החשבונות מקושרים באמצעות תהליכים מרומזים וקודי הרשאה של OAuth 2.0, בהתאם לתקנים המקובלים בתחום. השירות צריך לתמוך בנקודות קצה של הרשאה והחלפת אסימונים שתואמות ל-OAuth 2.0.
בתהליך העקיף, Google פותחת את נקודת הקצה (endpoint) של ההרשאה בדפדפן של המשתמש. אחרי הכניסה, מחזירים ל-Google אסימון גישה לטווח ארוך. טוקן הגישה הזה נכלל עכשיו בכל בקשה שנשלחת מ-Google.
בתהליך הרשאה באמצעות קוד, נדרשים שני נקודות קצה:
נקודת הקצה של ההרשאה, שבה מוצג ממשק המשתמש של הכניסה למשתמשים שעדיין לא מחוברים. נקודת הקצה להרשאה יוצרת גם קוד הרשאה לטווח קצר כדי לתעד את הסכמת המשתמשים לגישה המבוקשת.
נקודת הקצה החלפת אסימונים, שאחראית לשני סוגים של החלפות:
- מחליפה קוד הרשאה באסימון רענון לטווח ארוך ובאסימון גישה לטווח קצר. המרות כאלה מתרחשות כשהמשתמש עובר את תהליך קישור החשבון.
- המרת אסימון רענון לטווח ארוך באסימון גישה לטווח קצר. ההחלפה הזו מתרחשת כש-Google זקוקה לאסימון גישה חדש כי התוקף של האסימון הקודם פג.
בחירת תהליך OAuth 2.0
אמנם קל יותר להטמיע את התהליך המשתמע, אבל Google ממליצה שלא יהיה תאריך תפוגה לטוקני הגישה שהונפקו בתהליך המשתמע. הסיבה לכך היא שהמשתמש נדרש לקשר מחדש את החשבון שלו אחרי שתוקף האסימון פג בתהליך המשתמעות. אם אתם צריכים שתוקף האסימון יפוג, מומלץ מאוד להשתמש במקום זאת בתהליך של הרשאה לקוד.
הנחיות עיצוב
בקטע הזה מתוארות הדרישות וההמלצות לגבי העיצוב של מסך המשתמש שאתם מארחים בתהליכי הקישור של OAuth. אחרי שהאפליקציה של Google קוראת לאפליקציה, הפלטפורמה מציגה למשתמש מסך הסכמה לכניסה לדף של Google ולקישור חשבונות. המשתמש מופנה חזרה לאפליקציה של Google אחרי שהסכים לקישור החשבונות.
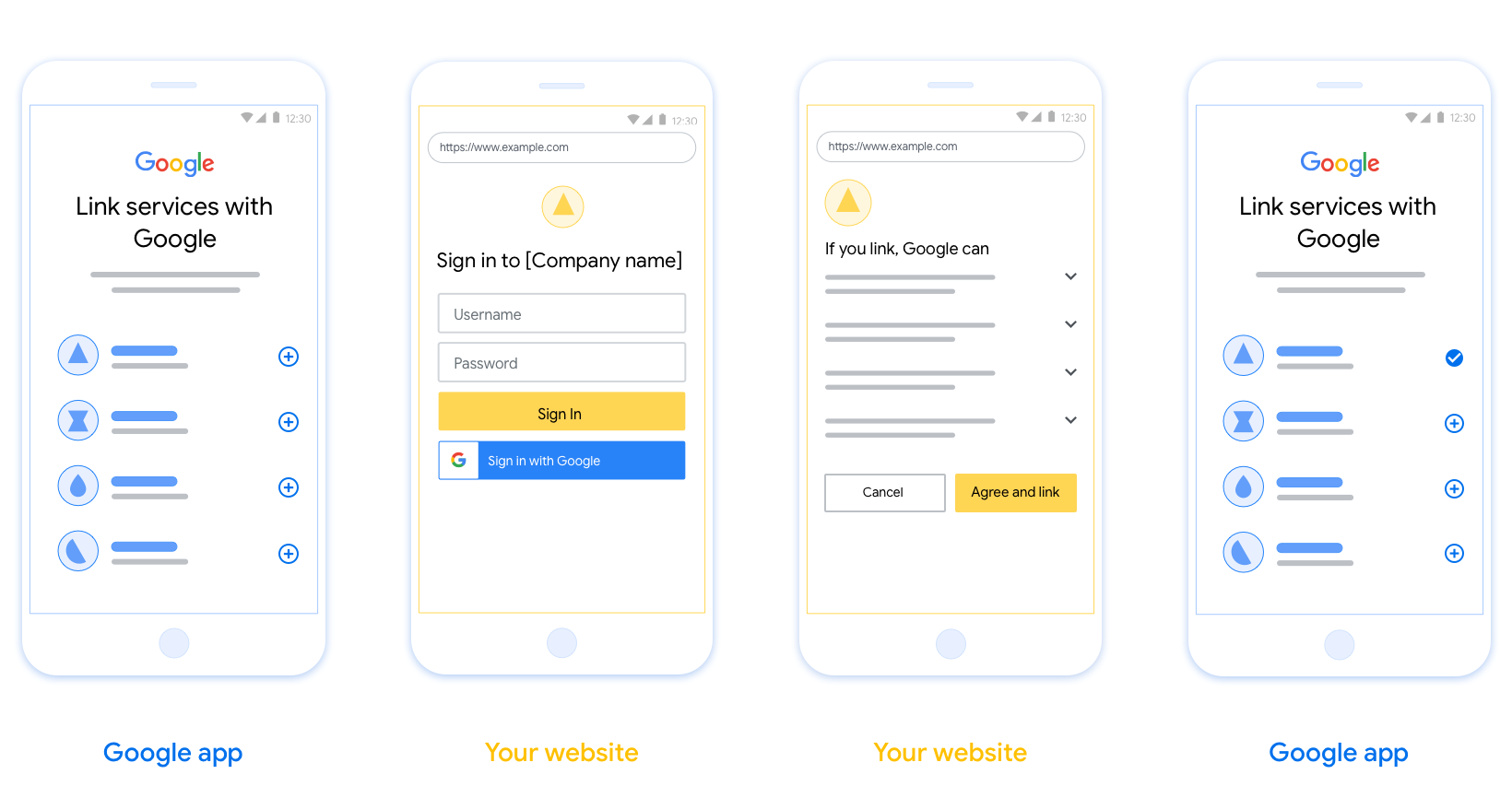
דרישות
- עליך לציין שחשבון המשתמש יקושר ל-Google, לא למוצר ספציפי של Google, כמו Google Home או Google Assistant.
המלצות
מומלץ לבצע את הפעולות הבאות:
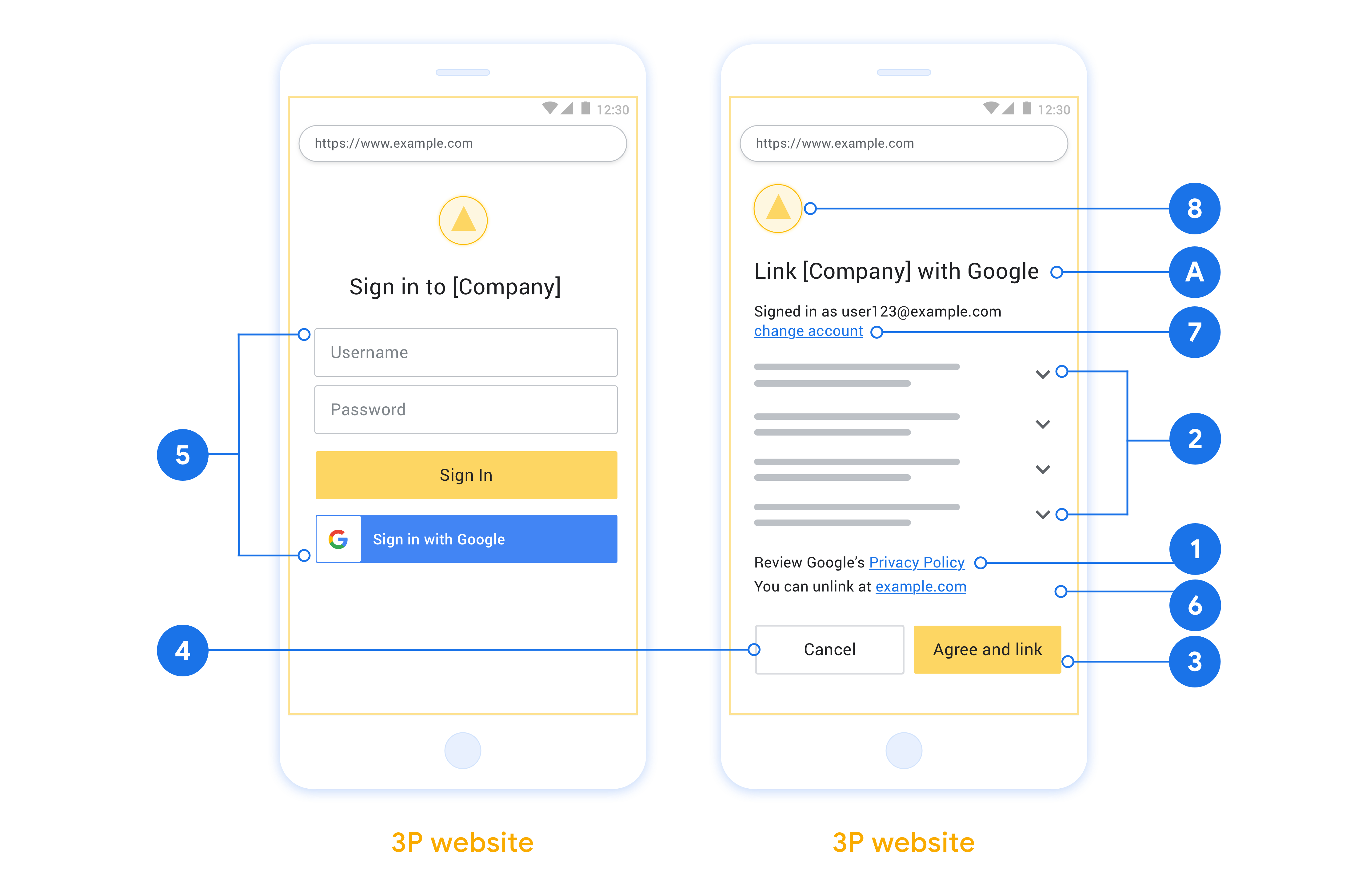
הצגת מדיניות הפרטיות של Google צריך לכלול קישור למדיניות הפרטיות של Google במסך ההסכמה.
נתונים לשיתוף. חשוב להשתמש בשפה ברורה ותמציתית כדי להסביר למשתמשים אילו נתונים Google צריכה מהם ולמה.
קריאה ברורה לפעולה עליכם לציין במסך ההסכמה קריאה ברורה לפעולה, למשל 'מסכים/ה וקישור'. הסיבה לכך היא שהמשתמשים צריכים להבין אילו נתונים הם נדרשים לשתף עם Google כדי לקשר את החשבונות שלהם.
אפשרות לבטל צריך לספק למשתמשים אפשרות לחזור אחורה או לבטל, אם הם בוחרים לא לקשר.
תהליך כניסה נקי. חשוב לוודא שלמשתמשים יש שיטה ברורה לכניסה לחשבון Google, כמו שדות של שם המשתמש והסיסמה או כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google.
היכולת לבטל את הקישור. להציע למשתמשים מנגנון לביטול הקישור, כמו כתובת URL להגדרות החשבון שלהם בפלטפורמה שלכם. לחלופין, אפשר לכלול קישור לחשבון Google שבו המשתמשים יכולים לנהל את החשבון המקושר.
יכולת לשנות את חשבון המשתמש כדאי להציע למשתמשים שיטה להחלפת החשבונות. האפשרות הזו שימושית במיוחד אם למשתמשים יש כמה חשבונות.
- אם משתמש צריך לסגור את מסך ההסכמה כדי לעבור לחשבון אחר, צריך לשלוח ל-Google הודעת שגיאה שניתן לשחזור כדי שהמשתמש יוכל להיכנס לחשבון הרצוי באמצעות קישור OAuth והתהליך המשתמע.
מוסיפים את הלוגו שלכם. להציג את הלוגו של החברה במסך ההסכמה. השתמשו בהנחיות הסגנון שלכם כדי למקם את הלוגו. אם רוצים להציג גם את הלוגו של Google, אפשר לעיין במאמר סמלי לוגו וסימנים מסחריים.
יצירת הפרויקט
כדי ליצור את הפרויקט לשימוש בקישור לחשבון:
- לוחצים על יצירת פרויקט.
- מזינים שם או מאשרים את ההצעה שנוצרה.
- מאשרים או עורכים את השדות שנותרו.
- לוחצים על יצירה.
כדי לראות את מזהה הפרויקט:
- מחפשים את הפרויקט בטבלה בדף הנחיתה. מזהה הפרויקט מופיע בעמודה ID.
הגדרת מסך ההסכמה של OAuth
תהליך קישור חשבון Google כולל מסך הסכמה שבו מוצגת למשתמש האפליקציה שמבקשת גישה לנתונים שלו, סוג הנתונים שהיא מבקשת והתנאים הרלוונטיים. תצטרכו להגדיר את מסך ההסכמה ל-OAuth לפני שתפיקו מזהה לקוח של Google API.
- פותחים את הדף מסך ההסכמה ל-OAuth ב-Google APIs Console.
- אם מתבקשים, בוחרים את הפרויקט שיצרתם.
בדף 'מסך הסכמה ל-OAuth', ממלאים את הטופס ולוחצים על הלחצן 'שמירה'.
שם האפליקציה: שם האפליקציה שמבקשת הסכמה. השם צריך לשקף במדויק את האפליקציה שלכם ולהיות זהה לשם האפליקציה שמוצג למשתמשים במקומות אחרים. שם האפליקציה יוצג במסך ההסכמה לקישור החשבון.
הלוגו של האפליקציה: תמונה במסך ההסכמה שתעזור למשתמשים לזהות את האפליקציה שלכם. הלוגו מוצג במסך ההסכמה לקישור החשבון ובהגדרות החשבון
כתובת אימייל לתמיכה: כדי שהמשתמשים יוכלו ליצור איתכם קשר עם שאלות לגבי הסכמתם.
היקפים של ממשקי Google API: היקפים מאפשרים לאפליקציה שלכם לגשת לנתונים פרטיים של המשתמשים ב-Google. במקרה השימוש של קישור חשבון Google, היקף ברירת המחדל (אימייל, פרופיל, openid) מספיק, ואין צורך להוסיף היקפים רגישים. בדרך כלל מומלץ לבקש היקפי הרשאה באופן מצטבר, בזמן שנדרשת גישה, ולא מראש. מידע נוסף
דומיינים מורשים: כדי להגן עליכם ועל המשתמשים שלכם, Google מאפשרת רק לאפליקציות שעוברות אימות באמצעות OAuth להשתמש בדומיינים מורשים. הקישורים לאפליקציות שלכם צריכים להתארח בדומיינים מורשים. מידע נוסף
קישור לדף הבית של האפליקציה: דף הבית של האפליקציה. הן חייבות להתארח בדומיין מורשה.
קישור למדיניות הפרטיות של האפליקציה: מוצג במסך ההסכמה לקישור חשבון Google. הן חייבות להתארח בדומיין מורשה.
קישור לתנאים ולהגבלות של האפליקציה (אופציונלי): הקישור חייב להיות מאוחסן בדומיין מורשה.

איור 1. מסך הסכמה לקישור חשבון Google לאפליקציה פיקטיבית, Tunery
בודקים את 'סטטוס האימות'. אם האפליקציה שלכם צריכה אימות, לוחצים על הלחצן 'שליחה לאימות' כדי לשלוח את האפליקציה לאימות. פרטים נוספים זמינים במאמר בנושא דרישות האימות של OAuth.
הטמעת שרת OAuth
יישום של שרת OAuth 2.0 של תהליך קוד ההרשאה כולל שתי נקודות קצה, שהשירות שלך מספק באמצעות HTTPS. נקודת הקצה הראשונה היא נקודת הקצה של ההרשאה, שאחראית למצוא או להשיג הסכמה של משתמשים לקבלת גישה לנתונים. נקודת הקצה של ההרשאה מציגה לכניסה למשתמשים שעדיין לא נכנסו לחשבון ומתעדים הסכמה ל: את הרשאת הגישה המבוקשת. נקודת הקצה השנייה היא נקודת הקצה של המרת אסימונים, משמשות לקבלת מחרוזות מוצפנות, שנקראות אסימונים, שמאשרות למשתמש ניגשים לשירות.
כשאפליקציה של Google צריכה לשלוח קריאה לאחד מממשקי ה-API של השירות שלכם, Google משתמשת את נקודות הקצה האלה יחד כדי לקבל מהמשתמשים הרשאה לקרוא לממשקי ה-API בשמם.
בסשן של זרימת קוד הרשאה OAuth 2.0 ש-Google יזמה התהליך הבא:
- Google פותחת את נקודת הקצה להרשאה בדפדפן של המשתמש. אם התהליך שמופעל במכשיר עם קול בלבד עבור פעולה, Google מעבירה את בטלפון.
- המשתמש נכנס לחשבון, אם הוא עדיין לא מחובר, ומעניק ל-Google הרשאה לגשת לנתונים שלהם באמצעות ה-API, אם הוא עדיין לא העניק הרשאה.
- השירות שלכם יוצר קוד הרשאה ומחזיר אותו ל-Google. לבצע לכן, להפנות את הדפדפן של המשתמש חזרה אל Google עם קוד ההרשאה שמצורף לבקשה.
- Google שולחת את קוד ההרשאה לנקודת הקצה של המרת האסימון, מאמת את האותנטיות של הקוד ומחזיר אסימון גישה, רענון של אסימון. אסימון הגישה הוא אסימון לטווח קצר שהשירות שלך מקבל כפרטי כניסה לגישה לממשקי API. אסימון הרענון הוא לטווח ארוך אסימון ש-Google יכולה לאחסן ולהשתמש בו כדי לקבל אסימוני גישה חדשים כשהם שפג תוקפן.
- אחרי שהמשתמש משלים את תהליך קישור החשבון, כל קישור הבקשה שנשלחה מ-Google מכילה אסימון גישה.
טיפול בבקשות הרשאה
מתי צריך לבצע קישור חשבונות באמצעות קוד הרשאה מסוג OAuth 2.0 Google שולחת את המשתמש לנקודת הקצה (endpoint) של ההרשאה בבקשה כוללת את הפרמטרים הבאים:
| פרמטרים של נקודת קצה להרשאה | |
|---|---|
client_id |
מזהה הלקוח שהקצית ל-Google. |
redirect_uri |
כתובת ה-URL שאליה שולחים את התגובה לבקשה הזו. |
state |
ערך של ניהול חשבונות שמועבר אל Google ללא שינוי URI להפניה אוטומטית. |
scope |
אופציונלי: קבוצה מופרדת ברווחים של מחרוזות היקף שמציינות את התג הנתונים ש-Google מבקשת עבורם הרשאה. |
response_type |
סוג הערך שיוחזר בתשובה. ל-OAuth 2.0
הרשאה באמצעות קוד, סוג התגובה הוא תמיד code.
|
user_locale |
הגדרת השפה בחשבון Google בקטע RFC5646 , משמש להתאמת התוכן שלך לשפה המועדפת של המשתמש. |
לדוגמה, אם נקודת הקצה להרשאה זמינה ב-
https://myservice.example.com/auth, בקשה עשויה להיראות כך:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code&user_locale=LOCALE
כדי שנקודת הקצה להרשאה תטפל בבקשות כניסה, צריך לבצע את הפעולות הבאות שלבים:
- צריך לוודא שה-
client_idתואם למזהה הלקוח שהקצית ל-Google, ושה-redirect_uriתואם לכתובת ה-URL להפניה אוטומטית ש-Google סיפקה לשירות שלך. הבדיקות האלה חשובות כדי למנוע גישה לאפליקציות לקוח לא מכוונות או שהוגדרו באופן שגוי. אם אתם תומכים בכמה מוצרים, תהליכי OAuth 2.0, מאשרים גם שה-response_typeהואcode. - לבדוק אם המשתמש נכנס לשירות. אם המשתמש לא מחובר, להשלים את תהליך הכניסה או ההרשמה לשירות.
- אפשר ליצור קוד הרשאה ש-Google תשתמש בו כדי לגשת ל-API. קוד ההרשאה יכול להיות כל ערך מחרוזת, אבל הוא חייב להיות ייחודי שמייצג את המשתמש, את הלקוח שעבורו האסימון מיועד ואת תאריך התפוגה של הקוד זמן אחר, ואסור לנחש אותו. בדרך כלל אתם מנפיקים הרשאה קודים שהתוקף שלהם פג לאחר כ-10 דקות.
- מוודאים שכתובת ה-URL שצוינה על ידי הפרמטר
redirect_uriכוללת את בצורה הבאה:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- מפנים את דפדפן המשתמש לכתובת ה-URL שצוינה ב-
הפרמטר
redirect_uri. מוסיפים את קוד ההרשאה שנוצר עכשיו והערך של המצב המקורי שלא השתנה כאשר מבצעים הפניה אוטומטית על ידי הוספת הפרמטריםcodeו-state. זוהי דוגמה דוגמה לכתובת ה-URL שתתקבל:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
טיפול בבקשות להחלפת אסימונים
נקודת הקצה (endpoint) של המרת האסימונים של השירות אחראית על שני סוגים של אסימונים Exchanges:
- המרת קודי הרשאה באסימוני גישה ובאסימוני רענון
- המרת אסימוני רענון באסימוני גישה
בקשות להחלפת אסימונים כוללות את הפרמטרים הבאים:
| פרמטרים של נקודת קצה להחלפת אסימונים | |
|---|---|
client_id |
מחרוזת המזהה את מקור הבקשה כ-Google. המחרוזת הזו חייבת יהיה רשום במערכת שלך כמזהה הייחודי של Google. |
client_secret |
מחרוזת סודית שרשמתם ב-Google לשירות שלכם. |
grant_type |
סוג האסימון המוחלף. זה או אחת מהאפשרויות
authorization_code או refresh_token. |
code |
כשהערך הוא grant_type=authorization_code, הפרמטר הזה
קוד ש-Google קיבלה מהכניסה או מהמרת האסימון
נקודת הקצה. |
redirect_uri |
כשהערך הוא grant_type=authorization_code, הפרמטר הזה
כתובת ה-URL ששימשה בבקשת ההרשאה הראשונית. |
refresh_token |
כשהערך הוא grant_type=refresh_token, הפרמטר הזה
אסימון הרענון ש-Google קיבלה מנקודת הקצה של המרת האסימונים שלך. |
המרת קודי הרשאה באסימוני גישה ובאסימוני רענון
אחרי שהמשתמש נכנס לחשבון ונקודת הקצה (endpoint) של ההרשאה מחזירה דוח לטווח קצר. את קוד ההרשאה ל-Google, Google שולחת בקשה להמרת האסימון שתחליף את קוד ההרשאה באסימון גישה וברענון ב-Assistant.
בבקשות האלה, הערך של grant_type הוא authorization_code,
הערך code הוא הערך של קוד ההרשאה שנתת בעבר
ל-Google. הדוגמה הבאה היא בקשה להחלפת
קוד הרשאה עבור אסימון גישה ואסימון רענון:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
כדי להחליף קודי הרשאה באסימון גישה ובאסימון רענון,
נקודת הקצה (endpoint) של המרת אסימונים מגיבה לבקשות POST על ידי ביצוע
שלבים:
- יש לוודא שה-
client_idמזהה את מקור הבקשה כגורם מורשה origin, ושה-client_secretתואם לערך הצפוי. - מוודאים שקוד ההרשאה בתוקף, ושהוא לא בתוקף. מזהה הלקוח שצוין בבקשה תואם את מזהה הלקוח המשויך אל קוד הרשאה.
- מוודאים שכתובת ה-URL שצוינה על ידי הפרמטר
redirect_uriזהה לערך שנעשה בו שימוש בבקשת ההרשאה הראשונית. - אם לא ניתן לאמת את כל הקריטריונים שלמעלה, מוחזר
שגיאה מסוג 'בקשה שגויה' 400 עם
{"error": "invalid_grant"}בגוף ההודעה. - אחרת, משתמשים במזהה המשתמש מקוד ההרשאה כדי ליצור רענון וגם אסימון גישה. האסימונים האלה יכולים להיות כל ערכי מחרוזת, אבל הם לייצג את המשתמש ואת הלקוח שעבורו האסימון מיועד באופן ייחודי, שלא ניתן לנחש. עבור אסימוני גישה, צריך לרשום גם את זמן התפוגה של את האסימון, שזמינה בדרך כלל שעה אחרי הנפקת האסימון. אין תפוגה לאסימוני רענון.
- מחזירים את אובייקט ה-JSON הבא בגוף תגובת ה-HTTPS:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google מאחסנת את אסימון הגישה ואת אסימון הרענון עבור המשתמש והרשומות את אסימון הגישה. כשפג התוקף של אסימון הגישה, Google משתמשת אסימון הרענון כדי לקבל אסימון גישה חדש מנקודת הקצה של המרת האסימונים.
המרת אסימוני רענון באסימוני גישה
כשפג התוקף של אסימון הגישה, Google שולחת בקשה להחלפת האסימון של נקודת הקצה להחלפת אסימון רענון באסימון גישה חדש.
בבקשות האלה, הערך של grant_type הוא refresh_token והערך
של refresh_token הוא הערך של אסימון הרענון שהענקת לו בעבר
Google. דוגמה לבקשה להחלפת אסימון רענון
לאסימון גישה:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
כדי להחליף אסימון רענון באסימון גישה, נקודת הקצה של המרת האסימון
מגיב לבקשות POST על ידי ביצוע השלבים הבאים:
- מוודאים ש-
client_idמזהה את מקור הבקשה כ-Google, וכן שה-client_secretתואם לערך הצפוי. - יש לוודא שאסימון הרענון חוקי, ושמזהה הלקוח שצוין ב- הבקשה תואמת למזהה הלקוח שמשויך לאסימון הרענון.
- אם לא ניתן לאמת את כל הקריטריונים שלמעלה, מוחזר HTTP 400
שגיאת 'בקשה שגויה' עם
{"error": "invalid_grant"}בגוף ההודעה. - אחרת, משתמשים במזהה המשתמש מאסימון הרענון כדי ליצור גישה ב-Assistant. האסימונים האלה יכולים להיות כל ערכי מחרוזת, אבל הם חייבים להיות ייחודיים שמייצגים את המשתמש ואת הלקוח שעבורו האסימון מיועד, ואסור שהוא בלתי מונחית לניחוש. עבור אסימוני גישה, צריך גם לתעד את זמן התפוגה של האסימון, בדרך כלל שעה לאחר הנפקת האסימון.
- החזרת אובייקט ה-JSON הבא בגוף ה-HTTPS
תגובה:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
טיפול בבקשות למידע על משתמשים
נקודת הקצה של userinfo היא משאב מוגן ב-OAuth 2.0 שמחזיר תלונות לגבי המשתמש המקושר. ההטמעה והאירוח של נקודת הקצה של userinfo הם אופציונליים, חוץ מאשר בתרחישים הבאים לדוגמה:
- כניסה לחשבון המקושר באמצעות Google One Tap.
- מינוי פשוט וקל ב-AndroidTV.
אחרי שהאחזור של אסימון הגישה מנקודת הקצה של האסימון מתבצע, Google שולחת בקשה לנקודת הקצה (endpoint) של userinfo כדי לאחזר פרטי פרופיל בסיסיים של המשתמש המקושר.
| כותרות של בקשות של נקודות קצה של userinfo | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
אסימון הגישה מסוג נושא. |
לדוגמה, אם נקודת הקצה של Userinfo זמינה
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo, בקשה עשויה להיראות כך:
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
כדי שנקודת הקצה של userinfo תטפל בבקשות, מבצעים את השלבים הבאים:
- מחלצים את אסימון הגישה מהכותרת Authorization ומחזירים מידע עבור המשתמש שמשויך לאסימון הגישה.
- אם אסימון הגישה לא חוקי, צריך להחזיר שגיאה מסוג HTTP 401 מאושר עם שימוש בכותרת התגובה
WWW-Authenticate. דוגמה לתגובה עם שגיאה של userinfo:HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
אם אסימון הגישה תקין, מוחזר ותגובת HTTP 200 עם אובייקט ה-JSON הבא בגוף ה-HTTPS תגובה:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }תגובה של נקודת הקצה של userinfo subמזהה ייחודי שמזהה את המשתמש במערכת שלכם. emailכתובת האימייל של המשתמש. given_nameאופציונלי: השם הפרטי של המשתמש. family_nameאופציונלי: שם המשפחה של המשתמש. nameאופציונלי: השם המלא של המשתמש. pictureאופציונלי: תמונת פרופיל של המשתמש.
אימות ההטמעה
אפשר לאמת את ההטמעה באמצעות הכלי OAuth 2.0 Playground.
בכלי, מבצעים את הפעולות הבאות:
- לוחצים על Configuration (הגדרה) כדי לפתוח את חלון ההגדרה של OAuth 2.0.
- בשדה תהליך OAuth, בוחרים באפשרות צד הלקוח.
- בשדה נקודות קצה של OAuth, בוחרים באפשרות בהתאמה אישית.
- מציינים את נקודת הקצה (endpoint) של OAuth 2.0 ואת מזהה הלקוח שהקציתם ל-Google בשדות המתאימים.
- בקטע שלב 1, לא בוחרים היקפי גישה של Google. במקום זאת, צריך להשאיר את השדה הזה ריק או להקליד היקף תקין לשרת (או מחרוזת שרירותית אם לא משתמשים בהיקפים של OAuth). בסיום, לוחצים על Authorize API.
- בקטעים שלב 2 ושלב 3, מבצעים את התהליך OAuth 2.0 ומוודאים שכל שלב פועל כמו שצריך.
אפשר לאמת את ההטמעה באמצעות הכלי הדגמה של קישור לחשבון Google.
בכלי, מבצעים את השלבים הבאים:
- לוחצים על הלחצן כניסה באמצעות חשבון Google.
- בוחרים את החשבון שרוצים לקשר.
- מזינים את מזהה השירות.
- אפשר להזין היקף אחד או יותר שלגביו רוצים לבקש גישה.
- לוחצים על התחלת הדגמה.
- כשמופיעה הבקשה, מאשרים את האפשרות להביע הסכמה לדחיית בקשת הקישור.
- מוודאים שאתם מופנים מחדש לפלטפורמה שלכם.