लॉयल्टी पास, टेंप्लेट रेंडरिंग के साथ काम करते हैं. अगर कोई टेंप्लेट तय नहीं किया गया है, तो डिफ़ॉल्ट नाम का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है.
टेंप्लेट की परिभाषा
पास टेंप्लेट को क्लास लेवल पर तय किया जाता है. साथ ही, इसका इस्तेमाल क्लास से जुड़ा होता है. टेंप्लेट तय करता है कि अलग-अलग फ़ील्ड में कौनसे फ़ील्ड दिखाए जाएं सेक्शन शामिल होते हैं.
टेंप्लेट को इन सेक्शन में बांटा गया है:
Android

वेब

कार्ड शीर्षक
Android

|
डिफ़ॉल्ट कार्ड का टाइटल
चौड़े लोगो वाले कार्ड का टाइटल
|
वेब

|
डिफ़ॉल्ट कार्ड का टाइटल
चौड़े लोगो वाले कार्ड का टाइटल
|
कार्ड के टाइटल वाले सेक्शन में लोगो, जारी करने वाले का नाम, और प्रोग्राम का टाइटल दिखता है. न तो सक्षम और न ही असक्षम उन्हें पॉप्युलेट करने के लिए इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस और न ही उनकी स्थिति बदली जा सकती है.
जब चौड़े लोगो वाला फ़ील्ड सेट किया जाता है, तो Android डिवाइसों पर डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट हेडर होता है. लोगो और जारी करने वाले के नाम को चौड़ा लोगो से बदल दिया गया है.
कृपया चौड़े लोगो की इमेज से जुड़े दिशा-निर्देश: पास पर आपकी इमेज नहीं दिखेगी.
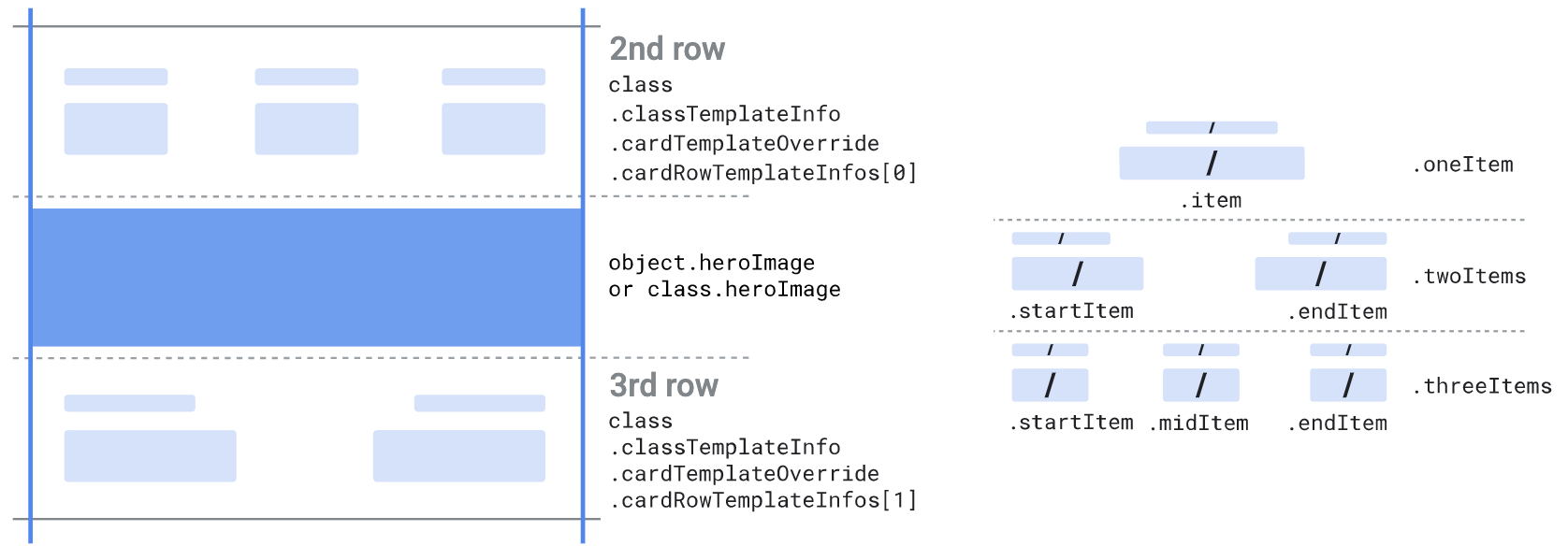
कार्ड टेंप्लेट
Android
वेब

कार्ड टेंप्लेट सेक्शन का इस्तेमाल, ज़्यादा लाइनें दिखाने के लिए किया जाता है. इन पंक्तियों में ये काम किए जा सकते हैं टेक्स्ट पर आधारित स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड या टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड होने चाहिए.
उन पंक्तियों की संख्या तय की जा सकती है जो
class.classTemplateInfo.cardTemplateOverride.cardRowTemplateInfos[] अभी तक किसी भी व्यक्ति ने चेक इन नहीं किया है
सूची. सूची में कम से कम एक एलिमेंट होना ज़रूरी है और हमारा सुझाव है कि ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा उसका इस्तेमाल करें
दो एलिमेंट होने चाहिए. हर एलिमेंट इनमें से किसी एक टाइप का होना चाहिए:
-
oneItem, जो एक आइटम स्वीकार करता है:item
-
twoItems, जो दो आइटम स्वीकार करता है:startItemendItem
-
threeItems, जिसमें तीन आइटम स्वीकार किए जाते हैं:startItemmiddleItemendItem
हर आइटम को किसी एक फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर के तौर पर सेट किया जा सकता है
(.firstValue), दो फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर (.firstValue और
.secondValue) या पहले से तय किया गया आइटम
(.predefinedItem). चुने गए फ़ील्ड की वैल्यू और उनके
लेबल दिखेंगे. जब आप दो फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर तय करते हैं, तो
चुने गए फ़ील्ड की वैल्यू, "/" के साथ दिखती हैं सेपरेटर. एक जैसा
चुने गए फ़ील्ड के लेबल पर जाएं. पहले से तय आइटम का इस्तेमाल इन कामों के लिए किया जाता है
तो और जटिल रेंडरिंग कैसे तय की जा सकती है.
नीचे दिया गया कोड सैंपल, कार्ड टेंप्लेट की कार्ड लाइन को बदलने का तरीका बताता है
सेक्शन का इस्तेमाल करें. हर लाइन में तीन आइटम होते हैं. हर लाइन में
संदर्भ के तौर पर छह क्लास-लेवल के textModuleData कस्टम फ़ील्ड और उनके
हेडर लेबल के रूप में:
Python
{ ... //Rest of class "textModulesData": [ { "header": "Label 1", "body": "Some info 1", "id": "myfield1" }, { "header": "Label 2", "body": "Some info 2", "id": "myfield2" }, { "header": "Label 3", "body": "Some info 3", "id": "myfield3" }, { "header": "Label 4", "body": "Some info 4", "id": "myfield4" }, { "header": "Label 5", "body": "Some info 5", "id": "myfield5" }, { "header": "Label 6", "body": "Some info 6", "id": "myfield6" } ], "classTemplateInfo": { "cardTemplateOverride": { "cardRowTemplateInfos": [{ "threeItems": { "startItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield1']" }] } }, "middleItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield2']" }] } }, "endItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield3']" }] } }, } },{ "threeItems": { "startItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield4']" }] } }, "middleItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield5']" }] } }, "endItem": { "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.textModulesData['myfield6']" }] } }, } }] } } }
Java
// Rest of class .setTextModulesData((new ArrayList<TextModuleData>() { { add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 1") .setBody("Some info 1") .setId("myfield1")); add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 2") .setBody("Some info 1") .setId("myfield2")); add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 3") .setBody("Some info 3") .setId("myfield3")); add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 4") .setBody("Some info 4") .setId("myfield4")); add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 5") .setBody("Some info 5") .setId("myfield5")); add((new TextModuleData()).setHeader("Label 6") .setBody("Some info 5") .setId("myfield6")); } })) .setClassTemplateInfo((new ClassTemplateInfo()) .setCardTemplateOverride((new CardTemplateOverride()) .setCardRowTemplateInfos(new ArrayList<CardRowTemplateInfo>() { { add((new CardRowTemplateInfo()).setThreeItems((new CardRowThreeItems()) .setStartItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield1']")); } }))) .setMiddleItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield2']")); } }))) .setEndItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield3']")); } }))) )); add((new CardRowTemplateInfo()).setThreeItems((new CardRowThreeItems()) .setStartItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield4']")); } }))) .setMiddleItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield5']")); } }))) .setEndItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield6']")); } }))) )); } })))
PHP
// Rest of class $textModulesData1 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData1->setBody("Some info 1"); $textModulesData1->setHeader("Label 1"); $textModulesData1->setId("myfield1"); $textModulesData2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData2->setBody("Some info 2"); $textModulesData2->setHeader("Label 2"); $textModulesData2->setId("myfield2"); $textModulesData3 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData3->setBody("Some info 3"); $textModulesData3->setHeader("Label 3"); $textModulesData3->setId("myfield3"); $textModulesData4 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData4->setBody("Some info 4"); $textModulesData4->setHeader("Label 4"); $textModulesData4->setId("myfield4"); $textModulesData5 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData5->setBody("Some info 5"); $textModulesData5->setHeader("Label 5"); $textModulesData5->setId("myfield5"); $textModulesData6 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TextModuleData(); $textModulesData6->setBody("Some info 6"); $textModulesData6->setHeader("Label 6"); $textModulesData6->setId("myfield6"); $textModulesDatas = array($textModulesData1, $textModulesData2, $textModulesData3, $textModulesData4, $textModulesData5, $textModulesData6); $startItemField = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $startItemField->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield1']"); $startItemFirstValue = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $startItemFirstValue->setFields(array($startItemField)); $startItem = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $startItem->setFirstValue($startItemFirstValue); $middleItemField = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $middleItemField->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield2']"); $middleItemFirstValue = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $middleItemFirstValue->setFields(array($middleItemField)); $middleItem = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $middleItem->setFirstValue($middleItemFirstValue); $endItemField = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $endItemField->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield3']"); $endItemFirstValue = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $endItemFirstValue->setFields(array($endItemField)); $endItem = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $endItem->setFirstValue($endItemFirstValue); $cardRowTemplate = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardRowThreeItems(); $cardRowTemplate->setStartItem($startItem); $cardRowTemplate->setMiddleItem($middleItem); $cardRowTemplate->setEndItem($endItem); $cardRowTemplateInfo1 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardRowTemplateInfo(); $cardRowTemplateInfo1->setThreeItems($cardRowTemplate); $startItemField2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $startItemField2->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield4']"); $startItemFirstValue2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $startItemFirstValue2->setFields(array($startItemField2)); $startItem2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $startItem2->setFirstValue($startItemFirstValue2); $middleItemField2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $middleItemField2->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield5']"); $middleItemFirstValue2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $middleItemFirstValue2->setFields(array($middleItemField2)); $middleItem2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $middleItem2->setFirstValue($middleItemFirstValue2); $endItemField2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $endItemField2->setFieldPath("class.textModulesData['myfield6']"); $endItemFirstValue2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $endItemFirstValue2->setFields(array($endItemField2)); $endItem2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $endItem2->setFirstValue($endItemFirstValue2); $cardRowTemplate2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardRowThreeItems(); $cardRowTemplate2->setStartItem($startItem2); $cardRowTemplate2->setMiddleItem($middleItem2); $cardRowTemplate2->setEndItem($endItem2); $cardRowTemplateInfo2 = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardRowTemplateInfo(); $cardRowTemplateInfo2->setThreeItems($cardRowTemplate2); $cardTemplateOverride = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardTemplateOverride(); $cardTemplateOverride->setCardRowTemplateInfos(array($cardRowTemplateInfo1, $cardRowTemplateInfo2)); $classTemplateInfo = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ClassTemplateInfo(); $classTemplateInfo->setCardTemplateOverride($cardTemplateOverride); $payload->setTextModulesData($textModulesDatas); $payload->setClassTemplateInfo($classTemplateInfo);
यह कोड, इस कोड टेंप्लेट सेक्शन फ़ॉर्मैट का इस्तेमाल करके पास बनाता है:

अगर कोई आइटम खाली है, तो वह नहीं दिखता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, यह देखें फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस. अगर किसी पंक्ति में मौजूद सभी आइटम खाली है, तो यह पंक्ति नहीं दिखती है. अगर लाइन में मौजूद सभी आइटम के बजाय कुछ आइटम खाली हैं, तो जो आइटम खाली नहीं हैं उन्हें फिर से व्यवस्थित किया जाता है और कम आइटम के साथ एक पंक्ति के तौर पर दिखाया जाता है.
अगर कार्ड टेंप्लेट को नहीं बदला जाता है, तो पंक्तियों की डिफ़ॉल्ट संख्या, आइटम की डिफ़ॉल्ट संख्या, और डिफ़ॉल्ट फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. ज़्यादा के लिए जानकारी के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट देखें.
तय करने के बाद:
हीरो इमेज, पहली पंक्ति के बाद दिख सकती है, अगर
cardRowTemplateInfos सूची या पंक्ति के ऊपर, अगर सिर्फ़
एक.
कार्ड का बारकोड
Android

|
|
वेब

|
|
कार्ड के बारकोड सेक्शन का इस्तेमाल, बारकोड. इस सेक्शन में कोई भी फ़ील्ड ज़रूरी नहीं है.
तीन फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर हैं, जिनका इस्तेमाल साथ-साथ दो फ़ील्ड तय करने के लिए किया जा सकता है कोड के नीचे और एक टाइटल बॉक्स के नीचे. इन्हें बिना किसी लेबल के दिखाया जाता है. इन्हें टेक्स्ट पर आधारित स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड, टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड या इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड. अगर आपको इमेज का इस्तेमाल नहीं करना चाहिए, तो ये ब्रैंड के दिशा-निर्देशों के मुताबिक होनी चाहिए.
बारकोड को टाइप और वैल्यू के हिसाब से तय किया जाता है. इस्तेमाल किए जा सकने वाले बारकोड टाइप की सूची देखने के लिए, रेफ़रंस देखें. इसके अलावा, टेक्स्ट कोई भी बारकोड के ठीक नीचे दिखाई देता है. इस टेक्स्ट से बारकोड को स्कैन करना आसान हो जाता है. इसके अलावा, इस्तेमाल किए जाते हैं.
नीचे दिया गया कोड सैंपल, किसी पास को दिखाने के लिए उसके बारकोड सेक्शन को बदलने का तरीका बताता है बारकोड के ऊपर की इमेज:
Python
#... rest of class "imageModulesData": [ { "mainImage": { "sourceUri": { "uri": "http://farm4.staticflickr.com/3738/12440799783_3dc3c20606_b.jpg", "description": "Coffee" } }, "id": "myimage" } ], "classTemplateInfo": { "cardBarcodeSectionDetails": { "firstTopDetail": { "fieldSelector": { "fields": [ { "fieldPath": "class.imageModulesData['myimage'].mainImage" } ] } } } } }
Java
//... rest of class .setImageModulesData((new ArrayList<ImageModuleData>() { { add((new ImageModuleData()) .setId("myimage") .setMainImage((new Image()).setSourceUri((new ImageUri()).setDescription("Coffee beans") .setUri("http://farm4.staticflickr.com/3738/12440799783_3dc3c20606_b.jpg")))); } })) .setClassTemplateInfo((new ClassTemplateInfo()) .setCardBarcodeSectionDetails((new CardBarcodeSectionDetails()) .setFirstTopDetail((new BarcodeSectionDetail()) .setFieldSelector((new FieldSelector()) .setFields((new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.imageModulesData['myimage'].mainImage")); } }))))) }
PHP
//... rest of class $imageUri = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ImageUri(); $imageUri->setUri("https://farm8.staticflickr.com/7340/11177041185_a61a7f2139_o.jpg"); $imageUri->setDescription("Baconrista flights image"); $image = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_Image(); $image->setSourceUri($imageUri); $imageModulesData = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ImageModuleData(); $imageModulesData->setMainImage($image); $imageModulesData->setId("myimage"); $cardBarcodeFieldReference = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $cardBarcodeFieldReference->setFieldPath("class.imageModulesData['myimage'].mainImage"); $cardBarcodeFieldSelector = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $cardBarcodeFieldSelector->setFields(array($cardBarcodeFieldReference)); $cardBarcodeDetail = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_BarcodeSectionDetail(); $cardBarcodeDetail->setFieldSelector($cardBarcodeFieldSelector); $cardBarcodeSectionDetails = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_CardBarcodeSectionDetails(); $cardBarcodeSectionDetails->setFirstTopDetail($cardBarcodeDetail); $classTemplateInfo = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ClassTemplateInfo(); $classTemplateInfo->setCardBarcodeSectionDetails($cardBarcodeSectionDetails); $payload->setClassTemplateInfo($classTemplateInfo); $payload->setImageModuleData($imageModulesData);
यह कोड, बारकोड सेक्शन के इस फ़ॉर्मैट में पास बनाता है:

अगर बारकोड सेक्शन को नहीं बदला जाता है, तो डिफ़ॉल्ट बारकोड फ़ील्ड का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट देखें.
ब्यौरे वाला टेंप्लेट
Android

|
|
वेब

|
|
ब्यौरे वाला टेंप्लेट सेक्शन, आइटम की सूची है
class.classTemplateInfo.detailsTemplateOverride.detailsItemInfos[]. आइटम ये कर सकते हैं
किसी भी तरह के स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड, टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड, लिंक मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड, इमेज मॉड्यूल को शामिल किया जा सकता है
फ़ील्ड, या संदेश.
हर आइटम को फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर (.firstValue) में से किसी एक के तौर पर दिया जा सकता है,
दो फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर (.firstValue और .secondValue) या
पहले से तय आइटम (.predefinedItem). चुने गए फ़ील्ड की वैल्यू और उनके
लेबल दिखेंगे. जब आप दो फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर को परिभाषित करते हैं, तो
चुने गए फ़ील्ड "/" के साथ दिखाए जाते हैं सेपरेटर. यही बात
चुने गए फ़ील्ड. पहले से तय आइटम का इस्तेमाल, ज़्यादा जटिल रेंडरिंग को तय करने के लिए किया जाता है. इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड
पूरी चौड़ाई में बिना किसी लेबल के रेंडर किए जाते हैं.
नीचे दिया गया कोड सैंपल, पास की जानकारी वाले सेक्शन को बदलने का तरीका बताता है.
linksModuleData फ़ील्ड के लेबल की यह है:
Python
//... rest of class "linksModuleData": { "uris": [ { "uri": "http://maps.google.com/", "description": "Nearby Locations", "id":"mylink" } ] }, "classTemplateInfo": { "detailsTemplateOverride": { "detailsItemInfos": [ { "item":{ "firstValue": { "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "class.linksModuleData.uris['mylink']" }] } } } ] } } //... rest of class
Java
//... rest of class .setLinksModuleData((new ArrayList<LinksModuleData>() { { add((new LinksModuleData()).setDescription("Nearby Locations") .setUri("http://maps.google.com/") .setId("mylink")); })) .setClassTemplateInfo((new ClassTemplateInfo()) .setDetailsTemplateOverride((new DetailsTemplateOverride()) .setDetailsItemInfos(new ArrayList<DetailsItemInfo>(){ { add((new DetailsItemInfo()) .setItem((new TemplateItem()).setFirstValue((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("class.linksModuleData.uris['mylink']")); } })))); } })) //... rest of class
PHP
//... rest of class building $locationUri = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_Uri(); $locationUri->setUri("http://maps.google.com/"); $locationUri->setDescription("Nearby Locations"); $locationUri->setId("mylink"); $linksModuleData = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_LinksModuleData(); $linksModuleData->setUris(array($locationUri)); $detailItemFieldReference = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $detailItemFieldReference->setFieldPath("class.linksModuleData.uris['mylink']"); $detailItemFieldSelector = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $detailItemFieldSelector->setFields(array($detailItemFieldReference)); $detailItem = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_TemplateItem(); $detailItem->setFirstValue($detailItemFieldSelector); $detailsItemInfo = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_DetailsItemInfo(); $detailsItemInfo->setItem($detailItem); $cardDetailsTemplateOverride = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_DetailsTemplateOverride(); $cardDetailsTemplateOverride->setDetailsItemInfos(array($detailsItemInfo)); $classTemplateInfo = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ClassTemplateInfo(); $classTemplateInfo->setDetailsTemplateOverride($cardDetailsTemplateOverride); $payload->setClassTemplateInfo($classTemplateInfo); $payload->setLinksModuleData($linksModuleData); //... rest of class
यह कोड, जानकारी वाले इस सेक्शन के फ़ॉर्मैट में पास बनाता है:
अगर कोई आइटम खाली है, तो वह नहीं दिखता है. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, यह देखें फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस.
अगर जानकारी वाले टेंप्लेट को नहीं बदला जाता है, तो डिफ़ॉल्ट क्रम दिखेगा. ज़्यादा जानकारी के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट देखें.
सूची टेंप्लेट

|
|
लिस्ट टेंप्लेट सेक्शन का इस्तेमाल, यह चुनने के लिए किया जाता है कि "पास" में कौनसा फ़ील्ड दिखाना है का व्यू Google Wallet ऐप्लिकेशन खोलें. पास को सूची में लोगो, बैकग्राउंड के रंग, और तीन पंक्तियां.
नीचे दिया गया कोड सैंपल, पास के सूची टेंप्लेट को बदलने का तरीका बताता है. सूची टेंप्लेट की पहली लाइन में सिंगल पास के ऑब्जेक्ट के खत्म होने की तारीख वाला फ़ील्ड:
Python
#... rest of class definition "classTemplateInfo": { "listTemplateOverride":{ "firstRowOption": { "fieldOption":{ "fields": [{ "fieldPath": "object.validTimeInterval.end" }] } } } } }
Java
//... rest of class .setClassTemplateInfo((new ClassTemplateInfo()) .setListTemplateOverride((new ListTemplateOverride()) .setFirstRowOption((new FirstRowOption()) .setFieldOption((new FieldSelector()).setFields(new ArrayList<FieldReference>(){ { add((new FieldReference()).setFieldPath("object.validTimeInterval.end")); } })))) //... rest of class
PHP
//... rest of class $fieldReference = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldReference(); $fieldReference->setFieldPath("object.validTimeInterval.end"); $fieldOption = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FieldSelector(); $fieldOption->setFields(array($fieldReference)); $firstRowOption = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_FirstRowOption(); $firstRowOption->setFieldOption($fieldOption); $listTemplateOverride = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ListTemplateOverride(); $listTemplateOverride->setFirstRowOption($firstRowOption); $classTemplateInfo = new Google_Service_Walletobjects_ClassTemplateInfo(); $classTemplateInfo->setListTemplateOverride($listTemplateOverride); $payload->setClassTemplateInfo($classTemplateInfo); //... rest of class
कोड, नीचे दिए गए सूची टेंप्लेट के हिसाब से पास बनाता है:

तीन पंक्तियों को फ़ील्ड सिलेक्टर की मदद से तय किया जा सकता है. फ़ील्ड बिना किसी लेबल के दिखाए जाते हैं.
लेबल
सभी स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड के लिए, Google से एक लेबल मिला होता है. Google इनके लिए ज़िम्मेदार है आपने इन लेबल का अनुवाद सभी भाषाओं में उपलब्ध कराया हो.
इनमें से कुछ लेबल को अपनी पसंद के मुताबिक बनाने के लिए, इनमें से किसी एक का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है
class.custom<name_of_the_field>Label फ़ील्ड. लेबल को पसंद के मुताबिक बनाते समय,
तो आप उस लेबल के लिए सभी भाषाओं में अनुवाद उपलब्ध कराने के लिए ज़िम्मेदार होते हैं
जिसके लिए आपको मदद चाहिए.
फ़ील्ड के रेफ़रंस
फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस का इस्तेमाल, टेंप्लेट के अलग-अलग हिस्सों में
class.classTemplateInfo.*.fields[] फ़ॉर्म. फ़ील्ड के रेफ़रंस में एक सूची मौजूद है
के पाथ का स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड, टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड, लिंक मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड, इमेज मॉड्यूल
फ़ील्ड, या संदेश.
हर फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस में सभी तरह के पाथ की अनुमति नहीं है. उदाहरण के लिए, कुछ फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट पर आधारित स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड या टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड के पाथ की अनुमति देते हैं. टेक्स्ट पर आधारित स्ट्रक्चर्ड फ़ील्ड, स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड होते हैं. इन फ़ील्ड के टाइप की स्ट्रिंग, स्थानीय भाषा के मुताबिक स्ट्रिंग, या पैसा.
इस सूची का इस्तेमाल, फ़ॉलबैक लॉजिक को लागू करने के लिए किया जा सकता है. इसका मतलब यह है कि यदि पहले पथ में सूची खाली फ़ील्ड में बदल जाती है और अगले पाथ का आकलन किया जाता है. फ़ॉलबैक लॉजिक यह है मुख्य रूप से टेक्स्ट पर आधारित स्ट्रक्चर्ड डेटा फ़ील्ड या टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड को टारगेट किया जाता है. मिक्स न करें फ़ील्ड के अलग-अलग टाइप चुनें. फ़ॉलबैक लॉजिक का इस्तेमाल सावधानी से करें. साथ ही, इसका इस्तेमाल सिर्फ़ खास स्थितियों में, जब आपको कुछ ऐसे फ़ील्ड के एक जैसे पैटर्न की उम्मीद हो जो कुछ चीज़ों के लिए कर सकते हैं, लेकिन अन्य नहीं. ज़्यादातर मामलों में, इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण अलग-अलग करें.
अगर किसी फ़ील्ड रेफ़रंस सूची के सभी पाथ खाली फ़ील्ड में बदल जाते हैं, तो वह आइटम जो फ़ील्ड का रेफ़रंस नहीं दिखता है. अगर आपको ऐसा आइटम चाहिए जो हमेशा मौजूद रहें, पक्का करें कि कम से कम एक पाथ खाली न हो. हमारा सुझाव है कि शून्य वैल्यू को दिखाने के लिए, फ़ील्ड को किसी खास वर्ण पर सेट करें, जैसे कि ‘-’ फ़ील्ड में सिर्फ़ खाली जगह देकर स्ट्रिंग इस्तेमाल की जा सकती हैं.
सूची में शामिल फ़ील्ड का रेफ़रंस देने के लिए, फ़ील्ड के इंडेक्स का इस्तेमाल
सूची या ज़्यादातर मामलों में रेफ़रंस आईडी का इस्तेमाल करें. सूची के ऐसे आइटम जिनका रेफ़रंस दिया जा सकता है
आईडी के हिसाब से .id फ़ील्ड होना चाहिए. हमारा सुझाव है कि आप इंडेक्स के बजाय, रेफ़रंस आईडी का इस्तेमाल करें
सूची में फ़ील्ड को खाली नहीं किया जा सकता.
सूची में मौजूद फ़ील्ड का रेफ़रंस देने का तरीका यहां दिया गया है.
object.imageModulesData[0].id = my-first-idobject.imageModulesData[1].id = my-second-idclass.detailsTemplateOverride.detailsItemInfos[0].item.firstValue.fields[0].fieldPath = object.imageModulesData[‘my-second-id’]class.detailsTemplateOverride.detailsItemInfos[1].item.firstValue.fields[0].fieldPath = object.imageModulesData[0]
इस मामले में, पास की जानकारी वाले सेक्शन में पहले आइटम के लिए, एलान की गई दूसरी इमेज का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है ऑब्जेक्ट में. हालांकि, पास की जानकारी वाले सेक्शन में दूसरे आइटम के लिए, पहली इमेज का इस्तेमाल किया जाता है ऑब्जेक्ट में बताया गया है.
डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट
Android

|
|
वेब

|
|
इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड के लिए, हम क्लास से एक और सिर्फ़ एक इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड दिखाते हैं और ऑब्जेक्ट से सिर्फ़ एक इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड हो. अगर आपको यहां दिए गए एक से ज़्यादा इमेज मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड की ज़रूरत है लेवल तय करने के लिए, डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट को बदलें.
टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड के लिए, हम क्लास से ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 20 टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड और 20 फ़ील्ड दिखाते हैं टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड की मदद से कॉपी करें. फ़ील्ड उसी क्रम में दिखाए जाते हैं जिस क्रम में वे तय करें. अगर आपको किसी भी लेवल पर 20 से ज़्यादा टेक्स्ट मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड की ज़रूरत है, तो डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट.
संदेशों के लिए, हम कक्षा के अधिकतम 20 संदेश और ऑब्जेक्ट को हाइलाइट करने की सुविधा मिलती है. हम यह गारंटी नहीं देते कि मैसेज का क्रम सही है. अगर आपको या किसी भी ऑर्डर के लिए गारंटी का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है.
लिंक मॉड्यूल फ़ील्ड के लिए, uri की कोई सीमा तय नहीं है. यूरिस यह हैं हर लेवल (क्लास या ऑब्जेक्ट) के लिए, इस क्रम में नीचे बताए गए ग्रुप में दिखाया गया:
- मैप के निर्देशांक
- टेलीफ़ोन नंबर
- ईमेल पते
- वेब पेज
हर ग्रुप के लिए, यूआरआई उसी क्रम में दिखाए जाते हैं जिसमें उन्हें अरे में तय किया गया है. अगर आपको कोई अलग क्रम चाहिए, तो डिफ़ॉल्ट टेंप्लेट को बदलें.

|
|
