Interfejs Checks Guardrails API jest teraz dostępny w wersji alfa w ramach prywatnej wersji przedpremierowej. Poproś o dostęp do prywatnej wersji przedpremierowej za pomocą formularza zainteresowania.
Guardrails API to interfejs API, który umożliwia sprawdzenie, czy tekst może być szkodliwy lub niebezpieczny. Możesz użyć tego interfejsu API w aplikacji z generatywną AI, aby chronić użytkowników przed potencjalnie szkodliwymi treściami.
Jak korzystać z mechanizmów ochronnych?
Używaj zabezpieczeń w przypadku danych wejściowych i wyjściowych generatywnej AI, aby wykrywać i ograniczać występowanie tekstu, który narusza Twoje zasady.
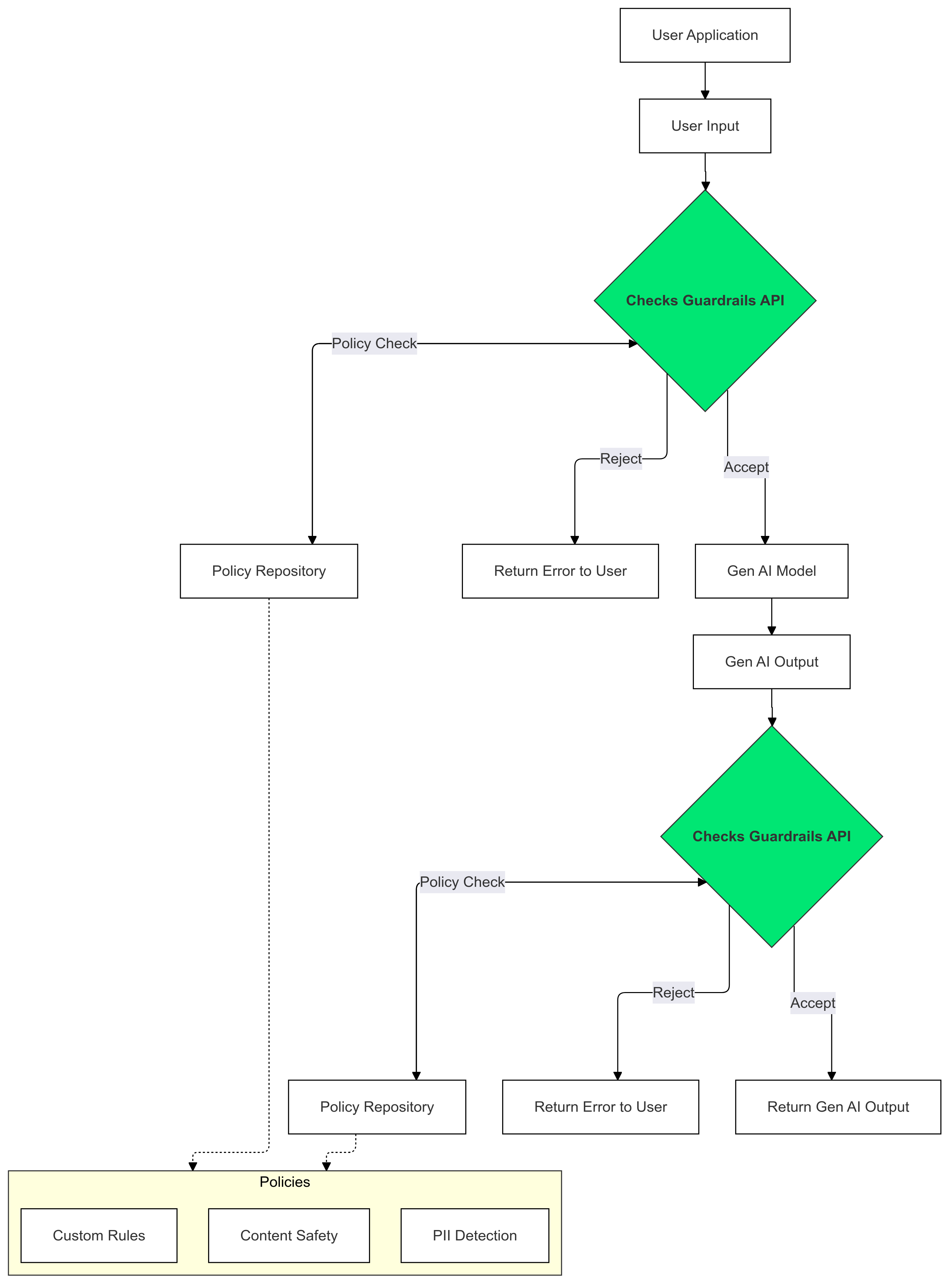
Dlaczego warto korzystać z funkcji Guardrails?
Modele LLM mogą czasami generować potencjalnie szkodliwe lub nieodpowiednie treści. Zintegrowanie interfejsu Guardrails API z aplikacją GenAI ma kluczowe znaczenie dla zapewnienia odpowiedzialnego i bezpieczniejszego korzystania z dużych modeli językowych (LLM). Pomaga ono zmniejszać ryzyko związane z wygenerowanymi treściami, ponieważ odfiltrowuje szeroki zakres potencjalnie szkodliwych danych wyjściowych, w tym niestosowny język, dyskryminujące uwagi i treści, które mogą ułatwiać wyrządzanie szkód. W ten sposób nie tylko chronisz użytkowników, ale też dbasz o reputację aplikacji i zwiększasz zaufanie odbiorców. Dzięki temu, że Guardrails stawia na pierwszym miejscu bezpieczeństwo i odpowiedzialność, możesz tworzyć innowacyjne i bezpieczniejsze aplikacje oparte na generatywnej AI.
Pierwsze kroki
Ten przewodnik zawiera instrukcje korzystania z interfejsu Guardrails API do wykrywania i filtrowania nieodpowiednich treści w aplikacjach. Interfejs API oferuje różne wstępnie wytrenowane zasady, które mogą identyfikować różne rodzaje potencjalnie szkodliwych treści, takie jak wypowiedzi szerzące nienawiść, przemoc i materiały o charakterze jednoznacznie seksualnym. Możesz też dostosować działanie interfejsu API, ustawiając progi dla poszczególnych zasad.
Wymagania wstępne
- uzyskać zgodę na korzystanie z prywatnej wersji podglądowej funkcji Checks AI Safety w projekcie Google Cloud; Jeśli jeszcze tego nie zrobiono, poproś o dostęp za pomocą formularza zainteresowania.
- Włącz interfejs Checks API.
- Upewnij się, że możesz wysyłać autoryzowane żądania, korzystając z naszego przewodnika autoryzacji.
Obsługiwane zasady
| Nazwa zasady | Opis zasad | Wartość typu wyliczeniowego interfejsu Policy Type API |
|---|---|---|
| Treści niebezpieczne | Treści, które ułatwiają, promują lub umożliwiają dostęp do szkodliwych produktów, usług i aktywności. | DANGEROUS_CONTENT |
| Nakłanianie do ujawnienia i ujawnianie informacji umożliwiających identyfikację | Treści, które proszą o podanie lub ujawniają poufne dane osobowe lub informacje. | PII_SOLICITING_RECITING |
| Nękanie | treści, które są złośliwe, zastraszające, dręczące lub obraźliwe w stosunku do innych osób; | HARASSMENT |
| Treści seksualne | treści o charakterze jednoznacznie seksualnym; | SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT |
| Szerzenie nienawiści | Treści, które są powszechnie uznawane za szerzące nienawiść. | HATE_SPEECH |
| Informacje medyczne | Treści, które ułatwiają, promują lub umożliwiają dostęp do szkodliwych porad lub wskazówek medycznych, są zabronione. | MEDICAL_INFO |
| Przemoc i okrucieństwo | Treści, które zawierają nieuzasadnione opisy realistycznej przemocy lub okrucieństwa. | VIOLENCE_AND_GORE |
| Treści nieprzyzwoite i wulgaryzmy | Treści zawierające wulgarny, obsceniczny lub obraźliwy język są niedozwolone. | OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY |
Fragmenty kodu
Python
Zainstaluj klienta interfejsu API Google w Pythonie, uruchamiając pip install
google-api-python-client.
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
SECRET_FILE_PATH = 'path/to/your/secret.json'
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
SECRET_FILE_PATH, scopes=['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks']
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.',
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'}
], # Default Checks-defined threshold is used
}
)
response = request.execute()
for policy_result in response['policyResults']:
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
Przeczytaj
Zainstaluj klienta interfejsu Checks API w Go, uruchamiając polecenie
go get google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha.
package main
import (
"context"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
const credsFilePath = "path/to/your/secret.json"
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
checksService, err := checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint("https://checks.googleapis.com"),
option.WithCredentialsFile(credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes("https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks"),
)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"}, // Default Checks-defined threshold is used
},
}
classificationResults, err := checksService.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
for _, policy := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
slog.Info("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policy.PolicyType, "Score", policy.Score, "Violation Result", policy.ViolationResult)
}
}
REST
Uwaga: w tym przykładzie używamy oauth2l narzędzia interfejsu wiersza poleceń.
Zastąp YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID identyfikatorem Twojego projektu Google Cloud, który ma dostęp do interfejsu Guardrails API.
curl -X POST https://checks.googleapis.com/v1alpha/aisafety:classifyContent \
-H "$(oauth2l header --scope cloud-platform,checks)" \
-H "X-Goog-User-Project: YOUR_GCP_PROJECT_ID" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"input": {
"text_input": {
"content": "Mix, bake, cool, frost, and enjoy.",
"language_code": "en"
}
},
"policies": [
{
"policy_type": "HARASSMENT",
"threshold": "0.5"
},
{
"policy_type": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
},
]
}'
Przykładowa odpowiedź
{
"policyResults": [
{
"policyType": "HARASSMENT",
"score": 0.430,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "DANGEROUS_CONTENT",
"score": 0.764,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "OBSCENITY_AND_PROFANITY",
"score": 0.876,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "SEXUALLY_EXPLICIT",
"score": 0.197,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "HATE_SPEECH",
"score": 0.45,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "MEDICAL_INFO",
"score": 0.05,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "VIOLENCE_AND_GORE",
"score": 0.964,
"violationResult": "VIOLATIVE"
},
{
"policyType": "PII_SOLICITING_RECITING",
"score": 0.0009,
"violationResult": "NON_VIOLATIVE"
}
]
}
Przypadki użycia
Interfejs Guardrails API można zintegrować z aplikacją LLM na różne sposoby, w zależności od konkretnych potrzeb i tolerancji ryzyka. Oto kilka przykładów typowych zastosowań:
Brak interwencji w ramach ochrony – logowanie
W tym scenariuszu interfejs Guardrails API jest używany bez wprowadzania zmian w działaniu aplikacji. Potencjalne naruszenia zasad są jednak rejestrowane na potrzeby monitorowania i kontroli. Informacje te mogą być wykorzystywane do identyfikowania potencjalnych zagrożeń związanych z bezpieczeństwem LLM.
Python
import logging
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT'},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def log_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
logging.warning(
'Policy: %s, Score: %s, Violation result: %s',
policy_result['policyType'],
policy_result['score'],
policy_result['violationResult'],
)
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
log_violations(user_prompt)
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
log_violations(llm_response, user_prompt)
print(llm_response)
Przeczytaj
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log/slog"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT"},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"},
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func logViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) error {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return err
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
slog.Warn("Checks Guardrails violation: ", "Policy", policyResult.PolicyType, "Score", policyResult.Score, "Violation Result", policyResult.ViolationResult)
}
}
return nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
err := logViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
Blokada zabezpieczająca na podstawie zasad
W tym przykładzie interfejs Guardrails API blokuje niebezpieczne dane wejściowe użytkownika i odpowiedzi modelu. Sprawdza on, czy treści są zgodne z wstępnie zdefiniowanymi zasadami bezpieczeństwa (np. dotyczącymi szerzenia nienawiści czy niebezpiecznych treści). Zapobiega to generowaniu przez AI potencjalnie szkodliwych wyników i chroni użytkowników przed nieodpowiednimi treściami.
Python
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
# Checks API configuration
class ChecksConfig:
def __init__(self, scope, creds_file_path, default_threshold):
self.scope = scope
self.creds_file_path = creds_file_path
self.default_threshold = default_threshold
my_checks_config = ChecksConfig(
scope='https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks',
creds_file_path='path/to/your/secret.json',
default_threshold=0.6,
)
def new_checks_service(config):
"""Creates a new Checks API service."""
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(
config.creds_file_path, scopes=[config.scope]
)
service = build('checks', 'v1alpha', credentials=credentials)
return service
def fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context=''):
"""Fetches violation results from the Checks API."""
service = new_checks_service(my_checks_config)
request = service.aisafety().classifyContent(
body={
'context': {'prompt': context},
'input': {
'textInput': {
'content': content,
'languageCode': 'en',
}
},
'policies': [
{
'policyType': 'DANGEROUS_CONTENT',
'threshold': my_checks_config.default_threshold,
},
{'policyType': 'HATE_SPEECH'},
# ... add more policies
],
}
)
response = request.execute()
return response
def fetch_user_prompt():
"""Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user."""
return 'How do I bake a cake?'
def fetch_llm_response(prompt):
"""Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint."""
return 'Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy.'
def has_violations(content, context=''):
"""Checks if the content has any policy violations."""
classification_results = fetch_checks_violation_results(content, context)
for policy_result in classification_results['policyResults']:
if policy_result['violationResult'] == 'VIOLATIVE':
return True
return False
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
if has_violations(user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
llm_response = fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
if has_violations(llm_response, user_prompt):
print("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
else:
print(llm_response)
Przeczytaj
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
checks "google.golang.org/api/checks/v1alpha"
option "google.golang.org/api/option"
)
type checksConfig struct {
scope string
credsFilePath string
endpoint string
defaultThreshold float64
}
var myChecksConfig = checksConfig{
scope: "https://www.googleapis.com/auth/checks",
credsFilePath: "path/to/your/secret.json",
endpoint: "https://checks.googleapis.com",
defaultThreshold: 0.6,
}
func newChecksService(ctx context.Context, cfg checksConfig) (*checks.Service, error) {
return checks.NewService(
ctx,
option.WithEndpoint(cfg.endpoint),
option.WithCredentialsFile(cfg.credsFilePath),
option.WithScopes(cfg.scope),
)
}
func fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentResponse, error) {
svc, err := newChecksService(ctx, myChecksConfig)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create checks service: %w", err)
}
req := &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequest{
Context: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestContext{
Prompt: context,
},
Input: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestInputContent{
TextInput: &checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaTextInput{
Content: content,
LanguageCode: "en",
},
},
Policies: []*checks.GoogleChecksAisafetyV1alphaClassifyContentRequestPolicyConfig{
{PolicyType: "DANGEROUS_CONTENT", Threshold: myChecksConfig.defaultThreshold},
{PolicyType: "HATE_SPEECH"}, // default Checks-defined threshold is used
// ... add more policies
},
}
response, err := svc.Aisafety.ClassifyContent(req).Do()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
return response, nil
}
// Imitates retrieving the input prompt from the user.
func fetchUserPrompt() string {
return "How do I bake a cake?"
}
// Imitates the call to an LLM endpoint.
func fetchLLMResponse(prompt string) string {
return "Mix, bake, cool, frost, enjoy."
}
func hasViolations(ctx context.Context, content string, context string) (bool, error) {
classificationResults, err := fetchChecksViolationResults(ctx, content, context)
if err != nil {
return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to classify content: %w", err)
}
for _, policyResult := range classificationResults.PolicyResults {
if policyResult.ViolationResult == "VIOLATIVE" {
return true, nil
}
}
return false, nil
}
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
userPrompt := fetchUserPrompt()
hasInputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, userPrompt, "")
if err == nil && hasInputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
llmResponse := fetchLLMResponse(userPrompt)
hasOutputViolations, err := hasViolations(ctx, llmResponse, userPrompt)
if err == nil && hasOutputViolations {
fmt.Println("Sorry, I can't help you with this request.")
return
}
fmt.Println(llmResponse)
}
Przesyłanie strumieniowe danych wyjściowych LLM do Guardrails
W przykładach poniżej przesyłamy strumieniowo dane wyjściowe z LLM do interfejsu Guardrails API. Można to wykorzystać do zmniejszenia odczuwalnego przez użytkownika opóźnienia. Takie podejście może powodować fałszywe alarmy ze względu na niepełny kontekst, dlatego ważne jest, aby dane wyjściowe LLM zawierały wystarczający kontekst, który umożliwiłby systemowi Guardrails dokładną ocenę przed wywołaniem interfejsu API.
Synchroniczne wywołania wskazówek
Python
if __name__ == '__main__':
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
while not my_llm_model.finished:
chunk = my_llm_model.next_chunk()
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
Przeczytaj
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
var llmResponse string
for !model.finished {
chunk := model.nextChunk()
llmResponse += chunk + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
Wywołania asynchroniczne dotyczące wskazówek
Python
async def main():
user_prompt = fetch_user_prompt()
my_llm_model = MockModel(
user_prompt, fetch_llm_response(user_prompt)
)
llm_response = ""
chunk = ""
# Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
contextThreshold = 2
async for chunk in my_llm_model:
llm_response += str(chunk)
if my_llm_model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold:
log_violations(llm_response, my_llm_model.userPrompt)
asyncio.run(main())
Przeczytaj
func main() {
var textChannel = make(chan string)
model := mockModel{
userPrompt: "It's a sunny day and you want to buy ice cream.",
response: []string{"What a lovely day", "to get some ice cream.", "is the shop open?"},
}
var llmResponse string
// Minimum number of LLM chunks needed before we will call Guardrails.
const contextThreshold = 2
go model.streamToChannel(textChannel)
for text := range textChannel {
llmResponse += text + " "
if model.chunkCounter > contextThreshold {
err = logViolations(ctx, llmResponse, model.userPrompt)
if err != nil {
// Handle error
}
}
}
}
Najczęstsze pytania
Co zrobić, jeśli osiągnę limit wykorzystania interfejsu Guardrails API?
Aby poprosić o zwiększenie limitu, wyślij e-maila na adres checks-support@google.com. W e-mailu podaj te informacje:
- Numer projektu Google Cloud: pomoże nam to szybko zidentyfikować Twoje konto.
- Szczegóły dotyczące Twojego przypadku użycia: opisz, jak korzystasz z interfejsu Guardrails API.
- Żądana kwota limitu: podaj, o ile chcesz zwiększyć limit.
