as local habitats and is used as a surrogate variable to support species diversity and persistence.
-
The dataset is based on the 30m SRTM DEM and uses the multi-scale Topographic Position Index (mTPI) and the standard deviation of the Continuous Heat-Insolation Load Index (CHILI) to calculate topographic diversity.
-
This dataset is part of the Conservation Science Partners (CSP) Ecologically Relevant Geomorphology (ERGo) Datasets, intended for climate adaptation planning by identifying features of the landscape unlikely to change.
-
The dataset has a pixel size of 270 meters and includes a band named 'constant' representing SRTM-derived topographic diversity.
-
The dataset is available from 2006 to 2011 and is provided by Conservation Science Partners under the CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0 license.
- Dataset Availability
- 2006-01-24T00:00:00Z–2011-05-13T00:00:00Z
- Dataset Producer
- Conservation Science Partners
- Tags
Description
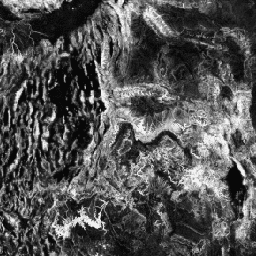
Topographic diversity (D) is a surrogate variable that represents the variety of temperature and moisture conditions available to species as local habitats. It expresses the logic that a higher variety of topo-climate niches should support higher diversity (especially plant) and support species persistence given climatic change.
To calculate D, the multi-scale Topographic Position Index (mTPI), being a dominant control of soil moisture (T), was used for measuring hillslope position. The mTPI was combined with the square-root transform for mTPI>0 (T') and with the standard deviation of the Continuous Heat-Insolation Load Index (CHILI), calculated at multiple scales (C') as: D = 1 - ((1-T') * (1-C'). It is based on the 30m SRTM DEM (available in EE as USGS/SRTMGL1_003).
The Conservation Science Partners (CSP) Ecologically Relevant Geomorphology (ERGo) Datasets, Landforms and Physiography contain detailed, multi-scale data on landforms and physiographic (aka land facet) patterns. Although there are many potential uses of these data, the original purpose for these data was to develop an ecologically relevant classification and map of landforms and physiographic classes that are suitable for climate adaptation planning. Because there is large uncertainty associated with future climate conditions and even more uncertainty around ecological responses, providing information about what is unlikely to change offers a strong foundation for managers to build robust climate adaptation plans. The quantification of these features of the landscape is sensitive to the resolution, so we provide the highest resolution possible given the extent and characteristics of a given index.
Bands
Pixel Size
270 meters
Bands
| Name | Min | Max | Pixel Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
constant |
-1323.63* | 8.81* | meters | SRTM-derived topographic diversity |
Terms of Use
Terms of Use
Citations
Theobald, D. M., Harrison-Atlas, D., Monahan, W. B., & Albano, C. M. (2015). Ecologically-relevant maps of landforms and physiographic diversity for climate adaptation planning. PloS one, 10(12), e0143619
Explore with Earth Engine
Code Editor (JavaScript)
var dataset = ee.Image('CSP/ERGo/1_0/Global/SRTM_topoDiversity'); var srtmTopographicDiversity = dataset.select('constant'); var srtmTopographicDiversityVis = { min: 0.0, max: 1.0, }; Map.setCenter(-111.313, 39.724, 6); Map.addLayer( srtmTopographicDiversity, srtmTopographicDiversityVis, 'SRTM Topographic Diversity');