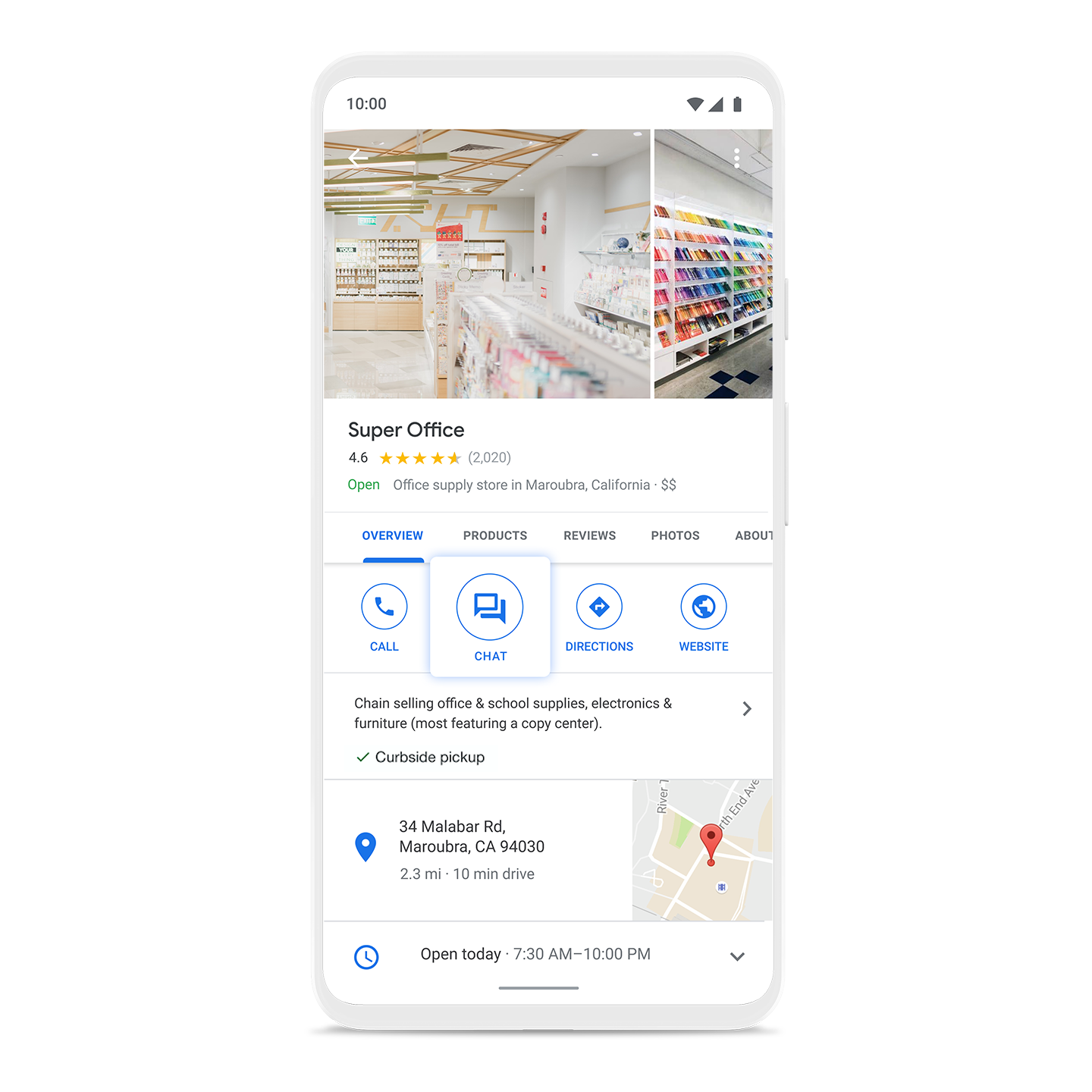
Meet customers where they are
Business Messages is a rich, asynchronous messaging service that enables users to engage with brands from a variety of entry points, including Google Search, Maps, Ads, and the brand's own channels.
Connect with customers over Business Messages
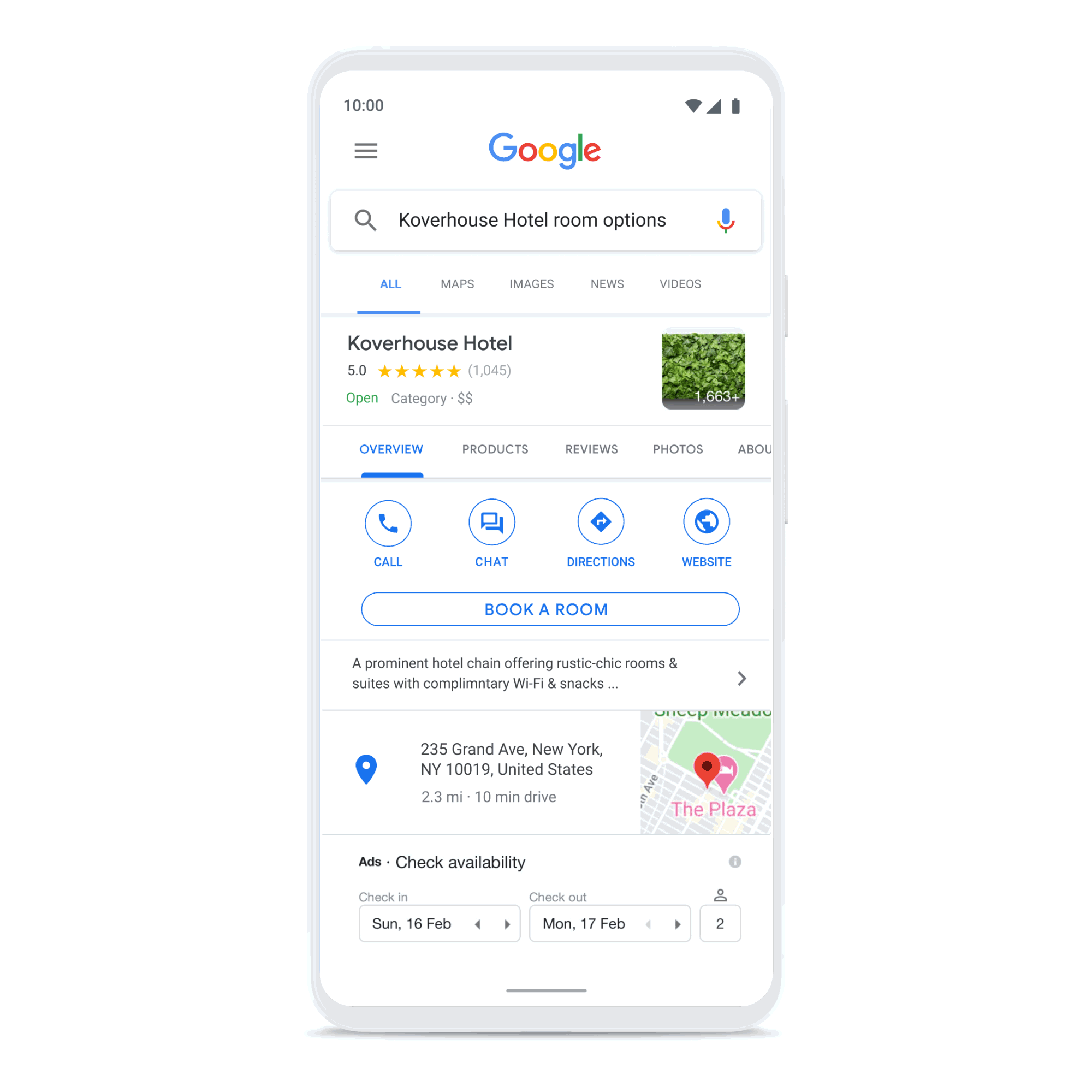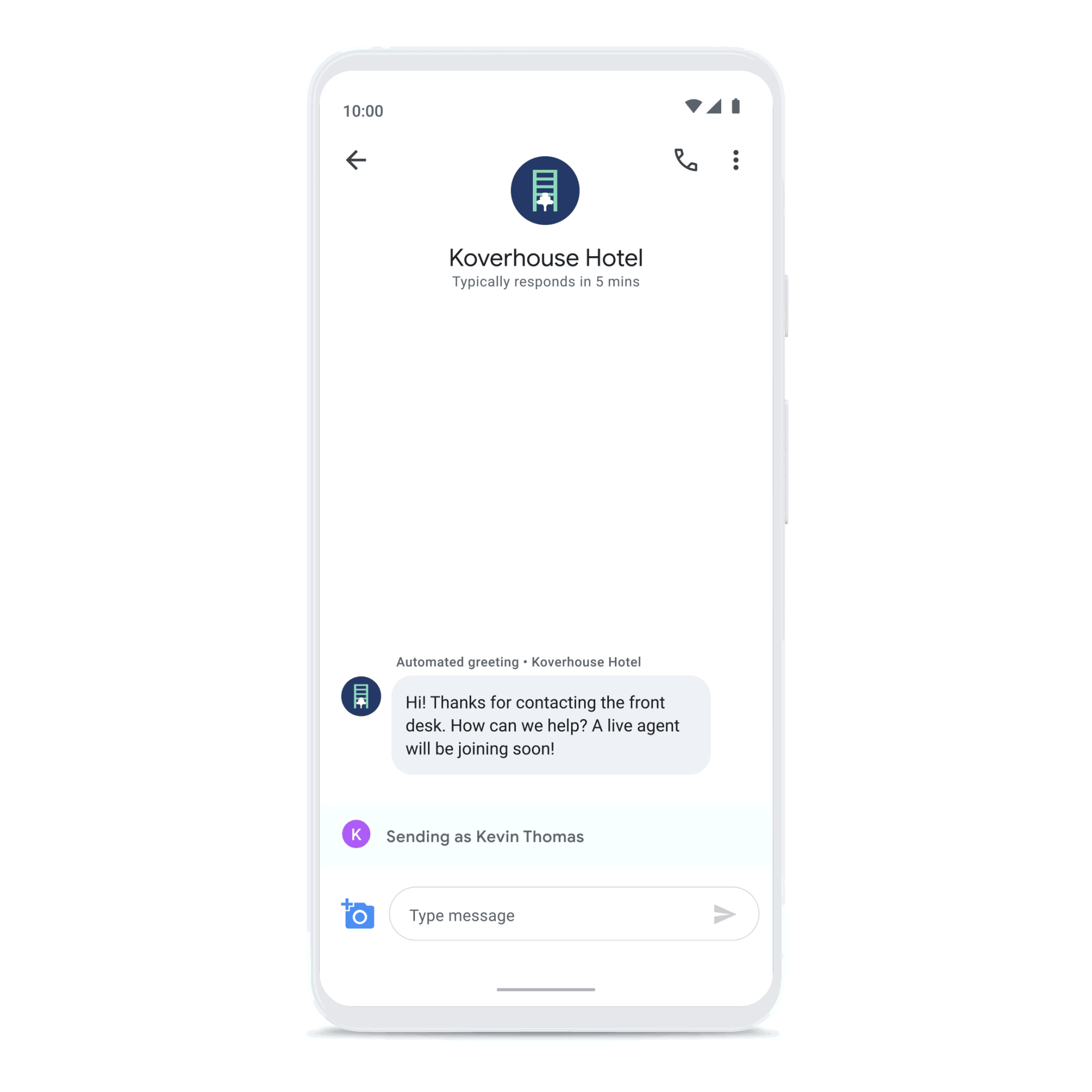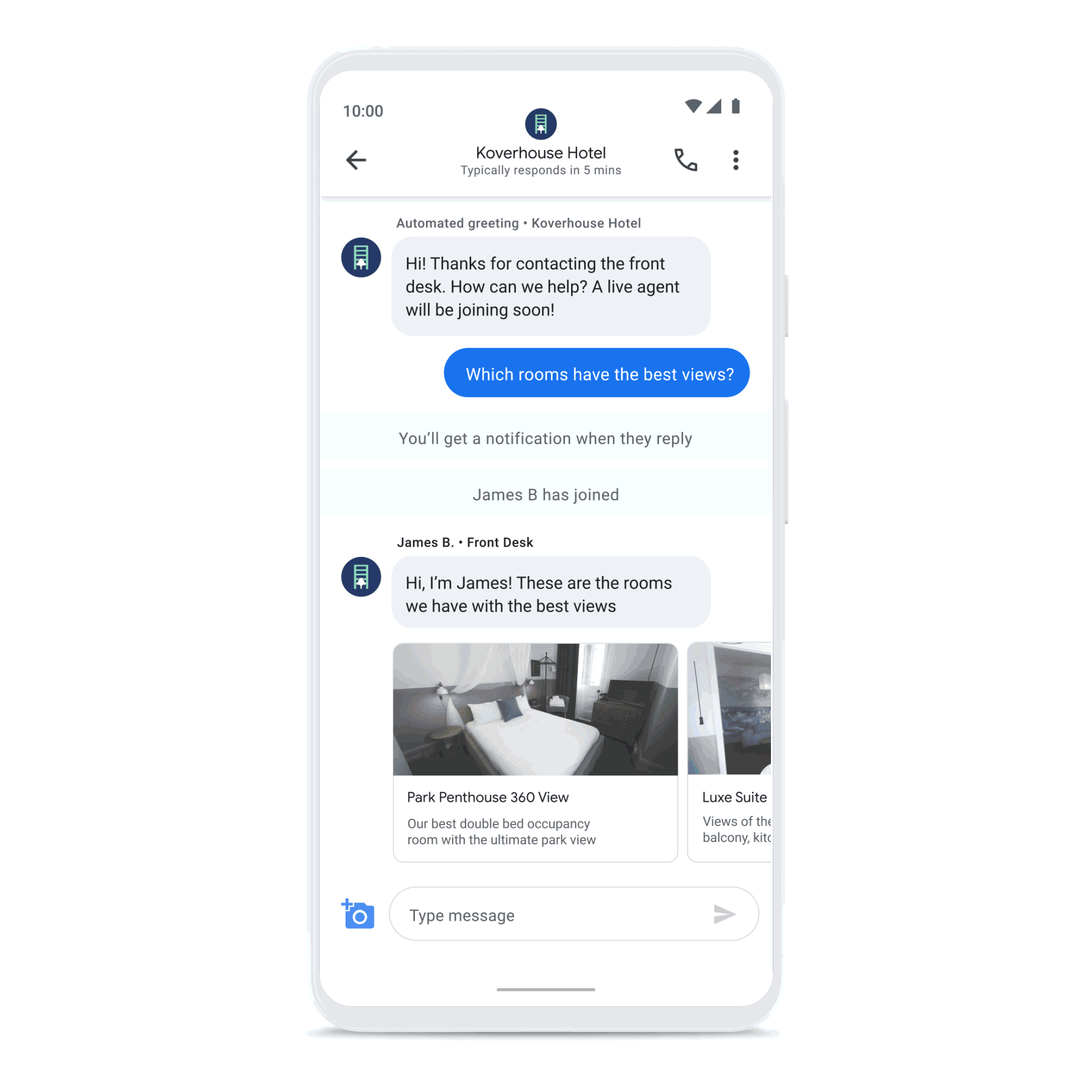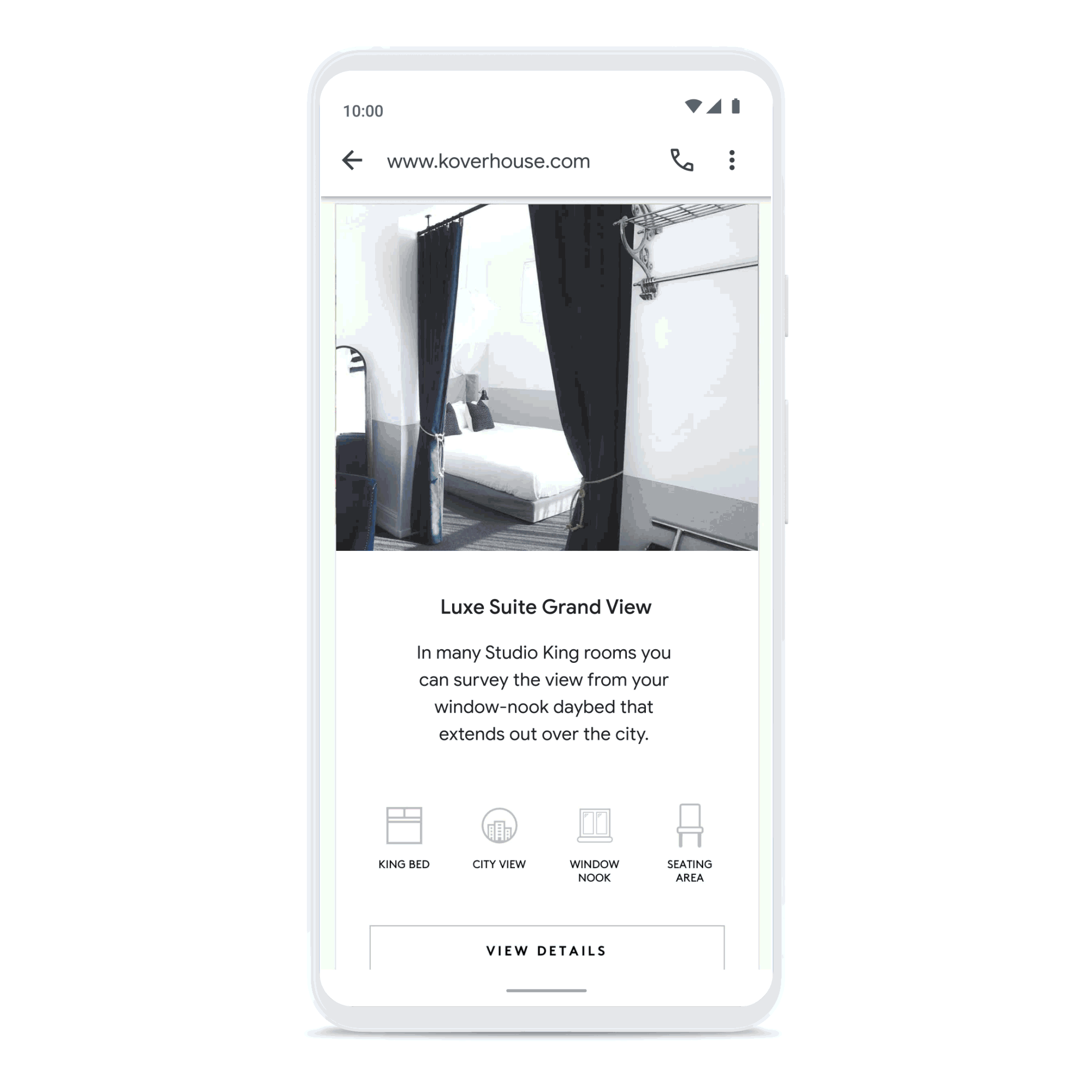
Create connections that count
Build consumer trust by showing expected wait times and answers to frequently asked questions, and enhance customer care with the ability to connect with a live agent. Drive loyalty, purchasing, scheduling, and upsell through rich features like carousels, suggested replies, and photos.
Business Messages gives brands a comprehensive business messaging solution across Android devices, and through Google Maps on iOS.
Optimize your program
The way we communicate has changed: 75% of consumers now prefer to engage with a brand over private messaging channels versus traditional channels. Business Messages can help route calls to chat, increase sales, and improve customer satisfaction with CSAT data and feedback. For more hands-on assistance, our team and partners can help brands develop a conversational marketing strategy.
