
Airports are large, multi-terminal complexes and precise navigation is critical for timely arrivals and departures. Google Maps Geocoding API would typically return a coordinate (Latitude/Longitude) which in most cases would be the centroid of the large airport complex. This app is an interactive tool designed specifically to help users pinpoint and visualize precise locations within a larger complex venue like specific terminals or pickup/drop-off points within an Airport.
Here's how it achieves this:
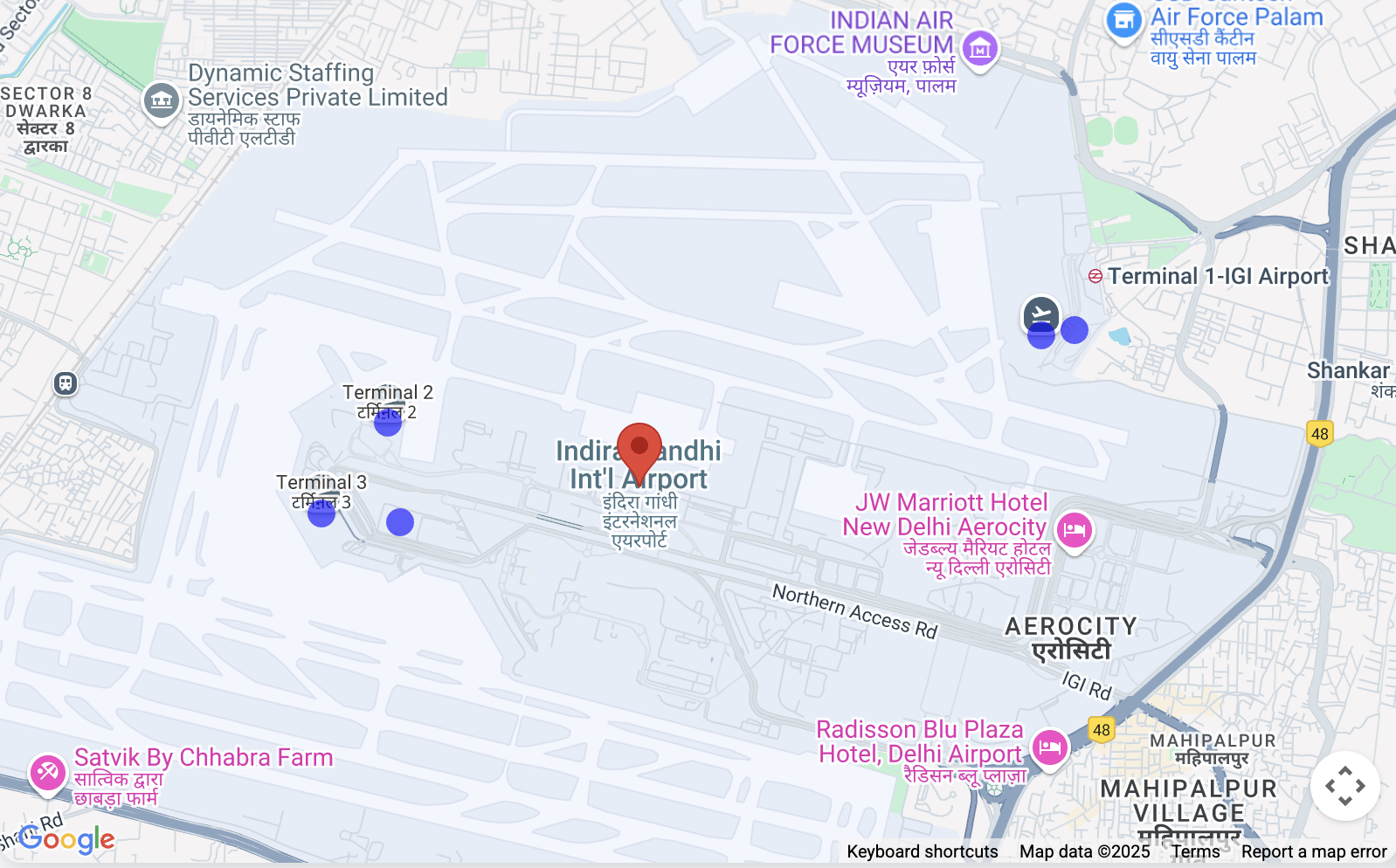
Airport/Venue Search: Users start by searching for a main location (e.g., "Indira Gandhi International Airport") using the Google Places Autocomplete input, which is restricted to India.
Sub-Location Discovery: Once a primary location is selected, the script uses the Google Places API to fetch details, crucially including any listed "sub-destinations" associated with that place (like Terminal 1, Terminal 3, specific gates, etc., if available in Google's data).
Visual Mapping: The script uses the Geocoding API to find the coordinates of the main location and its sub-destinations.
It then displays the main location and places distinct, clickable markers (blue circles) on the map for each identified sub-destination.
Precise Identification: Clicking on a sub-destination marker highlights it
(turns green) and opens an InfoWindow showing its name and other available
details (like address or type), allowing the user to confirm they've selected
the correct specific point.
Contextual View: The map automatically adjusts its view (fitBounds) to
verify all relevant markers (main location + sub-destinations) are clearly
visible.
Google Maps Platform APIs in the Airport Navigation App
This document explains the key Google Maps Platform APIs and their parameters used in the provided "Navigate to Airport" demo application. The app leverages several services to provide map display, place search, detailed place information, and advanced location insights.
1. Map Initialization and Display
The foundation of the application is the interactive map itself.
- API Used:
google.maps.Map(from the Maps JavaScript API) - Purpose: To create and display the interactive map on the webpage.
- Key Parameters:
center: Defines the initial geographical center of the map. In this app, it's initially set to Delhi's coordinates ({ lat: 28.461835685621395, lng: 77.05004035761647 }).zoom: Sets the initial zoom level of the map.DEFAULT_ZOOM_LEVEL(15) is used for a close-up view.mapId: A unique identifier for a map style configured in the Google Cloud Console.
2. Place Search and Autocomplete
The search bar functionality is powered by the Places API.
- API Used:
google.maps.places.Autocomplete(from the Places Library of the Maps JavaScript API) - Purpose: Provides predictive text completion for geographical searches as the user types, suggesting relevant places like airports.
- Key Parameters:
input: The HTML input element (#search-input) where the user types their query.componentRestrictions: Filters search results to a specific country. Here,{ country: 'in' }restricts results to India.fields: Specifies the data fields to be returned for the selected place.['place_id']is used initially to retrieve only the unique identifier for the place, optimizing data transfer.
- How to use Autocomplete
// Initialize Autocomplete
const autocomplete = new google.maps.places.Autocomplete(input, {
componentRestrictions: { country: 'in' },
fields: ['place_id'],
});
// Add listener to the Autocomplete
autocomplete.addListener('place_changed', async () => {
const place = autocomplete.getPlace();
if (!place.place_id) {
return;
}
// Once a place is selected, fetch details
await getPlaceDetails(place.place_id);
});
3. Retrieving Detailed Place Information and Handling Sub-Destinations
Once a place is selected from the autocomplete suggestions, more comprehensive details are fetched.
- API Used: Places API (via direct
fetchcall tohttps://places.googleapis.com/v1/places/{placeId}) - Purpose: To retrieve rich details about a specific place, including
its display name, address, types, and crucially, its
subDestinations(e.g., individual terminals or important areas within a larger complex like an airport). - Key Parameters in URL:
{placeId}: The unique identifier of the selected place.fields: Specifies the exact data fields to retrieve. The app requestsid,displayName,subDestinations,types, andformattedAddress. This is crucial for controlling costs and receiving only necessary data.
- How to get
subDestinationsgiven a location
async function getPlaceDetails(placeId) {
// Construct the URL for the Places API (v1) details endpoint
// The 'fields' parameter is crucial for requesting subDestinations
const url = `https://places.googleapis.com/v1/places/${placeId}?key=YOUR_API_KEY&fields=id,displayName,subDestinations,types,formattedAddress`;
const response = await fetch(url);
const data = await response.json();
// Accessing subDestinations from the Places API response
if (data.subDestinations && data.subDestinations.length > 0) {
for (const subDestination of data.subDestinations) {
// Each subDestination object contains an 'id' and 'displayName'
console.log(`Sub-destination ID: ${subDestination.id}`);
console.log(`Sub-destination Name: ${subDestination.displayName?.text}`);
// This subDestination.id is then used in a geocoding call (as shown in section 4)
}
}
}
**Handling `subDestinations`:** When the Places API returns
`subDestinations`, the application initiates a process for each one:
1. **Geocoding:** It uses the `google.maps.Geocoder` to convert
each `subDestination.id` into its precise geographical coordinates
(`lat`, `lng`).
1. **Marker Placement:** A distinct marker is added to the map for
each sub-destination. These markers are styled with a blue circle icon
to differentiate them.
1. **Map Bounds Adjustment:** The `google.maps.LatLngBounds` object
is used to dynamically expand the map's view to encompass all retrieved
sub-destinations, verifying they are all visible within the current map
frame.
1. **Interactive Information Window:** A `click` listener is
attached to each sub-destination marker. When clicked, the marker's
icon changes to green, and an `InfoWindow` appears, displaying the
sub-destination's name, address, and types. This provides immediate,
detailed context to the user.
4. Geocoding and Reverse Geocoding: Fetching Details for Sub-Destinations
The application uses geocoding for two main purposes: converting place IDs to coordinates and converting coordinates back to location details. This section specifically highlights how geocoding is used to get detailed information about sub-destinations.
- API Used:
google.maps.Geocoder(from the Maps JavaScript API) and Geocoding API (via directfetchcall tohttps://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json) - Purpose:
google.maps.Geocoder: Used to convert aplaceId(obtained from Autocomplete or Places API) into geographical coordinates (lat,lng) and a viewport, allowing the map to center and zoom correctly on the selected place and its sub-destinations.- Geocoding API (
fetch): Used for reverse geocoding (converting latitude and longitude to a human-readable address) and to retrieve advanced location data like building outlines and navigation points.
- Key Parameters:
google.maps.Geocoder.geocode():placeId: The Place ID to geocode.location: TheLatLngobject for reverse geocoding.
- Geocoding API
fetchcall:latlng: The latitude and longitude coordinates for reverse geocoding.extra_computations=BUILDING_AND_ENTRANCES: This critical parameter requests additional data, specifically building footprints and entrance information, which is then used to display building outlines and navigation points.
How to use the subDestination ID to fetch further details (e.g., location,
formatted address, types)
function geocodeAndAddMarker(subDestination, bounds) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const geocoder = new google.maps.Geocoder();
// Using the subDestination.id to geocode and get location details
geocoder.geocode({ placeId: subDestination.id }, (results, status) => {
if (status === "OK" && results[0]) {
const location = results[0].geometry.location;
const displayName = subDestination.displayName?.text || "Sub-destination";
const formattedAddress = results[0].formatted_address; // Further detail from Geocoding
const types = results[0].types; // Further detail from Geocoding
const marker = new google.maps.Marker({
map: map,
position: location,
title: displayName,
icon: {
path: google.maps.SymbolPath.CIRCLE,
fillColor: 'blue',
fillOpacity: 0.6,
strokeWeight: 0,
scale: 8
}
});
marker.addListener('click', () => {
marker.setIcon({
path: google.maps.SymbolPath.CIRCLE,
fillColor: 'green',
fillOpacity: 0.6,
strokeWeight: 0,
scale: 8
});
const infowindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow({
content: `<b>${displayName}</b><br><p>Address: ${formattedAddress}</p><p>Types: ${types.join(', ')}</p>`,
});
infowindow.open(map, marker);
});
bounds.extend(location);
resolve(true);
} else {
reject(new Error(`Geocoding failed for placeId: ${subDestination.id}`));
}
});
});
}
5. Displaying Markers
Markers are used to highlight specific locations on the map.
- API Used:
google.maps.Marker(from the Maps JavaScript API) andgoogle.maps.marker.AdvancedMarkerElementwithgoogle.maps.marker.PinElement(from the Marker Library of the Maps JavaScript API) - Purpose:
google.maps.Marker: Used for the initial draggable marker (thoughdraggableis set tofalsein the provided code, it's part of its capability) and for basic sub-destination markers as described in section 3.AdvancedMarkerElementandPinElement: Used for the more visually distinct navigation point markers, allowing for custom styling of the marker's pin.
- Key Parameters:
position: TheLatLngcoordinates where the marker will be placed.map: The map instance on which the marker will be displayed.title: Text displayed when hovering over the marker.icon: Allows custom icons forgoogle.maps.Marker(e.g.,google.maps.SymbolPath.CIRCLEwith custom colors).content: ForAdvancedMarkerElement, this allows embedding custom HTML content, includingPinElementfor pre-styled pins.PinElementparameters:background,borderColor,glyphColor,scalefor visual customization.
6. Displaying Building Outlines
The application can visually represent the footprint of buildings.
- API Used:
google.maps.Data(from the Maps JavaScript API) - Purpose: To display geographical data, such as building outlines
(returned as GeoJSON
display_polygonfrom the Geocoding API'sextra_computations). - Key Parameters:
map: The map instance to which the data layer is applied.style: Defines the visual appearance of the GeoJSON features (e.g.,strokeColor,fillColor,fillOpacity).addGeoJson(): Method to add GeoJSON data to the layer.
7. Map Bounds and Zoom
verifying the map view encompasses all relevant locations.
- API Used:
google.maps.LatLngBounds(from the Maps JavaScript API) - Purpose: To dynamically adjust the map's viewport to fit a collection of geographical points (e.g., the main place and all its sub-destinations).
- Key Methods:
extend(location): Adds aLatLngpoint to the bounds, expanding them if necessary.fitBounds(bounds): Adjusts the map's center and zoom level to display the entire area defined by theLatLngBoundsobject.
By combining these Google Maps Platform APIs, the application provides a comprehensive and interactive experience for searching places, viewing their details, and visualizing related geographical information like sub-destinations and building outlines.
Implementation Considerations Note that this does not work in all airports areas and is subject to (airport terminal) data availability.
Resources Geocoding API Places API Maps Javascript API
Authors:
