Tổng quan
Mục đích của quy trình xác thực là xác định và xác thực người dùng với Trình tích hợp thanh toán (tích hợp).
Cách sử dụng xác thực phổ biến nhất là làm đầu vào điều kiện tiên quyết cho các phương thức khác, đáng chú ý là generateDirectDebitAuthorization.
Dữ liệu đầu ra của lệnh uỷ quyền xác thực (là bằng chứng xác thực) được dùng làm dữ liệu đầu vào (tham số) cho phương thức nêu trên.
Phương thức uỷ quyền xác thực
Google Standard Payments hỗ trợ việc uỷ quyền xác thực thông qua Redirect
Authentication-Authorization.
Chuyển hướng uỷ quyền xác thực
Xác thực chuyển hướng xảy ra khi Google chuyển hướng người dùng đến một tài sản do nhà tích hợp sở hữu(ví dụ: ứng dụng web hoặc ứng dụng Android) để thực hiện việc xác thực. Sau khi hoàn tất, ứng dụng phải chuyển hướng trở lại Google. Ứng dụng đó có thể là ứng dụng web, ứng dụng Android hoặc cả hai.
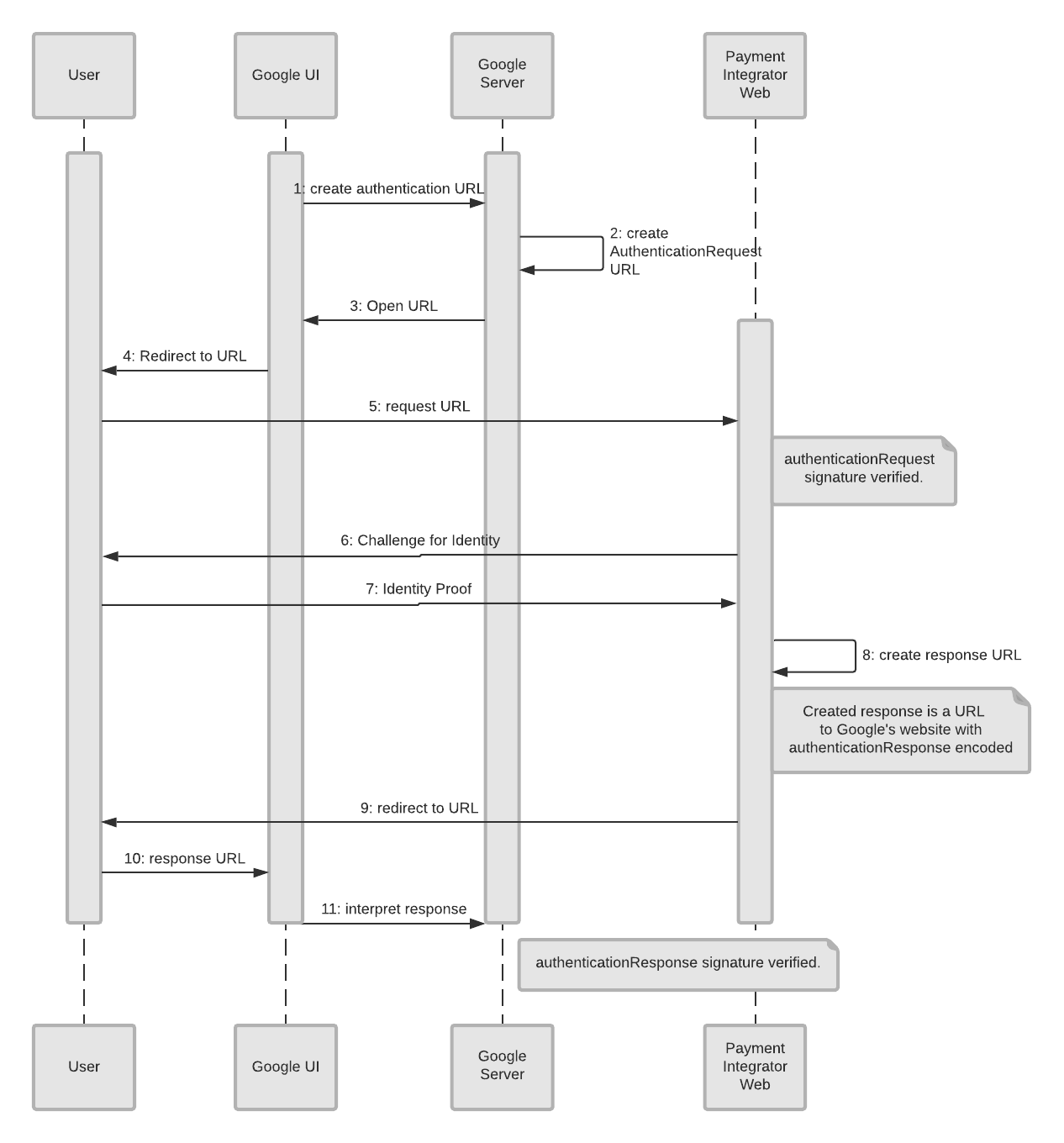
Việc cung cấp quy trình xác thực web dành cho thiết bị di động và web dành cho máy tính sẽ cho phép nhà tích hợp tiếp cận tất cả người dùng trên các nền tảng được hỗ trợ. Trình tích hợp cũng có thể tuỳ ý hỗ trợ lệnh chuyển hướng ứng dụng Android. Các trình tích hợp nên hỗ trợ ứng dụng Android vì ứng dụng này mang lại trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người dùng, mang lại tỷ lệ chuyển đổi cao nhất. Các tham số được truyền đến ứng dụng web và ứng dụng Android là như nhau. Lệnh chuyển hướng ứng dụng web sử dụng lệnh chuyển hướng HTTP GET với các tham số được mã hoá trong URL. Để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết về quá trình mã hoá này, hãy xem phần Xác thực web.
Kết quả từ mỗi cơ chế xác thực này là một phản hồi đã ký có tên là AuthenticationAuthorizationResponse. Việc trả về phản hồi này cho Google sẽ báo hiệu cho Google rằng quá trình uỷ quyền xác thực đã thành công. Khi được sử dụng ở chế độ độc lập, gspResult và chữ ký được dùng để xác định lần uỷ quyền xác thực thành công.
Để xác thực một luồng (ví dụ: chụp), requestId xác thực (từ AuthenticationAuthorizationRequest) sẽ được dùng làm bằng chứng về việc cho phép xác thực.
Sơ đồ trình tự sau đây cho thấy sự tương tác giữa trình duyệt của người dùng, Google và ứng dụng web của nhà tích hợp:
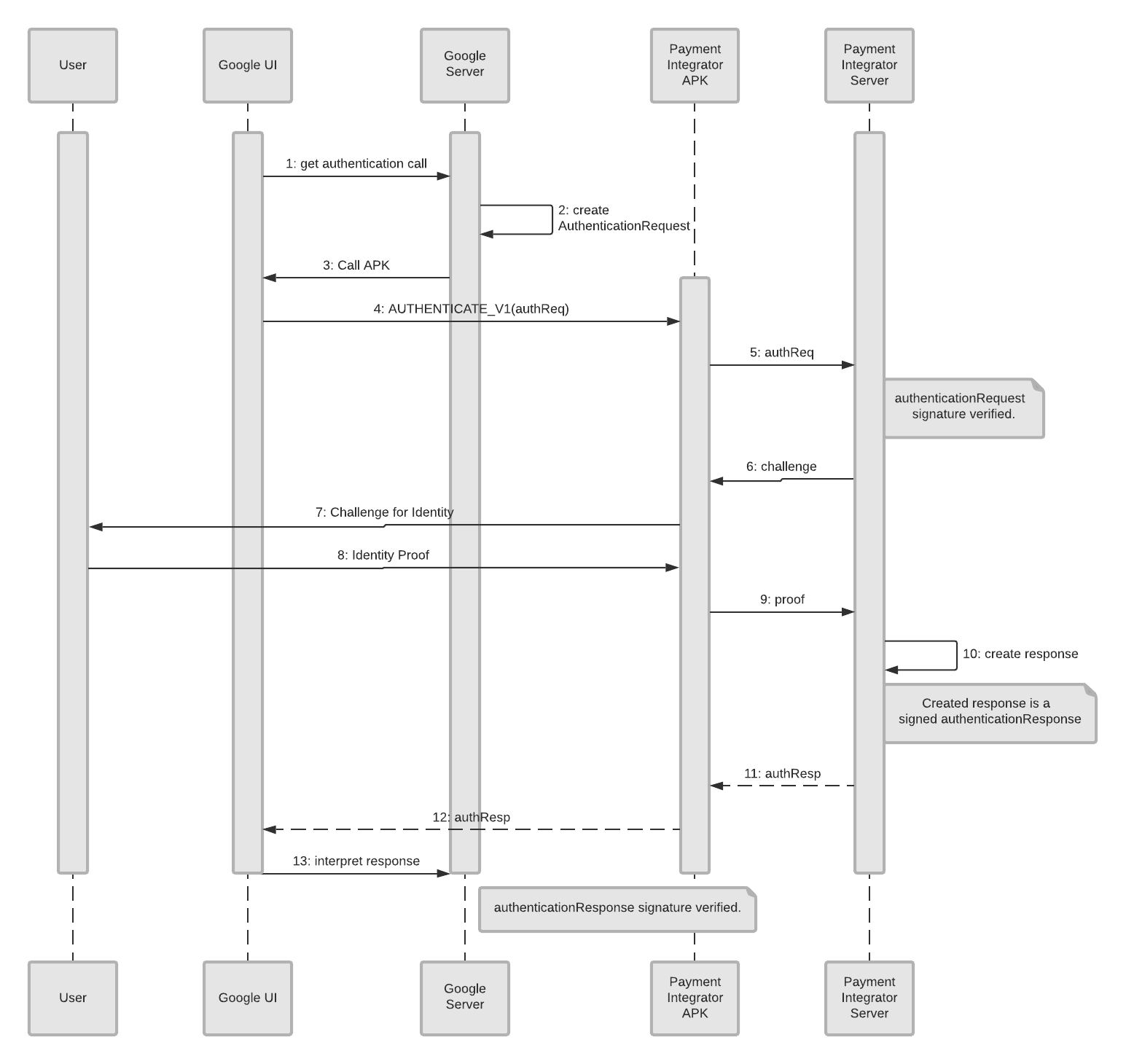
Quy trình uỷ quyền xác thực của Android sử dụng một Ý định Android để chuyển hướng người dùng. Để biết thêm thông tin chi tiết về tham số Ý định, hãy xem bài viết Xác thực Android.
Sơ đồ trình tự sau đây cho thấy sự tương tác giữa điện thoại của người dùng, Google và ứng dụng Android của nhà tích hợp: