- Dataset Availability
- 1975-01-01T00:00:00Z–2015-12-31T00:00:00Z
- Dataset Provider
- EC JRC
- Earth Engine Snippet
-
ee.ImageCollection("JRC/GHSL/P2016/SMOD_POP_GLOBE_V1") - Tags
Description
The GHSL relies on the design and implementation of new spatial data mining technologies allowing to automatically process and extract analytics and knowledge from large amount of heterogeneous data including: global, fine-scale satellite image data streams, census data, and crowd sources or volunteered geographic information sources.
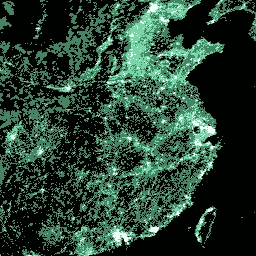
The GHS-SMOD is the rural-urban Settlement classification MODel adopted by the GHSL. It is the representation of the degree of urbanization (DEGURBA) concept into the GHSL data scenario. Each grid in the GHS-SMOD has been generated by integrating the GHSL built-up areas and GHSL population grids data for reference epochs: 1975, 1990, 2000, 2015.
The DEGURBA classification schema is a people-based definition of cities and settlements: it operates using as main input a 1 km² grid cell accounting for population at a given point in time. The DEGURBA discriminates the population grid cells in three main classes: 'urban centers' (cities), 'urban clusters' (towns and suburbs), and 'rural grid cells'. (base). These class abstractions translate to 'high density clusters (HDC)', 'low density clusters (LDC)', and 'rural grid cells (RUR)', respectively, in the GHS-SMOD implementation.
The 'HDC' differ from the DEGURBA 'urban centers' in that they account for the over-fragmentation of cities in regions with large low-density residential development by integrating the built-up layer. In the GHS-SMOD representation, the 'HDC' are the spatial generalization of contiguous population grid cells (4-connectivity, gap-filling) with a density of at least 1500 inhabitants per km² or a density of built-up surface > 50%, and a minimum total resident population of 50000. The 'LDC' are continuous grid cells with a density of at least 300 inhabitants per km² and a minimum total population of 5000. The 'RUR' are grid cells outside 'HDC' and 'LDC' with population > 0 and < 300. Everything else is classified as inhabited areas where population = 0.
This dataset was produced in the World Mollweide projection (EPSG:54009).
For more information visit: http://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ghs_smod.php.
The Global Human Settlement Layer (GHSL) project is supported by the European Commission, Joint Research Center, and Directorate-General for Regional and Urban Policy. The GHSL produces new global spatial information, evidence-based analytics, and knowledge describing the human presence in the planet.
Bands
Resolution
1000 meters
Bands
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
smod_code |
Degree of urbanization |
smod_code Class Table
| Value | Color | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | #000000 | Inhabited areas |
| 1 | #448564 | RUR (rural grid cells) |
| 2 | #70daa4 | LDC (low density clusters) |
| 3 | #ffffff | HDC (high density clusters) |
Terms of Use
Terms of Use
The GHSL has been produced by the EC JRC as open and free data. Reuse is authorised, provided the source is acknowledged. For more information, please read the use conditions (European Commission Reuse and Copyright Notice).
Citations
Pesaresi, Martino; Freire, Sergio (2016): GHS Settlement grid following the REGIO model 2014 in application to GHSL Landsat and CIESIN GPW v4-multitemporal (1975-1990-2000-2015). European Commission, Joint Research Centre (JRC) [Dataset] PID: https://data.europa.eu/89h/jrc-ghsl-ghs_smod_pop_globe_r2016a
Explore with Earth Engine
Code Editor (JavaScript)
var dataset = ee.ImageCollection('JRC/GHSL/P2016/SMOD_POP_GLOBE_V1')
.filter(ee.Filter.date('2015-01-01', '2015-12-31'));
var degreeOfUrbanization = dataset.select('smod_code');
var visParams = {
min: 0.0,
max: 3.0,
palette: ['000000', '448564', '70daa4', 'ffffff'],
};
Map.setCenter(114.96, 31.13, 4);
Map.addLayer(degreeOfUrbanization, visParams, 'Degree of Urbanization');