Page Summary
-
Media Actions feeds let you describe your media content to Google to enable users to discover and play your content on Google Search and the Google Assistant.
-
Media Actions are powered by a feed, a JSON object containing schema.org entities representing items in your media catalog.
-
To use Media Actions, you need to host your feed file for Google to access and fetch regularly.
-
Integrating your service with Media Actions involves several steps, including understanding requirements, creating and hosting a feed, submitting it to Google, and monitoring its status.
Media Actions feeds let you describe your media content to Google. This enables users to discover your content on Google Search and the Google Assistant and initiate playback of the content directly on your app or platform.
Figure 1. Media Actions on the Google Assistant.
Media Actions are powered by a feed, which contains the details of your media catalog. A feed is a JSON object that contains a collection of entities. An entity is a schema.org object that represents an item in your catalog: a TV episode, a TV series, a movie, a song, an album, and more.
For Google to obtain your feed, you need to store the feed in a file and host the file in a location where Google can access it. To ensure your content is up-to-date, Google regularly fetches the feed file from your host.
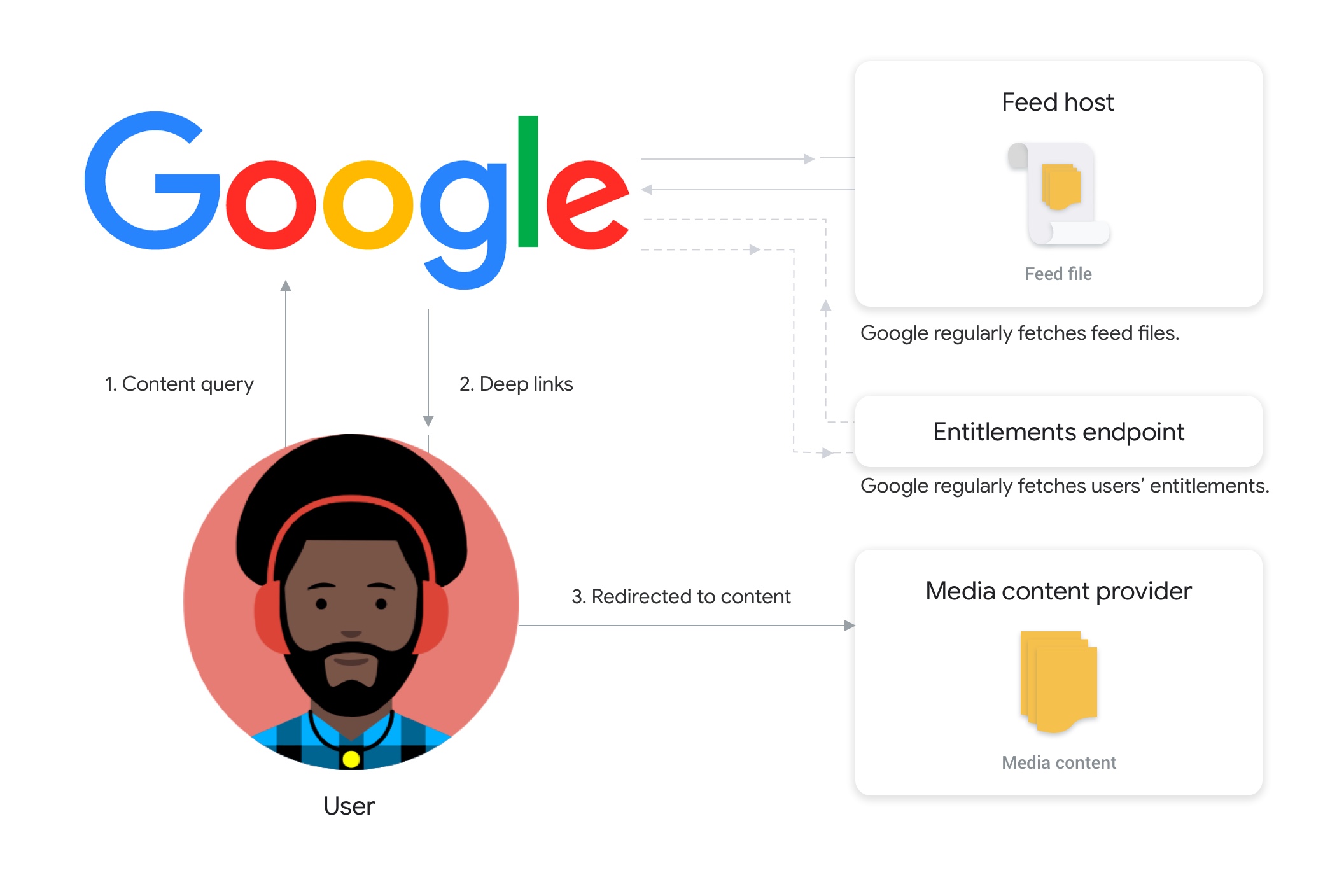
Figure 2. The flow of Media Actions.
To integrate your service with Media Actions, follow these steps:
- Understand the requirements and collect information about your media content.
- Understand the feed structure.
- Create a sample feed and populate the feed using your media catalog.
- Host the feed file using cloud storage service or a public/private hosting system.
- Complete the quality checklist and contact Google to submit your feed.
- Create an Actions on Google project to monitor the status of the feed.