A API Checks Guardrails agora está disponível na versão Alfa em pré-lançamento privado. Solicite acesso à visualização particular usando nosso formulário de interesse.
A API Guardrails permite verificar se o texto é potencialmente nocivo ou não seguro. Você pode usar essa API no seu aplicativo de IA generativa para evitar que os usuários sejam expostos a conteúdo potencialmente prejudicial.
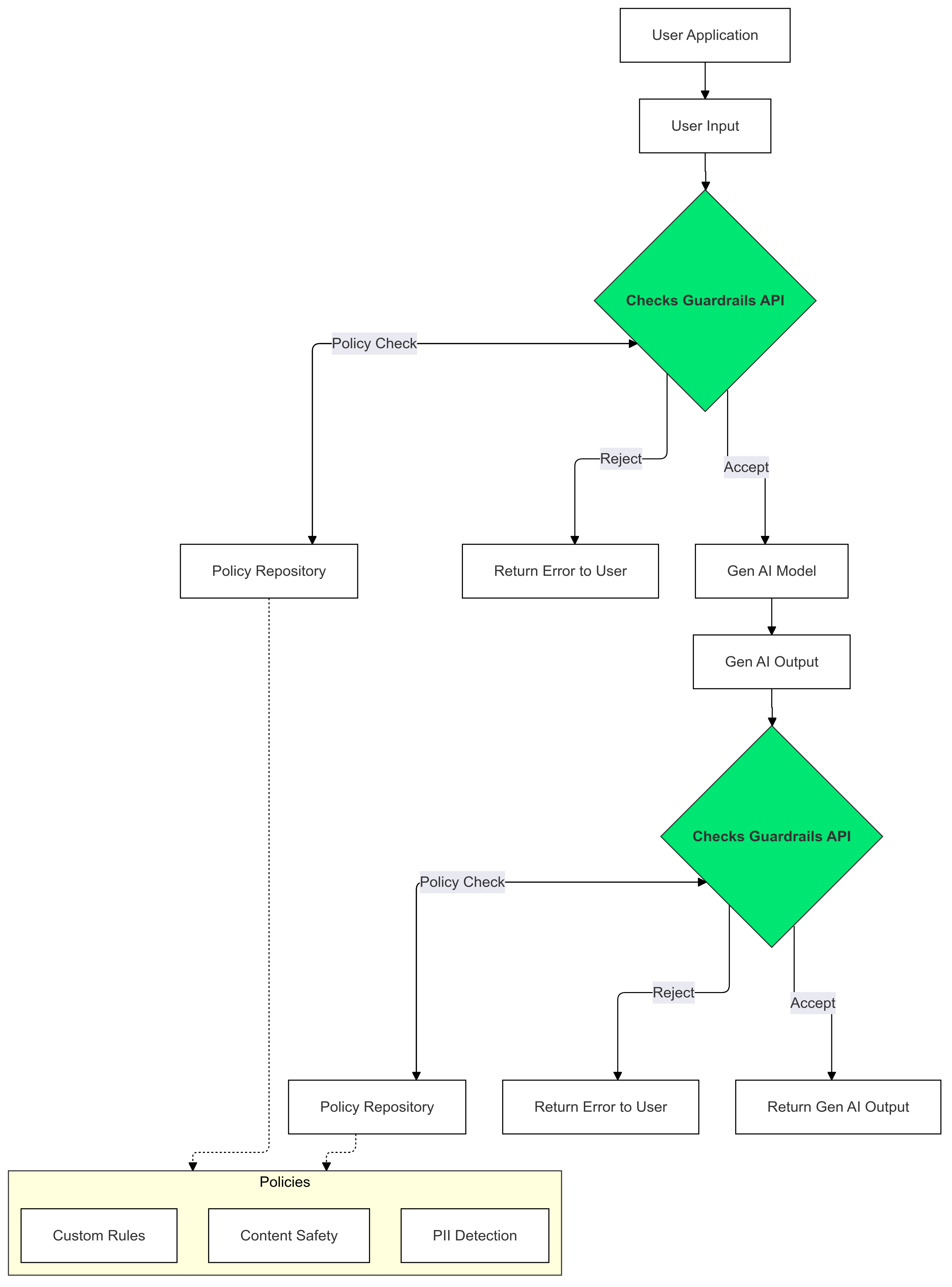
Como usar os guardrails?
Use as diretrizes de segurança de verificações nas entradas e saídas da IA generativa para detectar e reduzir a presença de texto que viola suas políticas.
Por que usar os guardrails?
Às vezes, os LLMs podem gerar conteúdo potencialmente nocivo ou inadequado. Integrar a API Guardrails ao seu aplicativo de IA generativa é fundamental para garantir o uso responsável e mais seguro de modelos de linguagem grandes (LLMs). Ele ajuda a reduzir os riscos associados ao conteúdo gerado, filtrando uma ampla variedade de saídas potencialmente nocivas, incluindo linguagem inadequada, comentários discriminatórios e conteúdo que pode facilitar danos. Isso não só protege seus usuários, mas também salvaguarda a reputação do aplicativo e promove a confiança entre o público. Ao priorizar a segurança e a responsabilidade, os Guardrails permitem criar aplicativos de IA generativa inovadores e mais seguros.
Primeiros passos
Este guia fornece instruções para usar a API Guardrails e detectar e filtrar conteúdo inadequado nos seus aplicativos. A API oferece várias políticas pré-treinadas que podem identificar diferentes tipos de conteúdo potencialmente prejudicial, como discurso de ódio, violência e material sexualmente explícito. Também é possível personalizar o comportamento da API definindo limites para cada política.
Pré-requisitos
- Ter seu projeto do Google Cloud aprovado para a prévia privada da segurança de IA do Checks. Se ainda não fez isso, solicite acesso usando nosso formulário de interesse.
- Ative a API Checks.
- Confira se você consegue enviar solicitações autorizadas usando nosso guia de autorização.
Políticas compatíveis
| Nome da política | Descrição da política | Valor de tipo enumerado da API Policy Type |
|---|---|---|
| Conteúdo perigoso | Conteúdo que facilita, promove ou permite o acesso a produtos, serviços e atividades prejudiciais. | DANGEROUS_CONTENT |
| Solicitar e recitar PII | Conteúdo que solicita ou revela informações ou dados pessoais sensíveis de um indivíduo. | PII_SOLICITING_RECITING |
| Assédio | Conteúdo malicioso, intimidante, abusivo ou de bullying direcionado a outra pessoa ou pessoas. | HARASSMENT |
| Sexualmente explícito | Conteúdo de natureza sexualmente explícita. | SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT |
| Discurso de ódio | Conteúdo geralmente aceito como discurso de ódio. | HATE_SPEECH |
| Informações de saúde | Não é permitido publicar conteúdo que facilite, promova ou permita o acesso a orientações ou conselhos médicos prejudiciais. | MEDICAL_INFO |
| Violência e imagens sangrentas | Conteúdo que inclua descrições sem custo financeiro de violência realista e/ou imagens sangrentas. | VIOLENCE_AND_GORE |
| Obscenidade e linguagem obscena | Conteúdo com linguagem vulgar, profana ou ofensiva é proibido. | OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY |
Snippets de código
Python
Instale o cliente Python da API do Google executando pip install
google-api-python-client.
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
SECRET_FILE_PATH = 'path/to/your/secret.json'
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
SECRET_FILE_PATH, scopes=['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks']
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.',
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'}
], # Default Checks-defined threshold is used
}
)
response = request.execute()
for policy_result in response['policyResults']:
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
Go
Instale o cliente Go da API Checks executando
go get google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha.
package main
import (
"context"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
const credsFilePath = "path/to/your/secret.json"
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
checksService, err := checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint("https://checks.googleapis.com"),
option.WithCredentialsFile(credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes("https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks"),
)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"}, // Default Checks-defined threshold is used
},
}
classificationResults, err := checksService.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
for _, policy := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
slog.Info("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policy.PolicyType, "Score", policy.Score, "Violation Result", policy.ViolationResult)
}
}
REST
Observação: este exemplo usa a ferramenta de linha de comando oauth2l.
Substitua YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID pelo ID do projeto do Google Cloud que recebeu acesso à API Guardrails.
curl -X POST https://checks.googleapis.com/v1alpha/aisafety:classifyContent \
-H "$(oauth2l header --scope cloud-platform,checks)" \
-H "X-Goog-User-Project: YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": {
"text_input": {
"content": "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
"language_code": "en"
}
},
"policies": [
{
"policy_type": "HARASSMENT",
"threshold": "0.5"
},
{
"policy_type": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
},
]
}'
Exemplo de resposta
{
"policyResults": [
{
"policyType": "HARASSMENT",
"score": 0.430,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
"score": 0.764,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY",
"score": 0.876,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT",
"score": 0.197,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "HATE_SPEECH",
"score": 0.45,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "MEDICAL_INFO",
"score": 0.05,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "VIOLENCE_AND_GORE",
"score": 0.964,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "PII_SOLICITING_RECITING",
"score": 0.0009,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
}
]
}
Casos de uso
A API Guardrails pode ser integrada ao seu aplicativo de LLM de várias maneiras, dependendo das suas necessidades específicas e da tolerância a riscos. Confira alguns exemplos de casos de uso comuns:
Nenhuma intervenção de proteção: geração de registros
Nesse cenário, a API Guardrails é usada sem mudanças no comportamento do app. No entanto, possíveis violações da política estão sendo registradas para fins de monitoramento e auditoria. Essas informações podem ser usadas para identificar possíveis riscos à segurança do LLM.
Python
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def log_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
log_violations(user_prompt)
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
log_violations(llm_response, user_prompt)
print(llm_response)
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"},
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func logViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) error {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
slog.Warn("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policyResult.PolicyType, "Score", policyResult.Score, "Violation Result", policyResult.ViolationResult)
}
}
return nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
err := logViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
Proteção bloqueada com base em uma política
Neste exemplo, a API Guardrails bloqueia entradas de usuários e respostas do modelo que não são seguras. Ele verifica os dois em relação a políticas de segurança predefinidas (por exemplo, discurso de ódio, conteúdo perigoso). Isso impede que a IA gere resultados potencialmente nocivos e protege os usuários contra conteúdo inadequado.
Python
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path, default_threshold):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
self.default_threshold = default_threshold
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
default_threshold=0.6,
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{
'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT',
'threshold': my_checks_config.default_threshold,
},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def has_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
if has_violations(user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
if has_violations(llm_response, user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
print(llm_response)
Go
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
defaultThreshold float64
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
defaultThreshold: 0.6,
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT", Threshold: myChecksConfig.defaultThreshold},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"}, // default Checks-defined threshold is used
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func hasViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (bool, error) {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
return true, nil
}
}
return false, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
hasInputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err == nil && hasInputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
hasOutputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err == nil && hasOutputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
Transmitir a saída do LLM para as proteções
Nos exemplos a seguir, transmitimos a saída de um LLM para a API Guardrails. Isso pode ser usado para diminuir a latência percebida pelo usuário. Essa abordagem pode gerar falsos positivos devido a um contexto incompleto. Por isso, é importante que a saída do LLM tenha contexto suficiente para que os Guardrails façam uma avaliação precisa antes de chamar a API.
Chamadas síncronas do Guardrails
Python
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
while not my_llm_model.finished:
chunk = my_llm_model.next_chunk()
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
Go
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
var llmResponse string
for !model.finished {
chunk := model.nextChunk()
llmResponse += chunk + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
Chamadas assíncronas do Guardrails
Python
async def main():
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
async for chunk in my_llm_model:
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
asyncio.run(main())
Go
func main() {
var textChannel = make(chan string)
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
var llmResponse string
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
go model.streamToChannel(textChannel)
for text := range textChannel {
llmResponse += text + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
Perguntas frequentes
O que devo fazer se eu atingir os limites de cota da API Guardrails?
Para solicitar um aumento de cota, envie um e-mail para checks-support@google.com com seu pedido. Inclua as seguintes informações no seu e-mail:
- O número do seu projeto do Google Cloud: isso nos ajuda a identificar sua conta rapidamente.
- Detalhes sobre seu caso de uso: explique como você está usando a API Guardrails.
- Quantidade de cota desejada: especifique a quantidade de cota adicional que você precisa.
