בקטע הזה מתואר ה-API של המקודד והפענוח שכלולים בספריית WebP. תיאור ה-API הזה מתייחס לגרסה 1.6.0.
כותרות וספריות
כשמתקינים את libwebp, ספרייה בשם webp/
תותקן במיקום הרגיל של הפלטפורמה. לדוגמה, בפלטפורמות Unix, קובצי הכותרת הבאים יועתקו אל /usr/local/include/webp/.
decode.h
encode.h
types.h
הספריות ממוקמות בספריות הרגילות. הספריות הסטטיות והדינמיות נמצאות ב-/usr/local/lib/ בפלטפורמות Unix.
Simple Decoding API
כדי להתחיל להשתמש ב-Decoding API, צריך לוודא שהספרייה וקבצי הכותרת מותקנים כמו שמתואר למעלה.
צריך לכלול את כותרת ה-API של הפענוח בקוד C/C++ באופן הבא:
#include "webp/decode.h"
int WebPGetInfo(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
הפונקציה הזו תאמת את הכותרת של תמונת WebP ותאחזר את הרוחב והגובה של התמונה. אפשר להעביר את הערך NULL למצביעים *width ו-*height אם הם לא רלוונטיים.
מאפייני הקלט
- נתונים
- מצביע לנתוני תמונה בפורמט WebP
- data_size
- זה הגודל של בלוק הזיכרון שאליו מצביע
dataשמכיל את נתוני התמונה.
החזרות
- false
- קוד השגיאה שמוחזר במקרה של שגיאות עיצוב.
- true
- במקרה של הצלחה.
*widthו-*heightתקפים רק אם ההחזרה מתבצעת בהצלחה. - רוחב ערך של מספר שלם
- . הטווח מוגבל ל-1 עד 16383.
- גובה ערך של מספר שלם
- . הטווח מוגבל לערכים מ-1 עד 16383.
struct WebPBitstreamFeatures {
int width; // Width in pixels.
int height; // Height in pixels.
int has_alpha; // True if the bitstream contains an alpha channel.
int has_animation; // True if the bitstream is an animation.
int format; // 0 = undefined (/mixed), 1 = lossy, 2 = lossless
}
VP8StatusCode WebPGetFeatures(const uint8_t* data,
size_t data_size,
WebPBitstreamFeatures* features);
הפונקציה הזו מאחזרת תכונות מזרם הסיביות. המבנה *features
מלא במידע שנאסף מזרם הביטים:
מאפייני הקלט
- נתונים
- מצביע לנתוני תמונה בפורמט WebP
- data_size
- זה הגודל של בלוק הזיכרון שאליו מצביע
dataשמכיל את נתוני התמונה.
החזרות
VP8_STATUS_OK- כשהתכונות מאוחזרות בהצלחה.
VP8_STATUS_NOT_ENOUGH_DATA- כשצריך עוד נתונים כדי לאחזר את התכונות מהכותרות.
במקרים אחרים, ערכי שגיאה נוספים VP8StatusCode.
- תכונות
- מצביע למבנה WebPBitstreamFeatures.
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGR(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
הפונקציות האלה מפענחות תמונת WebP שאליה מפנה data.
- הפונקציה
WebPDecodeRGBAמחזירה דוגמאות של תמונות בפורמט RGBA לפי הסדר[r0, g0, b0, a0, r1, g1, b1, a1, ...]. -
WebPDecodeARGBמחזירה דוגמאות של תמונות בפורמט ARGB בסדר[a0, r0, g0, b0, a1, r1, g1, b1, ...]. -
WebPDecodeBGRAמחזירה דוגמאות של תמונות בפורמט BGRA לפי הסדר[b0, g0, r0, a0, b1, g1, r1, a1, ...]. - הפונקציה
WebPDecodeRGBמחזירה דוגמיות של תמונות RGB בסדר[r0, g0, b0, r1, g1, b1, ...]. -
WebPDecodeBGRמחזירה דוגמאות של תמונות BGR בסדרWebPDecodeBGR.[b0, g0, r0, b1, g1, r1, ...]
הקוד שקורא לאחת מהפונקציות האלה חייב למחוק את מאגר הנתונים (uint8_t*) שמוחזר על ידי הפונקציות האלה באמצעות WebPFree().
מאפייני הקלט
- נתונים
- מצביע לנתוני תמונה בפורמט WebP
- data_size
- זהו הגודל של בלוק הזיכרון שאליו מצביע
dataשמכיל את נתוני התמונה - רוחב ערך של מספר שלם
- . הטווח מוגבל כרגע ל-1 עד 16,383.
- גובה ערך של מספר שלם
- . הטווח מוגבל כרגע ל-1 עד 16383.
החזרות
- uint8_t*
- מצביע לדוגמאות של תמונות WebP מפוענחות בסדר לינארי של RGBA/ARGB/BGRA/RGB/BGR בהתאמה.
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
הפונקציות האלה הן וריאציות של הפונקציות שלמעלה, והן מפענחות את התמונה ישירות לתוך מאגר output_buffer שהוקצה מראש. נפח האחסון המקסימלי שזמין במאגר הזה מצוין על ידי output_buffer_size. אם נפח האחסון הזה לא מספיק (או אם אירעה שגיאה), הפונקציה NULL מוחזרת. אחרת, מוחזר הערך output_buffer.
הפרמטר output_stride מציין את המרחק (בבייט) בין שורות הסריקה. לכן, הערך של output_buffer_size צפוי להיות לפחות output_stride * picture - height.
מאפייני הקלט
- נתונים
- מצביע לנתוני תמונה בפורמט WebP
- data_size
- זהו הגודל של בלוק הזיכרון שאליו מצביע
dataשמכיל את נתוני התמונה - output_buffer_size ערך של מספר שלם
- . גודל המאגר שהוקצה
- output_stride ערך של מספר שלם
- . מציין את המרחק בין שורות הסריקה.
החזרות
- output_buffer
- מצביע לתמונת WebP מפוענחת.
- uint8_t*
output_bufferאם הפונקציה מצליחה, אחרתNULL.
Advanced Decoding API
פענוח WebP תומך ב-API מתקדם כדי לספק אפשרות לחיתוך ולשינוי גודל בזמן אמת, דבר שימושי מאוד בסביבות עם מגבלות זיכרון כמו טלפונים ניידים. בעצם, השימוש בזיכרון יגדל בהתאם לגודל הפלט, ולא בהתאם לגודל הקלט, כשצריך רק תצוגה מקדימה מהירה או חלק מוגדל של תמונה גדולה מדי. אפשר גם לחסוך חלק מה-CPU.
יש שני סוגים של פענוח WebP: פענוח מלא של תמונה ופענוח מצטבר של מאגרי קלט קטנים. המשתמשים יכולים לספק מאגר זיכרון חיצוני לאחסון זמני של נתונים לצורך פענוח התמונה. בדוגמת הקוד הבאה מפורטים השלבים לשימוש ב-API המתקדם לפענוח.
קודם צריך לאתחל אובייקט הגדרה:
#include "webp/decode.h"
WebPDecoderConfig config;
CHECK(WebPInitDecoderConfig(&config));
// One can adjust some additional decoding options:
config.options.no_fancy_upsampling = 1;
config.options.use_scaling = 1;
config.options.scaled_width = scaledWidth();
config.options.scaled_height = scaledHeight();
// etc.
אפשרויות הפענוח מרוכזות במבנה WebPDecoderConfig:
struct WebPDecoderOptions {
int bypass_filtering; // if true, skip the in-loop filtering
int no_fancy_upsampling; // if true, use faster pointwise upsampler
int use_cropping; // if true, cropping is applied first
int crop_left, crop_top; // top-left position for cropping.
// Will be snapped to even values.
int crop_width, crop_height; // dimension of the cropping area
int use_scaling; // if true, scaling is applied afterward
int scaled_width, scaled_height; // final resolution
int use_threads; // if true, use multi-threaded decoding
int dithering_strength; // dithering strength (0=Off, 100=full)
int flip; // if true, flip output vertically
int alpha_dithering_strength; // alpha dithering strength in [0..100]
};
אופציונלית, אפשר לקרוא את התכונות של זרם הביטים לתוך config.input, אם צריך לדעת אותן מראש. לדוגמה, יכול להיות שימושי לדעת אם יש שקיפות בתמונה. שימו לב: הפקודה הזו תנתח גם את הכותרת של זרם הביטים, ולכן היא דרך טובה לדעת אם זרם הביטים נראה כמו WebP תקין.
CHECK(WebPGetFeatures(data, data_size, &config.input) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
לאחר מכן, צריך להגדיר את מאגר הזיכרון של הפענוח למקרה שנרצה לספק אותו ישירות במקום להסתמך על המפענח להקצאה שלו. צריך רק לספק את המצביע לזיכרון, את הגודל הכולל של המאגר ואת הצעד של השורה (המרחק בבייטים בין קווי הסריקה).
// Specify the desired output colorspace:
config.output.colorspace = MODE_BGRA;
// Have config.output point to an external buffer:
config.output.u.RGBA.rgba = (uint8_t*)memory_buffer;
config.output.u.RGBA.stride = scanline_stride;
config.output.u.RGBA.size = total_size_of_the_memory_buffer;
config.output.is_external_memory = 1;
התמונה מוכנה לפענוח. יש שתי גרסאות אפשריות לפענוח התמונה. אפשר לפענח את התמונה בבת אחת באמצעות:
CHECK(WebPDecode(data, data_size, &config) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
לחלופין, אפשר להשתמש בשיטה מצטברת כדי לפענח את התמונה באופן הדרגתי ככל שזמינים בייטים חדשים:
WebPIDecoder* idec = WebPINewDecoder(&config.output);
CHECK(idec != NULL);
while (additional_data_is_available) {
// ... (get additional data in some new_data[] buffer)
VP8StatusCode status = WebPIAppend(idec, new_data, new_data_size);
if (status != VP8_STATUS_OK && status != VP8_STATUS_SUSPENDED) {
break;
}
// The above call decodes the current available buffer.
// Part of the image can now be refreshed by calling
// WebPIDecGetRGB()/WebPIDecGetYUVA() etc.
}
WebPIDelete(idec); // the object doesn't own the image memory, so it can
// now be deleted. config.output memory is preserved.
התמונה המפוענחת נמצאת עכשיו ב-config.output (או ליתר דיוק ב-config.output.u.RGBA במקרה הזה, כי מרחב הצבעים של הפלט שנדרש היה MODE_BGRA). אפשר לשמור את התמונה, להציג אותה או לעבד אותה בדרכים אחרות. לאחר מכן, צריך רק לשחרר את הזיכרון שהוקצה לאובייקט של ההגדרה. אפשר להפעיל את הפונקציה הזו גם אם הזיכרון חיצוני ולא הוקצה על ידי WebPDecode():
WebPFreeDecBuffer(&config.output);
באמצעות ה-API הזה, אפשר גם לפענח את התמונה לפורמטים YUV ו-YUVA באמצעות MODE_YUV ו-MODE_YUVA בהתאמה. הפורמט הזה נקרא גם Y'CbCr.
Simple Encoding API
מסופקות כמה פונקציות פשוטות מאוד לקידוד מערכים של דגימות RGBA
ברוב הפריסות הנפוצות. הן מוצהרות בכותרת webp/encode.h באופן הבא:
size_t WebPEncodeRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
גורם האיכות quality_factor נע בין 0 ל-100 וקובע את האובדן והאיכות במהלך הדחיסה. הערך 0 מתאים לאיכות נמוכה ולגודל פלט קטן, ואילו הערך 100 מתאים לאיכות הכי גבוהה ולגודל פלט הכי גדול.
אם הפעולה תצליח, הבייטים הדחוסים ימוקמו במצביע *output, והגודל בבייטים יוחזר (אחרת יוחזר 0, במקרה של כשל). המתקשר צריך להפעיל את WebPFree() על מצביע *output כדי לפנות זיכרון.
מערך הקלט צריך להיות מערך ארוז של בייטים (אחד לכל ערוץ, כמו שניתן להסיק משם הפונקציה). stride מייצג את מספר הבייטים שצריך כדי לעבור משורה אחת לשורה הבאה. לדוגמה, הפריסה של BGRA היא:
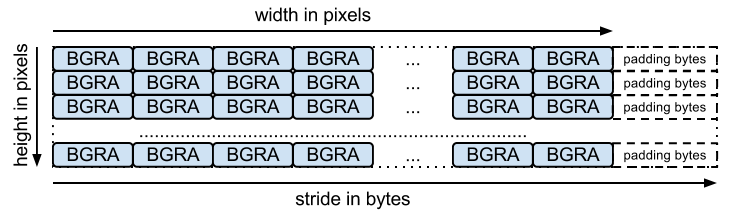
יש פונקציות מקבילות לקידוד ללא אובדן נתונים, עם החתימות הבאות:
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
שימו לב שהפונקציות האלה, כמו הגרסאות עם אובדן נתונים, משתמשות בהגדרות ברירת המחדל של הספרייה. במקרה של המרה ללא אובדן נתונים, האפשרות 'מדויק' מושבתת. ערכי RGB באזורים שקופים לחלוטין (כלומר, אזורים עם ערכי אלפא ששווים ל-0) ישונו כדי לשפר את הדחיסה. כדי למנוע את הבעיה הזו, צריך להשתמש ב-WebPEncode() ולהגדיר את WebPConfig::exact ל-1.
Advanced Encoding API
מתחת לפני השטח, המקודד מגיע עם פרמטרים רבים של קידוד מתקדם.
הם יכולים לעזור לכם למצוא את האיזון הנכון בין יעילות הדחיסה לבין זמן העיבוד.
הפרמטרים האלה נאספים במסגרת המבנה של WebPConfig.
השדות הכי שימושיים במבנה הזה הם:
struct WebPConfig {
int lossless; // Lossless encoding (0=lossy(default), 1=lossless).
float quality; // between 0 and 100. For lossy, 0 gives the smallest
// size and 100 the largest. For lossless, this
// parameter is the amount of effort put into the
// compression: 0 is the fastest but gives larger
// files compared to the slowest, but best, 100.
int method; // quality/speed trade-off (0=fast, 6=slower-better)
WebPImageHint image_hint; // Hint for image type (lossless only for now).
// Parameters related to lossy compression only:
int target_size; // if non-zero, set the desired target size in bytes.
// Takes precedence over the 'compression' parameter.
float target_PSNR; // if non-zero, specifies the minimal distortion to
// try to achieve. Takes precedence over target_size.
int segments; // maximum number of segments to use, in [1..4]
int sns_strength; // Spatial Noise Shaping. 0=off, 100=maximum.
int filter_strength; // range: [0 = off .. 100 = strongest]
int filter_sharpness; // range: [0 = off .. 7 = least sharp]
int filter_type; // filtering type: 0 = simple, 1 = strong (only used
// if filter_strength > 0 or autofilter > 0)
int autofilter; // Auto adjust filter's strength [0 = off, 1 = on]
int alpha_compression; // Algorithm for encoding the alpha plane (0 = none,
// 1 = compressed with WebP lossless). Default is 1.
int alpha_filtering; // Predictive filtering method for alpha plane.
// 0: none, 1: fast, 2: best. Default if 1.
int alpha_quality; // Between 0 (smallest size) and 100 (lossless).
// Default is 100.
int pass; // number of entropy-analysis passes (in [1..10]).
int show_compressed; // if true, export the compressed picture back.
// In-loop filtering is not applied.
int preprocessing; // preprocessing filter (0=none, 1=segment-smooth)
int partitions; // log2(number of token partitions) in [0..3]
// Default is set to 0 for easier progressive decoding.
int partition_limit; // quality degradation allowed to fit the 512k limit on
// prediction modes coding (0: no degradation,
// 100: maximum possible degradation).
int use_sharp_yuv; // if needed, use sharp (and slow) RGB->YUV conversion
};
שימו לב: לרוב הפרמטרים האלה יש גישה לניסויים באמצעות כלי שורת הפקודה cwebp.
דוגמאות הקלט צריכות להיות עטופות במבנה WebPPicture.
המבנה הזה יכול לאחסן דוגמאות קלט בפורמט RGBA או YUVA, בהתאם לערך של הדגל use_argb.
המבנה הוא כזה:
struct WebPPicture {
int use_argb; // To select between ARGB and YUVA input.
// YUV input, recommended for lossy compression.
// Used if use_argb = 0.
WebPEncCSP colorspace; // colorspace: should be YUVA420 or YUV420 for now (=Y'CbCr).
int width, height; // dimensions (less or equal to WEBP_MAX_DIMENSION)
uint8_t *y, *u, *v; // pointers to luma/chroma planes.
int y_stride, uv_stride; // luma/chroma strides.
uint8_t* a; // pointer to the alpha plane
int a_stride; // stride of the alpha plane
// Alternate ARGB input, recommended for lossless compression.
// Used if use_argb = 1.
uint32_t* argb; // Pointer to argb (32 bit) plane.
int argb_stride; // This is stride in pixels units, not bytes.
// Byte-emission hook, to store compressed bytes as they are ready.
WebPWriterFunction writer; // can be NULL
void* custom_ptr; // can be used by the writer.
// Error code for the latest error encountered during encoding
WebPEncodingError error_code;
};
למבנה הזה יש גם פונקציה להפקת הבייטים הדחוסים כשהם זמינים. למטה מופיעה דוגמה עם כלי כתיבה בזיכרון.
כותבים אחרים יכולים לאחסן נתונים ישירות בקובץ (דוגמה לכך מופיעה ב-examples/cwebp.c).
התהליך הכללי לקידוד באמצעות API מתקדם נראה כך:
קודם כול, צריך להגדיר הגדרות קידוד שמכילות את פרמטרי הדחיסה. שימו לב שאפשר להשתמש באותה הגדרה כדי לדחוס כמה תמונות שונות בהמשך.
#include "webp/encode.h"
WebPConfig config;
if (!WebPConfigPreset(&config, WEBP_PRESET_PHOTO, quality_factor)) return 0; // version error
// Add additional tuning:
config.sns_strength = 90;
config.filter_sharpness = 6;
config.alpha_quality = 90;
config_error = WebPValidateConfig(&config); // will verify parameter ranges (always a good habit)
לאחר מכן, צריך להפנות את דוגמאות הקלט אל WebPPicture באמצעות הפניה או העתקה. לדוגמה, כך מקצים את המאגר להחזקת הדגימות. אבל אפשר להגדיר בקלות 'תצוגה' למערך דגימות שכבר הוקצה. מידע נוסף מפורט בפונקציה WebPPictureView().
// Setup the input data, allocating a picture of width x height dimension
WebPPicture pic;
if (!WebPPictureInit(&pic)) return 0; // version error
pic.width = width;
pic.height = height;
if (!WebPPictureAlloc(&pic)) return 0; // memory error
// At this point, 'pic' has been initialized as a container, and can receive the YUVA or RGBA samples.
// Alternatively, one could use ready-made import functions like WebPPictureImportRGBA(), which will take
// care of memory allocation. In any case, past this point, one will have to call WebPPictureFree(&pic)
// to reclaim allocated memory.
כדי להפיק את הבייטים הדחוסים, מתבצעת קריאה ל-hook בכל פעם שיש בייטים חדשים. הנה דוגמה פשוטה עם memory-writer שהוגדר ב-webp/encode.h. סביר להניח שצריך לבצע את האתחול הזה לכל תמונה כדי לדחוס אותה:
// Set up a byte-writing method (write-to-memory, in this case):
WebPMemoryWriter writer;
WebPMemoryWriterInit(&writer);
pic.writer = WebPMemoryWrite;
pic.custom_ptr = &writer;
עכשיו אפשר לדחוס את דגימות הקלט (ולפנות את הזיכרון שלהן לאחר מכן):
int ok = WebPEncode(&config, &pic);
WebPPictureFree(&pic); // Always free the memory associated with the input.
if (!ok) {
printf("Encoding error: %d\n", pic.error_code);
} else {
printf("Output size: %d\n", writer.size);
}
לשימוש מתקדם יותר ב-API ובמבנה שלו, מומלץ לעיין במסמכי התיעוד שזמינים בכותרת webp/encode.h.
עיון בקוד לדוגמה examples/cwebp.c יכול לעזור לכם לגלות פרמטרים שפחות נמצאים בשימוש.
