Die Checks Guardrails API ist jetzt in der Alphaversion in der privaten Vorschau verfügbar. Fordern Sie über unser Antragsformular Zugriff auf die private Vorschau an.
Die Guardrails API ist eine API, mit der Sie prüfen können, ob Text potenziell schädlich oder unsicher ist. Sie können diese API in Ihrer GenAI-Anwendung verwenden, um zu verhindern, dass Ihre Nutzer potenziell schädlichen Inhalten ausgesetzt werden.
Schutzmaßnahmen verwenden
Mit Checks Guardrails für Ihre Gen AI-Ein- und ‑Ausgaben können Sie Text erkennen und minimieren, der gegen Ihre Richtlinien verstößt.
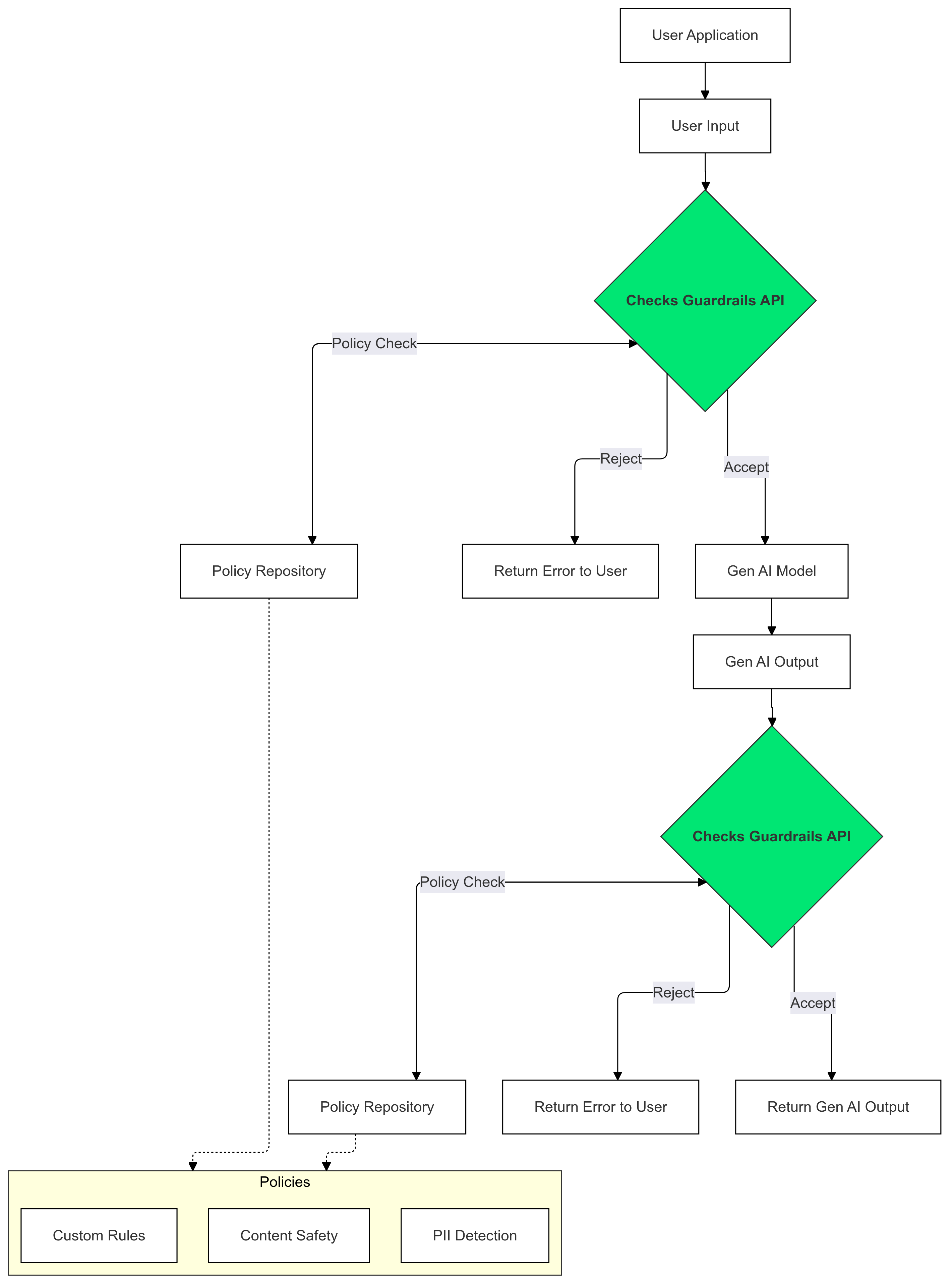
Vorteile von Guardrails
LLMs können manchmal potenziell schädliche oder unangemessene Inhalte generieren. Die Integration der Guardrails API in Ihre GenAI-Anwendung ist entscheidend für die verantwortungsvolle und sichere Nutzung von Large Language Models (LLMs). So können Sie die Risiken, die mit generierten Inhalten verbunden sind, minimieren, indem Sie eine Vielzahl potenziell schädlicher Ausgaben herausfiltern, darunter unangemessene Sprache, diskriminierende Bemerkungen und Inhalte, die Schaden anrichten könnten. Das schützt nicht nur Ihre Nutzer, sondern auch den Ruf Ihrer Anwendung und stärkt das Vertrauen Ihrer Zielgruppe. Durch die Priorisierung von Sicherheit und Verantwortung können Sie mit den Guardrails innovative und gleichzeitig sicherere Anwendungen auf Basis generativer KI entwickeln.
Erste Schritte
In diesem Leitfaden finden Sie eine Anleitung zur Verwendung der Guardrails API, um unangemessene Inhalte in Ihren Anwendungen zu erkennen und zu filtern. Die API bietet eine Vielzahl vortrainierter Richtlinien, mit denen verschiedene Arten potenziell schädlicher Inhalte wie Hassreden, Gewalt und sexuell explizites Material erkannt werden können. Sie können das Verhalten der API auch anpassen, indem Sie Grenzwerte für jede Richtlinie festlegen.
Vorbereitung
- Ihr Google Cloud-Projekt muss für die private Vorschau von Checks AI Safety genehmigt sein. Wenn Sie noch keinen Zugriff haben, können Sie ihn über unser Formular beantragen.
- Checks API aktivieren
- Achten Sie darauf, dass Sie autorisierte Anfragen gemäß unserem Autorisierungsleitfaden senden können.
Unterstützte Richtlinien
| Richtlinienname | Beschreibung der Richtlinie | API-Enum-Wert für Richtlinientyp |
|---|---|---|
| Gefährliche Inhalte | Inhalte, die den Zugriff auf schädliche Waren, Dienste und Aktivitäten ermöglichen, fördern oder erleichtern. | DANGEROUS_CONTENT |
| Anfordern und Rezitieren von personenidentifizierbaren Informationen | Inhalte, in denen vertrauliche personenbezogene Daten oder Informationen einer Person angefordert oder offengelegt werden | PII_SOLICITING_RECITING |
| Belästigung | Inhalte, die böswillig, einschüchternd, mobbend oder missbräuchlich gegenüber anderen Personen sind. | HARASSMENT |
| sexuell explizit | Inhalte, die sexuell explizit sind. | SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT |
| Hassrede | Inhalte, die allgemein als Hassrede bzw. Volksverhetzung gelten. | HATE_SPEECH |
| Medizinische Daten | Inhalte, die den Zugriff auf schädliche medizinische Ratschläge oder Anleitungen ermöglichen, fördern oder erleichtern, sind verboten. | MEDICAL_INFO |
| Gewaltdarstellungen | Inhalte mit unnötigen Beschreibungen von realistischer Gewalt und/oder Gewaltdarstellungen. | VIOLENCE_AND_GORE |
| Obszönitäten und vulgäre Sprache | Inhalte mit vulgärer, vulgärer oder anstößiger Sprache sind verboten. | OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY |
Code-Snippets
Python
Installieren Sie den Google API-Python-Client, indem Sie pip install
google-api-python-client ausführen.
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
SECRET_FILE_PATH = 'path/to/your/secret.json'
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
SECRET_FILE_PATH, scopes=['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks']
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.',
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'}
], # Default Checks-defined threshold is used
}
)
response = request.execute()
for policy_result in response['policyResults']:
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
Ok
Installieren Sie den Checks API Go-Client, indem Sie go get google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha ausführen.
package main
import (
"context"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
const credsFilePath = "path/to/your/secret.json"
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
checksService, err := checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint("https://checks.googleapis.com"),
option.WithCredentialsFile(credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes("https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks"),
)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"}, // Default Checks-defined threshold is used
},
}
classificationResults, err := checksService.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
for _, policy := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
slog.Info("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policy.PolicyType, "Score", policy.Score, "Violation Result", policy.ViolationResult)
}
}
REST
Hinweis: In diesem Beispiel wird das oauth2l-CLI-Tool verwendet.
Ersetzen Sie YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID durch Ihre Google Cloud-Projekt-ID, für die der Zugriff auf die Guardrails API gewährt wurde.
curl -X POST https://checks.googleapis.com/v1alpha/aisafety:classifyContent \
-H "$(oauth2l header --scope cloud-platform,checks)" \
-H "X-Goog-User-Project: YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": {
"text_input": {
"content": "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
"language_code": "en"
}
},
"policies": [
{
"policy_type": "HARASSMENT",
"threshold": "0.5"
},
{
"policy_type": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
},
]
}'
Beispielantwort
{
"policyResults": [
{
"policyType": "HARASSMENT",
"score": 0.430,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
"score": 0.764,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY",
"score": 0.876,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT",
"score": 0.197,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "HATE_SPEECH",
"score": 0.45,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "MEDICAL_INFO",
"score": 0.05,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "VIOLENCE_AND_GORE",
"score": 0.964,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "PII_SOLICITING_RECITING",
"score": 0.0009,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
}
]
}
Anwendungsfälle
Die Guardrails API kann je nach Ihren spezifischen Anforderungen und Ihrer Risikobereitschaft auf verschiedene Arten in Ihre LLM-Anwendung eingebunden werden. Hier einige Beispiele für häufige Anwendungsfälle:
Keine Guardrail-Intervention – Protokollierung
In diesem Szenario wird die Guardrails API ohne Änderungen am Verhalten der App verwendet. Potenzielle Richtlinienverstöße werden jedoch zu Überwachungs- und Prüfzwecken protokolliert. Diese Informationen können weiter verwendet werden, um potenzielle Sicherheitsrisiken von LLMs zu identifizieren.
Python
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def log_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
log_violations(user_prompt)
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
log_violations(llm_response, user_prompt)
print(llm_response)
Ok
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"},
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func logViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) error {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
slog.Warn("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policyResult.PolicyType, "Score", policyResult.Score, "Violation Result", policyResult.ViolationResult)
}
}
return nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
err := logViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
Guardrail wurde aufgrund einer Richtlinie blockiert
In diesem Beispiel werden unsichere Nutzereingaben und Modellantworten durch die Guardrails API blockiert. Dabei wird sowohl anhand vordefinierter Sicherheitsrichtlinien (z. B. Hassrede, gefährliche Inhalte) So wird verhindert, dass die KI potenziell schädliche Ausgaben generiert, und Nutzer werden vor unangemessenen Inhalten geschützt.
Python
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path, default_threshold):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
self.default_threshold = default_threshold
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
default_threshold=0.6,
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{
'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT',
'threshold': my_checks_config.default_threshold,
},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def has_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
if has_violations(user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
if has_violations(llm_response, user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
print(llm_response)
Ok
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
defaultThreshold float64
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
defaultThreshold: 0.6,
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT", Threshold: myChecksConfig.defaultThreshold},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"}, // default Checks-defined threshold is used
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func hasViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (bool, error) {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
return true, nil
}
}
return false, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
hasInputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err == nil && hasInputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
hasOutputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err == nil && hasOutputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
LLM-Ausgabe an Guardrails streamen
In den folgenden Beispielen streamen wir die Ausgabe eines LLM an die Guardrails API. So kann die von Nutzern wahrgenommene Latenz verringert werden. Bei diesem Ansatz kann es aufgrund unvollständigen Kontexts zu Falschmeldungen kommen. Daher ist es wichtig, dass die LLM-Ausgabe genügend Kontext für Guardrails enthält, damit eine genaue Bewertung erfolgen kann, bevor die API aufgerufen wird.
Synchrone Guardrails-Aufrufe
Python
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
while not my_llm_model.finished:
chunk = my_llm_model.next_chunk()
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
Ok
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
var llmResponse string
for !model.finished {
chunk := model.nextChunk()
llmResponse += chunk + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
Asynchrone Guardrails-Aufrufe
Python
async def main():
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
async for chunk in my_llm_model:
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
asyncio.run(main())
Ok
func main() {
var textChannel = make(chan string)
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
var llmResponse string
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
go model.streamToChannel(textChannel)
for text := range textChannel {
llmResponse += text + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
FAQ
Was soll ich tun, wenn ich die Kontingente für die Guardrails API erreicht habe?
Wenn Sie eine Kontingenterhöhung beantragen möchten, senden Sie eine E-Mail mit Ihrem Antrag an checks-support@google.com. Geben Sie in Ihrer E‑Mail die folgenden Informationen an:
- Ihre Google Cloud-Projektnummer: So können wir Ihr Konto schnell identifizieren.
- Details zu Ihrem Anwendungsfall: Erläutern Sie, wie Sie die Guardrails API verwenden.
- Gewünschtes Kontingent: Geben Sie an, wie viel zusätzliches Kontingent Sie benötigen.
